Labeling Parts of a Skull (sagittal view)
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
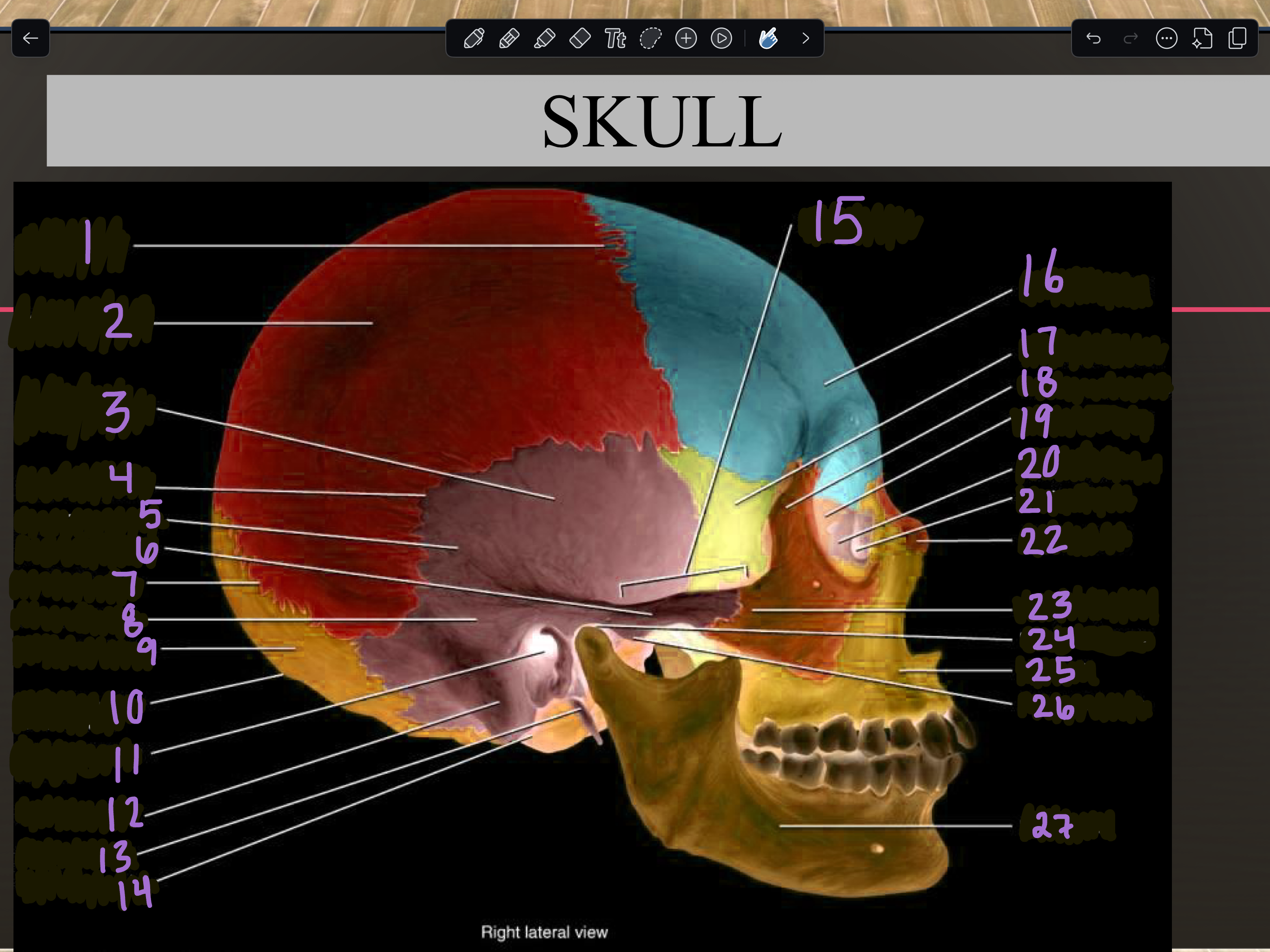
