Final Exam
1/160
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
161 Terms
Axon terminal
The region of the axon that contains mitochondria and synaptic vesicles (but not cytoskeletal proteins)
The vesicle was transported along microtubules (in the axon) before coming to the axon terminal
A secretory vesicle in the axon terminal contains a polypeptide neurotransmitter (similar to a small protein). Identify the correct statement about the secretory vesicle.
a.) The secretory vesicle originated from the axon terminal
b.) The vesicle was transported along microtubules (in the axon) before coming to the axon terminal
c.) It went through retrograde transport to arrive at the axon terminal.
d.) The vesicle contents were added at the axon terminal
RNA splicing
The process in which a single gene sequence can code for multiple proteins by interchanging exon sequences
Soma (cell body)
The endoplasmic reticulum would be restricted to the following cell structure
tubulin (cytoskeletal protein)
Which of the following proteins does NOT require synthesis at the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
a.) membrane receptor protein
b.) ion pump protein
c.) Ion channel protein
d.) tubulin (cytoskeletal protein)
All are correct
Which of the following proteins are synthesized on free ribosomes? (Ribosomes that are not ER bound)
a.) non-membrane bound proteins
b.) proteins that remain in the cytosol
c.) All are correct
d.) proteins that are transported to the nucleus
multipolar
Based on their appearance, both stellate and pyramidal neuronal cells would be classifed as ____________ neurons.
Axon
A glial cell produces a myelin sheath that is wrapped around the _____ of a neuronal cell.
The Schwann cell provides a myelin sheath to a motor neuron
Identify the correct statement regarding a Schwann cell:
a.) The Schwann cell provides a myelin sheath to cortical neurons located in the brain.
b.) All are correct
c.) The Schwann cell provides a myelin sheath to a motor neuron
d.) The Schwann cell is considered a neuronal cell.
Axon Hillock
If a neuronal cell is stimulated at the dendrites and the resultant action neuronal impulse travels down the axon , which part of the axon would be considered the "start" of the neuronal impulse?
K+
Because higher levels of the _______ ion can result in depolarization of the neuronal cell, an important function of astrocytes is to maintain the extracellular concentrations of this ion in the brain.
Ca++ = 10,000 : 1
Which of the following ion ratios between the inside and outside of the cell is incorrect?
Possible ratios are presented as
(Inside conc. : Outside conc.)
a.) Ca++ = 10,000 : 1
b.) K+ = 20 : 1
c.) Cl- = 1 : 11.5
d.) Na+ = 1 : 10
The concentration of the ion is higher on the inside of the cell
Which of the following conditions will NOT contribute to an ion entering a cell through diffusion?
a.) The ion is fully dissolved in water
b.) The concentration of the ion is higher on the inside of the cell
c.) The concentration of the ion is lower inside the cell
d.) Membrane channels specific for the ion are open
Ion channels for K+ are not present in the membrane
Which of the following conditions will prevent an equilibrium potential for K+ ion from forming?
a.) A concentration gradient of K+ exists between the inside and outside of the cell
b.) The diffusive force of K+ in one direction balances the electrical attraction in the opposite direction
c.) A charge difference forms as a result of K+ movement through the membrane
d.) Ion channels for K+ are not present in the membrane
Allows for passive transport of ions down their concentration gradient
Which of the following is NOT a feature of the different ion pumps in the membrane?
a.) Exchanges Na+ for K+ ions
b.) Allows for passive transport of ions down their concentration gradient
c.) All of the statements are corrrect
d.) Actively transports Ca++
The inner and outer concentrations of the ion are equal
If the Nernst equation calculates a value that is equal to zero, what is the possible reason (with regard to the inner and outer concentration of the ion)?
a.) The inner or outer concentration has no effect on the value
b.) The outer concentration of the ion is higher
c.) The inner concentration of the ion is higher
d.) The inner and outer concentrations of the ion are equal
Equilibrium potential
Using the Nernst equation, the ______ of an ion is calculated:
Permeability (P)
Unlike the Nernst equation, the Goldman equation takes into account the contribution of different ions and their ______ to the overall membrane potential.
(hint- this factor is not included in the Nernst equation)
Decreasing the permeability of an ion.
According to Ohm’s equation, I = gV, which situation would change the “g” value?
a.) Decreasing the permeability of an ion.
b.) Decreasing the membrane potential (Vm) relative to the equilibrium potential (Eion) of an ion.
c.) Increase in the inside (internal) concentration of an ion.
d.) Increase in the outside (external) concentration of an ion.
V (potential)
Which part of Ohm's laws refers to the force that is generated on a charged particle?
a.) I (current)
b.) R (resistance)
c.) V (potential)
d.) g (conductance)
Increased diameter of the axon
In addition to myelination of the axon membrane, the following characteristics of neurons will increase the speed of action potentials down the axon:
a.) Increased diameter of the axon
b.) Increased length of the axon
c.) Decreased diameter of the axon
d.) More dendrites
-40 mV
At which voltage level (of stimulation) will the voltage gated Na+ channel open? (what is the threshold value for the action potential)
a.) -80 mV
b.) -20 mV
c.) -60 mV
d.) -40 mV
Overshoot
The region of the action potential curve in which the current is above zero millivolts (> 1)
Cl- channel
When most transmitter-gated ion channels are activated (opened), they result in the stimulation of the neuronal cell. Which of the following ion channels is inhibitory when activated?
a.) Cl- channel
b.) K+ channel
c.) Na+ channel
d.) Ca+ channel
Voltage
The sodium (Na+) channels that open up to form part of the action potential along the axon (in response to threshold) are characterized as _________ gated channels.
K+ channel
Which voltage-gated ion channel is activated and open during the falling phase of the action potential?
a.) Cl-
b.) Ca++
c.) Na+ channel
d.) K+ channel
All the statements are correct
Which of the following statements about myelination is INCORRECT?
a.) All the statements are correct
b.) Provided by oligodendroglia cells in the CNS
c.) Contributes to saltatory conduction
d.) Provided by Schwann cells in the PNS
V
An important driving force for the Na+ current (INa) during an action potential is the differential value between the equilibrium potential of Na+ (Eo = +80mV) and the overall potential of the cell membrane (Vm = -65mV). Which part of Ohm's law reflects this contribution?
