Pelvic Pain
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Dysmenorrhea
Painful menses either due to the absence of other pathology (primary) or attributable to pelvic pathology (secondary)
Dyspareunia
Pain with intercourse
Dyschezia
Pain with bowel movements
Dysuria
Pain with urination
Vulvodynia
Pain of the vulva
Allodynia
Pain with non-noxious stimuli
Hyperalgesia
increased response to noxious stimuli
Acute
Which type of pain last under 3 months, signifies an acute disturbance from normal, and by removing the stimuli, the pain reduces
Chronic
Which type of pain last more than 6 months, may not be associated with a clear injury, and may have a social/sexual/emotional consequence?
Somatic (peritoneum, fascia, muscles, skin, bones - things with lots of nerves)
Which type of pain is often sharp, lateralized and maps to dermatomes?
Visceral (think bladder, bowel, uterus, ovaries)
Which type of pain is often dull/vague and the perceived location often corresponds to embryologic origin (midgut vs. hindgut)?
Dysuria, frequency, hematuria, incomplete voiding, incontinence, constipation/diarrhea (cyclic or chronic), Dyschezia, hematochezia, vaginal dryness, discharge, vulvar rash, dyspareunia, joint pain, rash, bruising, depression, anxiety, hx of abuse
Common associated symptoms of pelvic pain
herpes, yeast infection, syphilis trauma (straddle, hematoma, lac, assault), skene’s glands, bartholin’s cyst, abscess, vulvar disorders
Vulvar causes of acute pelvic pain
Trauma (penetrating (most common), pelvic fracture, hydraulic), vaginitis, foreign body, candida (burning/irritation), bacterial vaginosis
Vaginal causes of acute pelvic pain
cervicitis
Cervix causes of acute pelvic pain
PID, threatened/incomplete abortion, prolapsing myoma, degenerating myoma
Uterine causes of acute pelvic pain
ectopic pregnancy, PID, salpingitis, paratubal cyst
Fallopian tube causes of acute pelvic pain
PID, cyst/torsin, tuboovarian abscess, mittelschmerz, ectopic pregnancy
Ovarian causes of acute pelvic pain
Gastroenteritis, colitis, appendicitis, diverticulitis, constipation, IBS, IBD, SBO, mesenteric ischemia, malignancy, cystitis, pyelonephritis, nephrolithiasis, perinephric abscess, hernia, abdominal wall trauma, peritonitis, herpes zoster, opiate withdrawal, vasculitis, sickle cell crisis, AAA
Non-Gyn causes of acute pelvic pain
Abdominal exam (scars, distention, sounds, etc), Pelvic exam (speculum and bimanual)
Important tips for Physical Exam for Pelvic Pain
Qual Hcg (unless menopause, hysterectomy), UA/Urine culture (if urinary symptoms present), STI screening (based on risk factors), CBC (infection/anemia), CMP (associated N/V), Type and Screen if preg with vaginal bleeding (Rh status)
Lab evals for pelvic pain
U/S 🥇 (structural masses of the uterus, infected tubes, adnexal masses, free fluid), CT abdomen/pelvis (if it’s not giving gyn), MRI (safe for preggos - indicated for distorted pelvic anatomy, mullerian anomaly evaluation, large/poorly delineated masses)
Imaging studies for Pelvic pain
PID with unclear diagnosis, ovarian torsion, ruptured ectopic, persistent adnexal masses
What are the indications for a diagnostic laparoscopy for acute pain?
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
An ascending infection of the upper female reproductive tract (uterus/adnexa)
Cervical motion tenderness (chandelier’s sign), uterine tenderness, adnexal tender
Physical Exam findings in PID
Fever (over 101.6), mucopurulent discharge, abundant WBCs on saline microscopy, ESR/CRP elevation, N.gonorrhoeae or C.trachomatis
What are some findings that enhance specificity of physical exam findings of PID?