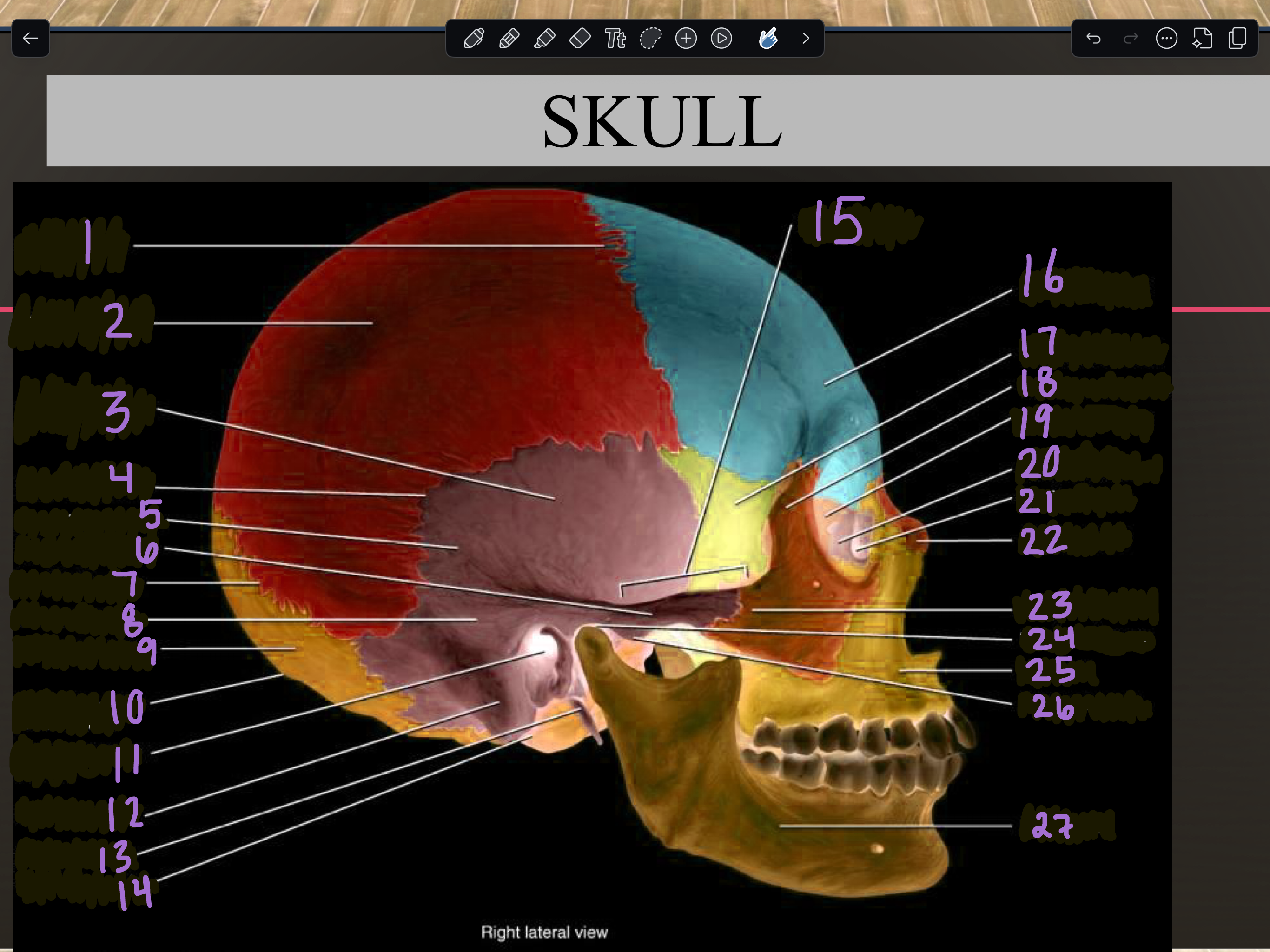
1
Coronal suture
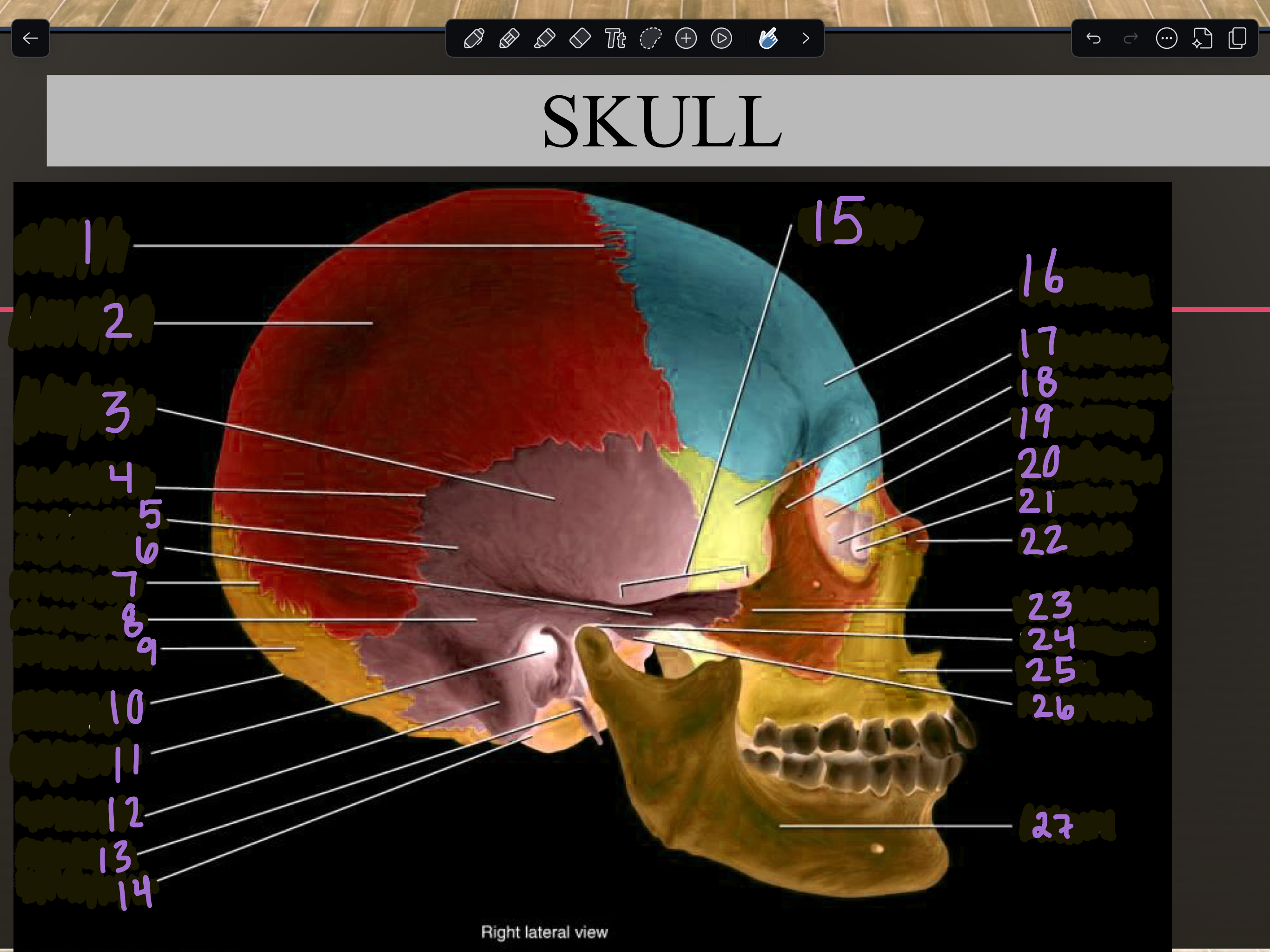
2
Parietal bone
