4TH LE - BOT 14
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
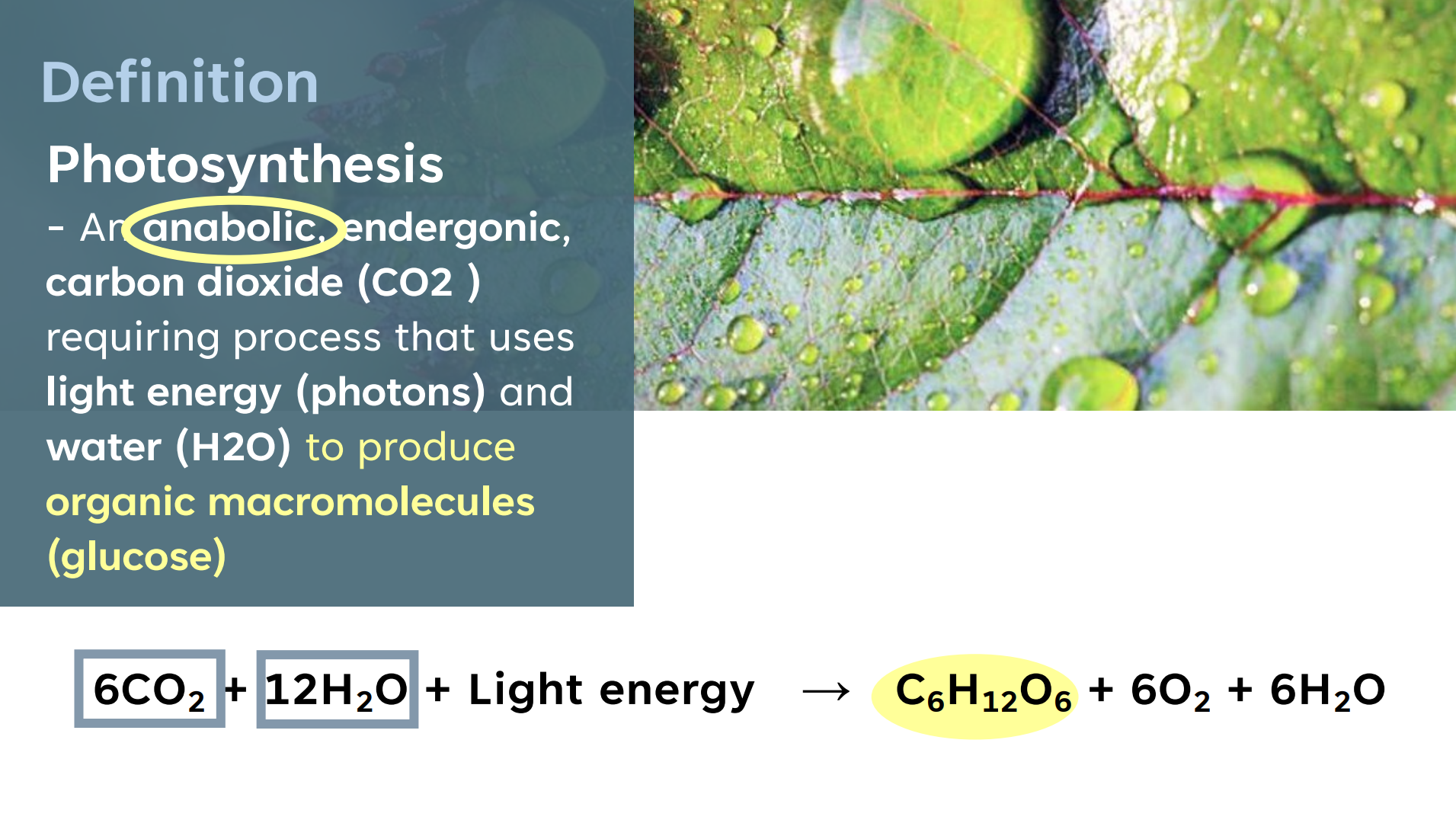
Photosynthesis
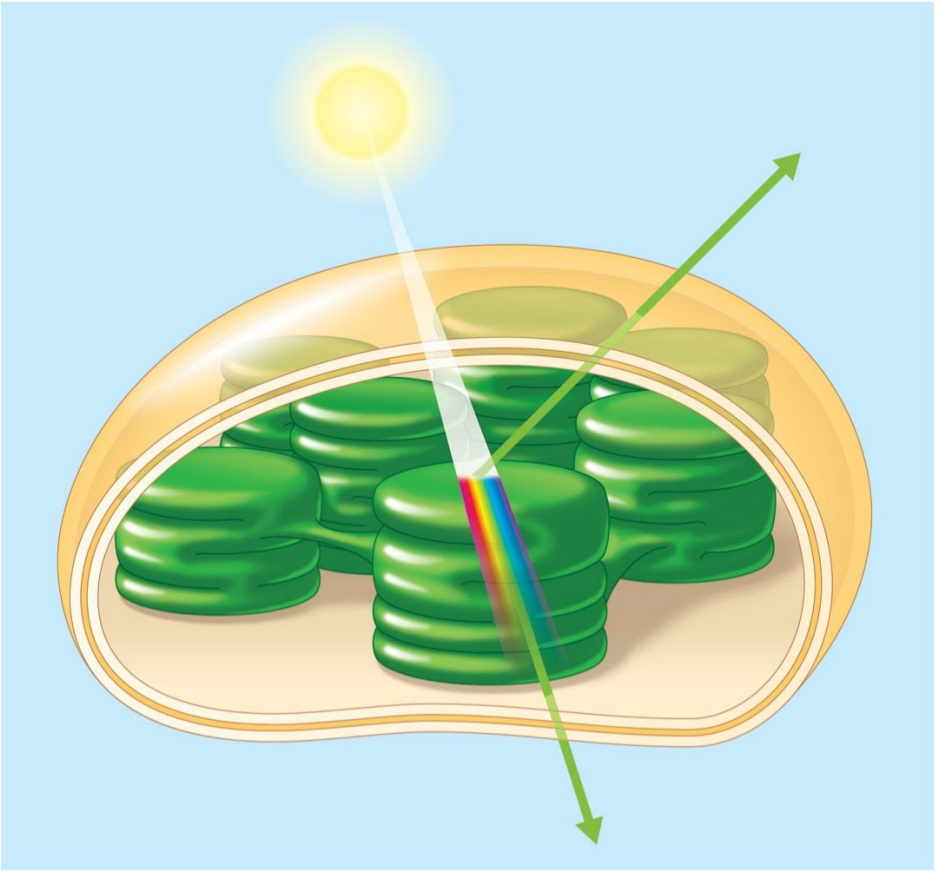
An anabolic, endergonic, carbon dioxide (CO2 ) requiring process that uses light energy (photons) and water (H2O) to produce organic macromolecules (glucose)

What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis?
Why is photosynthesis considered anabolic?
Why is photosynthesis considered endergonic?
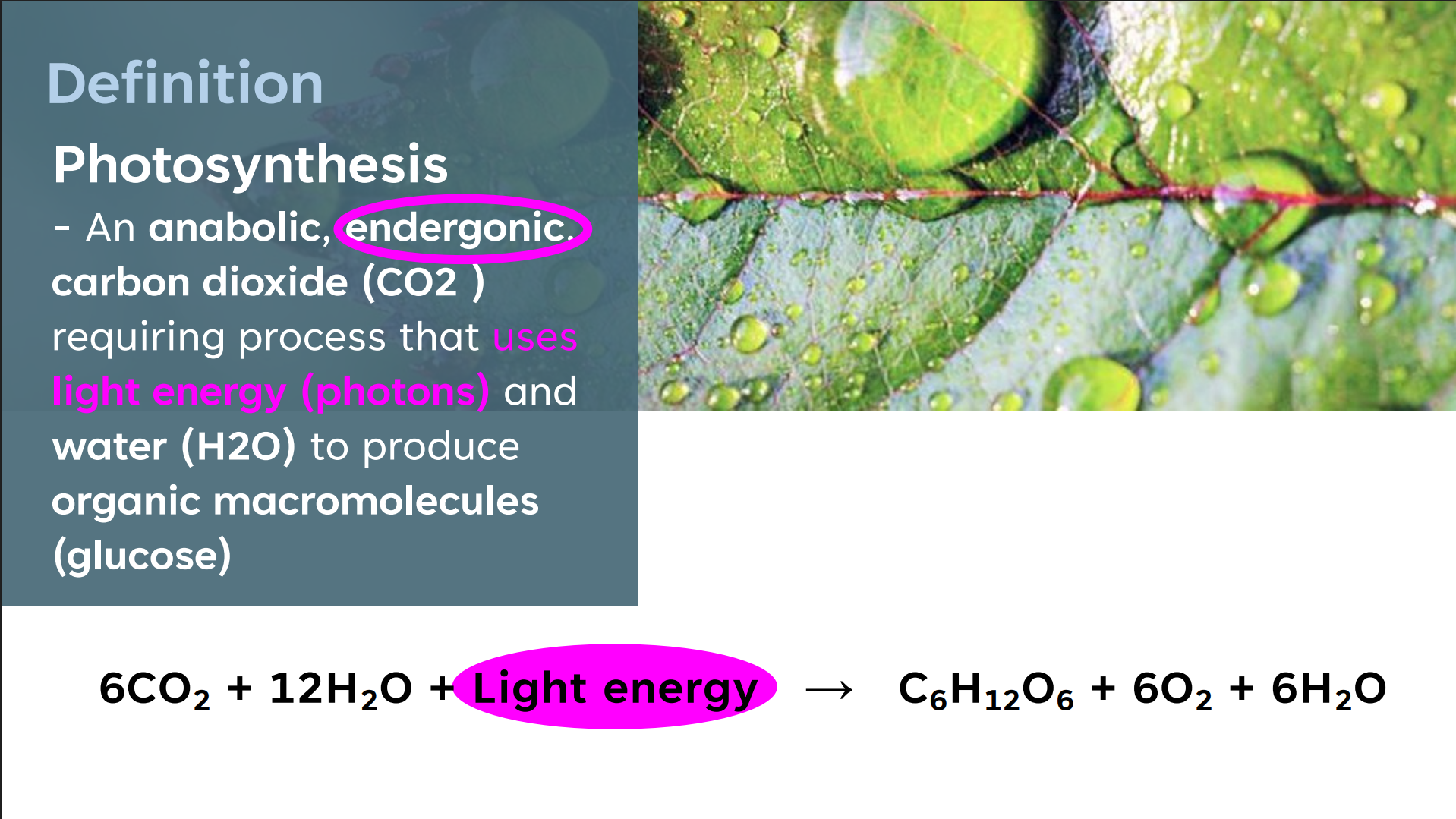
Photosynthesis
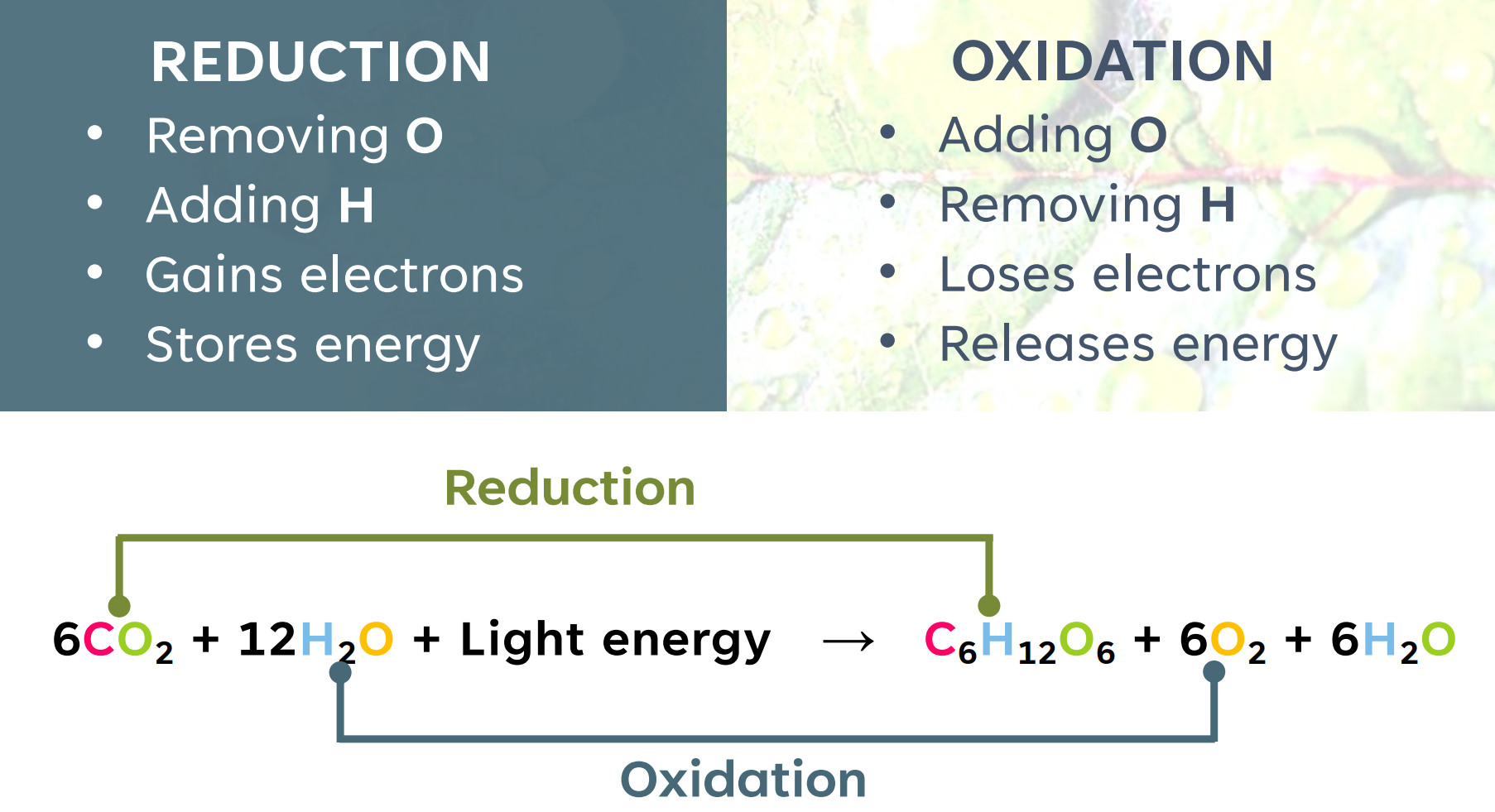
It is a redox process where carbon dioxide is reduced and water is oxidized



Photosynthesis; photoautotrophs
_________________ - Enables plants, algae and other photosynthetic organisms to make their own food (organic molecules) using light energy (________________)
Photosynthesis
Ensures the availability of energy source for humans and other heterotrophs
Provides oxygen, which is vital to respiration
Leaves
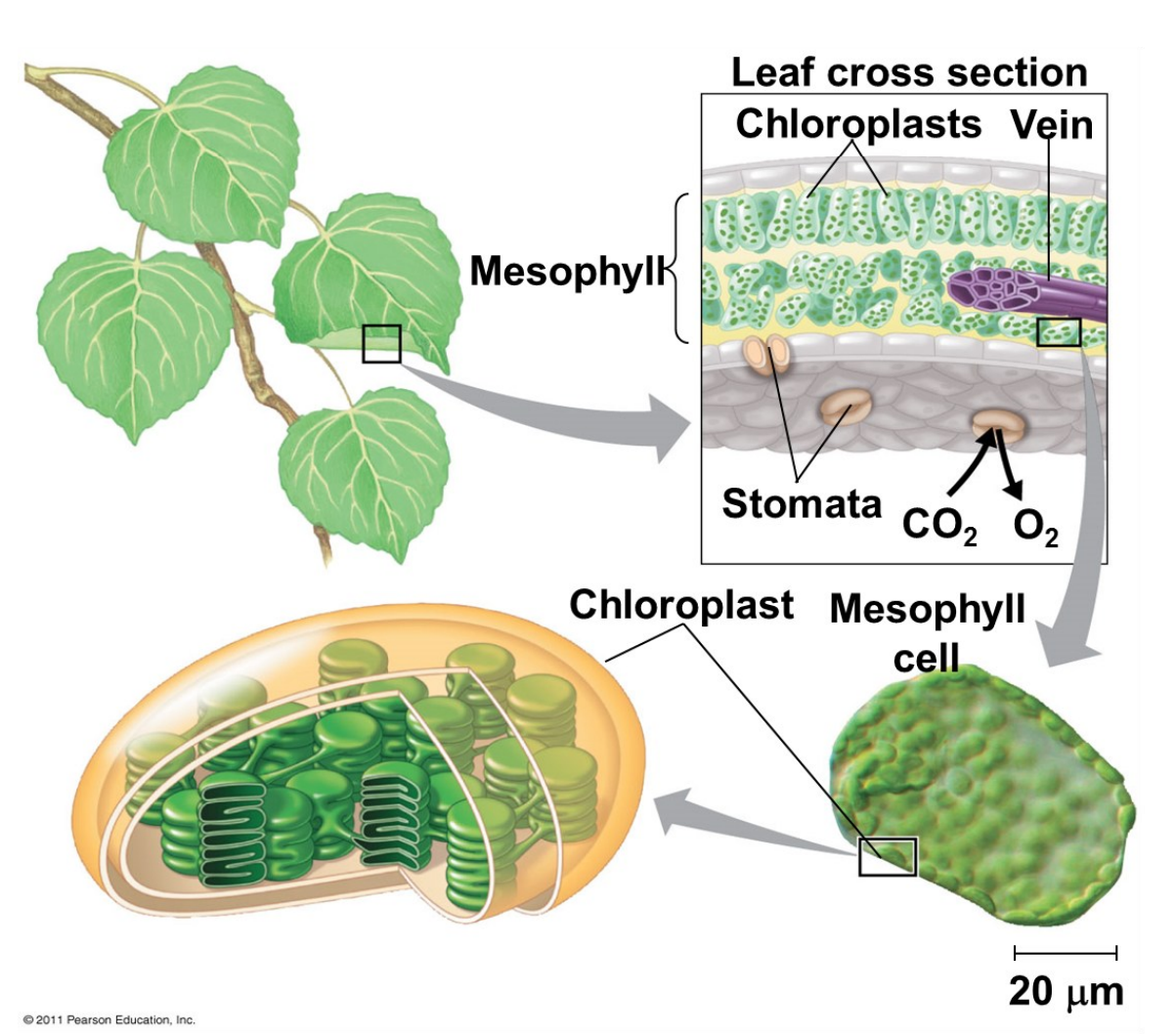
___________ are the major plant organ of photosynthesis
stomata

