Personality Traits (L1) and Literature
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:06 PM on 6/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
1
New cards
What did Hippocrates believe about personality?
Personality is the product of 4 humours (yellow bile, black bile, phlegm and blood) and maladaptive traits arise from a disbalance of the humours
2
New cards
What did FJ Gall pioneer?
Phrenology (1-1 link between brain regions and functions)
3
New cards
What did Francis Galton’s “lexical hypothesis” entail?
That you can collect personality by means of “personality words”. Allport extended this in 1930 by claiming there were 18,000 personality words
4
New cards
What are the three elements of the lexical hypothesis?
* Important personality traits will find its way into language
* More important personality traits are more likely to be encoded into language as a single word
* Principle Component Analysis of traits can be used to extract important aspects of variation
* More important personality traits are more likely to be encoded into language as a single word
* Principle Component Analysis of traits can be used to extract important aspects of variation
5
New cards
Personality
stable characteristics and behaviour that comprises and individual's unique adjustment to life
6
New cards
Personality trait
A relatively stable, consistent and enduring internal characteristic that is inferred from a pattern of behaviours, attitudes, feelings and habits
7
New cards
jingle/jangle fallacy
Most personality trait models are talking about the same traits, just with different names
8
New cards
What are some characteristics of the Big 5 questionnaire?
* Both of the extremes are somewhat maladaptive
* Personality traits are **hierarchically organised** (traits consist of facets that consist of items); e.g. Positive emotionality - Sociality (or something)
* Personality traits are **related to psychopathology** (e.g. neuroticism - depression and anxiety)
* Traits can **summarize** a person, but does not tell you much about personal narrative. Reasonable, but not great predictor of life events; not really an explanation
* Personality traits are **hierarchically organised** (traits consist of facets that consist of items); e.g. Positive emotionality - Sociality (or something)
* Personality traits are **related to psychopathology** (e.g. neuroticism - depression and anxiety)
* Traits can **summarize** a person, but does not tell you much about personal narrative. Reasonable, but not great predictor of life events; not really an explanation
9
New cards
What are some issues in studying personality models?
1. Lack of simple structure: Personality traits are not organized in a straightforward manner, and multiple traits can influence responses to a single indicator
2. Hierarchy: Traits can be understood hierarchically, ranging from specific traits to broader ones. A test can test both specific and general traits
3. Interstitiality: A single indicator can reflect multiple traits at the same level of abstraction. This means that an item designed to measure one trait may also indicate the presence of other traits. Failure to account for these cross-loadings can distort the interpretation of subordinate traits.
4. Range: Measures of personality traits often do not span the entire range of the trait being assessed. Different measures may focus on different ends of the trait distribution, leading to differences in content and empirical characteristics. This can create spurious factors and affect the relationships between measures.
5. Polarity: The association between extreme ends of a trait distribution and pathology is not always clear. Some hypothesize that both extremes are associated with impairment, while others suggest only one extreme is problematic.
1. Source: The source of information about an individual's personality is a central issue.
10
New cards
To what degree is personality in twins genes, shared environment and unique environment?
\~45% unique environment, \~45% additive genetic effects, \~10% common environment
11
New cards
Why are there individual differences in personality?
* **Life history theory**: Energy is finite, **choices** are made on how to use it -- individual differences (e.g. someone who's low on openness to experience will make more conservative choices)
* **Balancing selection**
* **Environmental heterogeneity in fitness optima**: different environments require different behaviours, therefore diversity is adaptive for the survival of the species
* **Frequency-dependent selection**: The occurrence of behaviour is related to the frequency of other people's behaviour (Prisoner's dilemma)
* **Balancing selection**
* **Environmental heterogeneity in fitness optima**: different environments require different behaviours, therefore diversity is adaptive for the survival of the species
* **Frequency-dependent selection**: The occurrence of behaviour is related to the frequency of other people's behaviour (Prisoner's dilemma)
12
New cards
**Supervenience**:
The idea that there "cannot be an A-difference without a B-difference", there has to be a change in the brain if there is a change in emotion (1-1 relation between emotion and brain activation)
13
New cards
**Multiple realizability:**
Different brain states related to the same mental state (the same brain regions will not necessarily light up for different people while thinking the same thing) **(compatible with supervenience**!)
14
New cards
**Identity theory:**
* Processes of the mind are identical to states of processes of the brain (if our personality is the same, the same brain regions will always be activated)
15
New cards
Equifinality
There are multiple ways to reach the same outcome
16
New cards
Why is multiple realizability the most realistic outcome?
Many brain-behaviour correlations are very weak (poorly replicable)
Brain regions are not specific to personality traits : brain regions and networks can only moderately predict personality disorders (\~55%)
Brain regions are not specific to personality traits : brain regions and networks can only moderately predict personality disorders (\~55%)
17
New cards
Person-situation debate
Is it the person, or the situation, that influences how people behave?
18
New cards
What is the conclusion of the person-situation debate?
There is both stability and variability in personality
Moment-to-moment behaviour can be quite different, week to week is quite stable
Dynamic system
Moment-to-moment behaviour can be quite different, week to week is quite stable
Dynamic system
19
New cards
Interactionism
Interactionists agree with situationists that the situation is primary and that psychologists should study the processes whereby people react to changing situations, but they also hypothesize that personality does exist. They propose that personality consists of differences between individuals in how they react to situations, rather than in general ways of acting (traits).