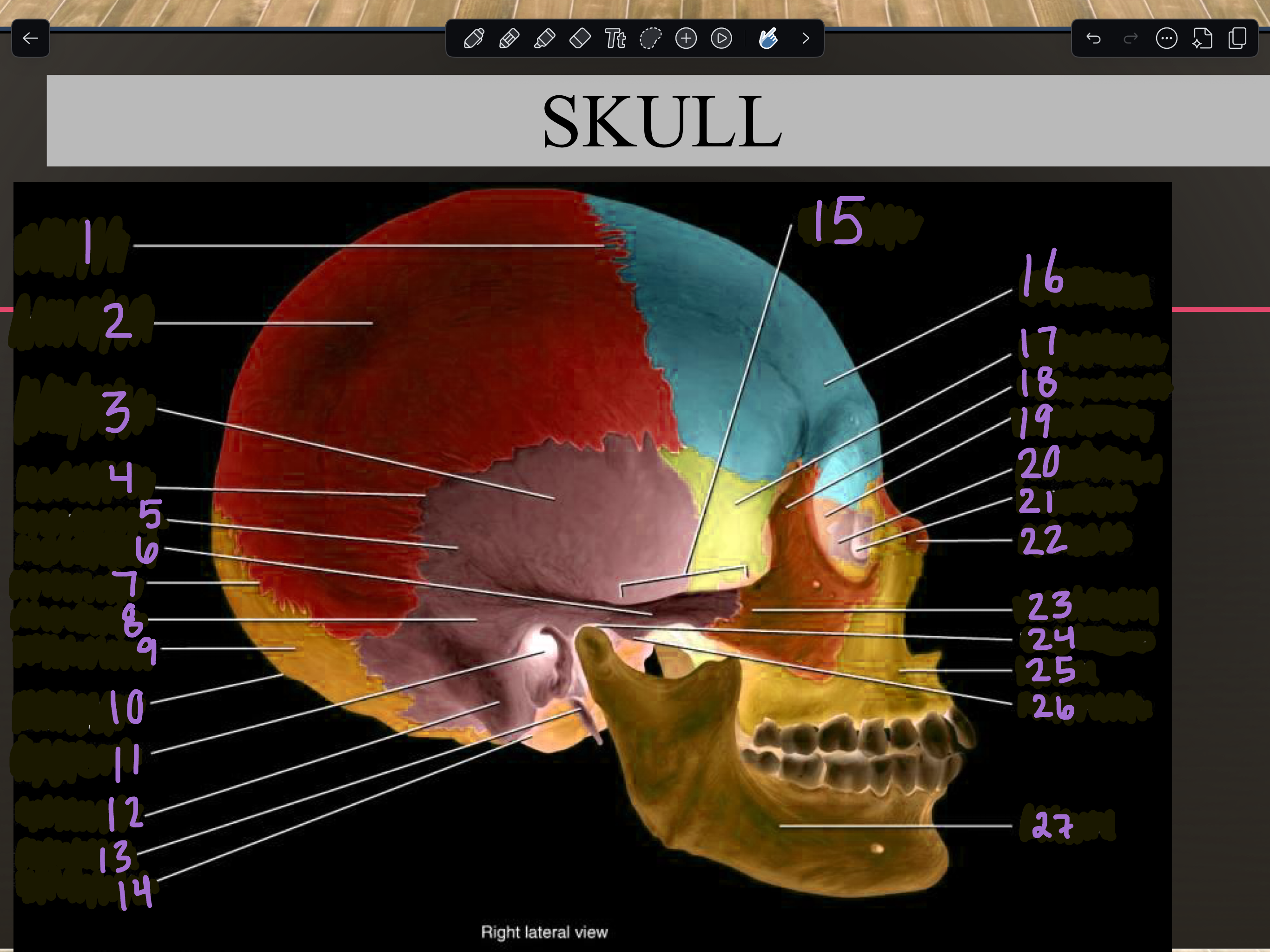
3
Temporal squama
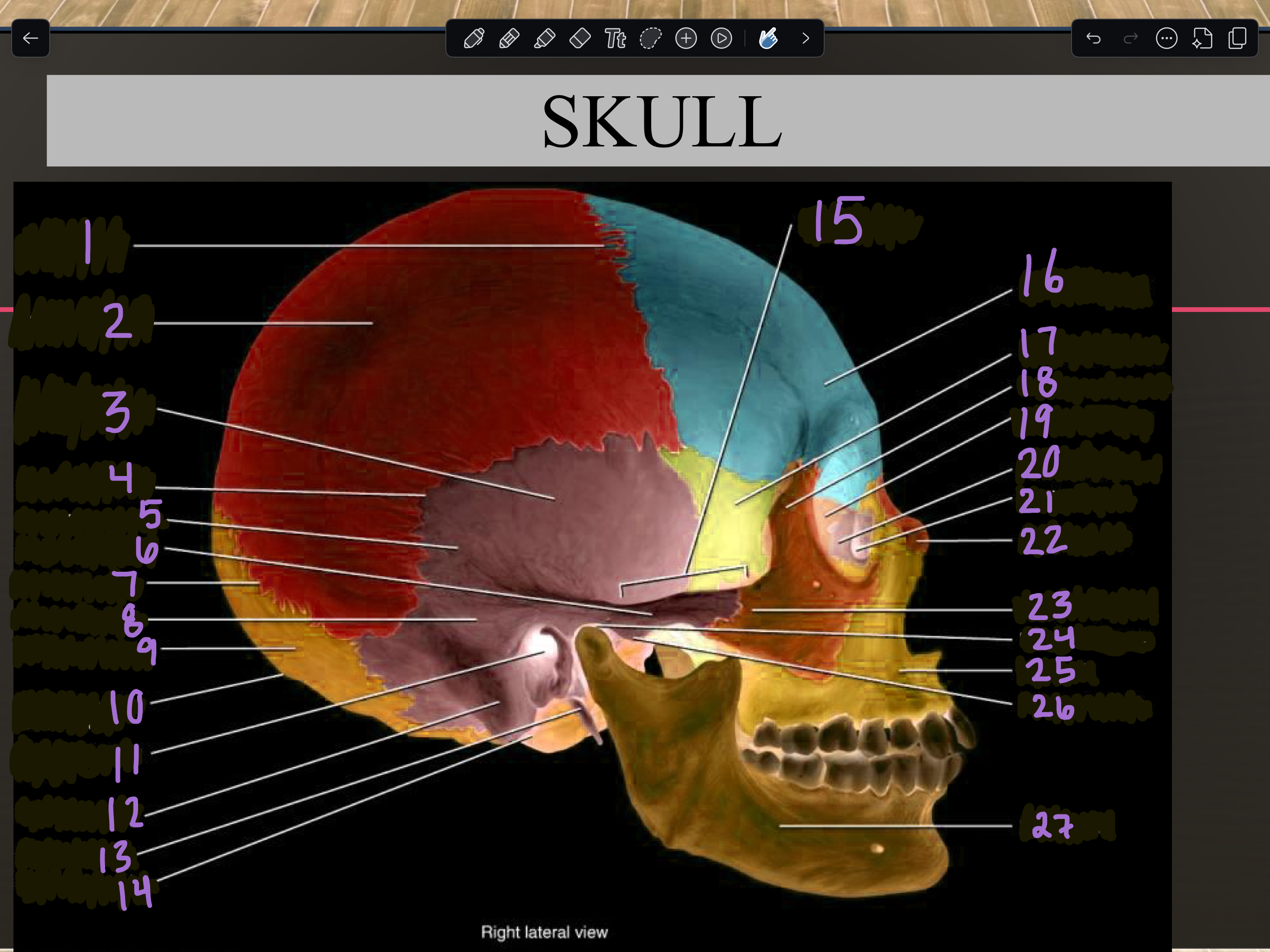
4
Squamous suture
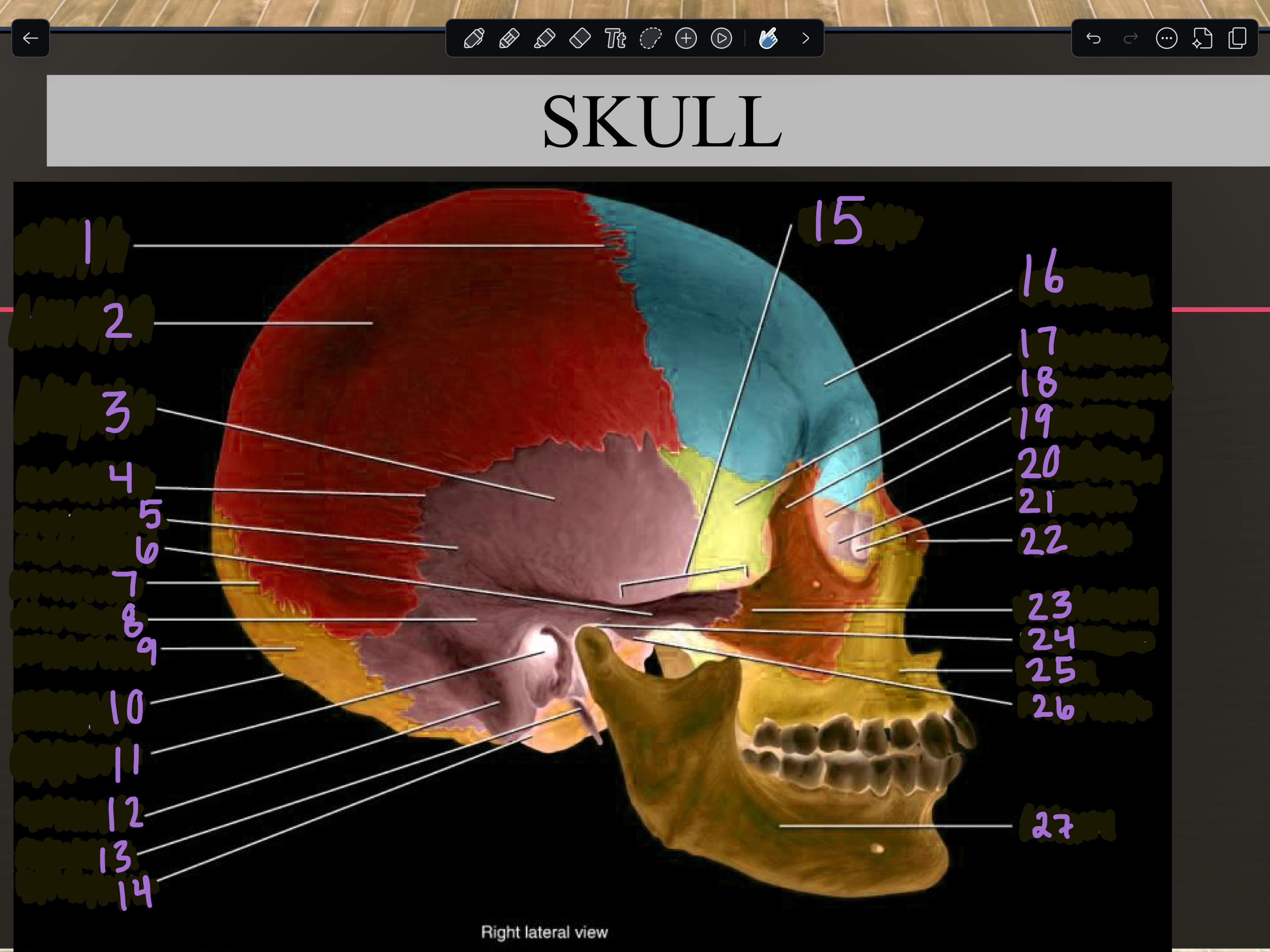