CO2 enters and O2 exits the through the __________
xylem
Sugars; phloem

Water enters the leaf through veins (________)
_________ (the products of photosynthesis) leave the leaf also through veins (________)
chlorophyll; chloroplasts

Green color is from __________, the green pigment within ___________
mesophyll

Chloroplasts are found mainly in cells of the ___________, the interior tissue of the leaf
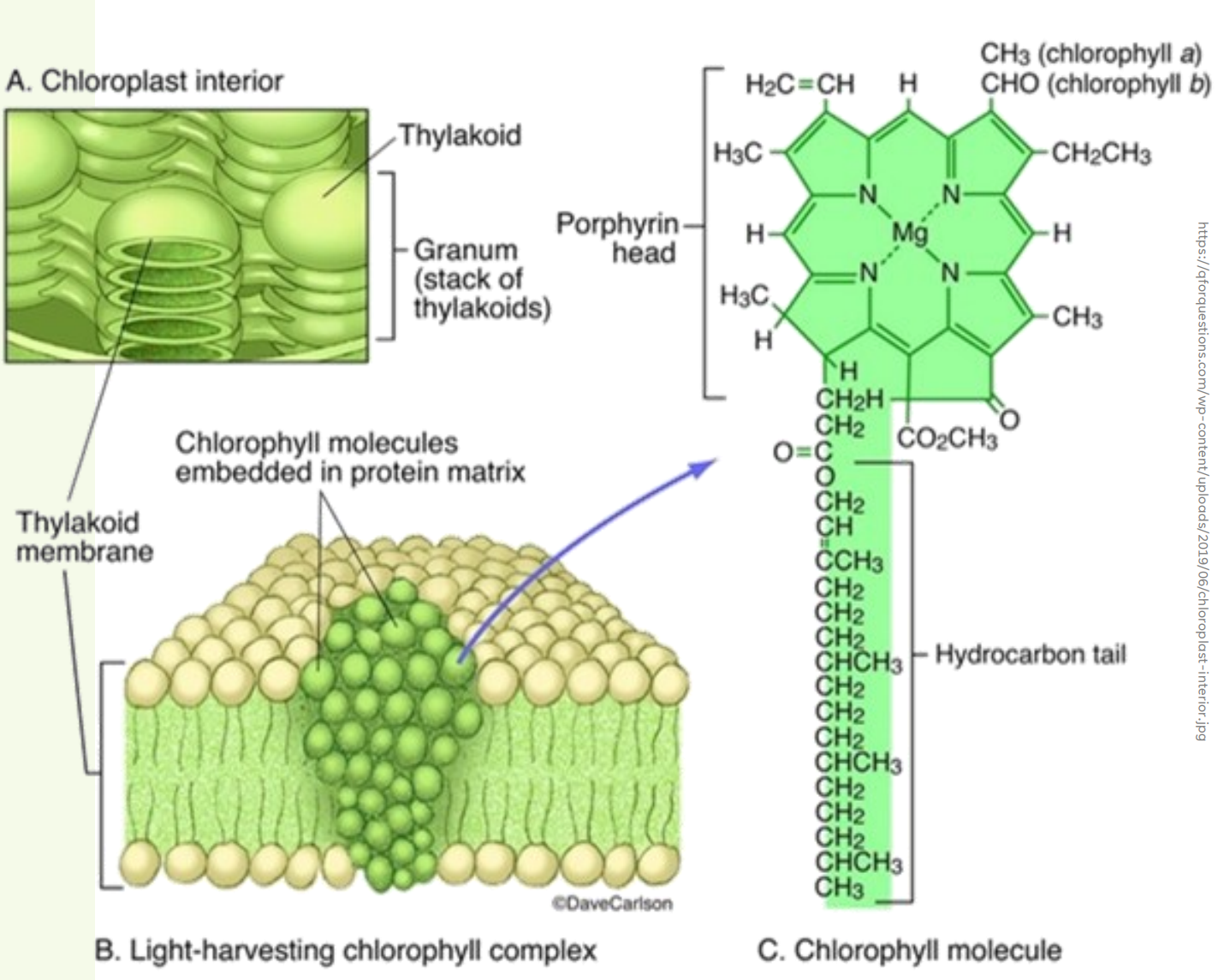
CHLOROPLAST
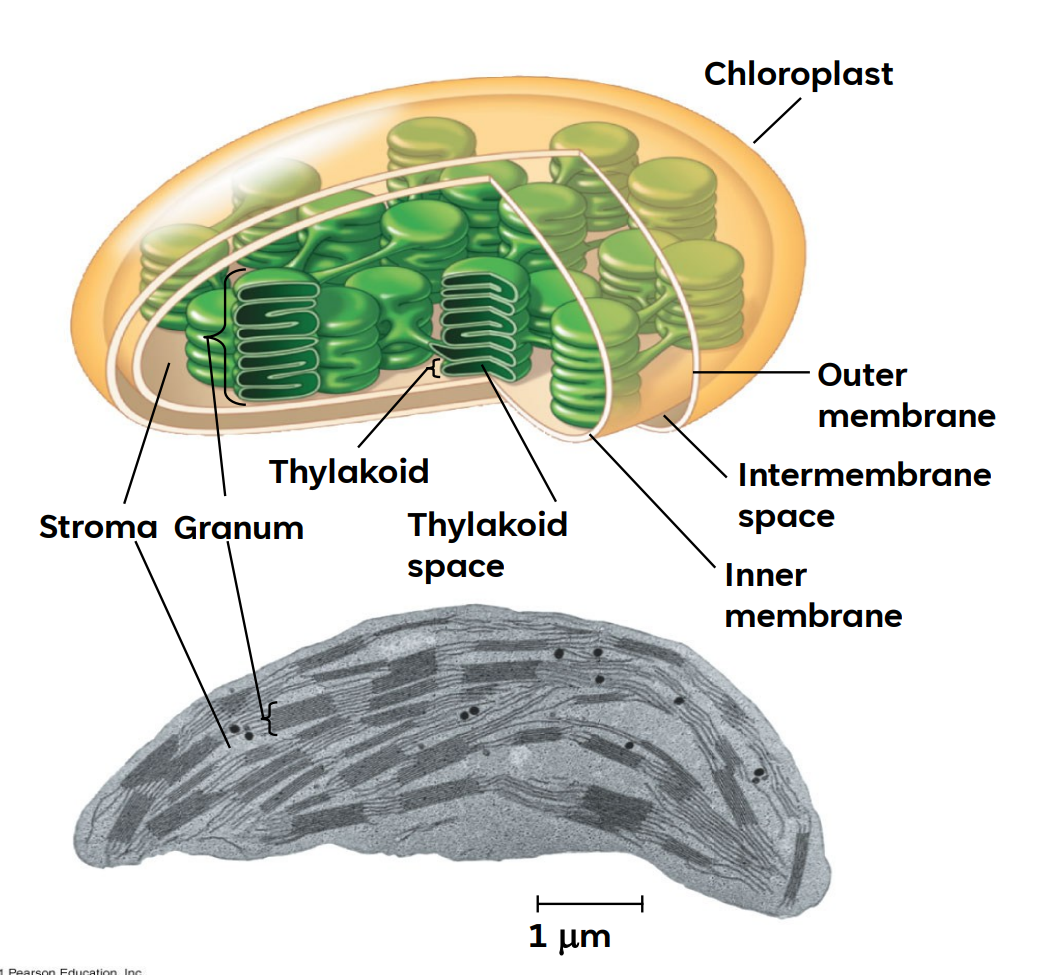
It is a 3 membrane system, the organelle responsible for photosynthesis
thylakoids

Chlorophyll and other pigments are in the membranes of ___________ (connected sacs in the chloroplast);
grana

thylakoids may be stacked in columns called __________
stroma

Chloroplasts also contain __________, a dense interior fluid
sunlight
ATP; NADP+; NADPH
ATP; NADPH
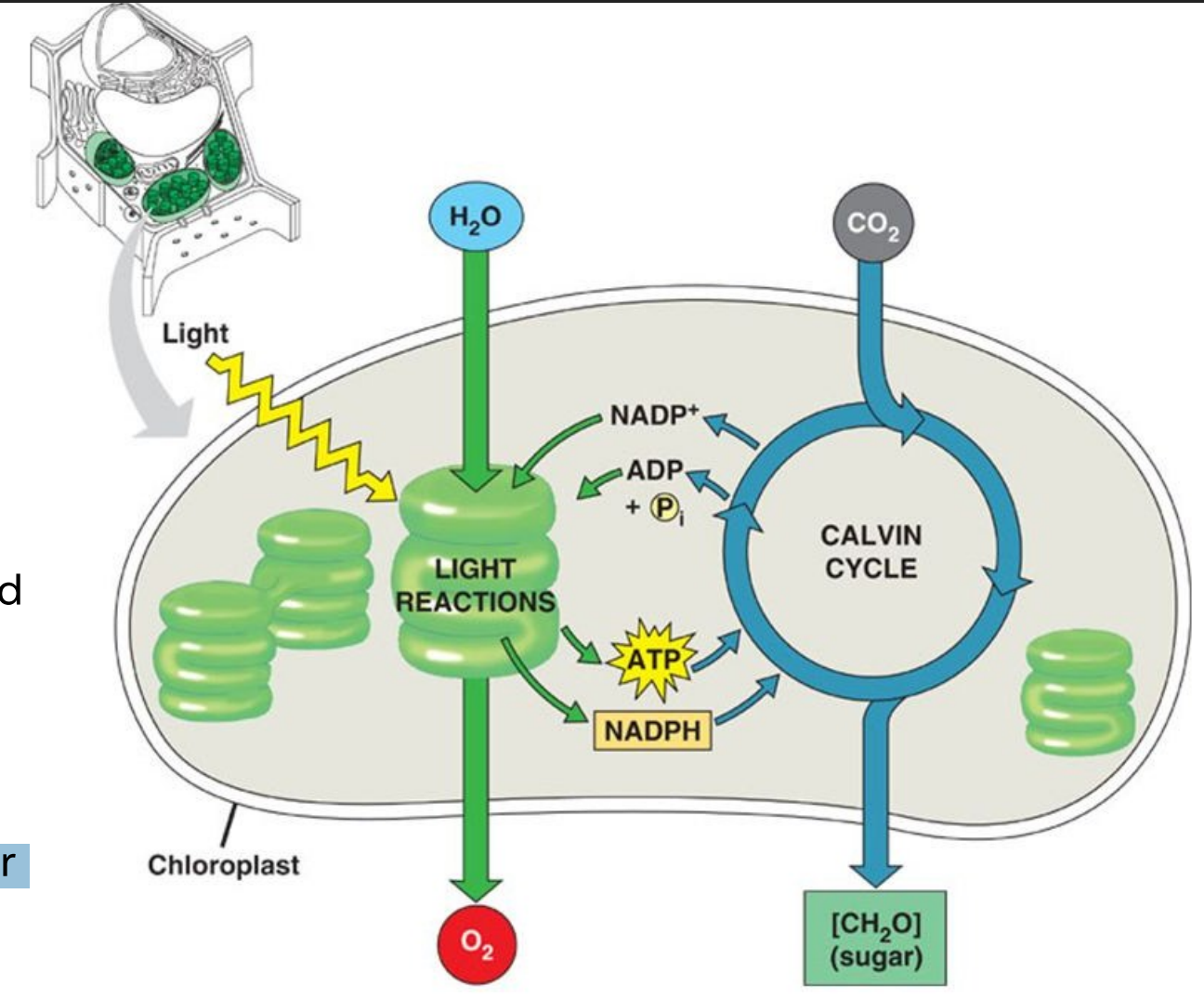
Two stages of photosynthesis
Light reactions
capturing energy from ________;
using the energy to make ____ and to reduce the compound _________, an electron carrier, to ________
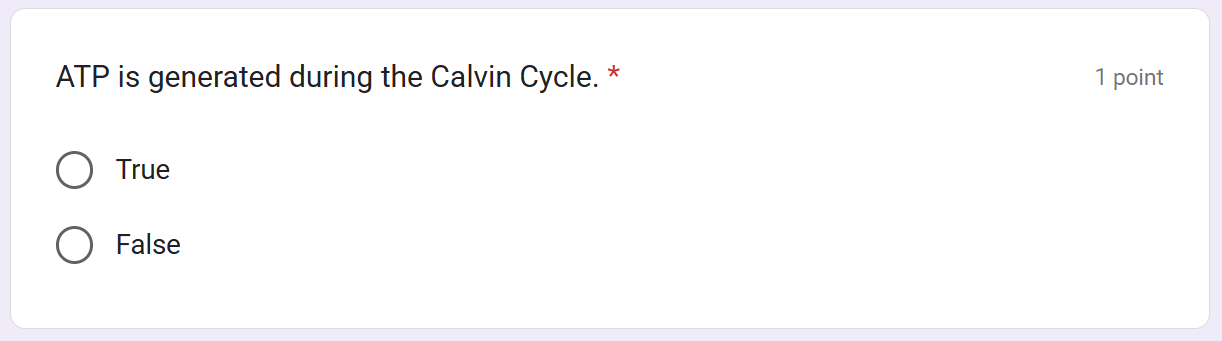
Calvin cycle
using the ____ and _______ to power the synthesis of organic molecules from CO2 in the air
electromagnetic spectrum
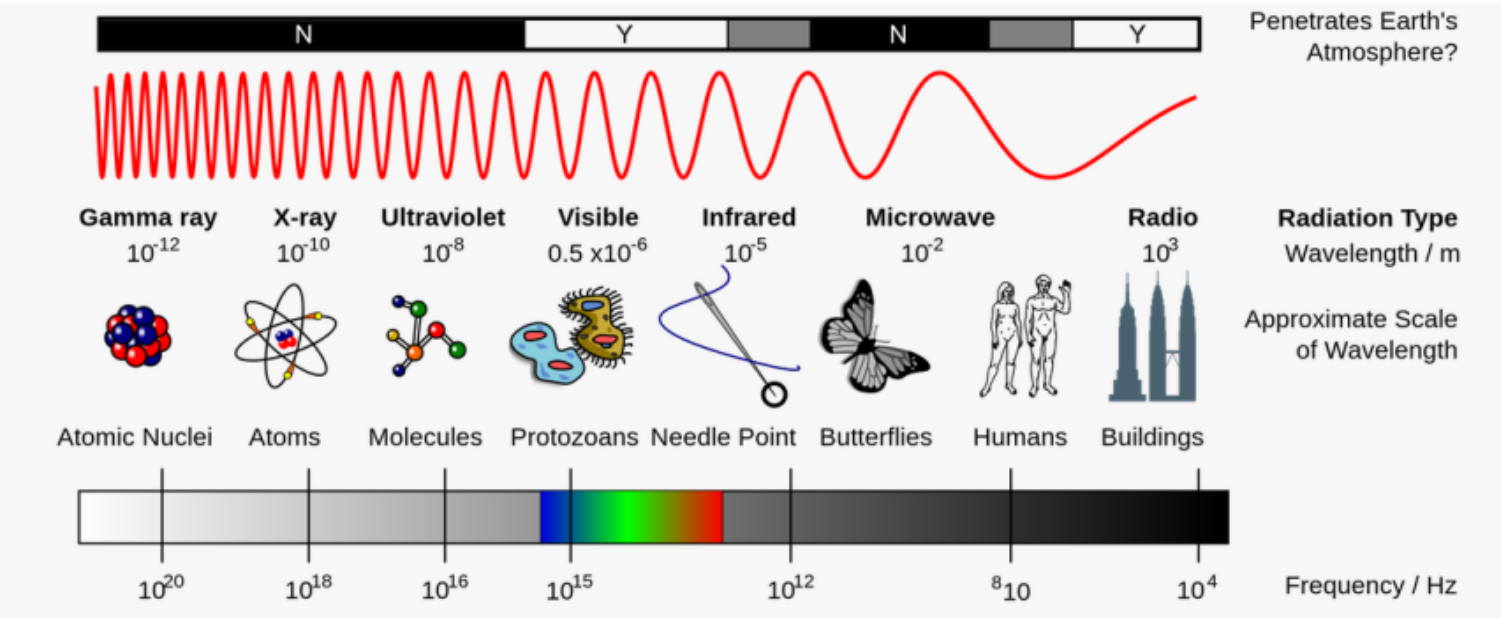
The _______________ is the entire range of electromagnetic energy (EME), or radiation hitting the Earth
Wavelength
Wavelength
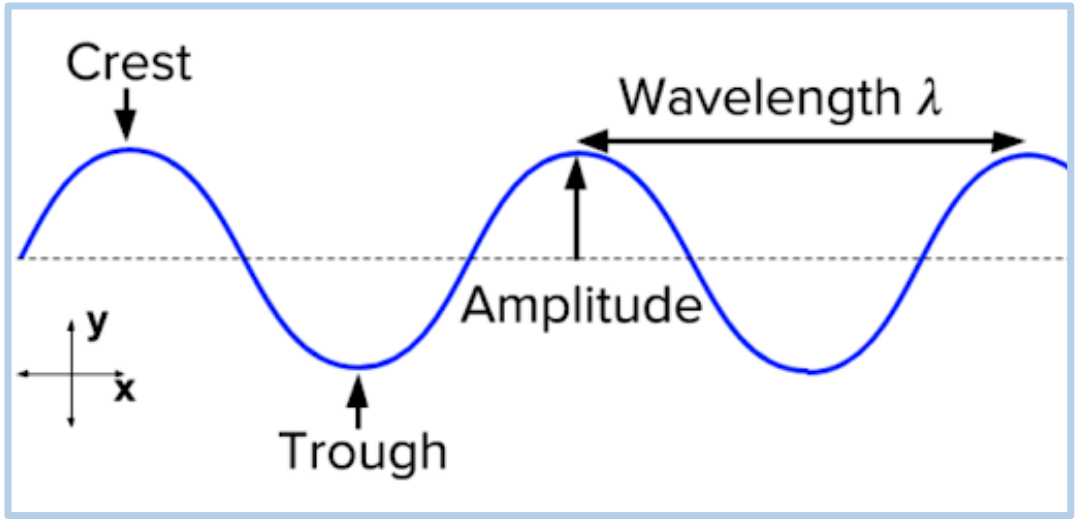