Where I = gV
and (R = 1/g)
K+ channel
There are two types of refractory periods associated with the action potential, absolute and relative.
The relative refractory period of the action potential is associated with the properties of the ___________.
There are two types of refractory periods associated with the action potential, absolute and relative. Which of the following properties of the neuron is associated with (or result from) the absolute refractory period?
a.) Limit to the frequency of neuronal firing (regardless of stimulation)
b.) All of the these situations are associated with/result from this period
c.) Na+ channels cannot open with depolarization of the membrane
d.) Orthodromic direction of the action potential under non-experimental conditions.
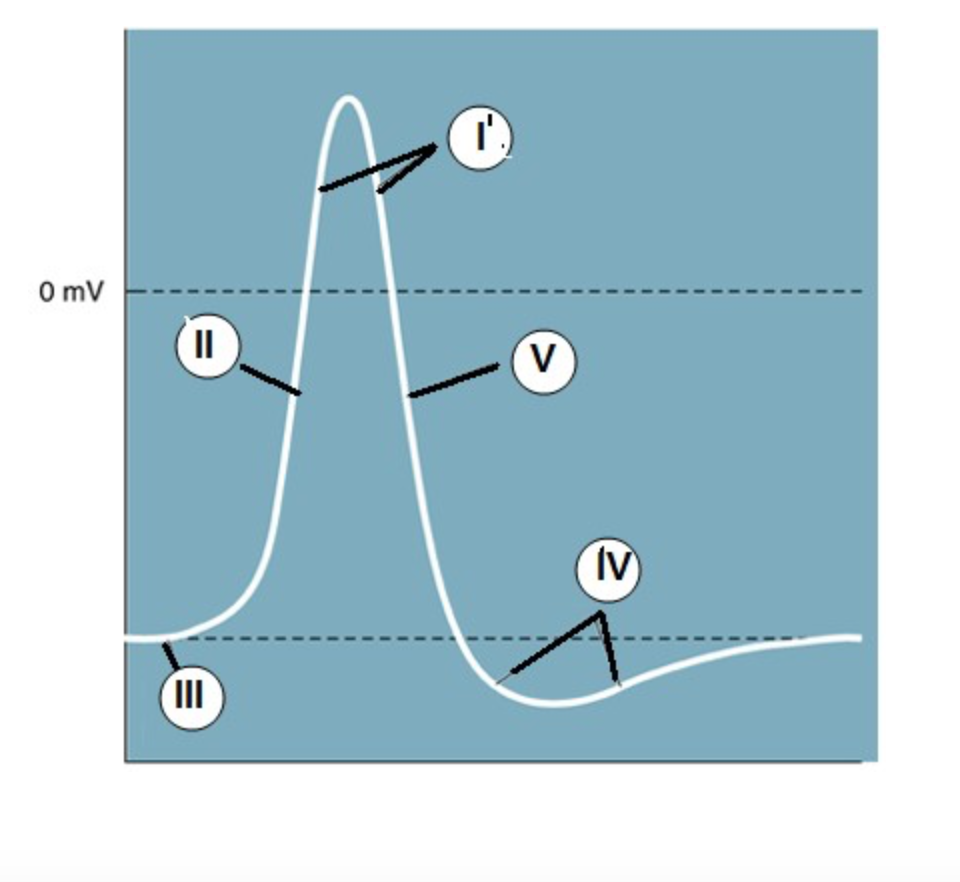
IV
Which region is known as the "undershoot" of the action potential?
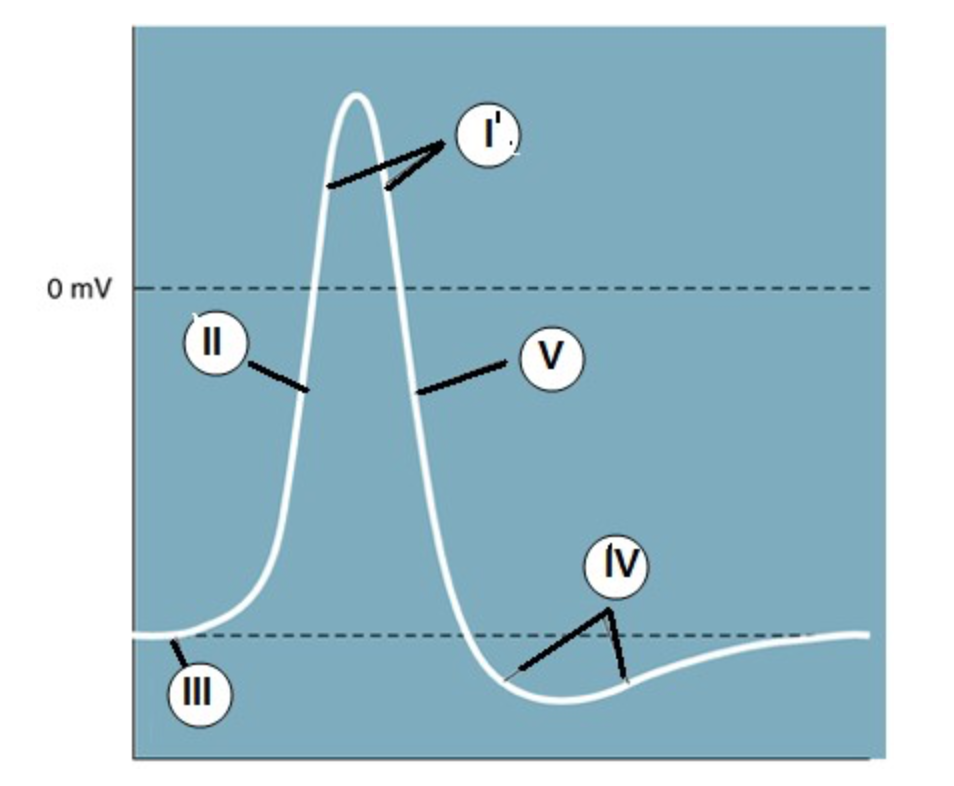
II
Which region identifies the "rising phase"?