5
Temporal bone
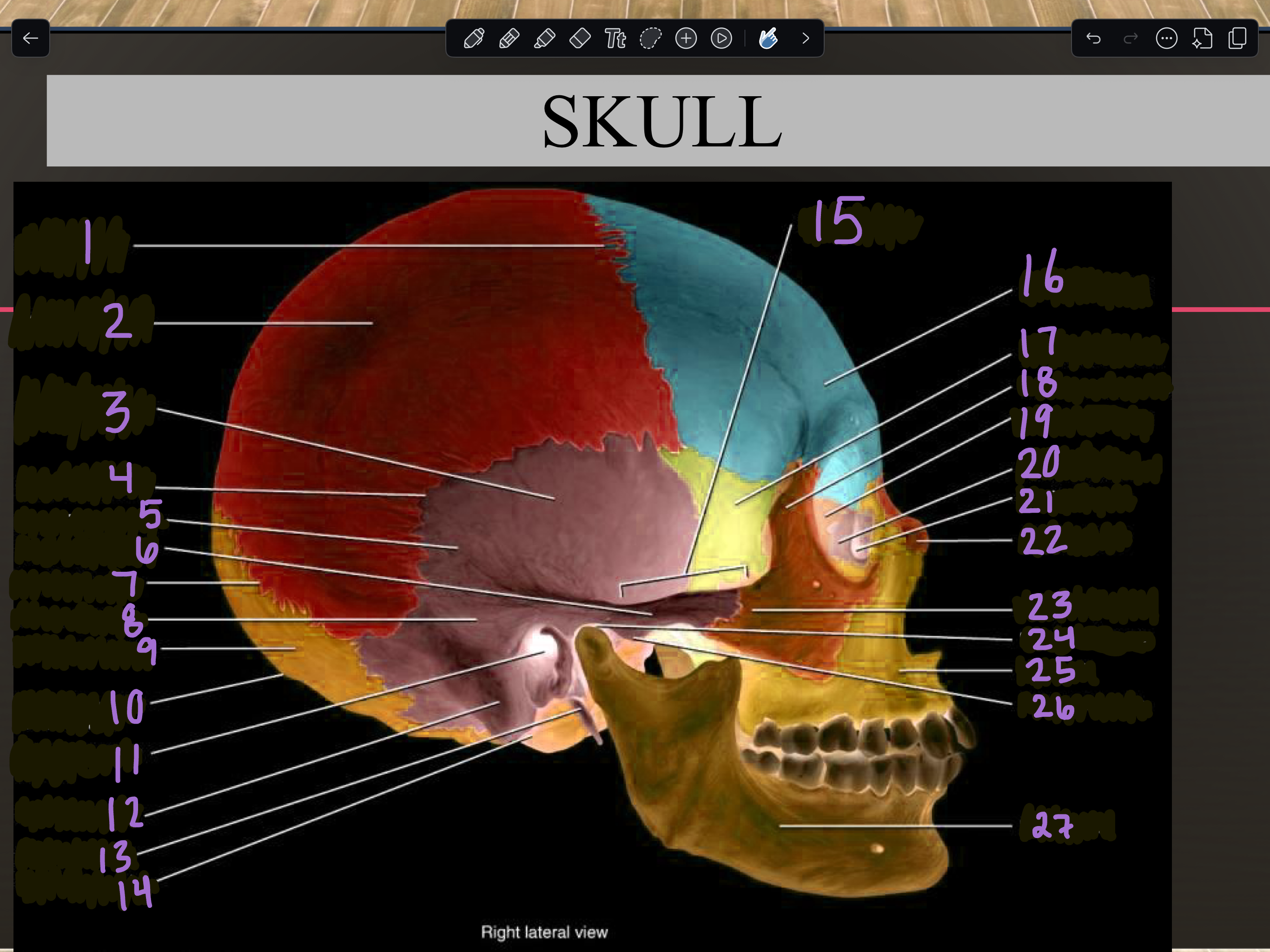
6
Zygomatic process
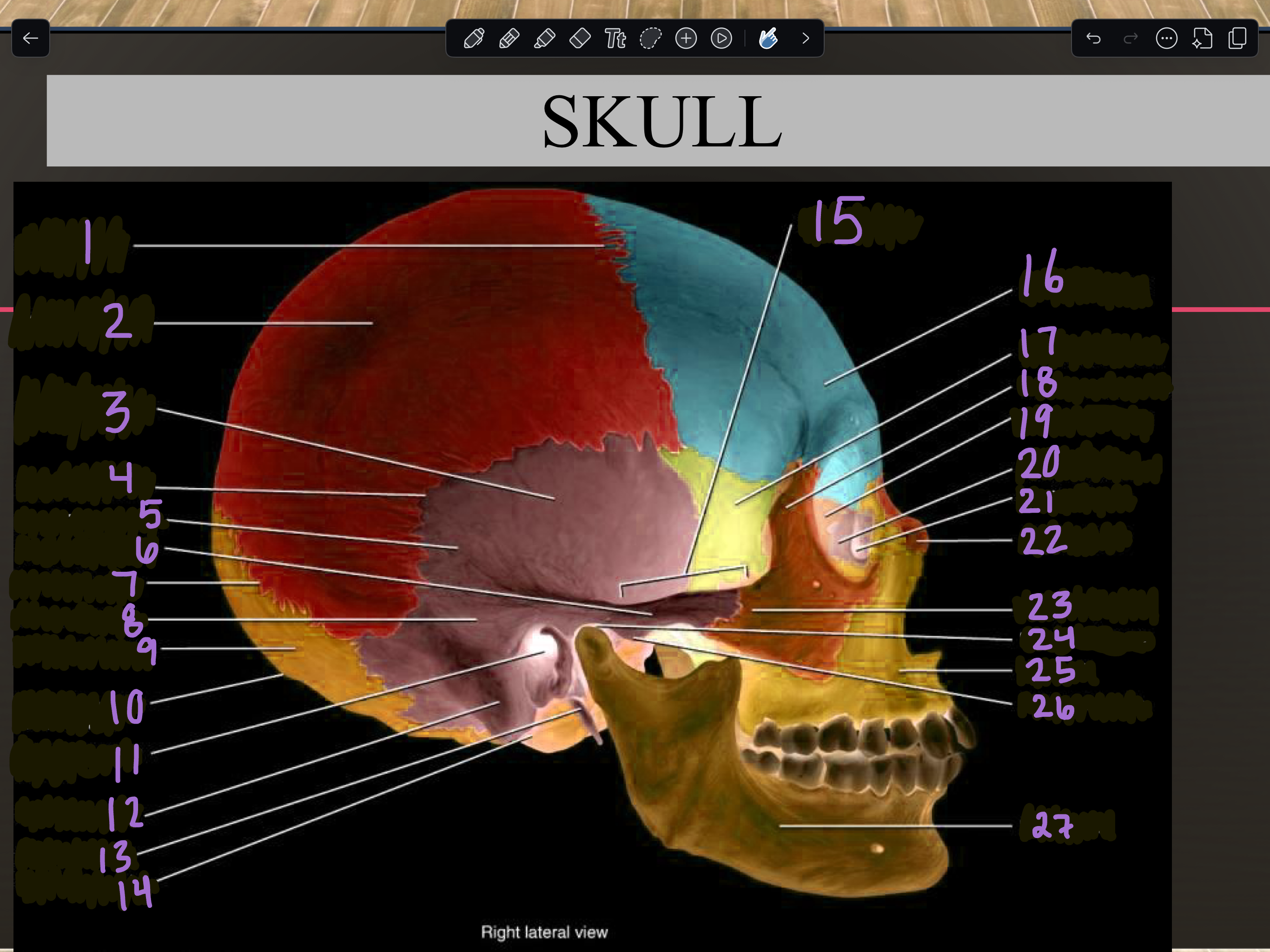
7