EME travels in rhythmic waves
_____________ is the distance between crests of waves
_____________ determines the type of EME
photons
750-380
EME consists of discrete particles, called _________; a photon has a fixed quantity of energy
Visible light consists of wavelengths that produce colors we can see (ROYGBIV; ________ nm wavelength, respectively)
Pigments
pigments
reflected
__________ are substances that absorb visible light
Different ______________ absorb different wavelengths
Wavelengths that are not absorbed are _________ or transmitted
Chlorophyll
Leaves appear green because chlorophyll reflects and transmits green light
___________ is the main photosynthetic pigment
Why are leaves green?
Chlorophyll a
main photosynthetic pigment (specify)
found in all photoautotroph
chlorophyll a
Chlorophyll b
Chlorophyll c
Chlorophyll d
Accessory chlorophyll pigments absorb different wavelengths of a light and pass the energy to ___________
Chlorophyll _
Chlorophyll _
Chlorophyll _
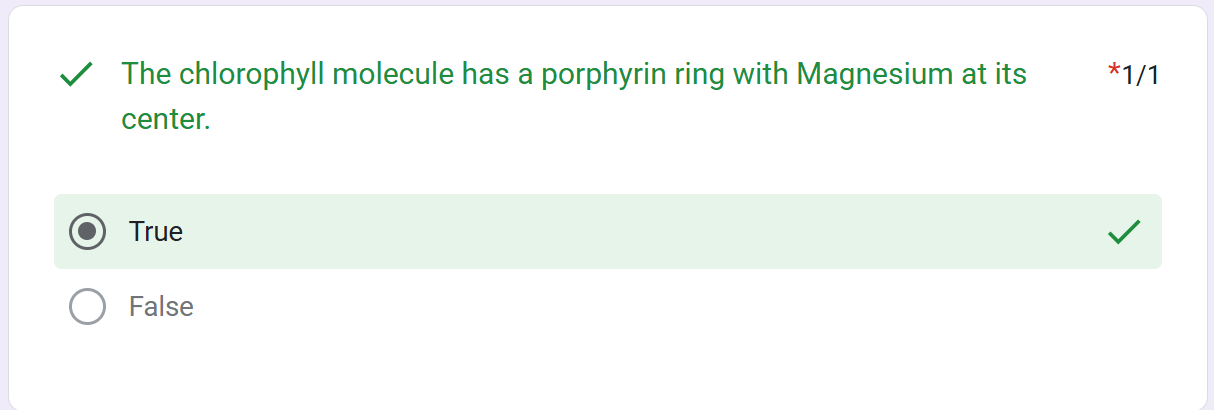
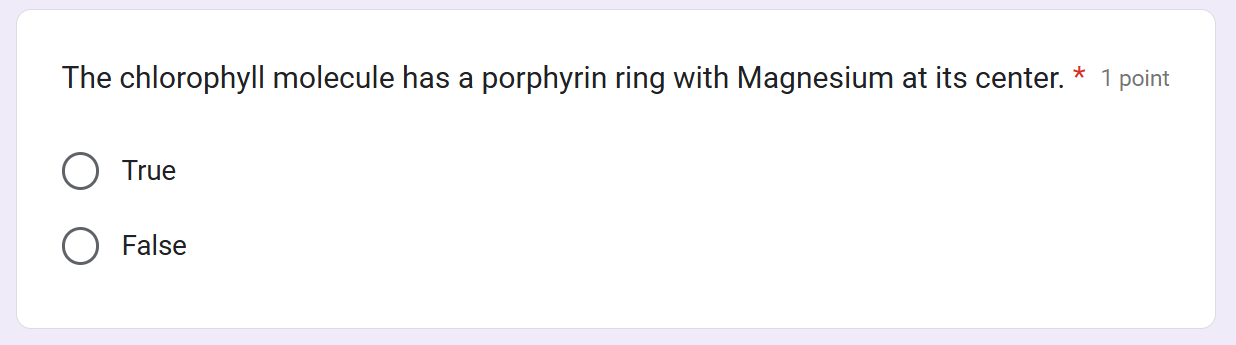
porphyrin
Mg
hydrocarbon; thylakoid membranes
Structure of chlorophyll:
_________ ring (absorbs light)
central ___ atom
__________ tail interacts with hydrophobic regions of proteins inside __________- of chloroplast
blue; red
Carotenoids
anthocyanins
fucoxanthin
xanthophylls
Chlorophyll a and b absorb mainly in the ______ (422-492 nm) and ______ (647-760 nm) regions
Other pigments include:
__________ (yellow & orange);
__________ (red);
__________ (brown);
__________ (yellow)
F
Absorb excess light that CAN damage chlorophylls
T or F
Absorb excess light that cannot damage chlorophylls
potential
heat; fluorescence
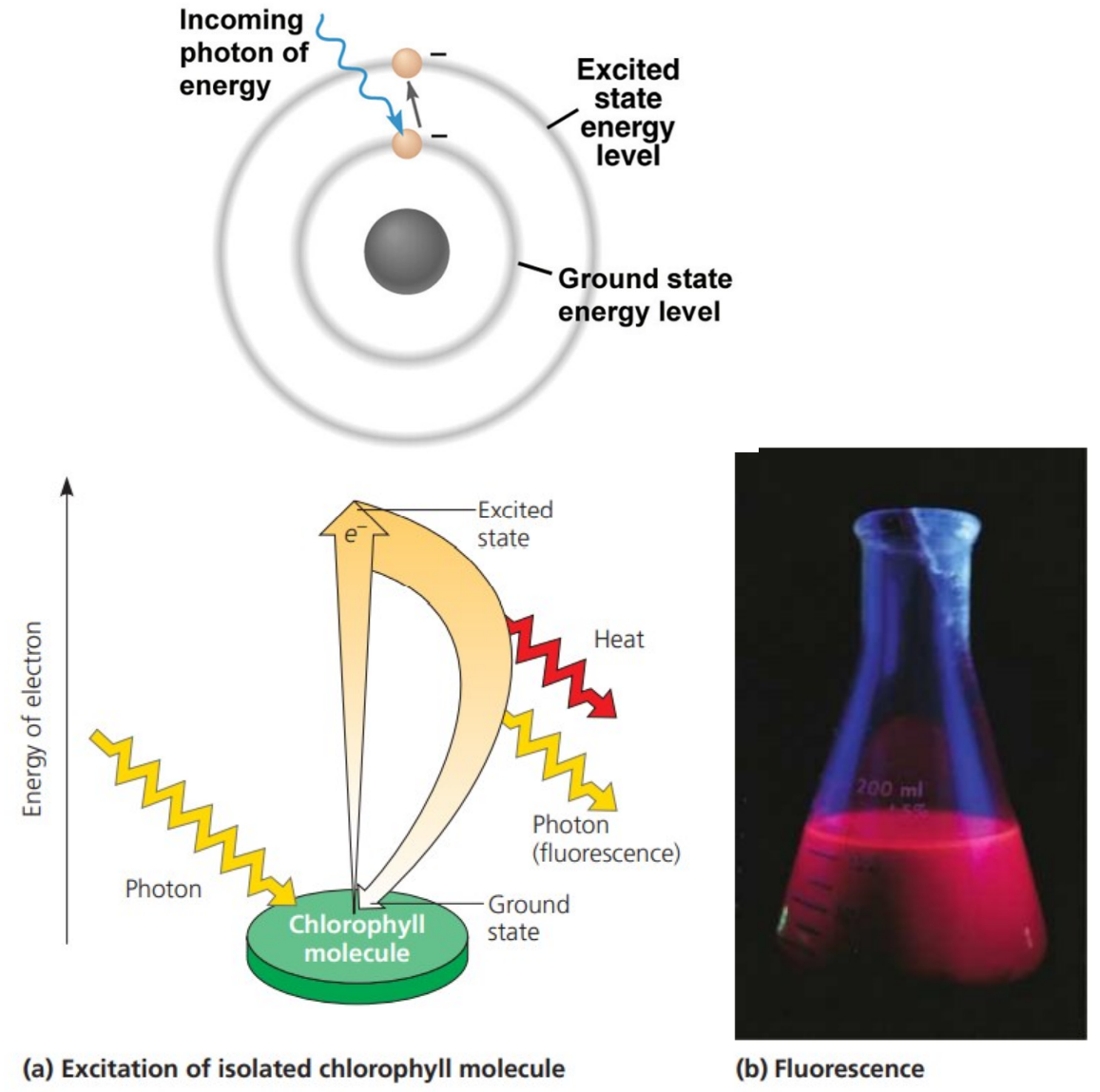
What happens when light is absorbed by atoms or molecules?
The photon boosts an electron to an orbital where it has more _________ energy
If the illuminated molecule is isolated, its excited electron immediately returns to ground state, releasing _______ and ______________
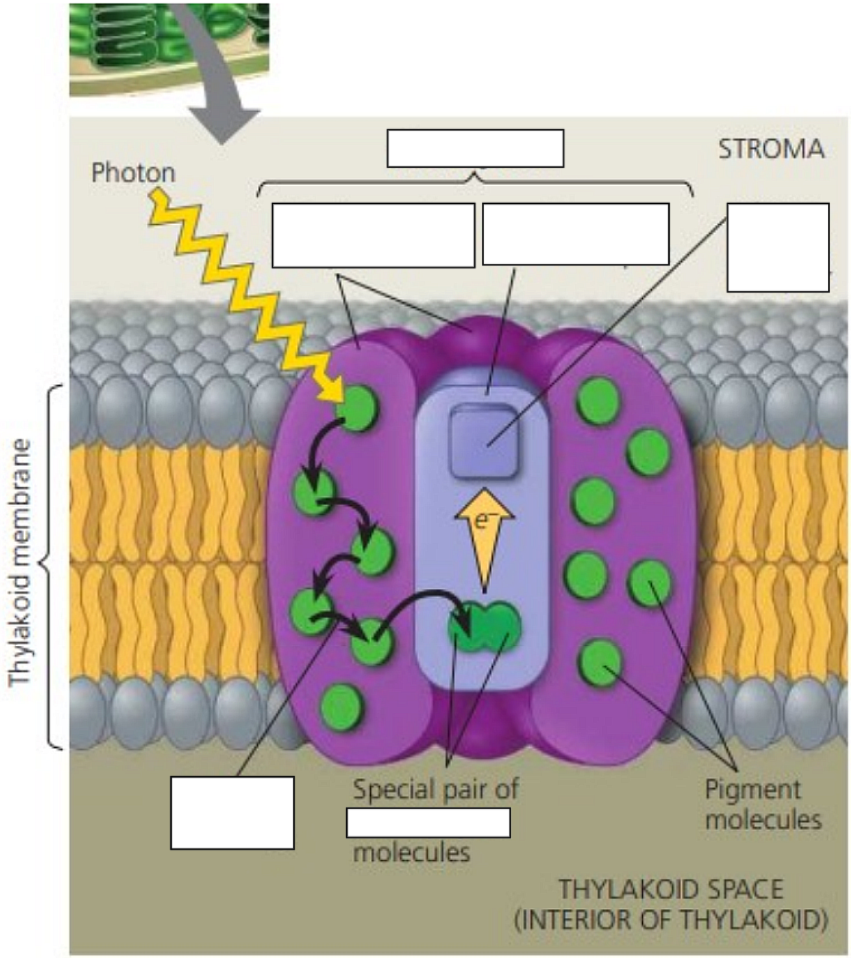
pigment antenna complexes; reaction center
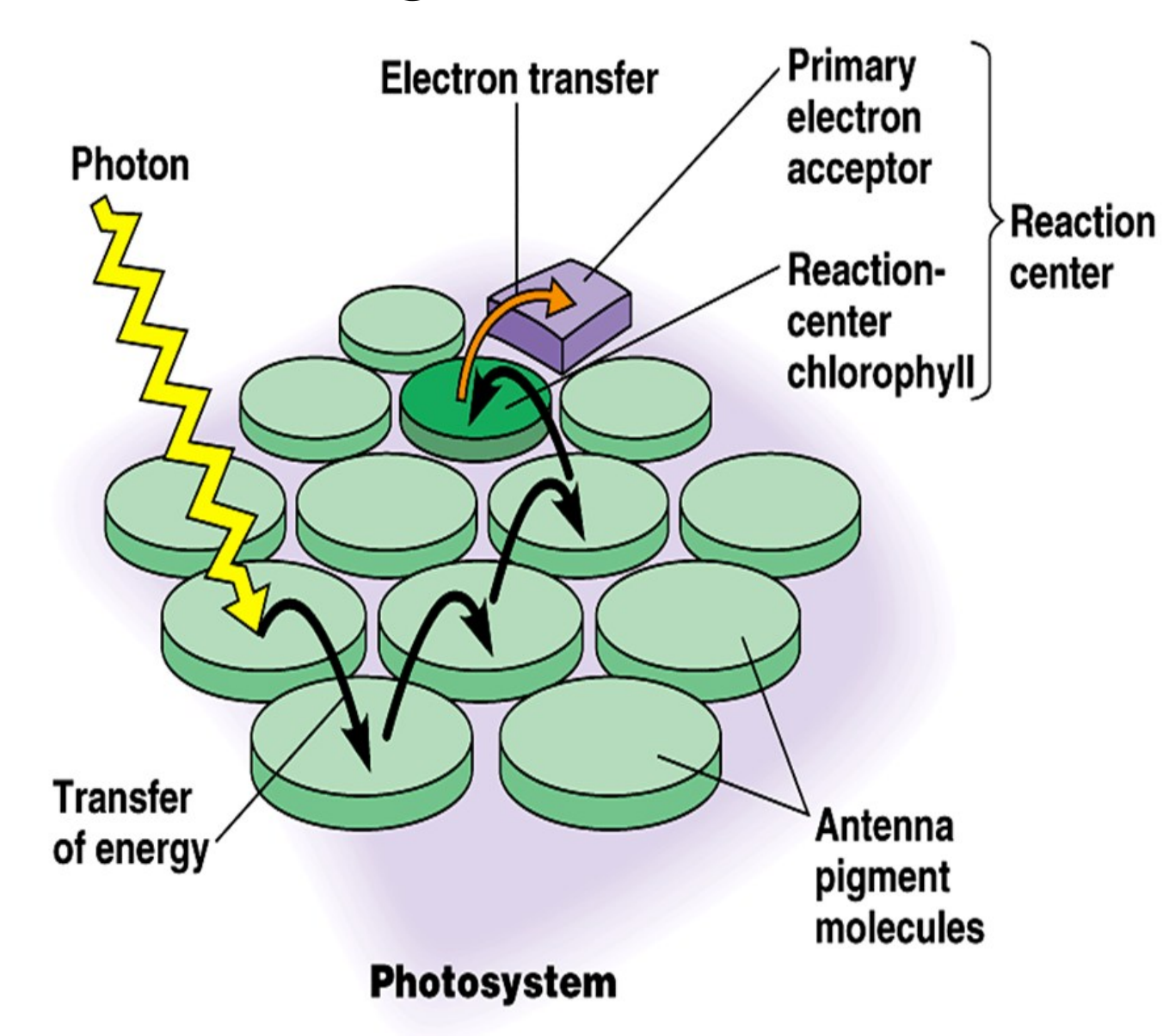
Photosystems I and II are light-harvesting units of the light-dependent reactions
A photosystem: _____________________ + _______________; found in thylakoid membrane
antenna complex/ light harvesting complex