CBC, NAAT (for STIs), pelvic U/S (check for the presence of tuboovarian abscess)
Workup for PID
Abx (Inpatient: cefotetan/Cefoxitin + doxy OR Clinda + gentamicin OR ampicillin/sulbactam + doxy; Outpatient: ceftriaxone/Cefoxitin and probenecid OR 3rd CPH + doxy with or w/o metro; Levofloxacin/ofloxacin with or w/o metro), antiemetics, pain control (NSAIDs)
Management of PID
Ectopic pregnancy
An Extrauterine pregnancy that occurs OUTSIDE the normal endometrium (95% are tubal)
location, size, patient preference, rupture risk
Medical vs. surgical treatment of ectopic pregnancy depends on
Adnexal torsion
A twisting of the adnexa (fallopian tubes/ovary) on a vascular pedicle resulting in ischemia - more common on the right side (increased mobility)
Sharp lower pelvic pain, adnexal pain/tenderness on exam, adnexal mass on U/S
Diagnostics for Adnexal torsion
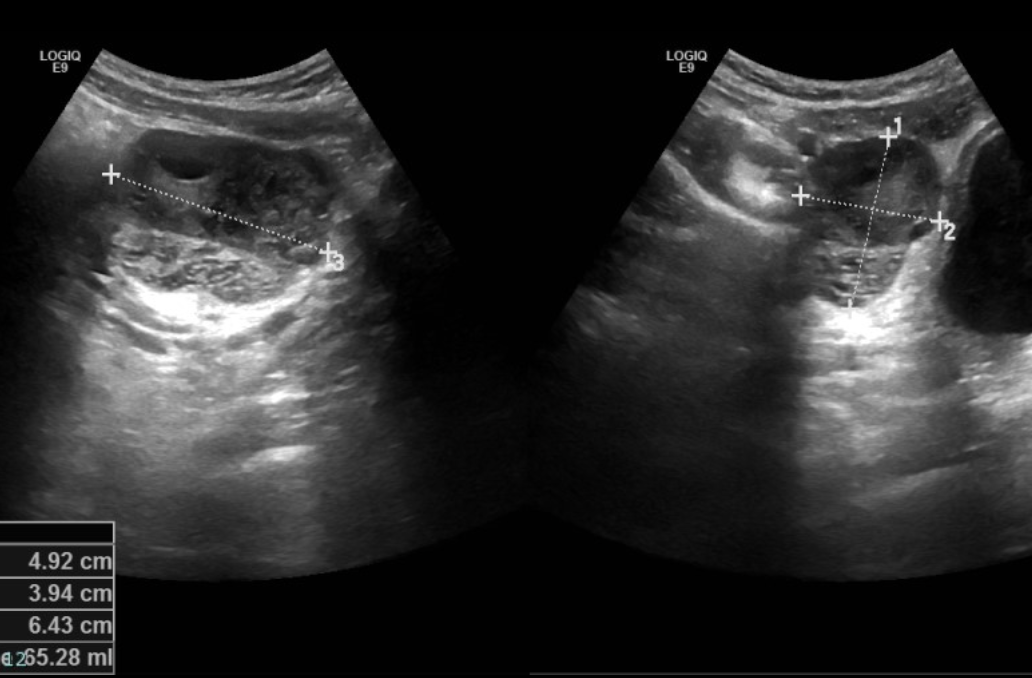
Surgical Emergency (laparoscopy preferred)
Management of Adnexal Torsion
Vaginitis, vaginal atrophy, cervicitis, adenomyosis, leiomyoma, salpingitis, hydrosalpinx, cysts, endometriosis, adhesive disease, pelvic organ prolapse, Pelvic congestion syndrome, malignancy
GYN causes of Chronic Pelvic Pain
Constipation, IBD, IBS, diverticulitis, stones, painful bladder syndrome, interstitial cystitis, pelvic floor dysfunction, fibromyalgia, arthritis, depression, medication dependency, PTSD, abuse
Non-GYN causes of chronic pelvic pain
Adenomyosis
An extension of the endometrial glands and stroma into the uterine musculature that occurs in 20-40% of hysterectomy specimens
heavy and painful periods, uterus symmetrically enlarged/tender/boggy on exam, Heterogenous appearance of the myometrium (TVUS), Hysterectomy 🏆
Findings in Adenomyosis
Uterine Leiomyomas
A benign smooth muscle neoplasms (most common uterine neoplasms) of the uterine musculature that is experienced by 70-80% of patients by their late 40s
pelvic pain, bulk symptoms (pressure), urinary symptoms (pressure on bladder), back pain, heavy/prolonged menstrual bleeding
Symptoms of uterine Leiomyomas (2/3s are asymptomatic)
Hormones (combined or progesterone only), GNRH agonist 🩹 (temporary), myomectomy (hysteroscopic/abdominal), uterine fibroid embolization, radiofrequency fibroid ablation, hystectomy
Treatment plan for Leiomyomas
Diameters of 3cm+, mobile, simple, not associated with ascites
Characteristics of a Functional Ovarian Cysts
U/S, palpable adnexal mass on exam
Diagnostics for Functional Ovarian Cysts
Observation (those under 10cm will likely regress), surgical management if persistent/symptomatic, OCPs (prevent future cyst - data doesn’t really prove this but oh well)