Lambdoid suture
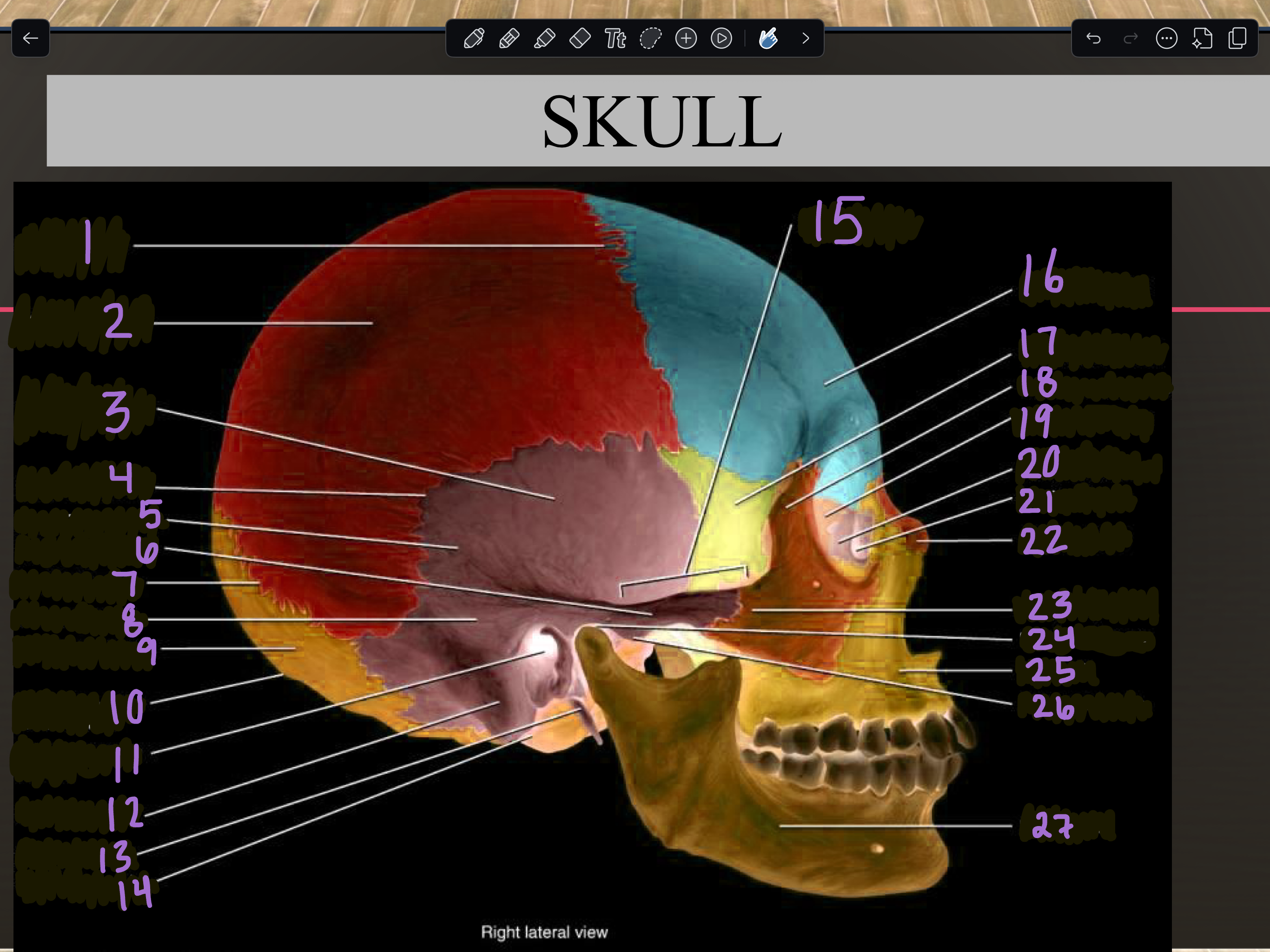
8
Mastoid portion
9
Occipital bone
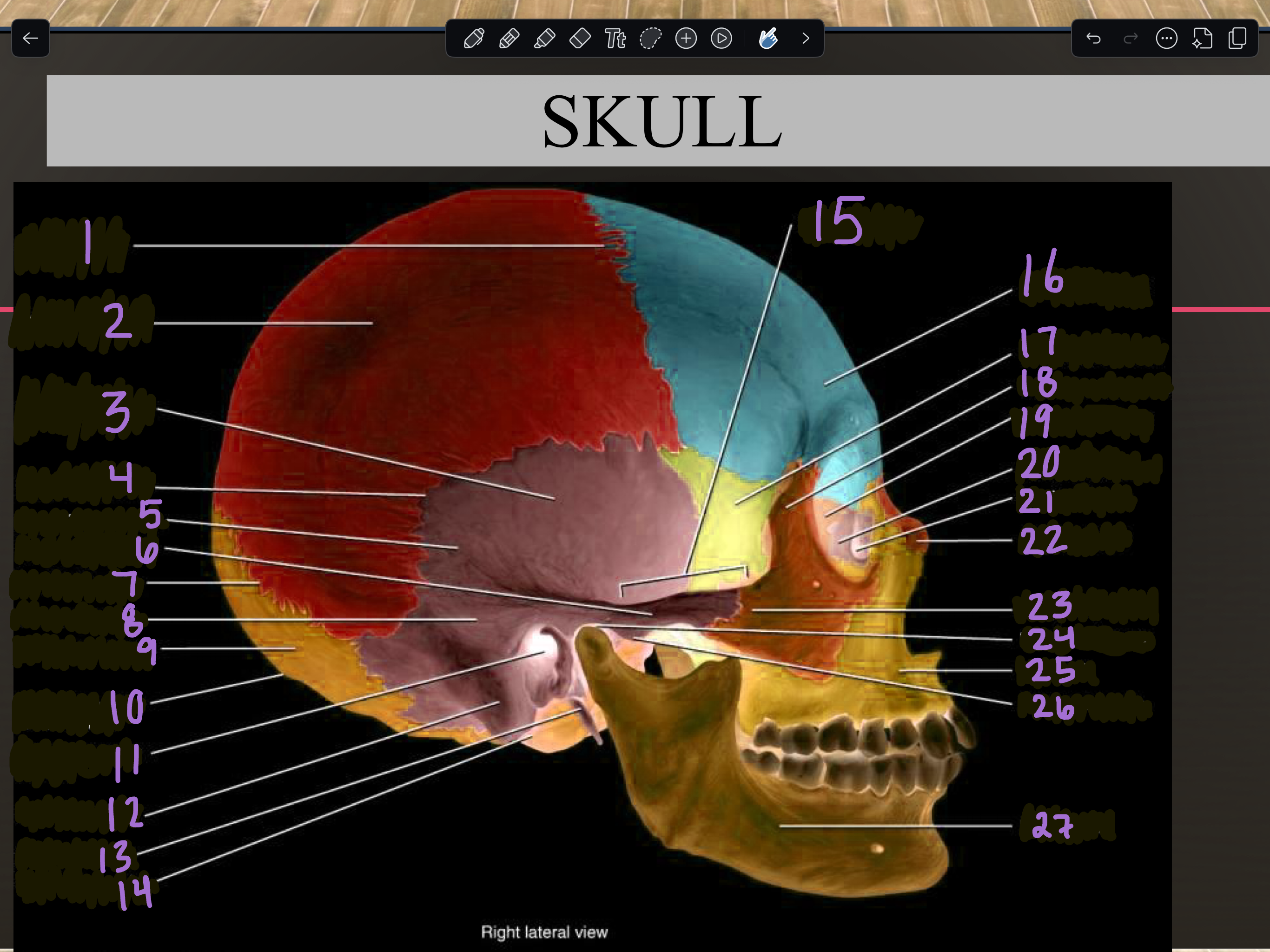
10