consists of chlorophyll molecules and accessory pigment molecules, with pigment binding proteins
reaction center

specialized chlorophyll a molecules and proteins + a primary electron acceptor
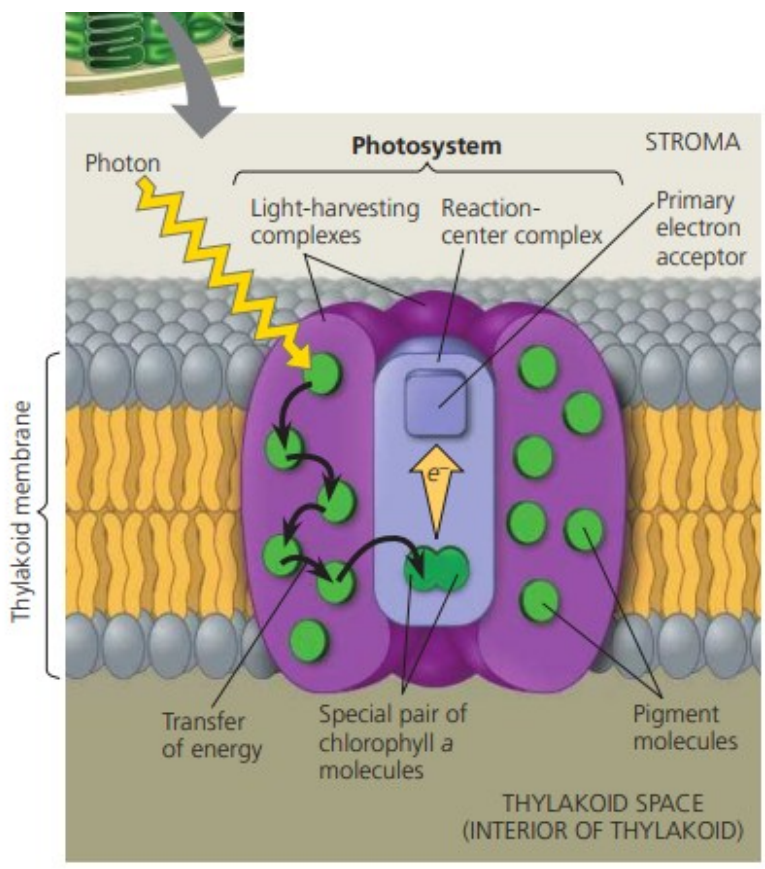
When a photon strikes a pigment molecule,
the energy is transferred from one molecule to another until it is passed to the pair of chlorophyll a molecules in the reaction-center.
This chlorophyll pair enables them to use the energy from light to boost their electrons to a higher energy level '
and transfer it to the primary electron acceptor, a molecule capable of accepting electrons and becoming reduced.
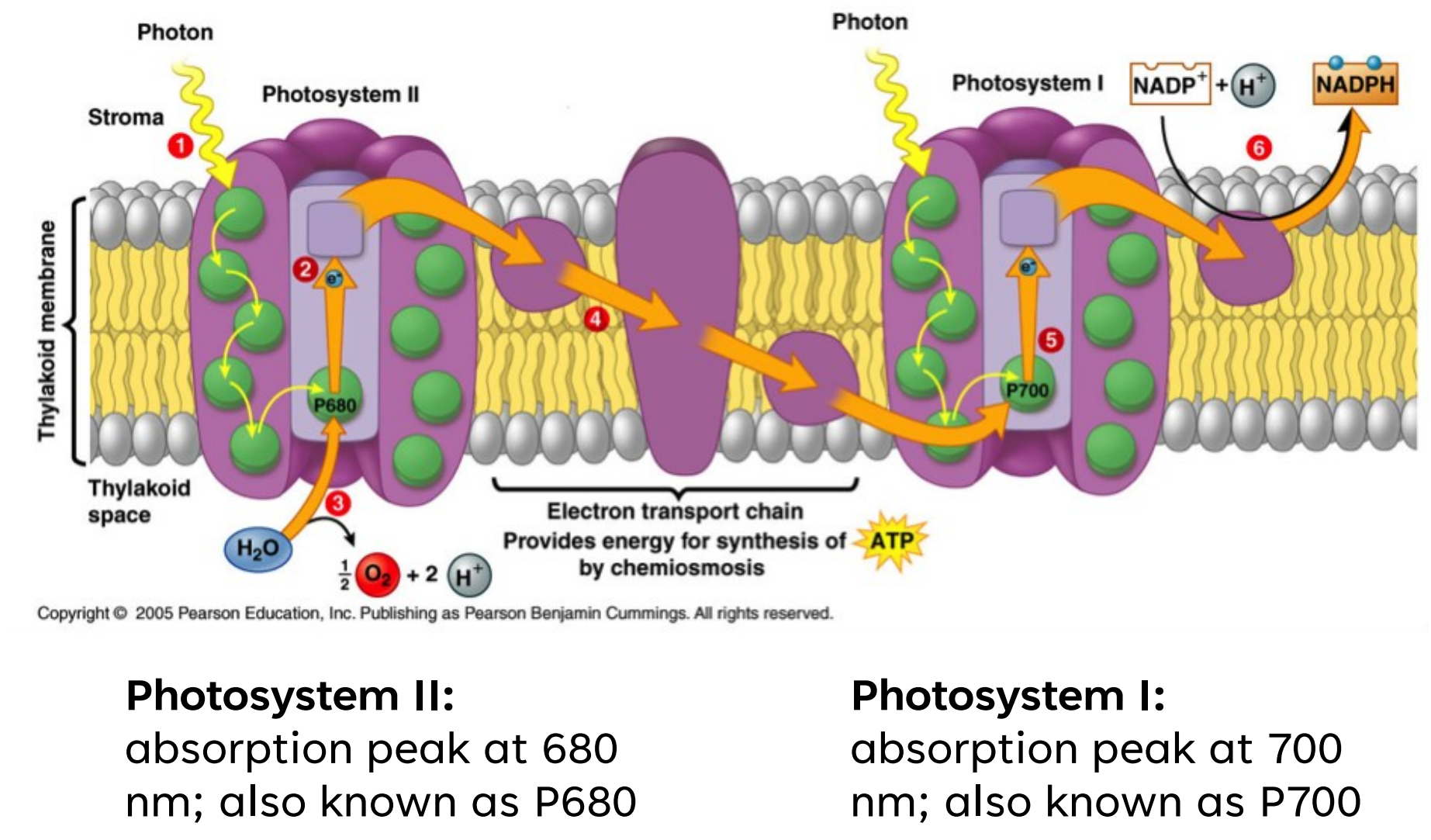
680; P680
700; P700

Photosystem II: absorption peak at ___ nm; also known as ____
Photosystem I: absorption peak at ___ nm; also known as ____
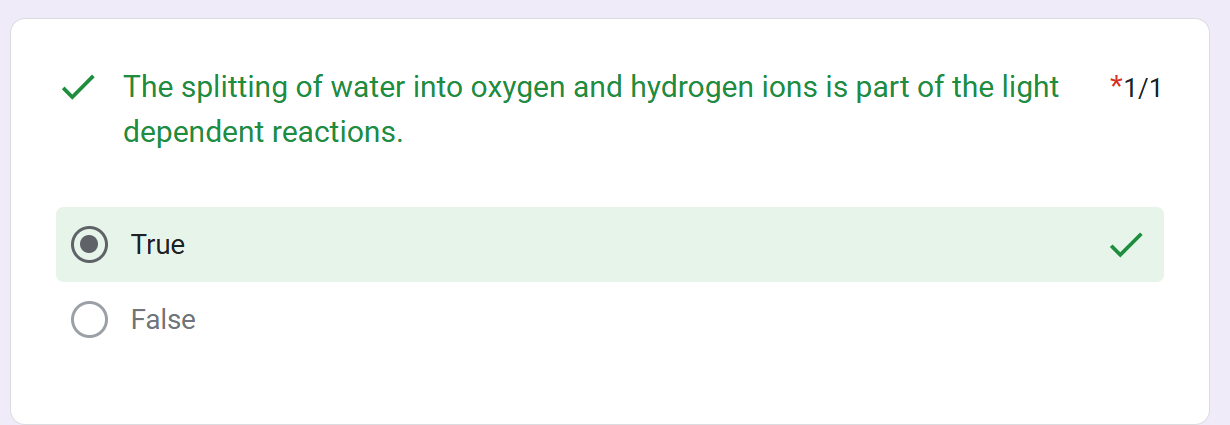
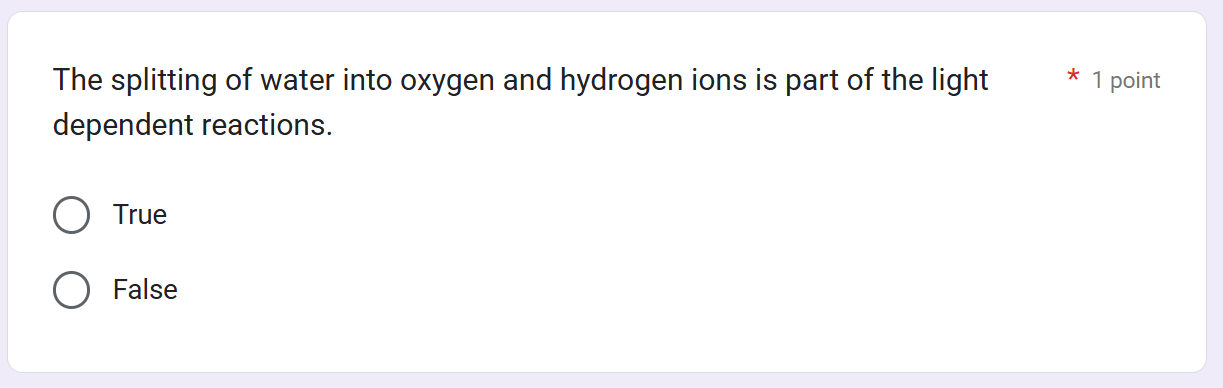
NON CYCLIC/LINEAR ELECTRON FLOW
Continuous, one-way flow of e- from water (ultimate esource) to NADP+ (terminal eacceptor)
ATP synthesis
NON CYCLIC/LINEAR ELECTRON FLOW
E released is used to to drive _____________
NON CYCLIC/LINEAR ELECTRON FLOW
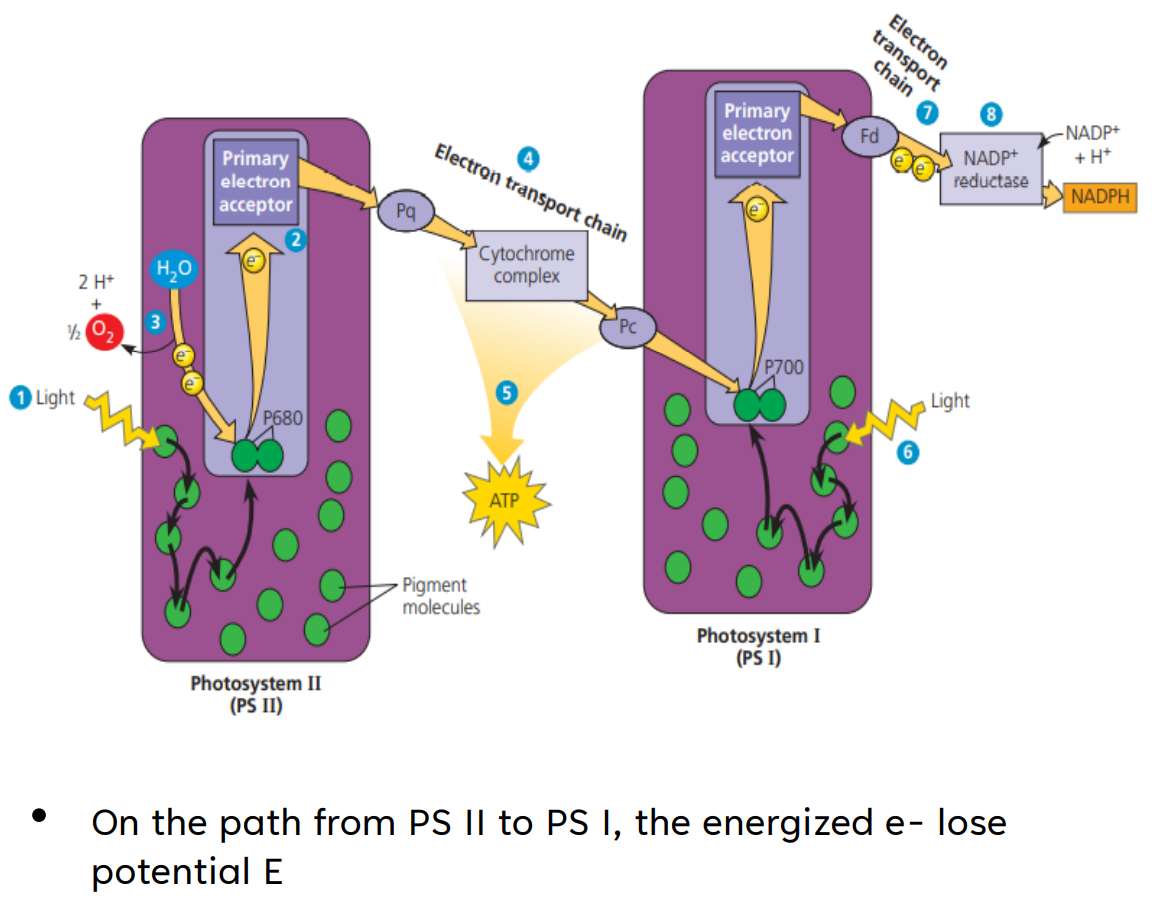
Overall pattern: Z-scheme or zigzag of E of the donated e-
Pigments; antenna complex
reaction center
2; P680; e- acceptor
e- transport chain (ETC)
P700
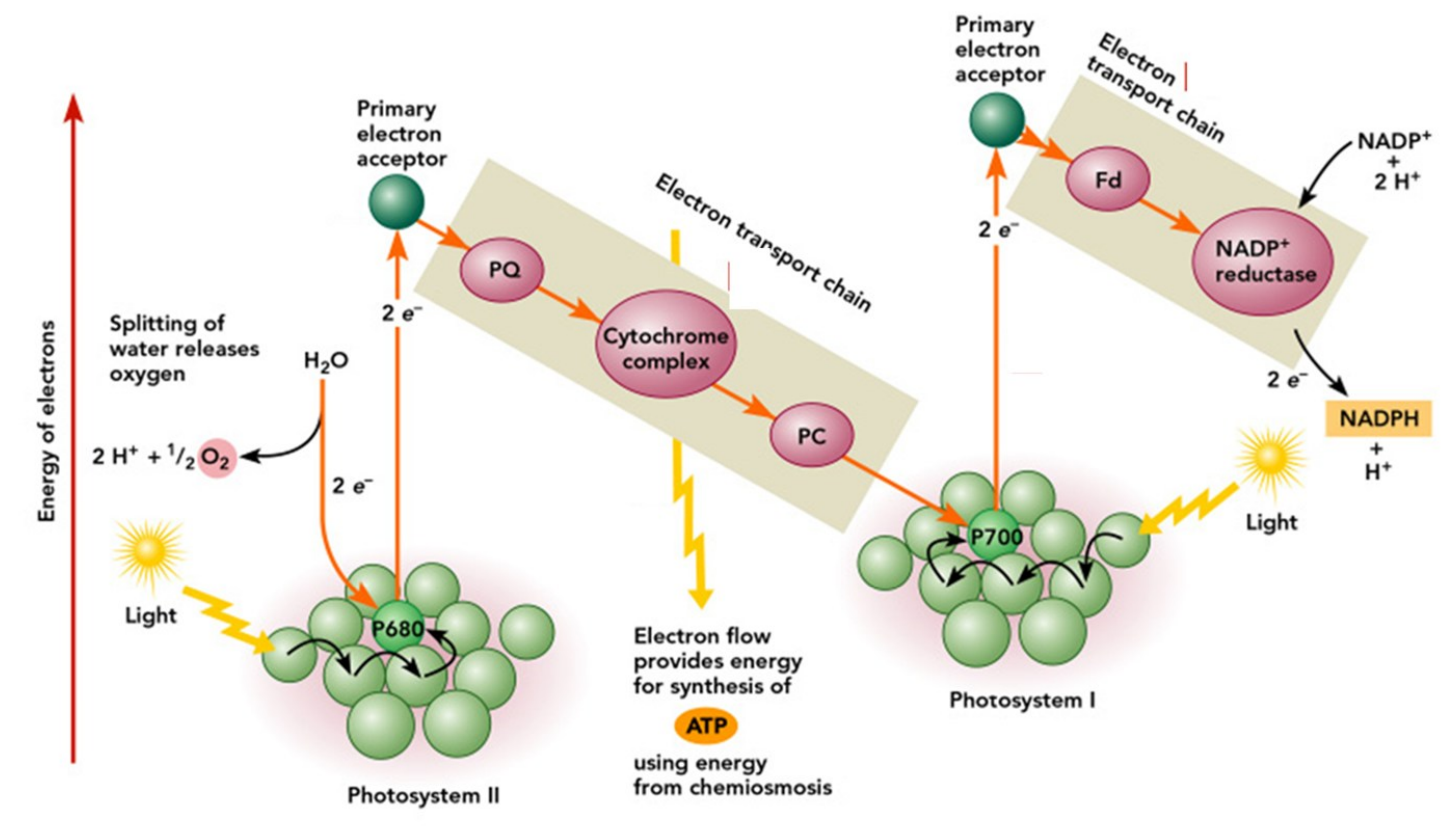
NON CYCLIC ELECTRON FLOW
__________ in _____________ in PS II absorb a photon of light
Absorbed E transferred from one molecule to another until it reaches ______________
_ e- s in ________ are energized, ejected, and passed on to a primary ___________ in the reaction center,
then to an ___________
e-s are donated to ______ in PS 1
splitting water
.
e- acceptor; ETC; NADP+
NADP+; H+; NADPH