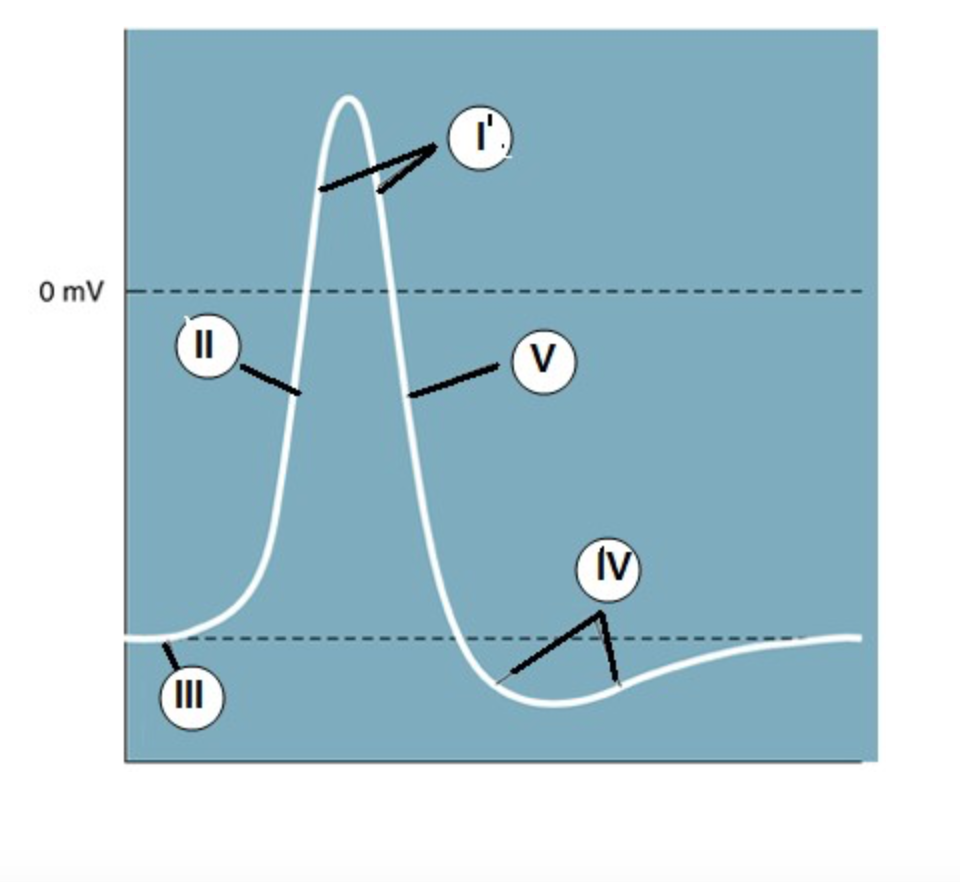
III
At which region is the cell at "resting potential"?
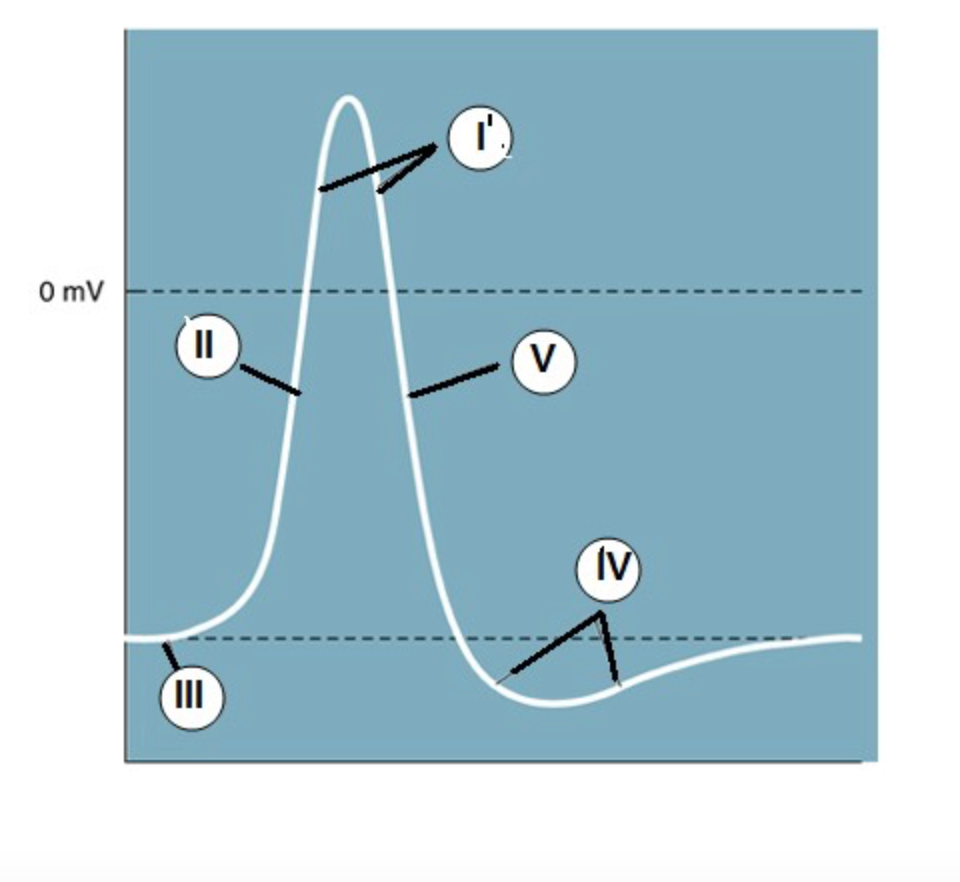
V
A net potassium (K+) efflux is associated with which region?
