Biology: Topic 2J Coordination and Response (Responding to Change)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What is a change in environment known as?
Any change in an environment is know as a stimulus
What do organisms have to detect stimuli?
Organisms have receptors that allow them to detect stimuli.
What is homeostasis? What is the relation to metabolic reactions?
Maintaining a constant internal environment is known as homeostasis.
Cells must be kept in the right conditions for all the metabolic reactions and enzymes to work properly.
What do receptor cells do?
Detect all the external and internal stimuli
What do effector cells do?
Bring about the required response.
These effectors are usually muscle cells or a gland.
What are the two parts of the Nervous system?
The Central Nervous System (CNS) which consists of the brain and spinal cord.
The Peripheral Nervous System which is all the nerves that take information from our sense organs into the CNS and from the CNS out to effectors (muscles or glands).
What cell is the nervous system made up of?
Neurones - long cells that carry electrical impulses around the body at high speeds of between 10 and 100 m/s.
What are the types of neurones and their function?
The sensory neurones take the impulse from the receptors to the CNS. The relay neurones link to other neurones within the CNS and then the motor neurones take an impulse to the effectors to cause a response.
What are synapses and their function?
a connection between two neurones.
The impulse is transferred from one neurone to the next using chemicals called neurotransmitters.
These chemicals diffuse across the synapse.
What are reflexes?
A response that bypasses the conscious part of the brain altogether and happens automatically.
What is a reflex arc?
The pathway taken by the information in a reflex
(The signal does not go up to the brain, but is processed in the spinal cord via a relay neurone!)
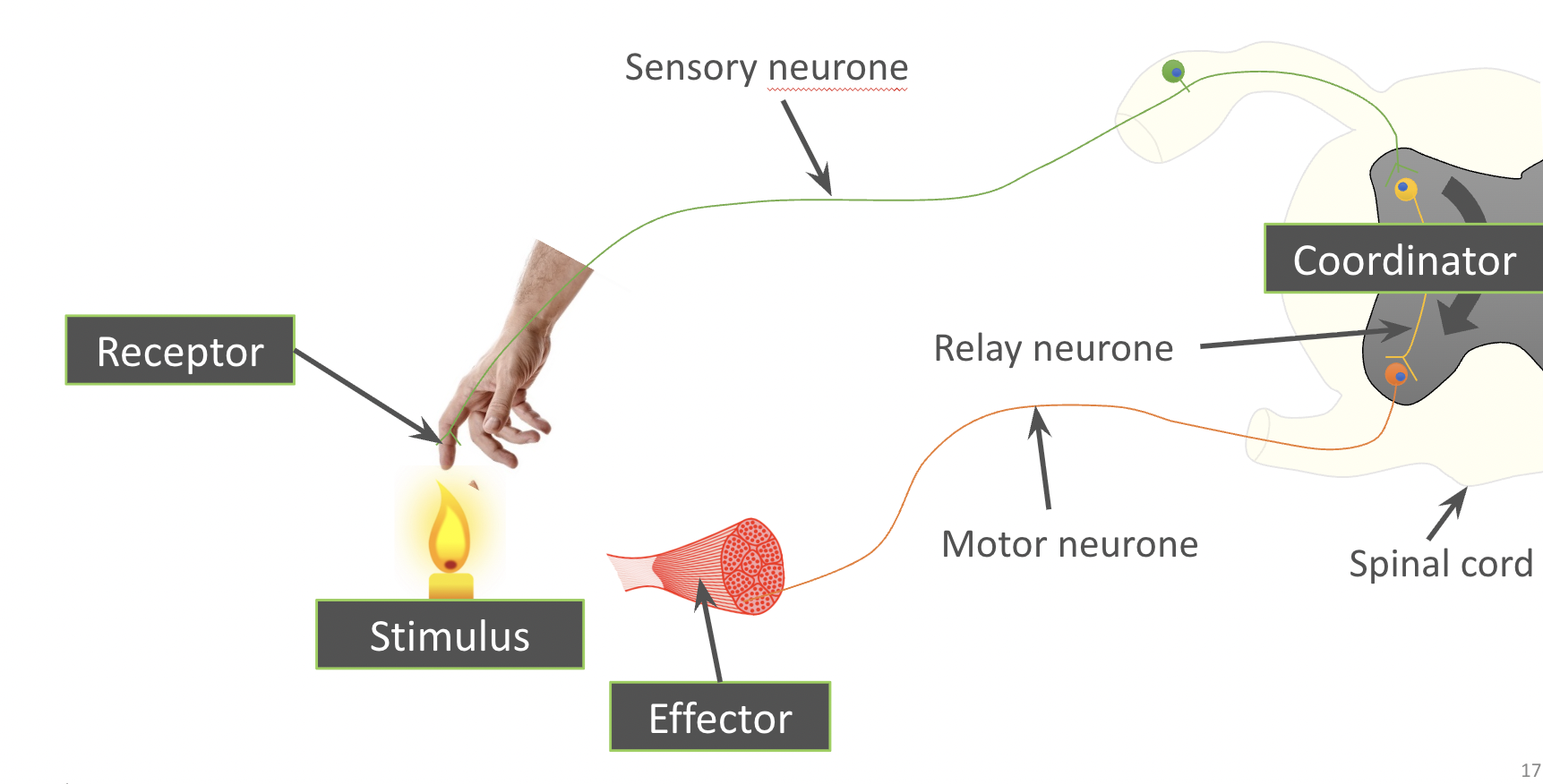
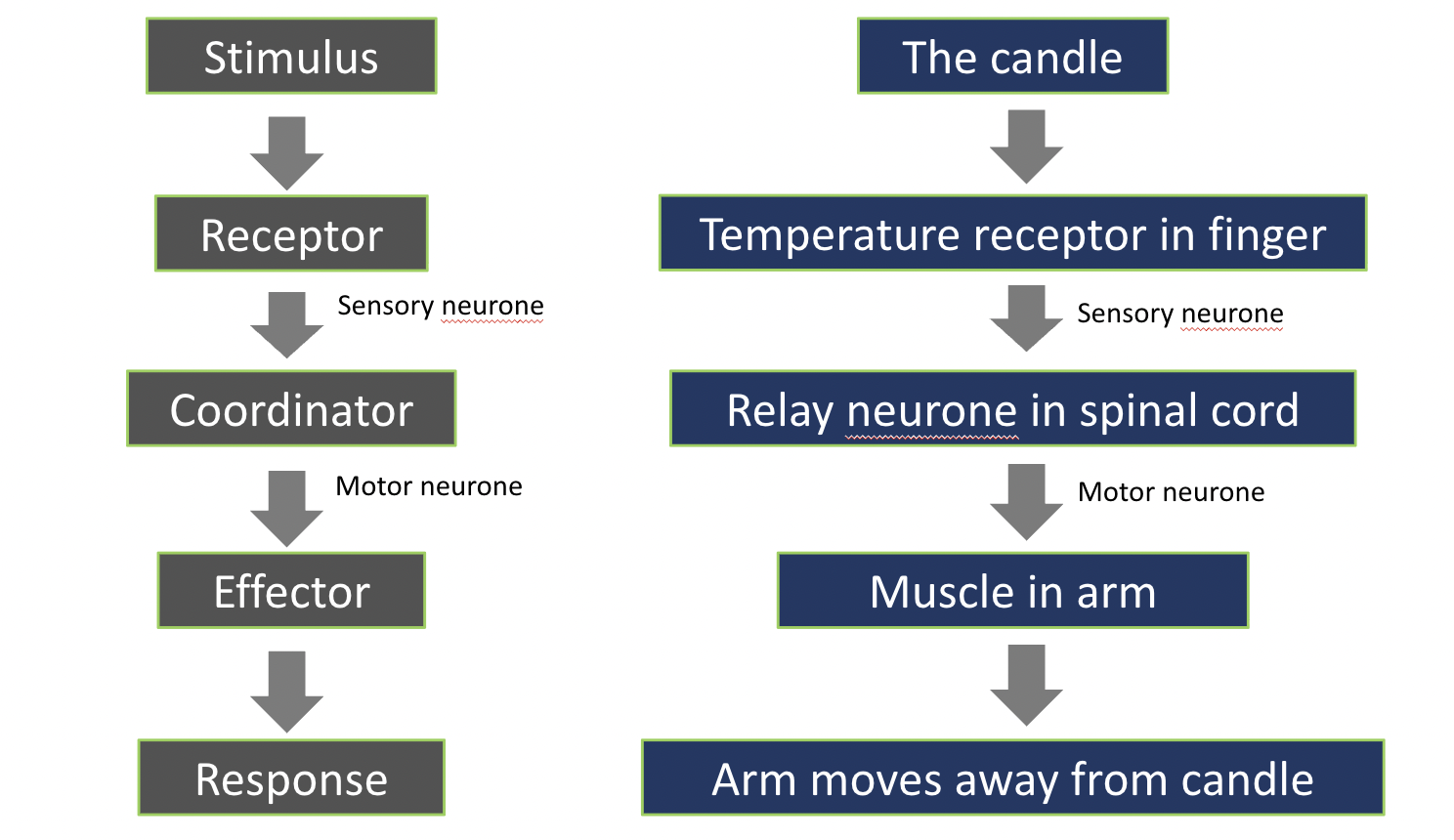
What are the steps in a reflex, and an example?
Stimulus → Receptor (sensory neurone)→ Coordinator (motor neurone) → Effector → Response
The Candle → Temperature Receptor in Finger (sensory neurone) → Relay neurone in spinal cord (motor neurone) → Muscle in arm → Arm moves away from candle