NON CYCLIC ELECTRON FLOW
PS II regains e- s by _________, leaving O2 gas as a by-product
PS I is activated when photon of light is absorbed (the same way as PS II)
Energized e-s flow from PS I to primary _________, to _____, finally to ________
________ accepts 2 e-, unites with a ___ in the chloroplast to form ________
CYCLIC ELECTRON FLOW
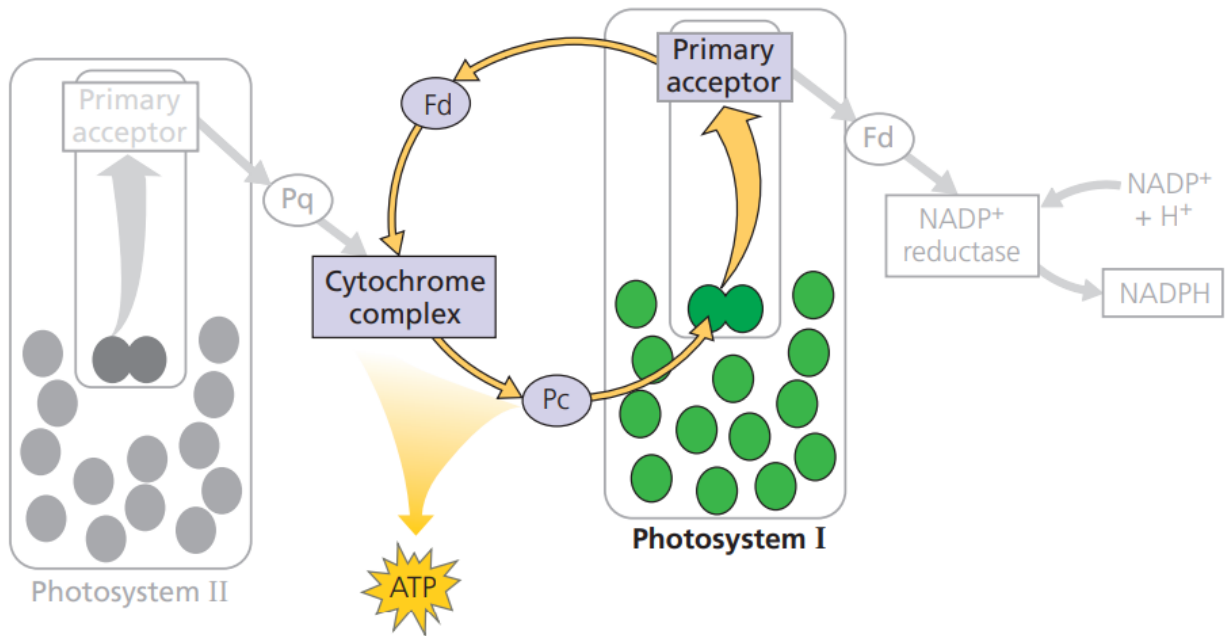
Cyclic flow of electrons through PS I which produces ATP
CYCLIC ELECTRON FLOW

In the presence of light, energized e- from PS I do not go to NADP+, but pass through acceptor molecules and cycle back to PS I
CYCLIC ELECTRON FLOW

No H2O split, no O2 released
ferredoxin (Fd); cytochrome complex; plastocyanin (Pc)
chemiosmosis; NADPH

CYCLIC ELECTRON FLOW
Photoexcited electrons from PS I are occasionally shunted back from _____________ to chlorophyll via the ____________ and _____________.
This electron shunt supplements the supply of ATP (via ______________) but produces no _________
CYCLIC ELECTRON FLOW

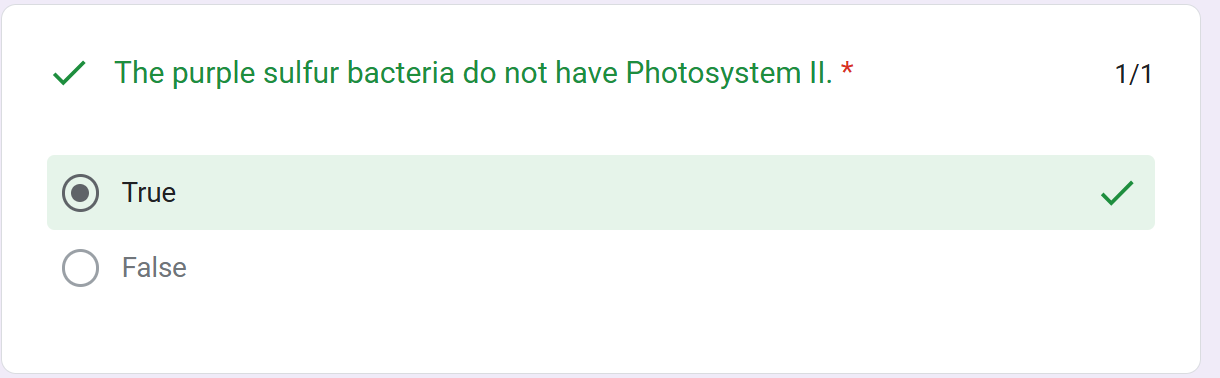
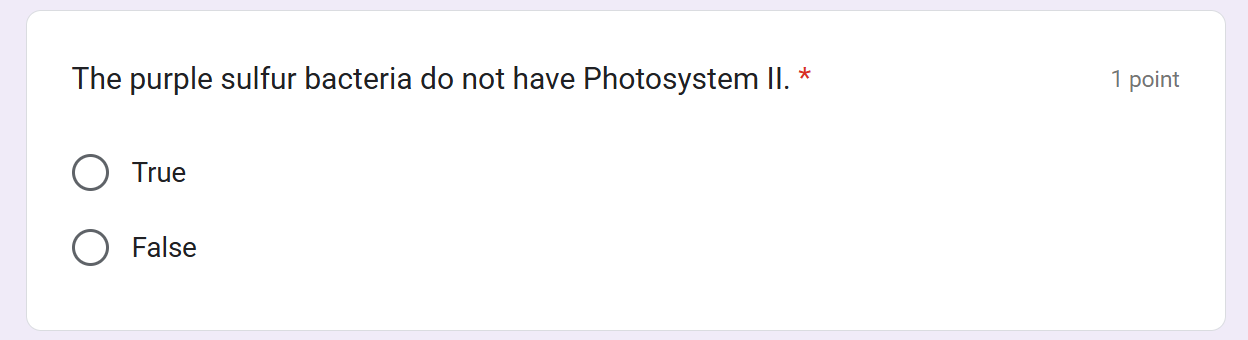
Some organisms such as purple sulfur bacteria have PS I but not PS II
CYCLIC ELECTRON FLOW