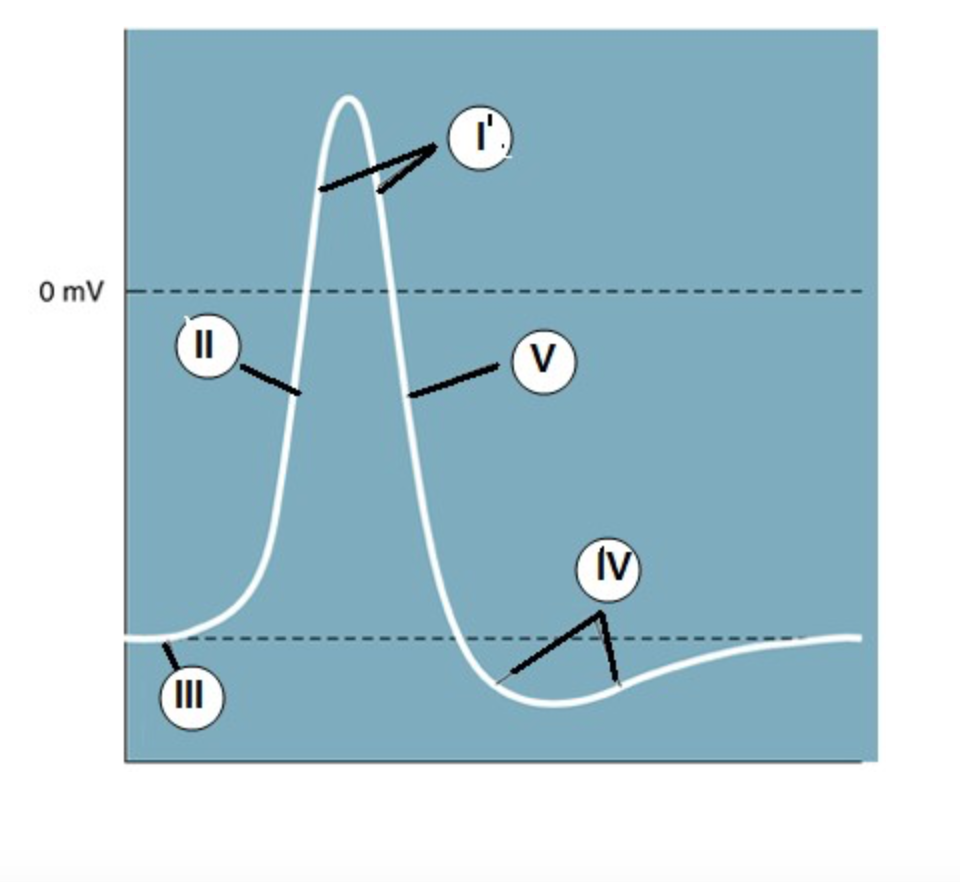
II
At which region is the gNa >> gK?
(when the permeability/conductance of Na is much higher than K)
Release of neurotransmitters from the presynaptic cell
An electrical synapse between two neurons could involve the following EXCEPT
a.) Resultant change in membrane potential in the post synaptic cell.
b.) Flow of ions from cell to cell
c.) Release of neurotransmitters from the presynaptic cell
d.) Possibility of 2-way communication between both neurons
Influx of Ca++ ion into the cell
As the action potential reaches the axon terminal, the release of synaptic vesicles containing neurotransmitter would be directly triggered by
a.) Influx of Ca++ ion into the cell
b.) Efflux of Ca++ ion out of the cell
c.) Influx of Cl- ion into the cell
d.) Efflux of Na+ ion out of the cell
Contain small proteins or peptides
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of synaptic vesicles?
a.) Contain neurotransmitters that are synthesized in the axon terminal
b.) Release contents into the synaptic cleft
c.) Have transporters to bring glutamate into the vesicle
d.) Contain small proteins or peptides
dendrodendritic
synapse type that would only be able to use electrical synapses (and not involve the release of neurotransmitters from vesicles)?
A large modified protein
Which of the following would be the LEAST practical as a neurotransmitter molecule?
a.) A modified amino acid
b.) A small polypeptide
c.) An amine molecule
d.) A large modified protein
Secretory granules
the other name for dense-core vesicles
Molecules that activate additional enzymes in the cytosol
What are second messengers?
a.) Molecules that activate additional enzymes in the cytosol
b.) Special proteins that span a 3 nm gap between two cell membranes
c.) Voltage-gated ion channel
d.) Peptide neurotransmitters
Enzymatic destruction and diffusion
How are released neurotransmitters cleared from the synaptic cleft?
a.) Both exocytosis and endocytosis
b.) Enzymatic destruction and diffusion
c.) Endocytosis
d.) Exocytosis
I and III
Which of the following statements regarding gap junctions are correct?
I. Gap junctions are composed of connexons
II. Gap junctions form chemical synapses
III. Gap junctions can facilitate the bidirectional flow of ions between cells
a.) III only
b.) II and III
c.) I, II , and III
d.) I and III
II only
Which of the following statements regarding an excitatory postynpatic potential (EPSP) are correct?