Treatment for Functional Ovarian Cysts
Mature cystic Teratoma (dermoid cysts)
The most common ovarian neoplasms that is composed of ectodermal tissues (sweat/sebaceous glands, hair follicles, teeth)
Cystectomy/oophorectomy (examine the other side during surgery as well), laparotomy/laparoscopic procedure (depends on the size of the cyst)
Management of teratomas
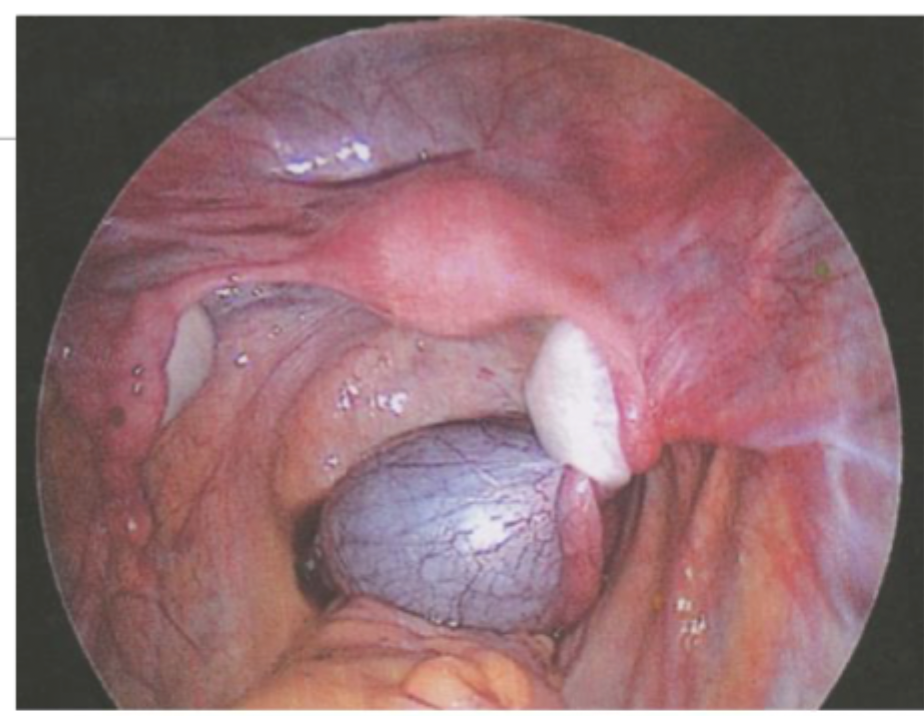
Endometriosis
The presence of endometrial glands and stroma outside the endometrial cavity or uterine musculature that is present in up to 80% of women with pelvic pain
Frequent/prolonged menses, white, family hx, early menarche, nulliparity, urine anomalies
Risk factors for Endometriosis
Dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, dyschezia, pelvic pain (70%), cyclic bowel/bladder symptoms, decreased fertlity
Symptoms of Endometriosis
stage, site, morphologic characteristics, severity of symptoms
When it comes to Endometriosis there is NO relationship between
Fixed uterus/adnexa, adnexal mass (endometrioma), uterosacral nodularity, retroverted uterus
Physical exam findings of Endometriosis
Laparoscopy (superficial powder burn lesions - black, blue, red, clear OR endometriomas (chocolate cysts))
Definitive diagnostics for Endometriosis 🏆
Hormonal management (continuous OCP or progesterone only, DMPA, hormonal IUD, Depo-lupron (GNRH agonist), Elagolix (GNRH antagonist)), Surgical excision/ablation, Hysterectomy with maybe bilateral salpingo-oophorecomy 🏆
Treatment plan for Endometriosis
Related to defection, associated with change in stool frequency/appearence
ROME IV Criteria for IBS
Education/lifestyle changes (mild), Loperamide (if moderate IBS-D); polyethylene glycol/pelvic floor therapy (if moderate IBS-C); Refer to GI or antidepressant if severe
Treatment for IBS
Bladder pain syndrome
An unpleasant sensation perceived to be related to the urinary bladder, associated with LUTS for longer than 6 weeks without infection or other identifiable cause
Worsened by bladder filling, certain foods/drinks, improved by voiding, urinary urgency/frequency, pain in the lower abdomen, perineum, urethra, low back pain
Symptoms of Bladder pain syndrome
Pain management (amitriptyline, cimetidine, PPS), patient education, stress management, self-care modification, PT, Intravesical DMSO/heparin/lidocaine, elimination diet challenge
Treatment plan for Bladder pain syndrome
Myofascial Pain Syndrome
A hyperirritable area within a muscle promotes persistent fiber contraction - “trigger points” can be identified with palpation of different pelvic floor muscle groups
Pelvic floor PT
Treatment for Myofascial Pain Syndrome