It is thought to have evolved before linear e-flow
CYCLIC ELECTRON FLOW

It may protect cells from light-induced damage
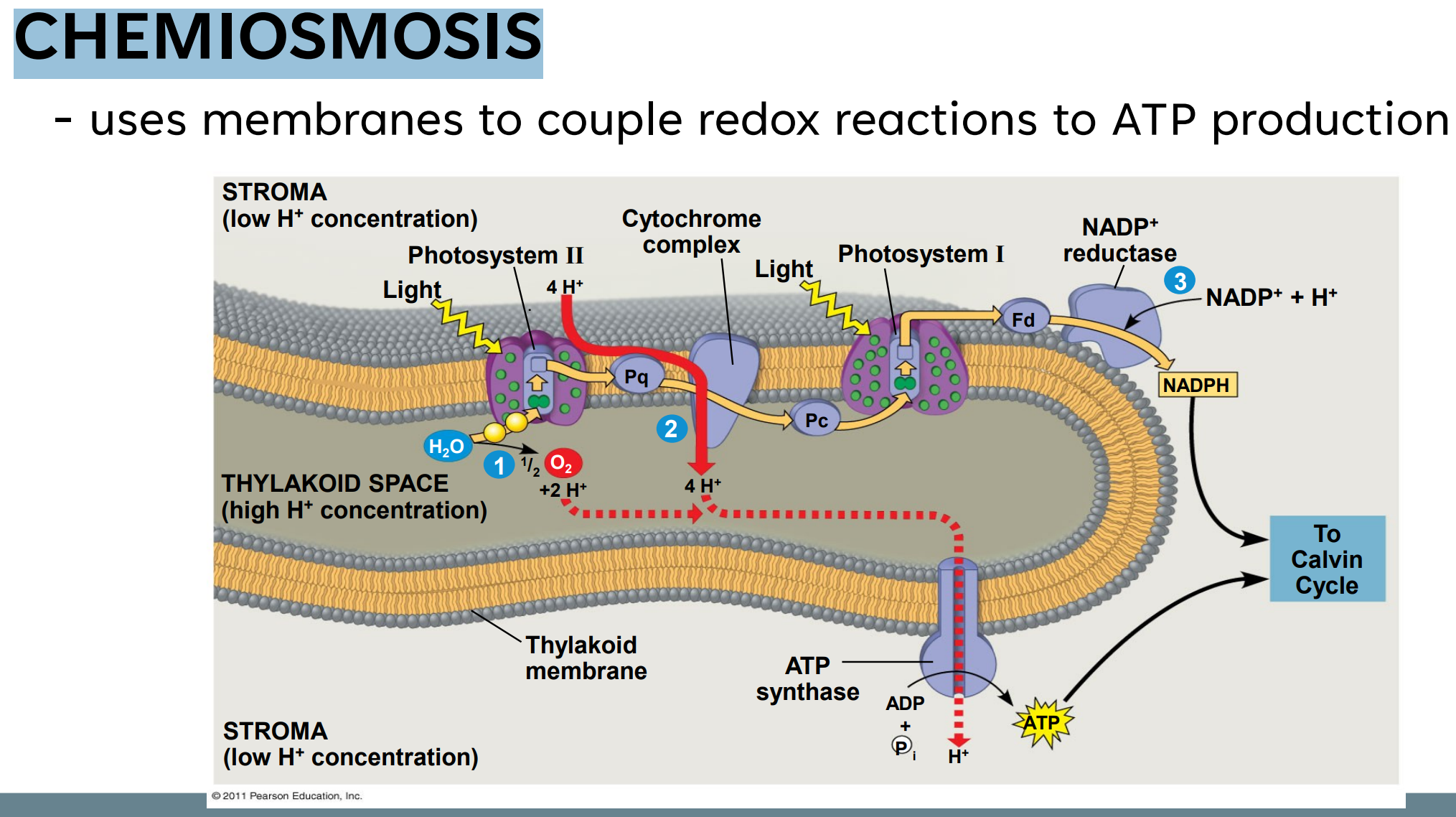
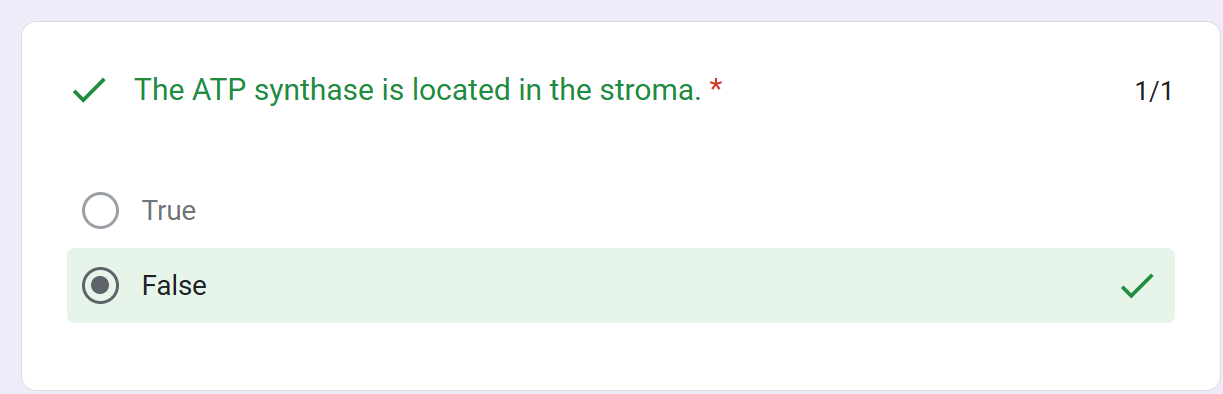
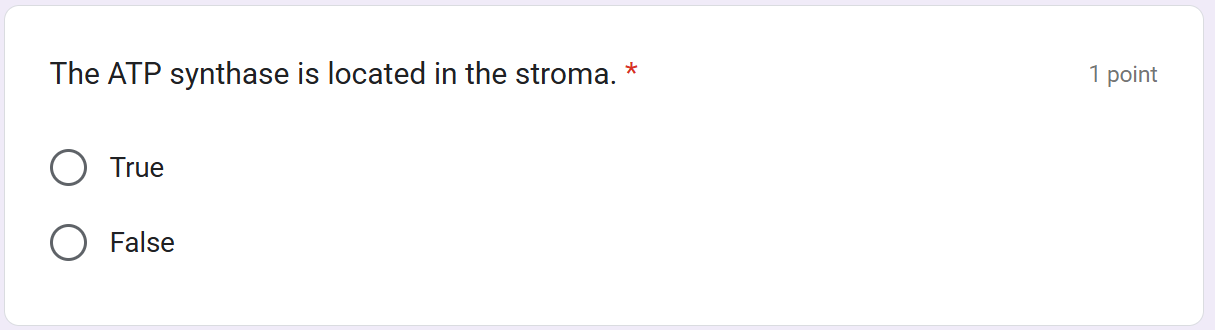
uses membranes to couple redox reactions to ATP production
H+ ions; stroma; thylakoid membrane; thylakoid lumen
Thylakoid lumen; proton motive force
H+ ions; ATP synthase
ATP synthase; phosphorylation
H+ ions; NADP+; NADPH
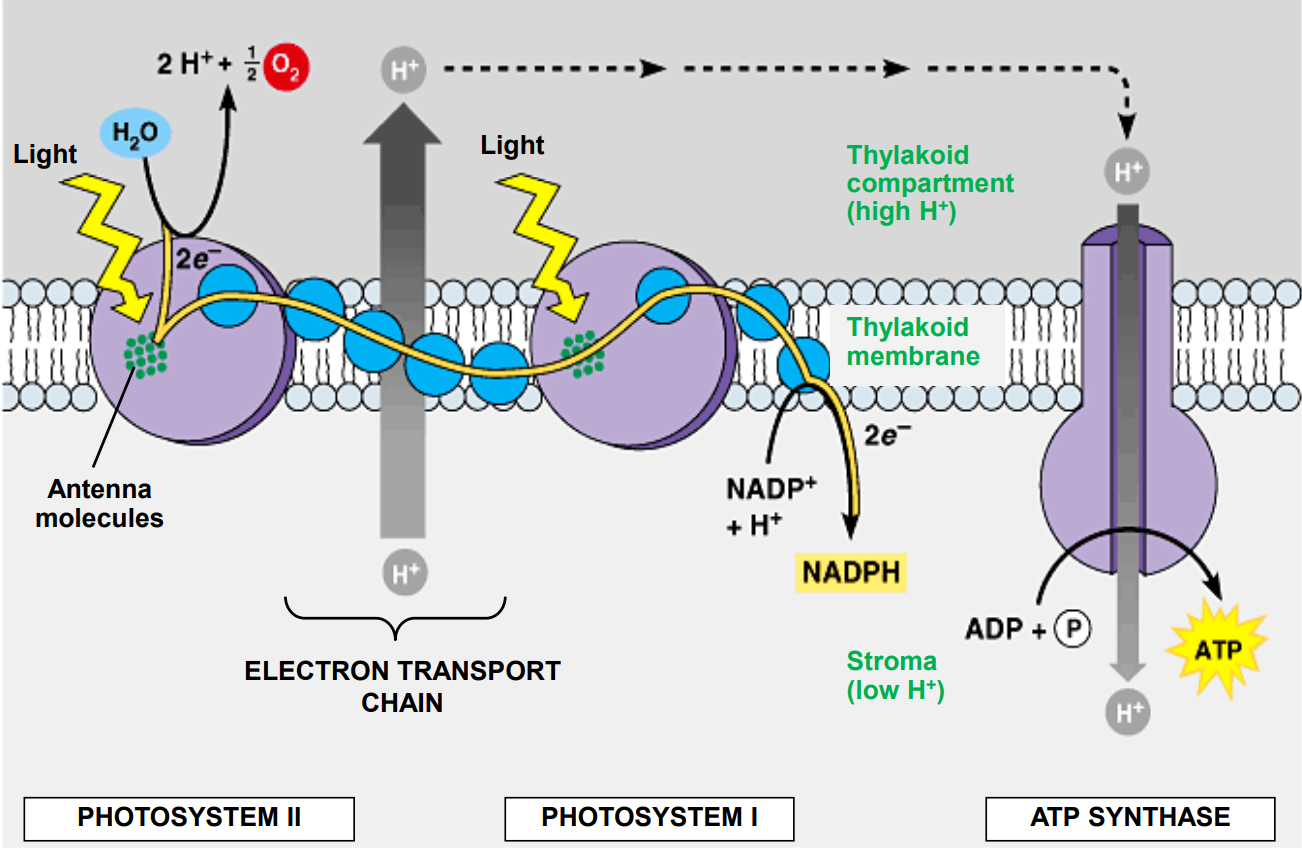
ETC uses light energy to pump ________, from the _______ across the ____________, to the _____________
_____________ becomes more acidic; a proton gradient is created (also called ______________); source of potential energy
Accumulated ________ move back towards the membrane; pass through a channel in ____________
____________ uses the energy to produce ATP by ________________
In the stroma, the _________ combine with ___________ to form ___________
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
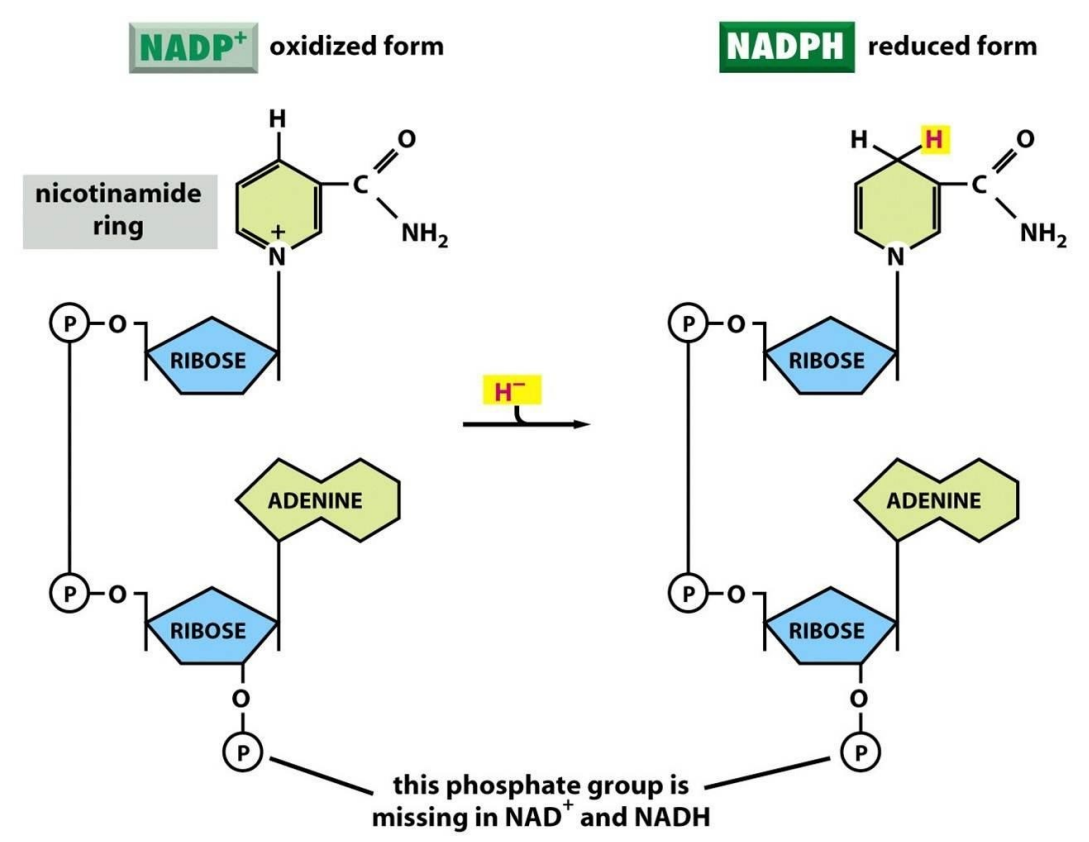
NADP (___________________)
NADP

a co-enzyme that temporarily stores energized electrons (an electron carrier)
ATP
energy currency of the cells
hydrolysis
phosphate
endergonic
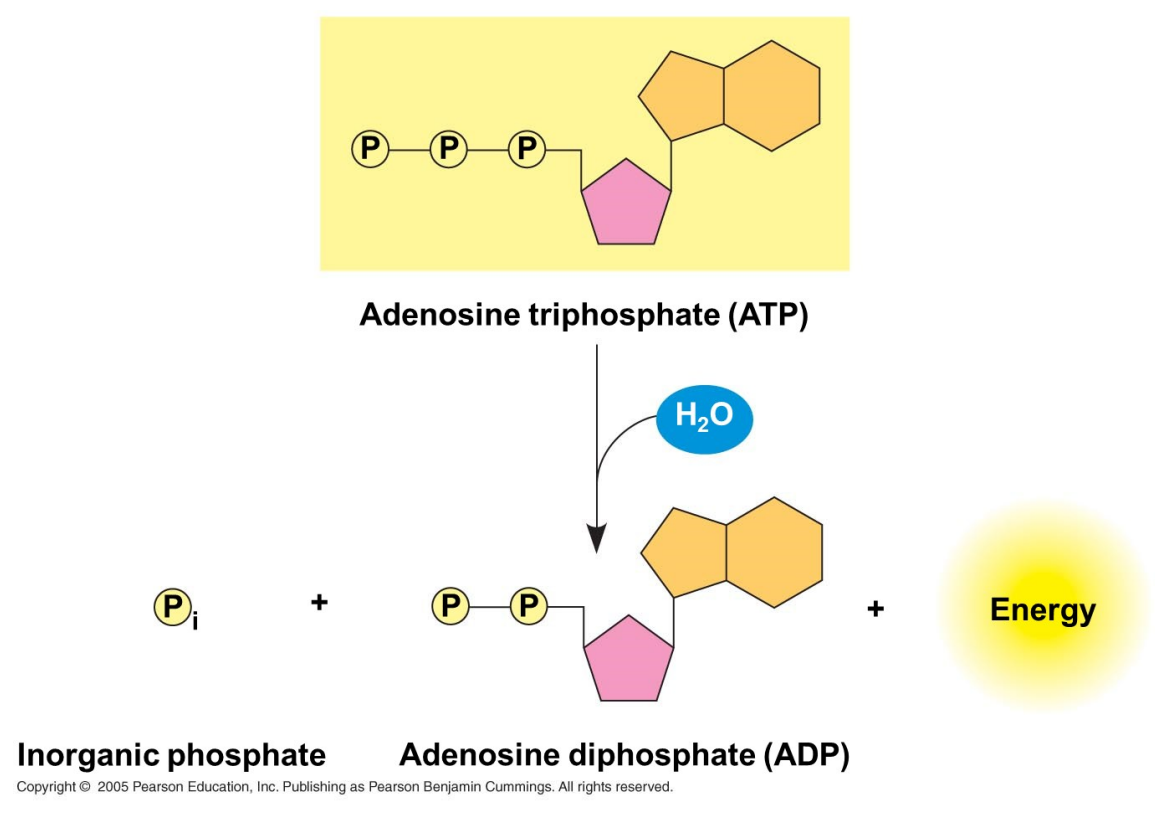
The bonds between the phosphate groups of ATP’s tail can be broken by __________
Energy is released when the bonds between ____________ groups are broken
Energy released used to drive an ___________ reaction in the cell
He discovered of the pathway by which plants convert CO2 to sugars
the first product is a 3-C molecule (PGA)
Calvin Cycle also known as C3 pathway: because _____________________?
one; phosphate; 5-C sugar phosphate
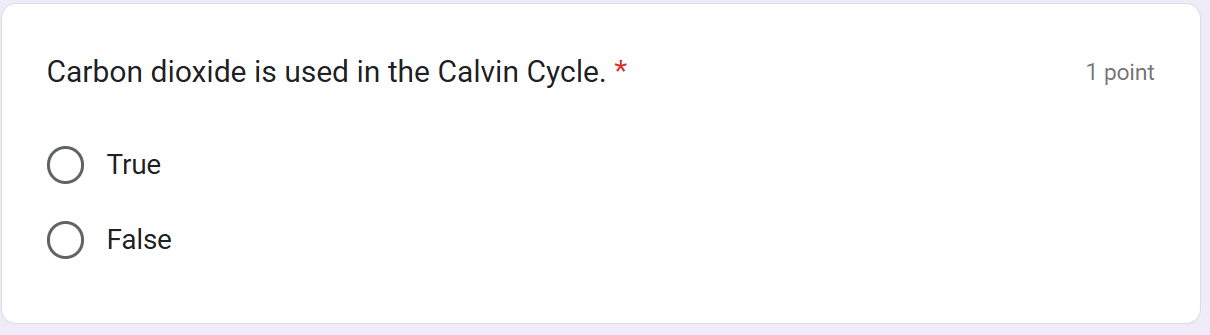
CO2; Ribulose Bisphosphate (RuBP)
3-Phosphoglycerate (PGA)
PGA
BPG
NADPH; BPG
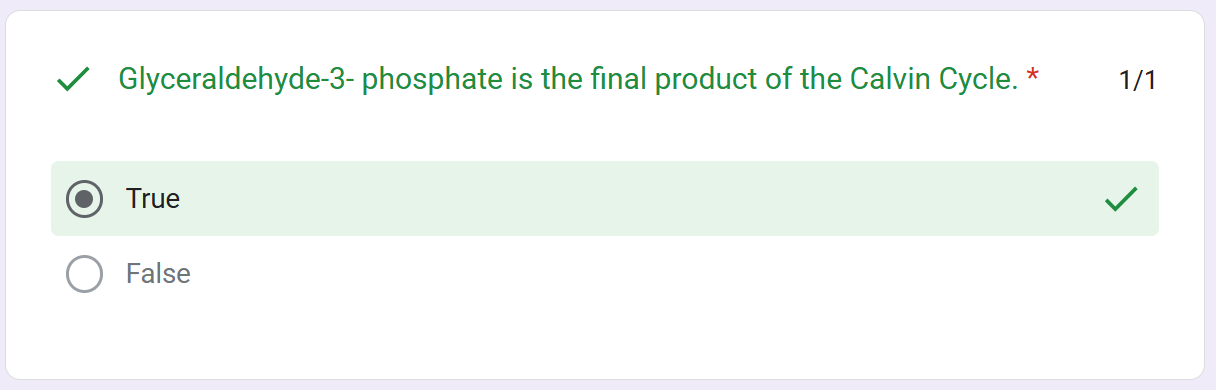
BPG; G3P
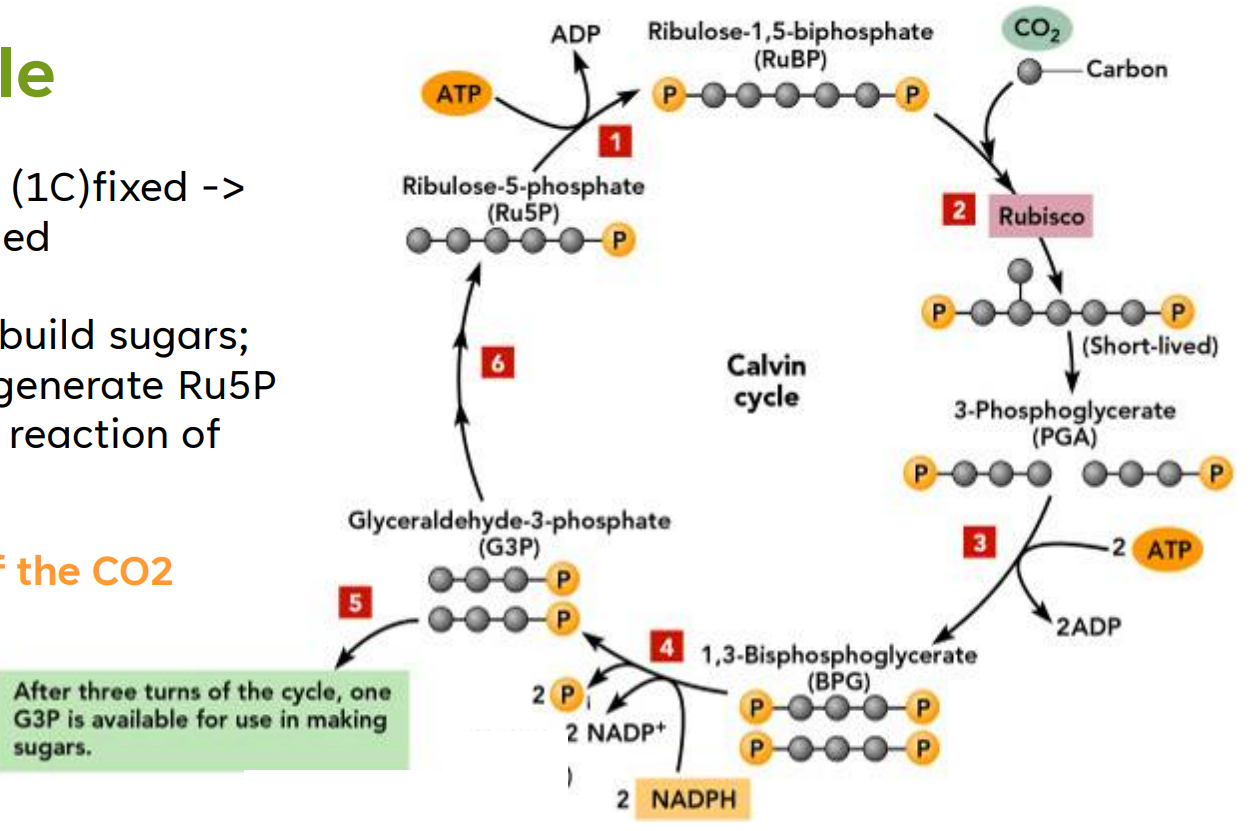
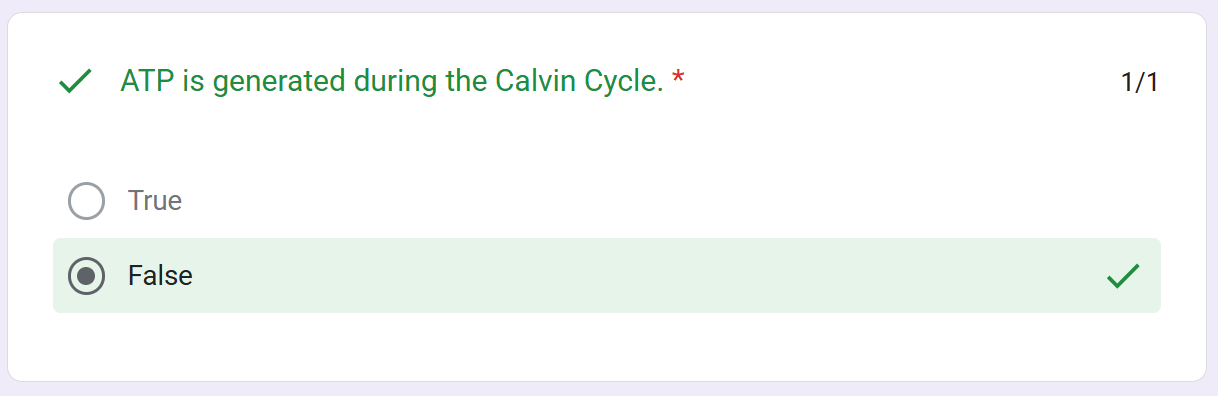
Calvin Cycle
___ ATP is used to power the addition of a __________ to a _____________
Carbon Fixation:
____ (1C) + _______________ (5C)
→2 Molecules of ________________ (3C)
Reduction Phase:
2 ATP’s add phosphates to the
2 molecules of ____ resulting to
2 molecules of (____)
Reduction Phase:
2 ______ add electrons to ____;
each ____ is reduced to ____
For every 1 CO2 (1C)fixed → 2 G3P (3C) formed
Regeneration of the CO2 acceptor