I. EPSPs occur in the presynaptic neuron
II. EPSPs are associated with the transient depolarization of the neuron
III. EPSPs occur through the activation of chloride (Cl-) channels.
a.) I and III
b.) II only
c.) I only
d.) I and II
glycine
An amino acid type neurotransmitter
chemical synapses
Neurotransmitters are used for communication between
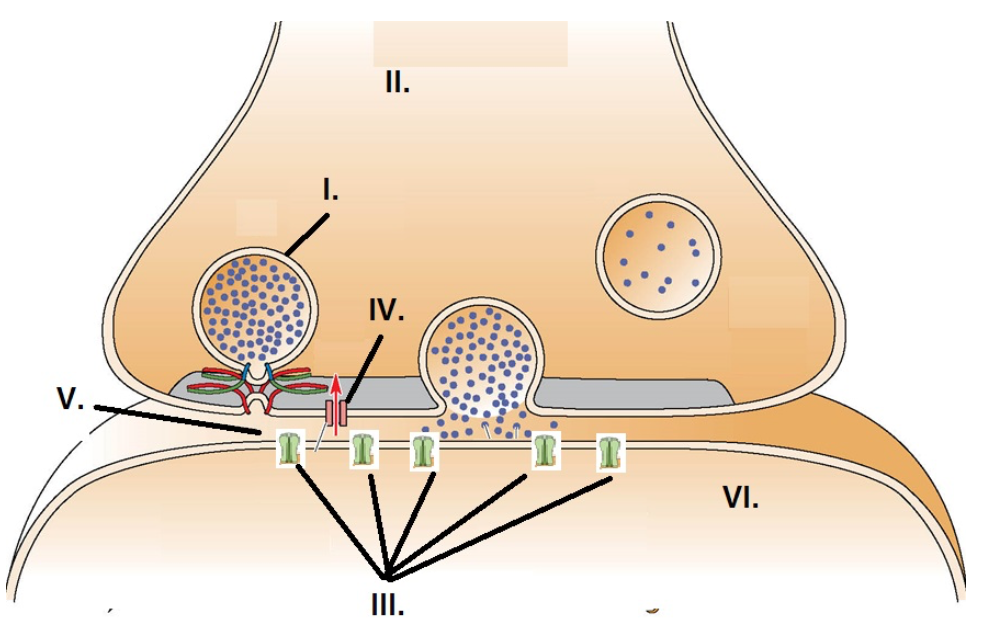
II
The presynaptic axon terminal is identified by:
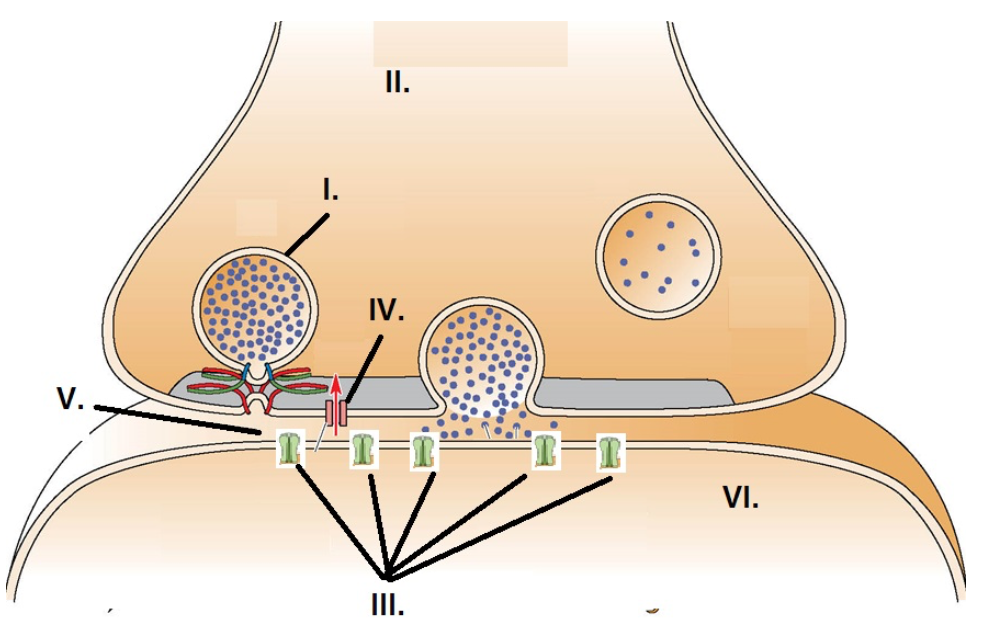
I
A synaptic vesicle is identified by:
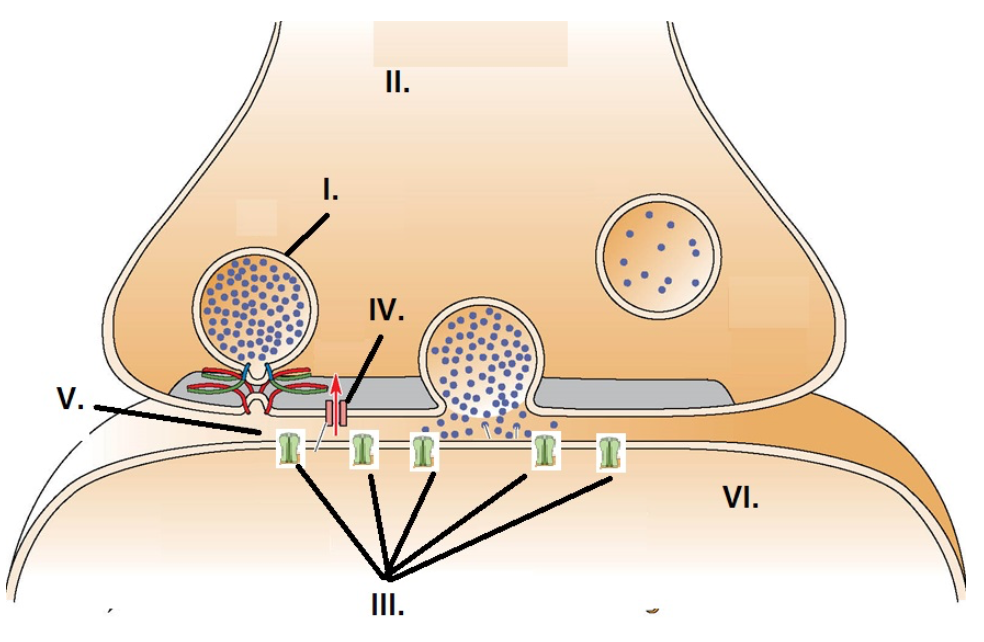
III
Neurotransmitter receptors are identified by:
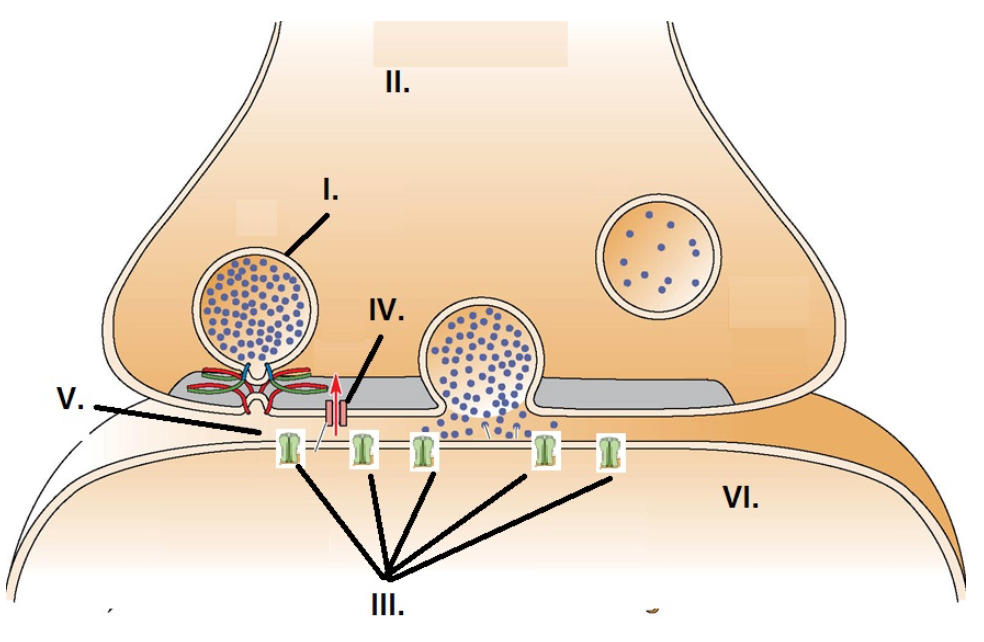
V
The synapse is identified by:
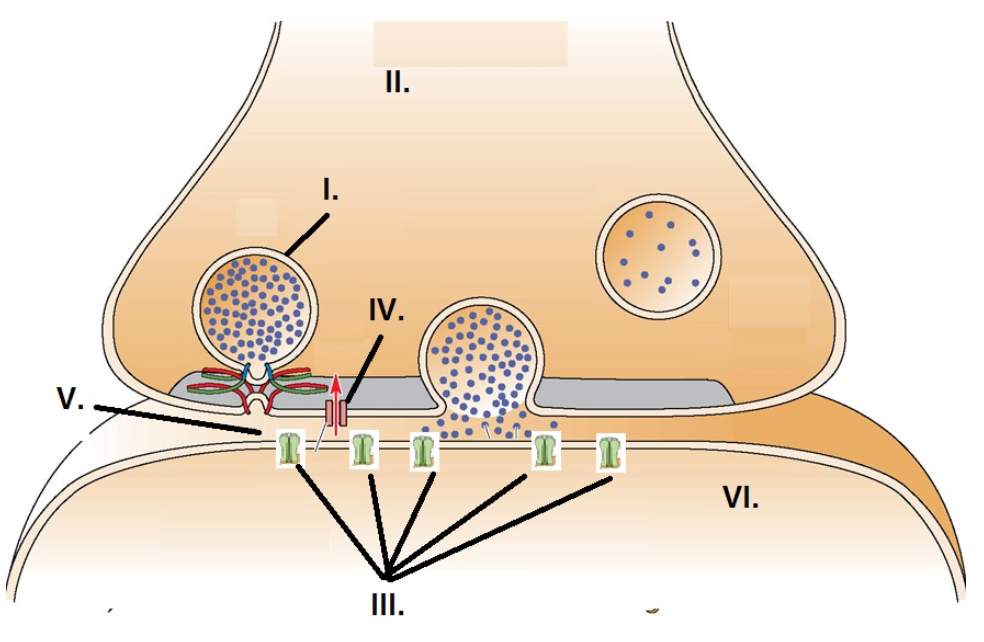
IV
The voltage gated calcium channel is identified by:
False
Dale's principle states that a neuron has at least two different neurotransmitters. True or false?
True
The amino acid tyrosine is the precursor for three different amine neurotransmitters: dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. True or false?
They produce IPSPs
Which of the following statements about nicotinic receptors is FALSE?
a.) cuarare is an antagonist
b.) they bind acetylcholine
c.) They produce IPSPs
d.) they are found in muscle tissue
alpha
When a G-protein gated receptor is activated by binding its neurotransmitter, which subunit protein of the associated G-protein complex will exchange GDP for GTP?
None of these are common to all
What is a common feature of transmitter-gated ion channels?
a.) They only bind Ach
b.) None of these are common to all
c.) They only bind neurotransmitters that IPSPs
d.) They only bind neurotransmitters that produce EPSPs
norepinephrine
Which of the following neurotransmitters is synthesized from a tyrosine precursor?
a.) serotonin
b.) norepinephrine
c.) Acetylcholine
d.) AMPA
GABA gated channel
All of the following channels produce EPSPs when activated EXCEPT the ______, which is a chloride channel:
a.)Ach gated channel
b.) GABA gated channel
Increase the amount of ACh that is released into the synapse