External occipital protuberance
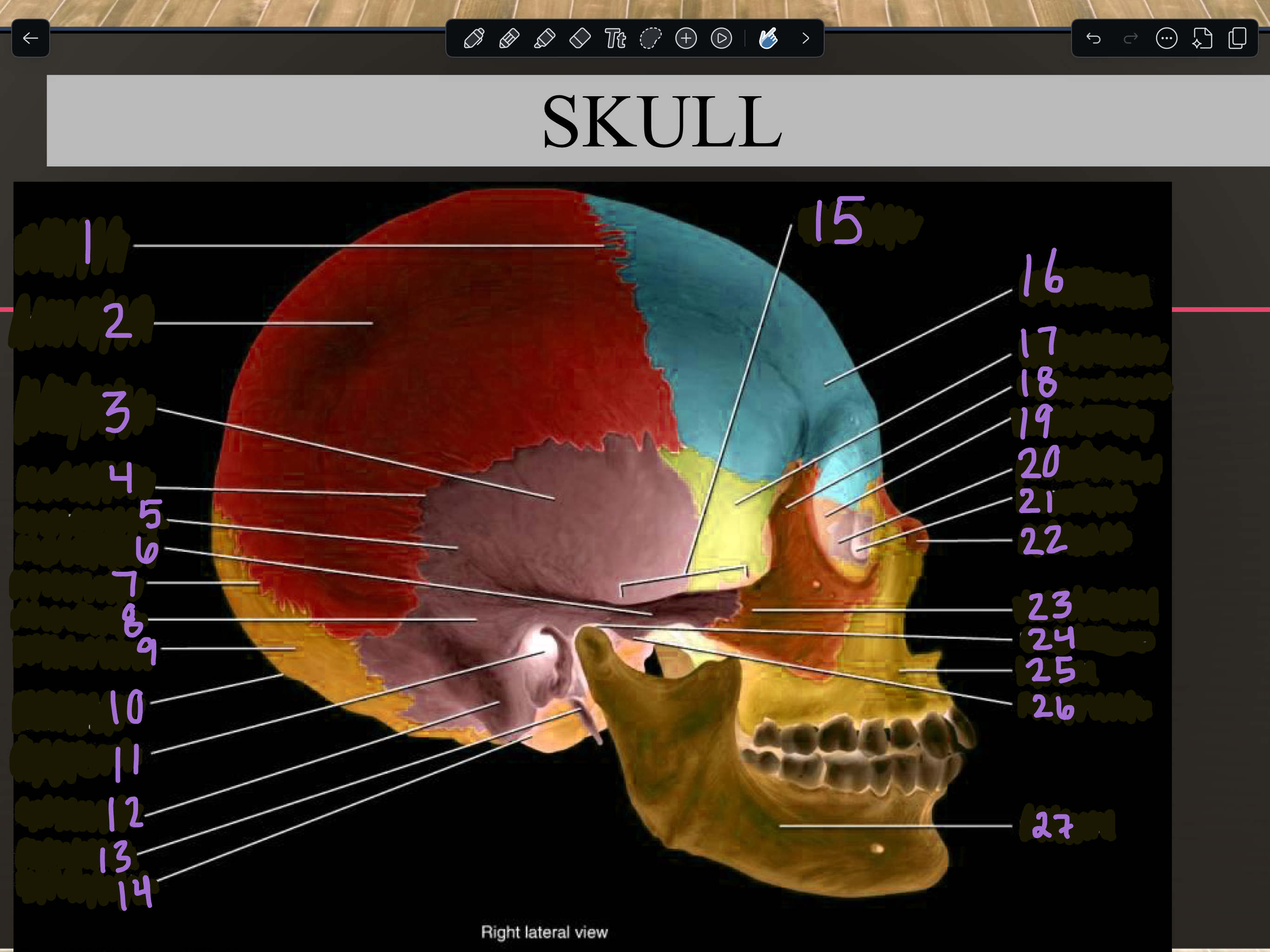
11
Internal auditory meatus
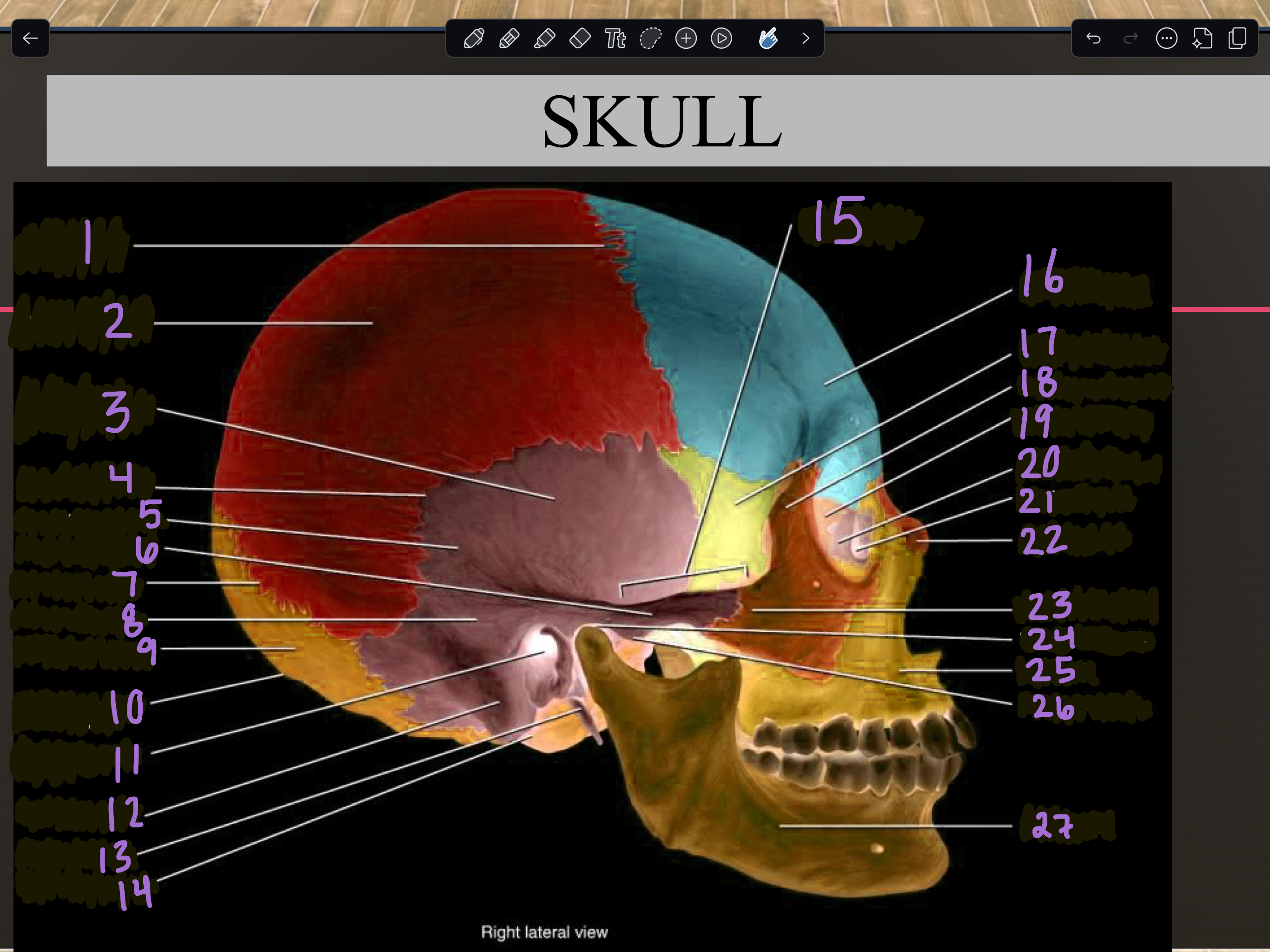