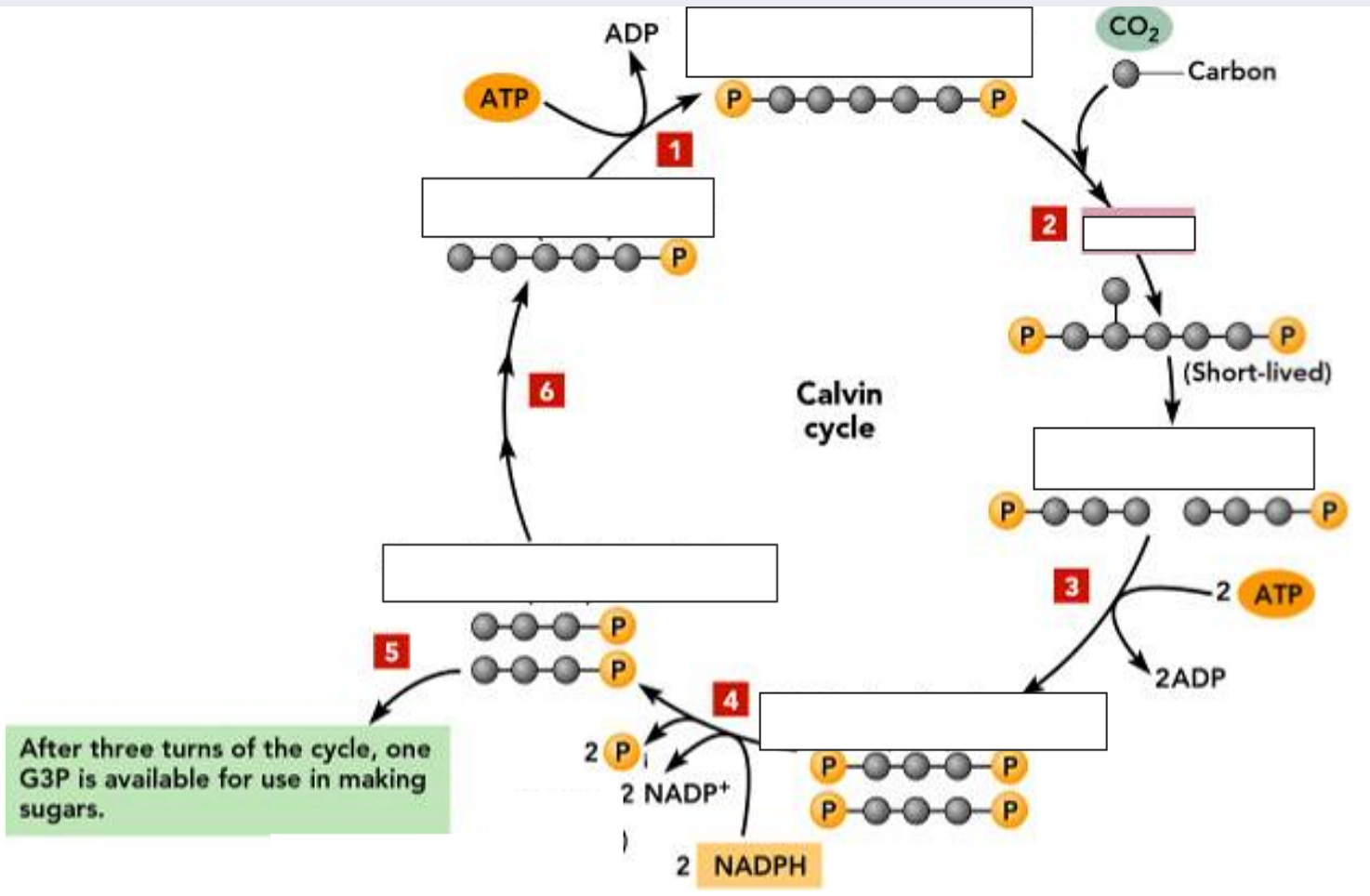
RuBisCO (Ribulose Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase)
Carbon Fixation in the Calvin cycle is catalyzed by the enzyme _____ (__________________________________)
RuBisCO (Ribulose Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase)
Known as the most abundant protein on earth
Carbon is converted from an inorganic form into an organic form and thereby “FIXED”.
Why is it called carbon fixation?
G3P (3C)

It is used to build sugars; also used to regenerate Ru5P (5C) in the first reaction of the cycle
three; 3
3; 6
1; 6; 5; 3
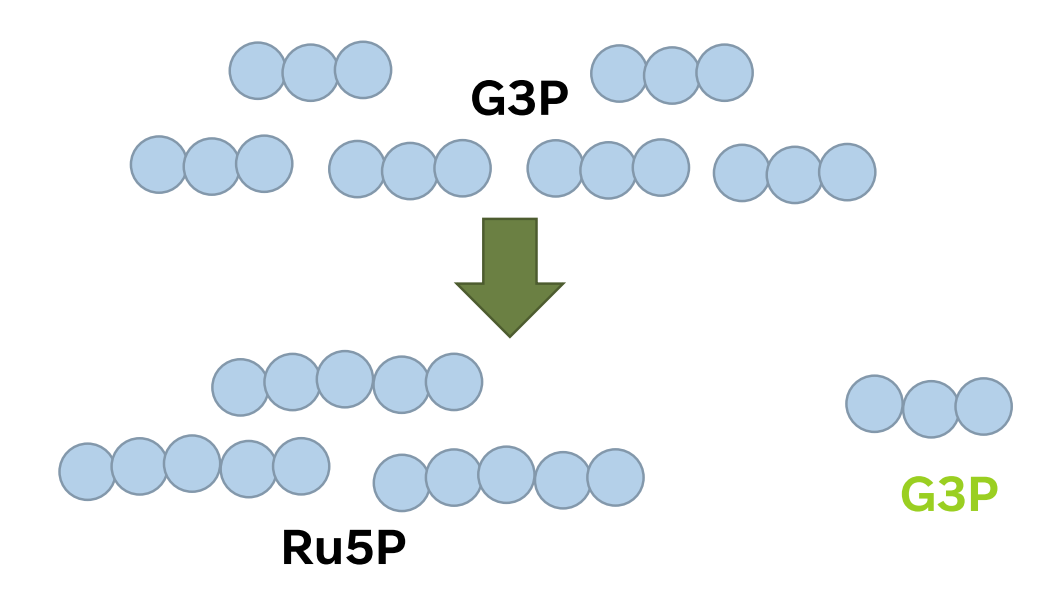
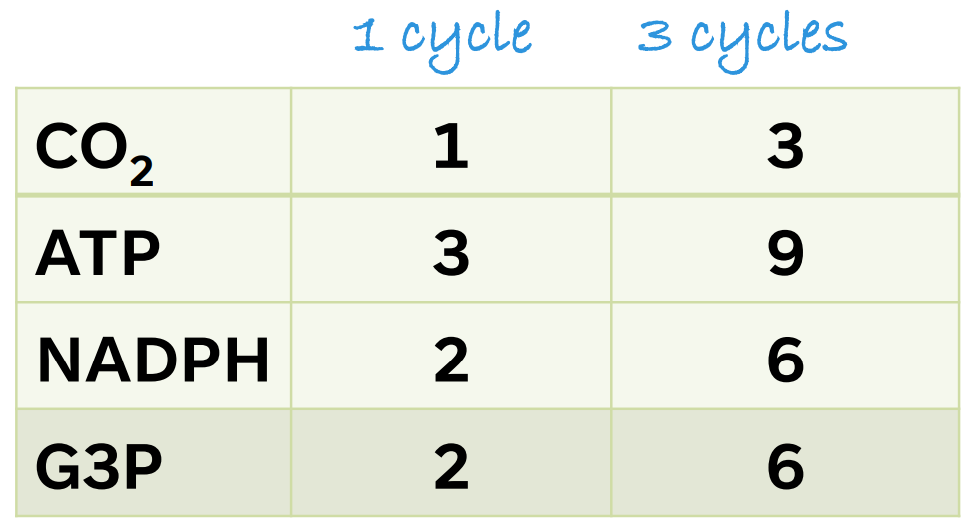
For net synthesis of 1 G3P, the cycle must take place ______ times, fixing _ molecules of CO2
For every _ CO2 → _ G3P is produced in total
But only _ G3P out the _ G3P can be counted as a gain and can exit the cycle to be used for the synthesis of sugars as the _ G3P are rearranged into _ Ru5P
PHOTORESPIRATION
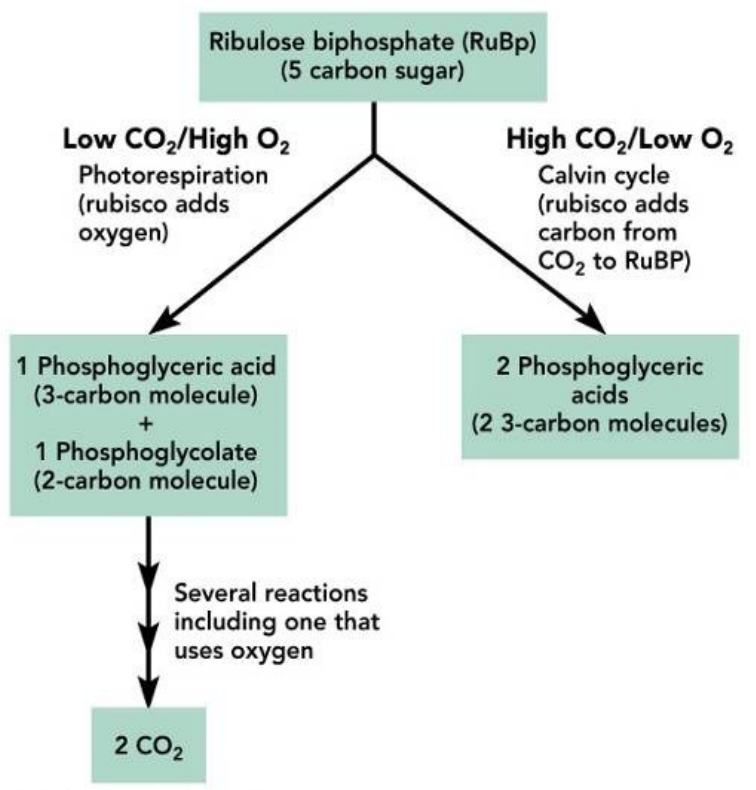
Observed in C3 plants when stomata are closed during hot, dry days
PHOTORESPIRATION

Thought to be an evolutionary relic (Rubisco’s affinity for O2 remains)
PHOTORESPIRATION

CO2 levels ↓ & O2 levels ↑
rubisco binds with O2 instead of CO2
PHOTORESPIRATION

Drains the Calvin cycle (↓ photosynthetic output)
PHOTORESPIRATION

No G3P produced
Considered to be wasteful and no benefit known
photorespiration; CO2

Rubisco and O2 under conditions of CO2 limitations initiates ____________ which breaks down sugars into ____
PHOTORESPIRATION

It occurs in the light (photo); consumes O2 while producing CO2 (respiration); and uses up ATP but produces no sugar molecules.
PHOTORESPIRATION; 50%