By inhibiting the enzyme AChE (acetylcholinesterase enzyme) in the synaptic cleft, you would cause the following:
a.) Increase the amount of ACh that is released into the synapse
b.) Decrease the amount of ACh that is released into the synapse
c.) Increase the amount of ACh that binds the postsynaptic neuron
d.) Decrease the amount of ACh that binds to the postsynaptic neuron
atropine is the agonist
Which of the following statements about nicotinic receptors is FALSE?
a.) they are classified as transmitter-gated ion channels
b.) atropine is the agonist
c.) they are activated by binding acetylcholine
d.) curare is an antagonist
ACh (Acetylcholine)
Nicotinic and muscarinic receptors both bind:
a.) Glutamate
b.) ACh (Acetylcholine)
Glutamate
NMDA, AMPA, and Kainite receptors can all bind to which neurotransmitter?
all are correct
Which of the following would be a target for an activated G-protein?
a.) None of these are targets
b.) Ion channel
c.) all are correct
d.) Adenylyl Cyclase
e.) PLC
Glycine
An amino acid-type neurotransmitter would be the following:
a.) Glycine
b.) Acetylcholine
c.) Serotonin
d.) Norepinephrine
none are correct
In the push-pull method of GPCR effector systems, both stimulatory and inhibitory norepinephrine (NE) neurotransmitter receptors will stimulate or inhibit the same target enzyme (respectively). The target enzyme is:
a.) none are correct
b.) Acetylcholinesterase
c.) PKA
d.) MAPK
ion channel
The short cut pathway for a GPCR involves the direct regulation of ______________ immediately following the activation of the G-protein subunits.
Protons (H+)
Identify the causative agent for acidity and sourness. Choose the correct option.
a.) High pH
b.) Na+
c.) Anions
d.) Protons (H+)
Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open, triggering the release of neurotransmitters
What changes occur in taste receptors when the membrane is depolarized during receptor potential?
a.) Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open, triggering the release of neurotransmitters.
b.) Voltage-gated K+ channels open, triggering the release of neurotransmitters.