12
Mastoid process
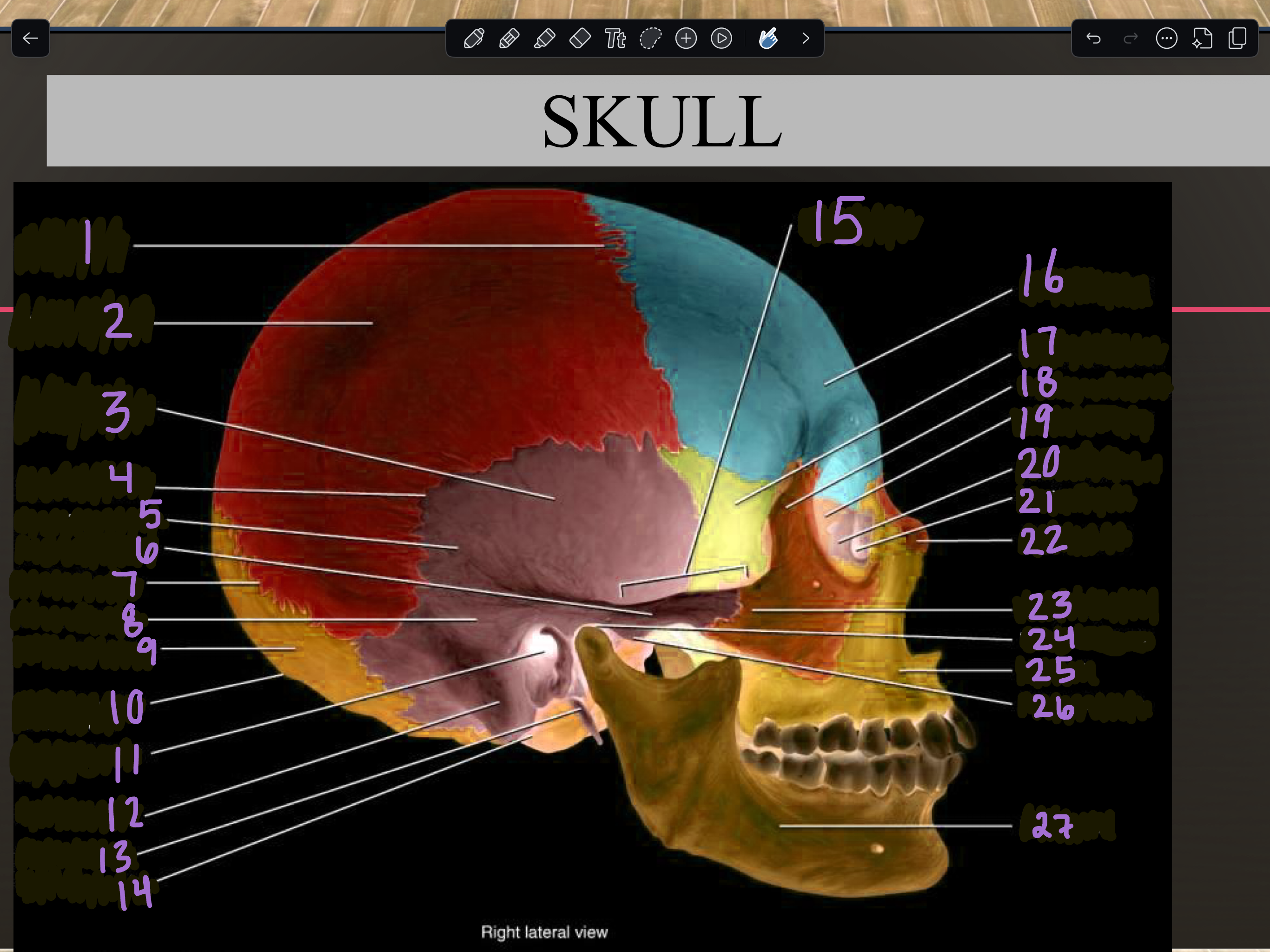
13
Styloid process
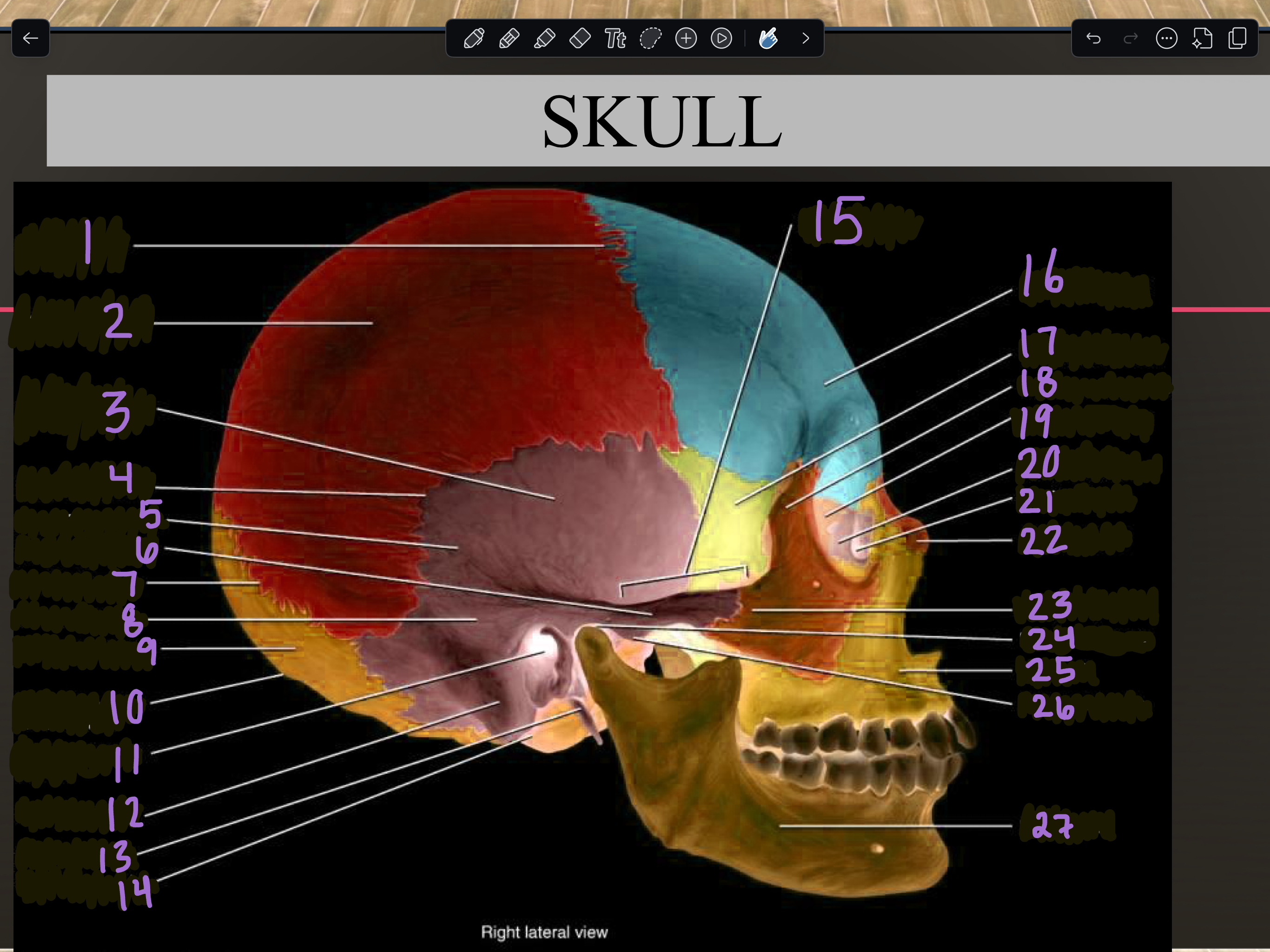
14