20
New cards
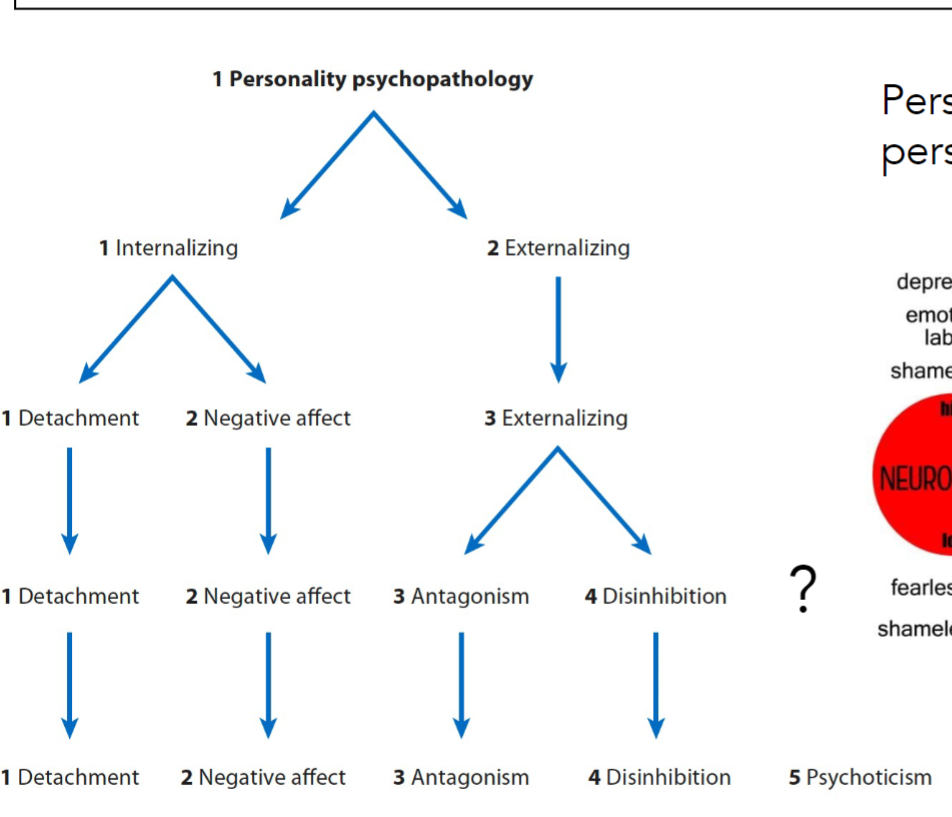
What do these correspond to in the Big 5?
Detachment - introversion
Negative affect - neuroticism
Antagonism - agreeableness
Disinhibition - Conscientiousness
Psychoticism - openness to experience
Negative affect - neuroticism
Antagonism - agreeableness
Disinhibition - Conscientiousness
Psychoticism - openness to experience
21
New cards
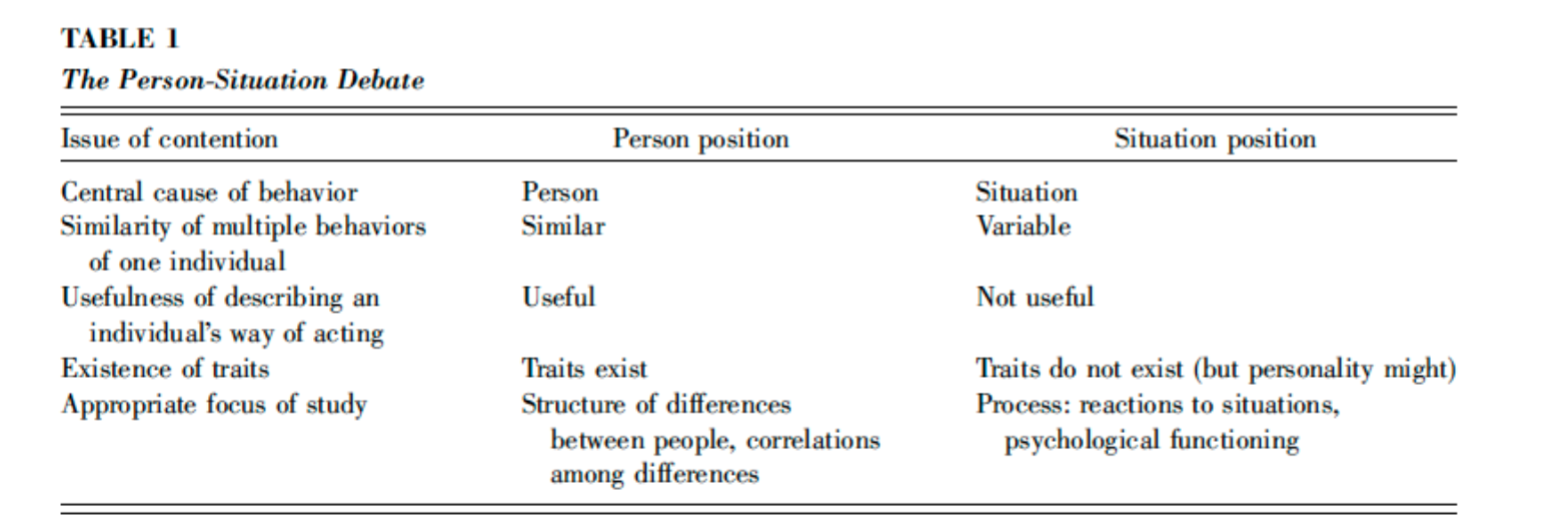
explain this
oki