True
Each olfactory receptor gene has a unique structure, which allows the receptor proteins encoded by these genes to bind to different odorants. True or false?
chemoreceptors
Chemically sensitive cells that serve as sensory receptors
Electrical synapse between the neurons
What is the function of a gap junction between neurons?
a.) Chemical synapse between the neurons
b.) Electrical synapse between the neurons
Immunocytochemistry
The use of antibodies to visualize specific molecules within the brain cells
in situ hybridization
Neurotransmitter is synthesized and stored in presynaptic neuron
microiontophoresis
When applied, mimics postsynaptic cell response produced by release of neurotransmitter from the presynaptic neuron
brain slide as a model
Neurotransmitter is released by presynaptic axon terminal
immunocytochemistry
Neurotransmitter is synthesized and stored in presynaptic neuron
None are correct
According to the Wernicke-Geschwind model, what is the correct sequence of brain regions that would be involved in the process of repeating a spoken word?
a.) Auditory cortex>Broca's area>Wernicke's area>arcuate fasciculus>Motor cortex
b.) None are correct
c.) Auditory cortex>Wernicke's area>Broca's area>arcuate fasciculus>motor cortex
Impaired repetition of words
Which speech disabilities are commonly seen in Broca's, Wernicke's, and conduction aphasia patients?
a.) Fluent speech
b.) Good comprehension
c.) Impaired repetition of words
fluent speech
The following would be associated with lesions in the frontal cortex EXCEPT:
a.) fluent speech
b.) good comprehension
c.) paraphrastic errors
Wernicke's area
Lesions in ___________________ , located in the temporal lobe just posterior to the auditory cortex, disrupt normal speech.
The Wada Procedure
used to determine which hemisphere is dominant for speech.
All are invovled
Specific language impairment (SLI) is found in individuals that have mutations in the ______________ gene.
a.) All are invovled
b.) CNTNAP2
c.) FOXP2
d.) KIAA0319
Most aphasias involve both comprehension and speech deficits.
Which of the following observations does NOT support the Wernicke-Geschwind model?
a.) Speech comprehension involves neurons in Wernicke's area
b.) Lesions in Broca's region result in speech deficits
c.) Most aphasias involve both comprehension and speech deficits.