______________ reduces photosynthetic efficiency of the Calvin cycle by as much as ___
four-carbon; mesophyll
Some plants minimize photorespiration – by incorporating CO2 into ___________ compounds in _________ cells
Alternative pathways to minimize photorespiration
Hatch-Slack pathway or C4 pathway
Crassulacean Acid Metabolism or CAM
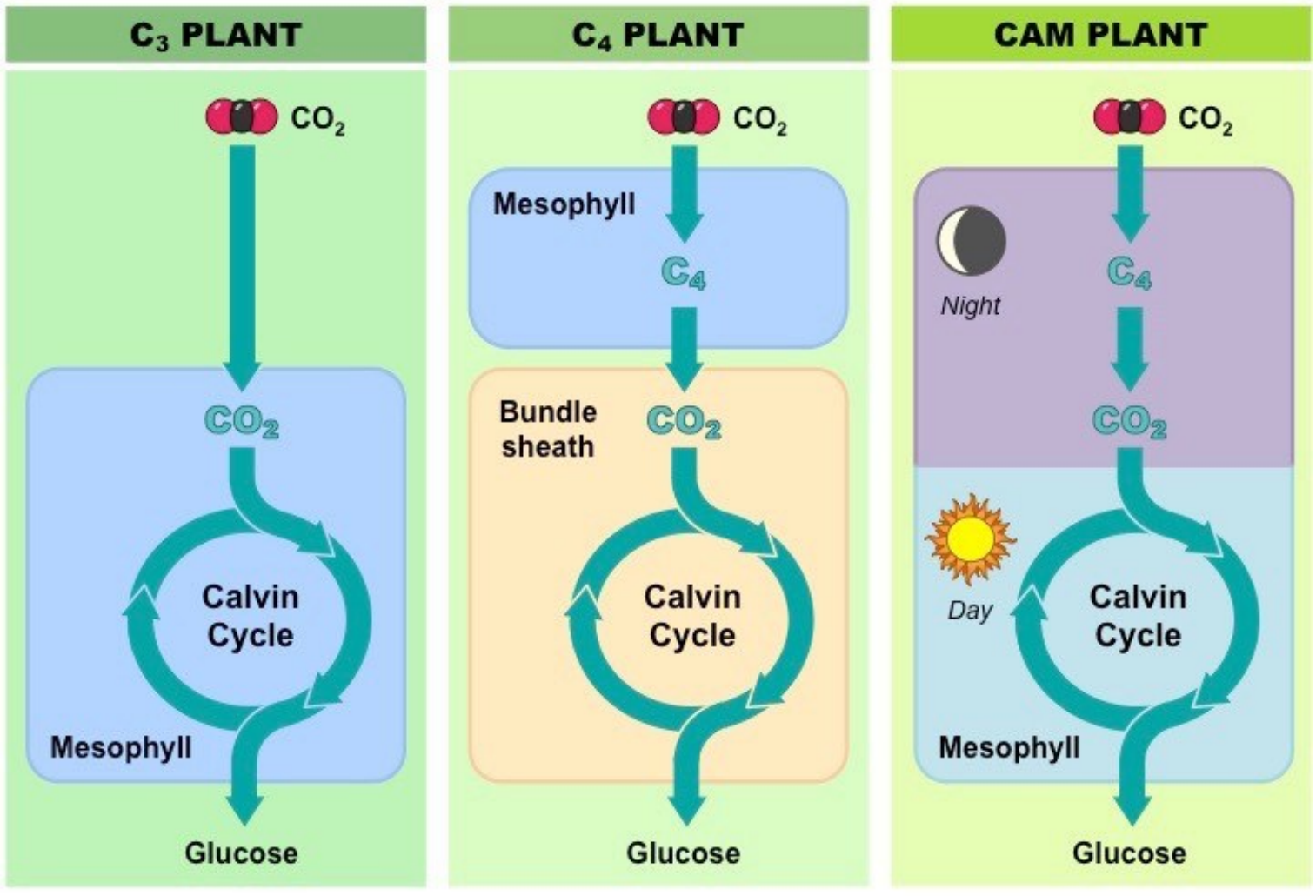
Alternative pathways to minimize photorespiration
_________________________________
_________________________________
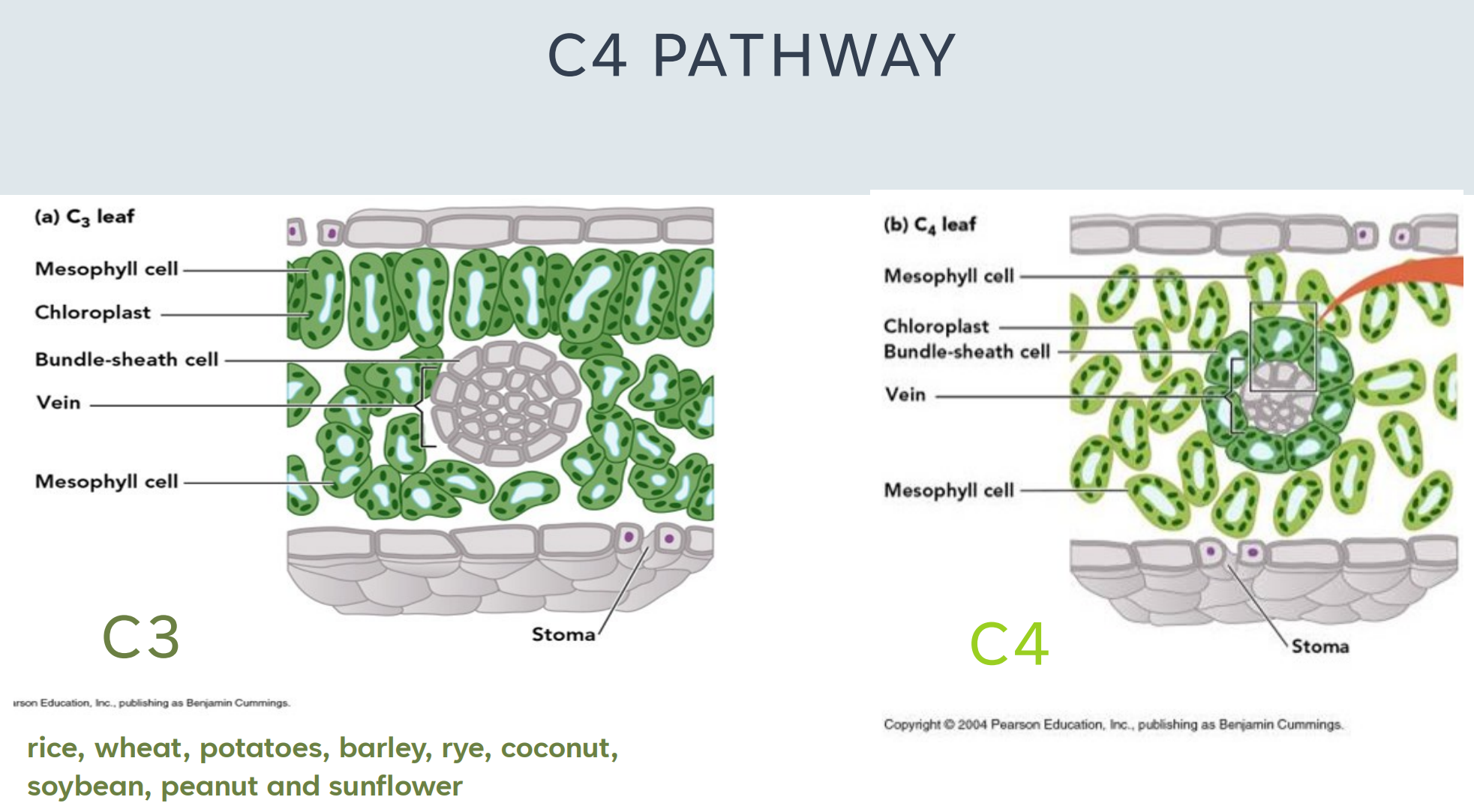

rice
wheat
potatoes
barley
rye
coconut
soybean
peanut
sunflower
What are plants can conduct the C3 pathway?
Mesophyll
PEP carboxylase
PEP (phosphoenolpyruvate); Oxaloacetate
Malate; bundle sheath; plasmodesmata
bundle sheath cells
mesophyll; stomata
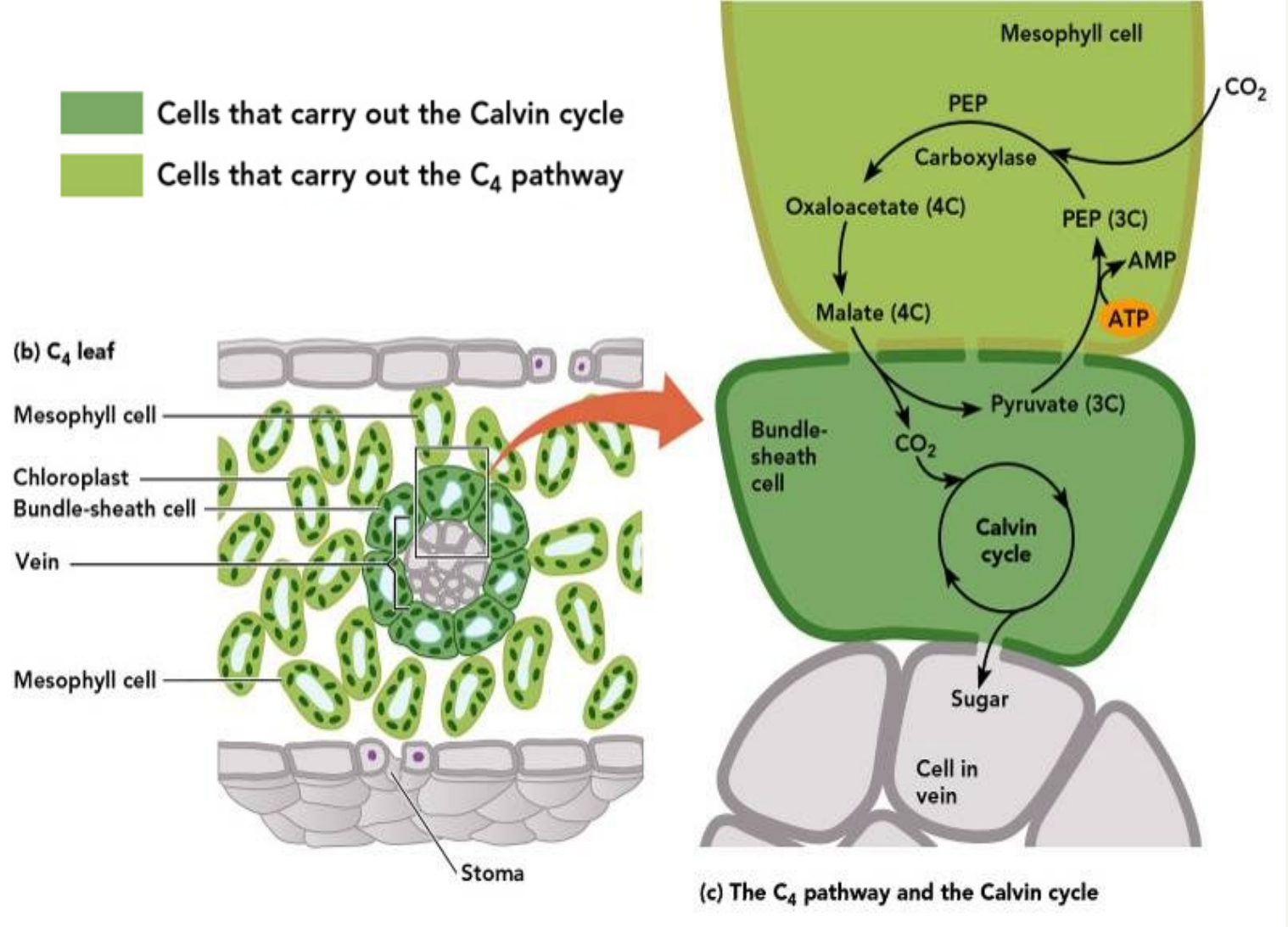
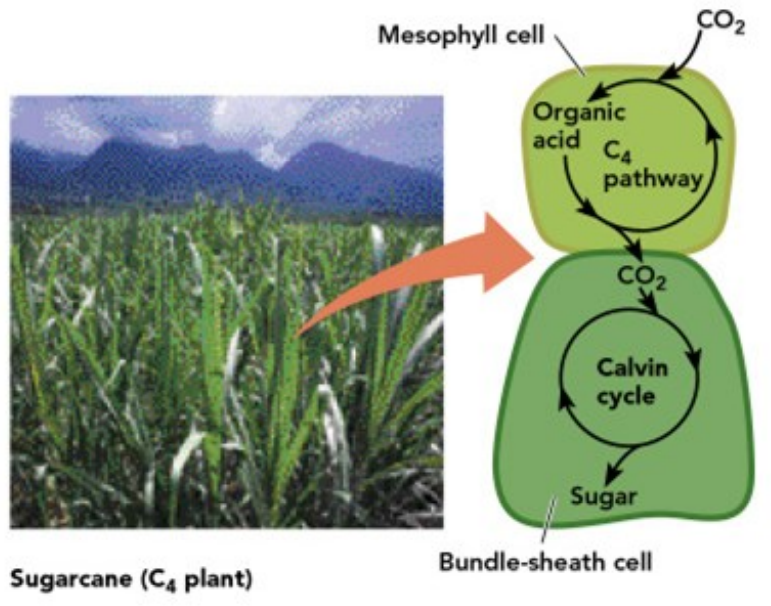
C4 PATHWAY
___________ cells carry out C4 pathway
_____________ binds CO2 even at low CO2 concentrations inside leaf
CO2 and ____________ combine to produce a 4-C compound called _____________
_________ (4C) is delivered to __________ cell through _____________
Calvin cycle (C3) pathway is confined to ______________
CO2 is continually fed into the Calvin cycle from the _________ cells even when the _________ are closed.
A high CO2 concentration is maintained for the Calvin cycle, which minimizes photorespiration.

Which alternative pathway?
Hot, dry environments (tropical grasslands)


Which alternative pathway?
Evolved 30 – 35 million years ago


Which alternative pathway?
3% of all land plants


Which alternative pathway?
79% of the ___ plants species are grasses and sedges


Which alternative pathway?
Examples: corn, sugarcane, sorghum, millet, carabao grass, Bermuda grass, cogon, tumbleweed


Which alternative pathway?
spatial separation of C4 and C3 pathways
Which alternative pathway?
Adapted in arid environments (high light intensity, little precipitation)


Which alternative pathway?
7% of land plants


Which alternative pathway?
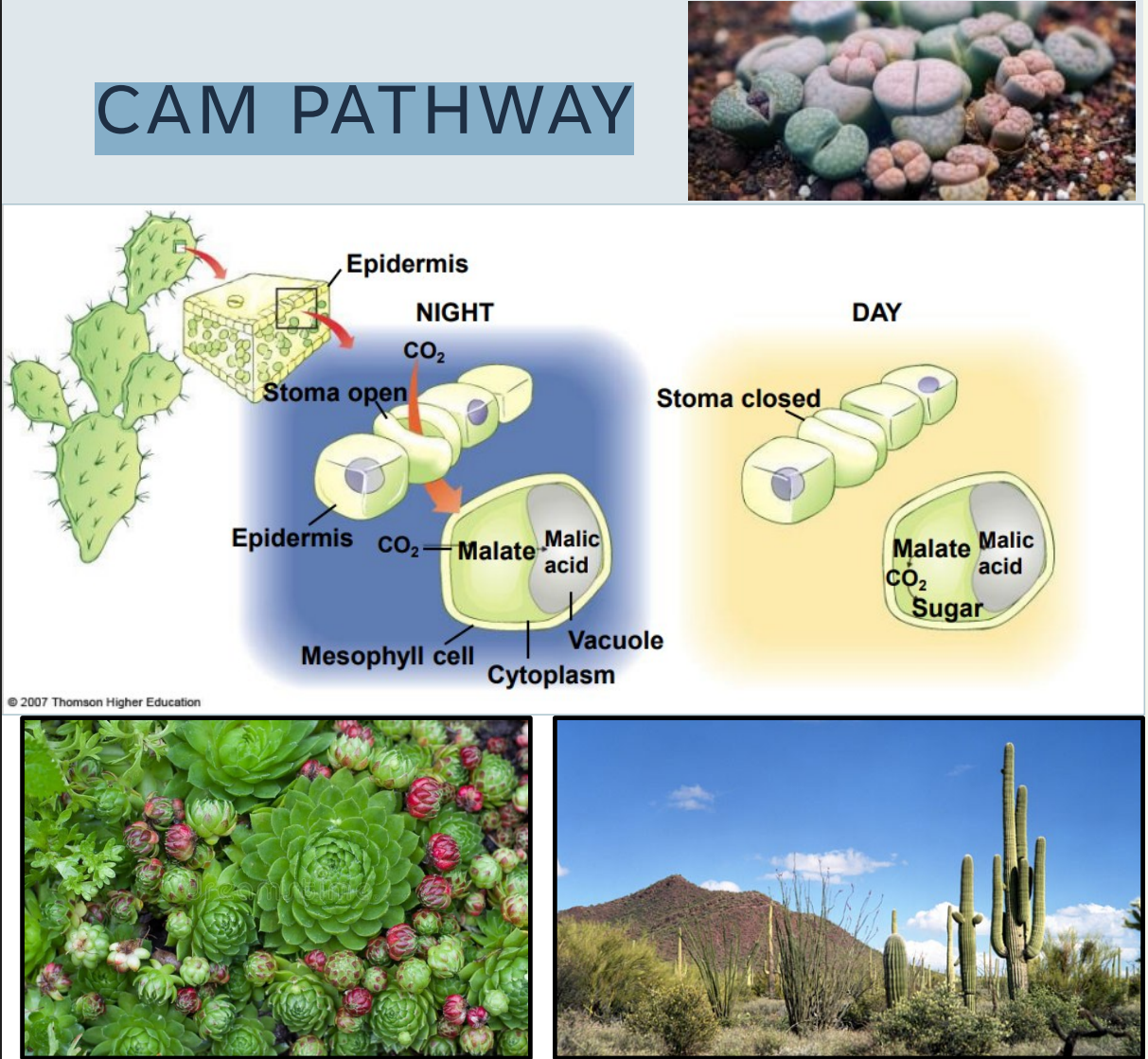
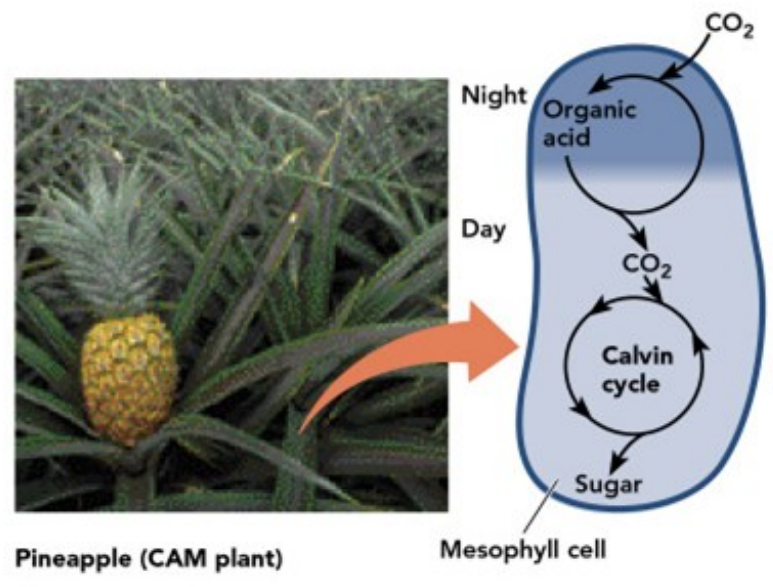
Close their stomata during the day and open them only at night. (reverse of typical plants)


Which alternative pathway?
Organic compounds made are “stored” at night in their vacuoles when the stomata are open then used later during the day.


Which alternative pathway?
Common in succulent plants such as: pineapple and cacti and stonecrops


Which alternative pathway?
temporal separation of C4 and C3 pathways