d.) Damage to the arcuate fasciculus will affect the repetition of spoken words
Involves defects in comprehension
Which of the following is NOT associated with conduction aphasia?
a.) Speech is still fluent
b.) Involves defects in comprehension
c.) difficulty in repeating words
d.) Can be attributed to disconnection lesion of arcuate fasciculus and parietal cortex
none of these will occur
Which of the following would occur in a person with left hemisphere dominance who has undergone a split-brain procedure?
a.) defects in speech
b.) Problems with comprehension on both sides
c.) all of these will occur
d.) severe behavioral effects
e.) none of these will occur
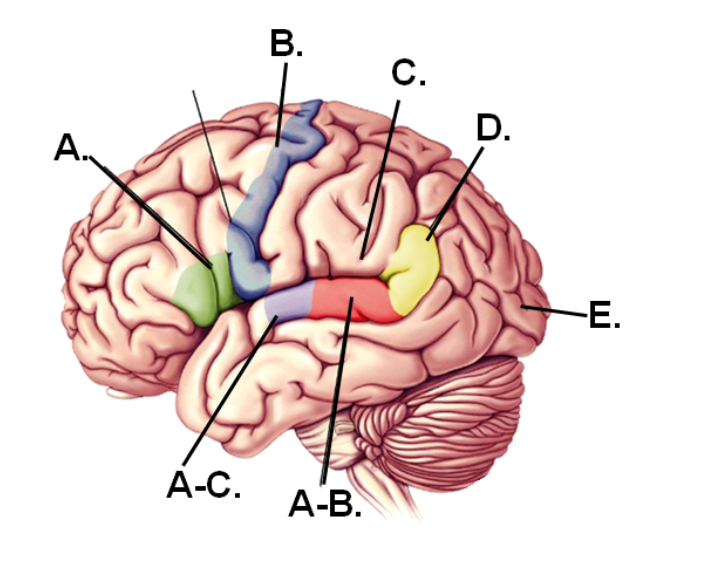
A-B
Area that would be damaged if the individual could speak properly but could not comprehend speech

E
Part of the brain that first receives visual information
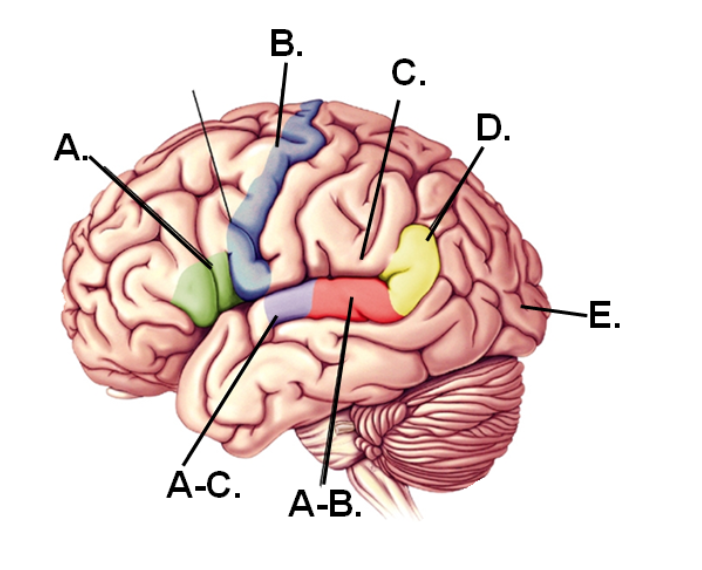
A-C
Region that first receives hearing information
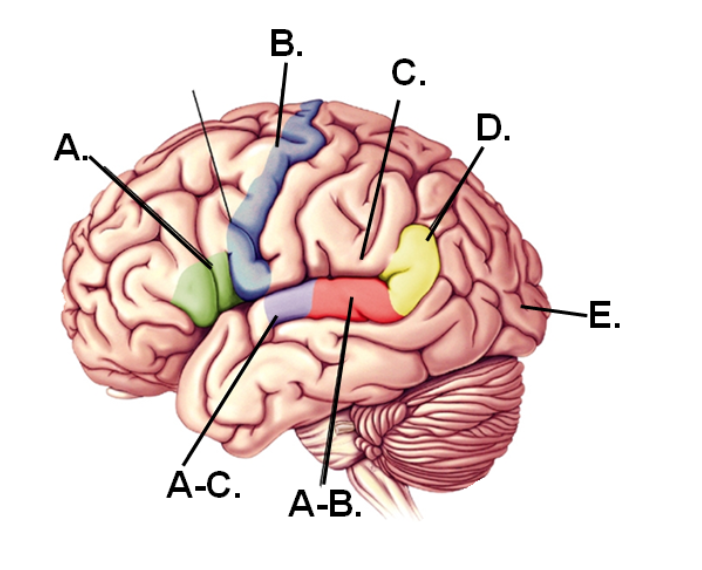
A
Area that would be damaged if the individual could comprehend speech but could not speak properly
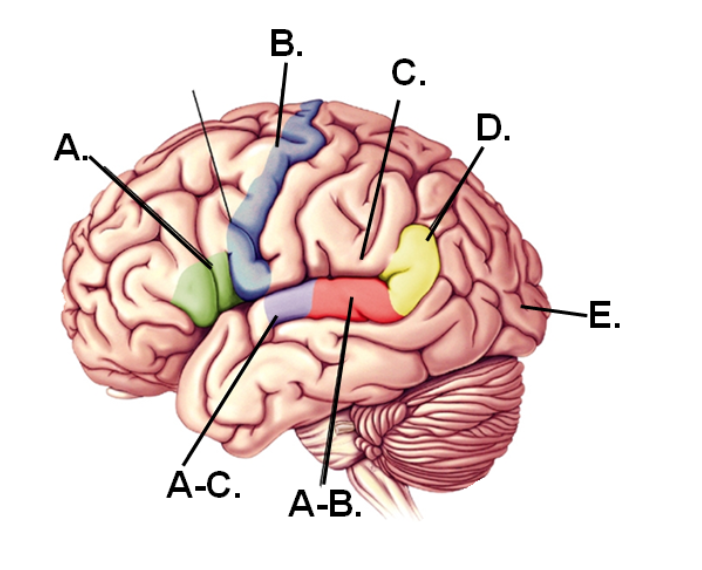
D
Region of the angular gyrus
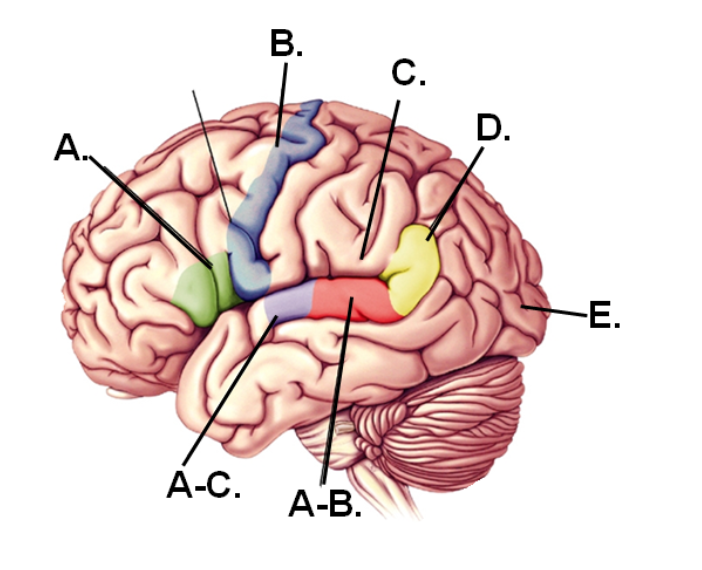
C
Lesions in this region would still have fluent speech and good comprehension BUT have difficulty repeating words
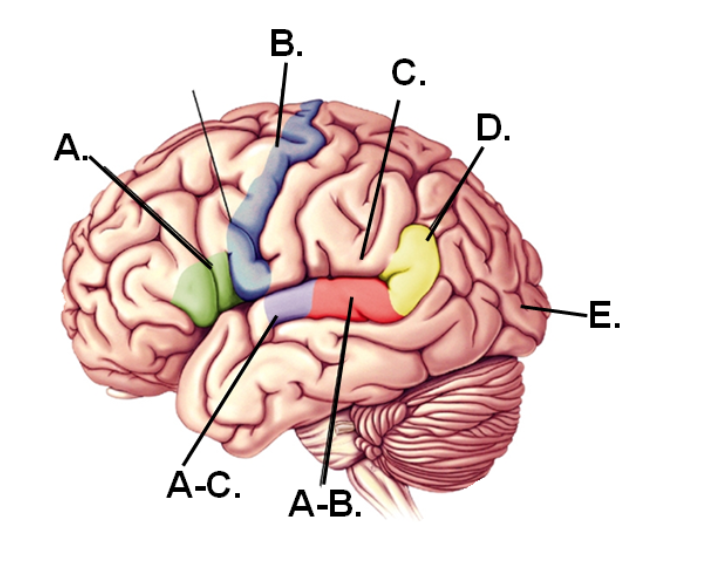
B
Region containing the motor cortex
Glutamate hypothesis
Which of these hypothesis is associated with schizophrenia?
a.) Monoamine hypothesis
b.) All of the above
c.) Glutamate hypothesis
d.) Diathesis-stress hypothesis
Glutamate hypothesis
The use of NMDA receptor blockers that result in symptoms similar to schizophrenic episodes is based on which hypothesis?
All of these
Which of the following drugs could be used as an antidepressant by increasing serotonin levels?
a.) fluoxetine
b.) MAO inhibitors
c.) tricyclics
d.) all of these
dopamine
Drugs for treating schizophrenia include potent blockers of _____________________-receptor action.
norepinephrine
Effects of mutations in the ______________________ receptor would be consistent with the monoamine hypothesis.
Glucocorticoid
Medications that increase the activity of the __________________receptor might be useful in treating certain stress disorders.
Dopaminergic system
Stimulation of the ___________ may play a role in schizophrenic episodes.