Occipital condyle
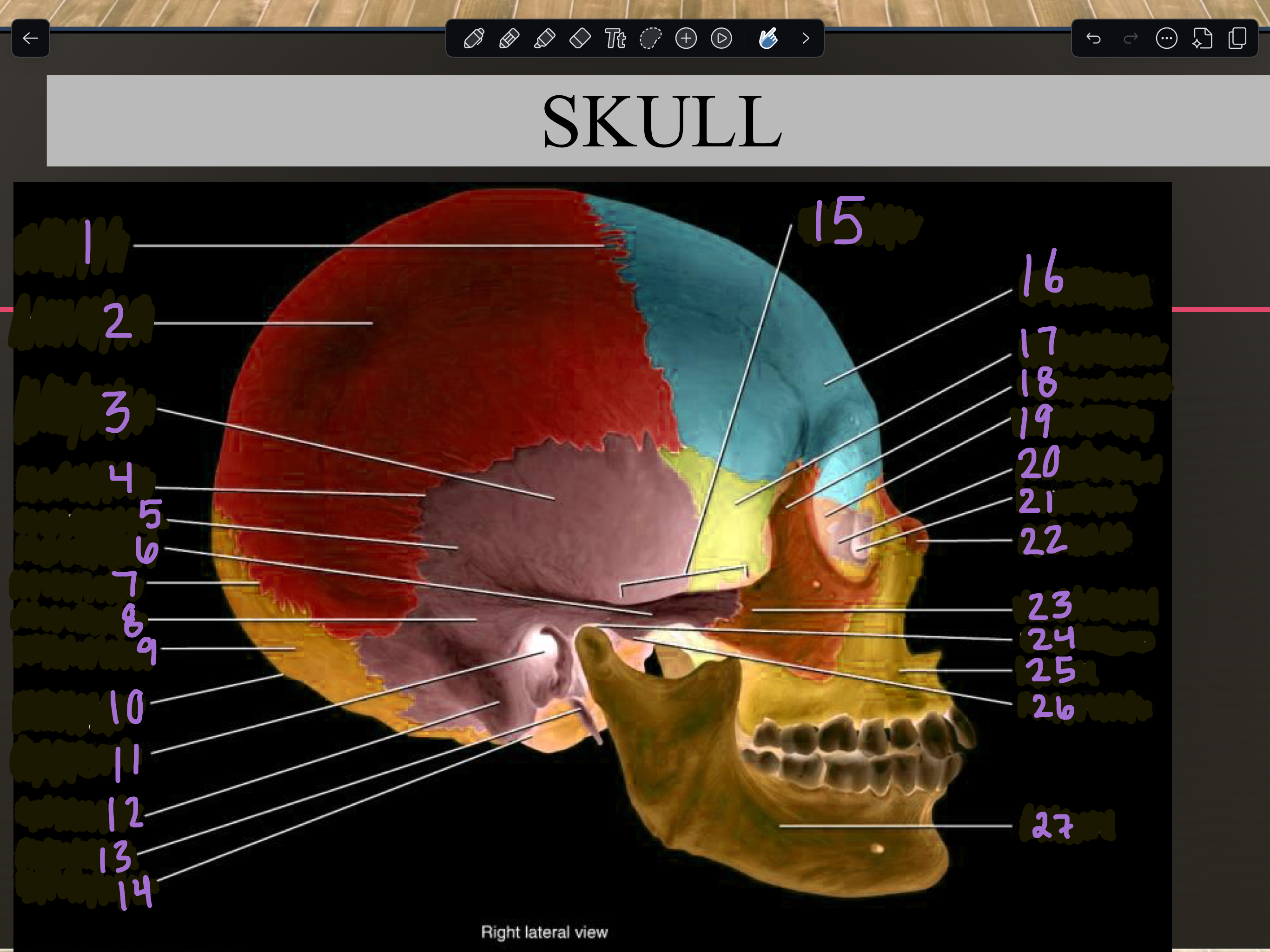
15
Zygomatic arch
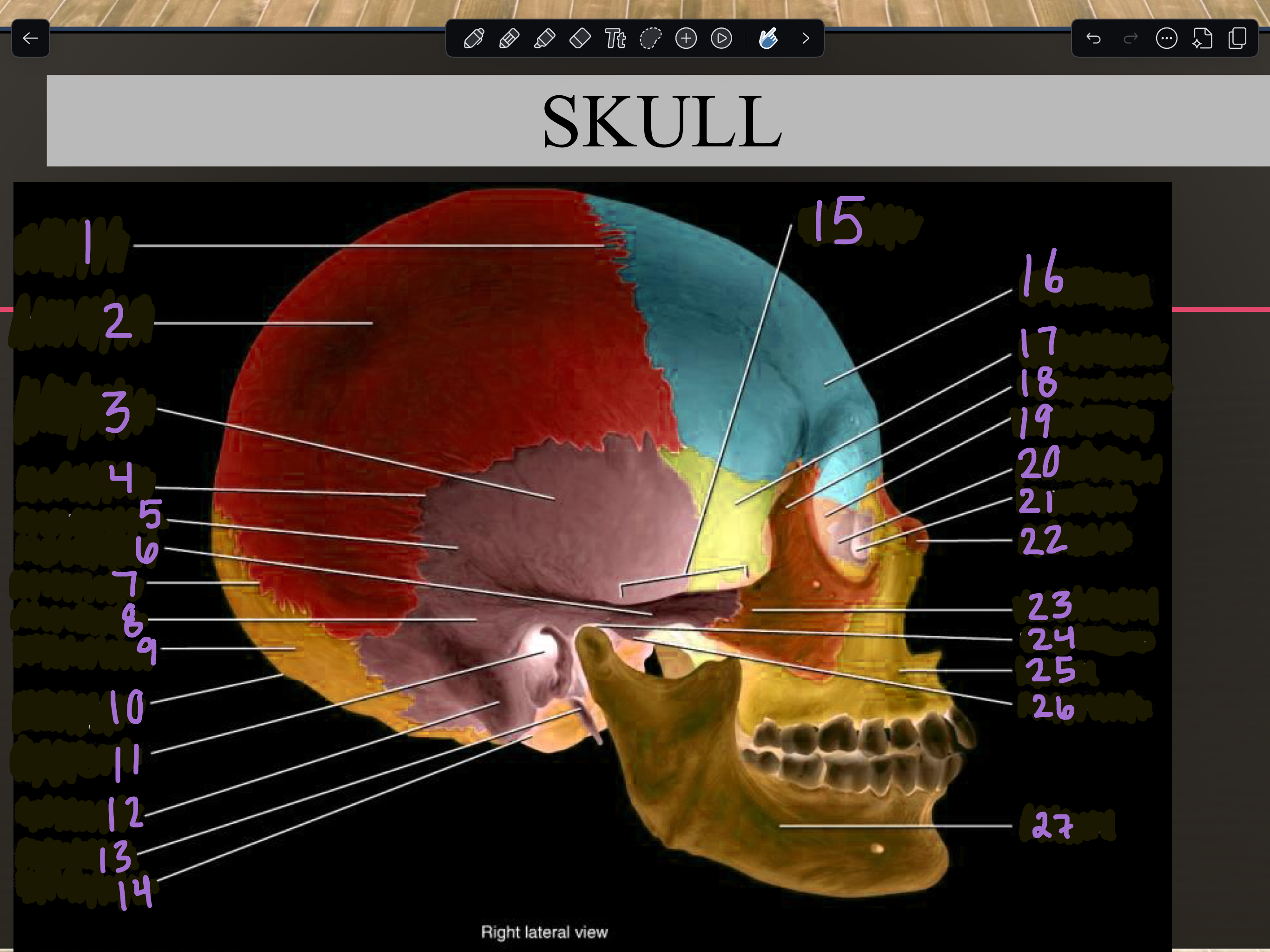
16
Frontal bone
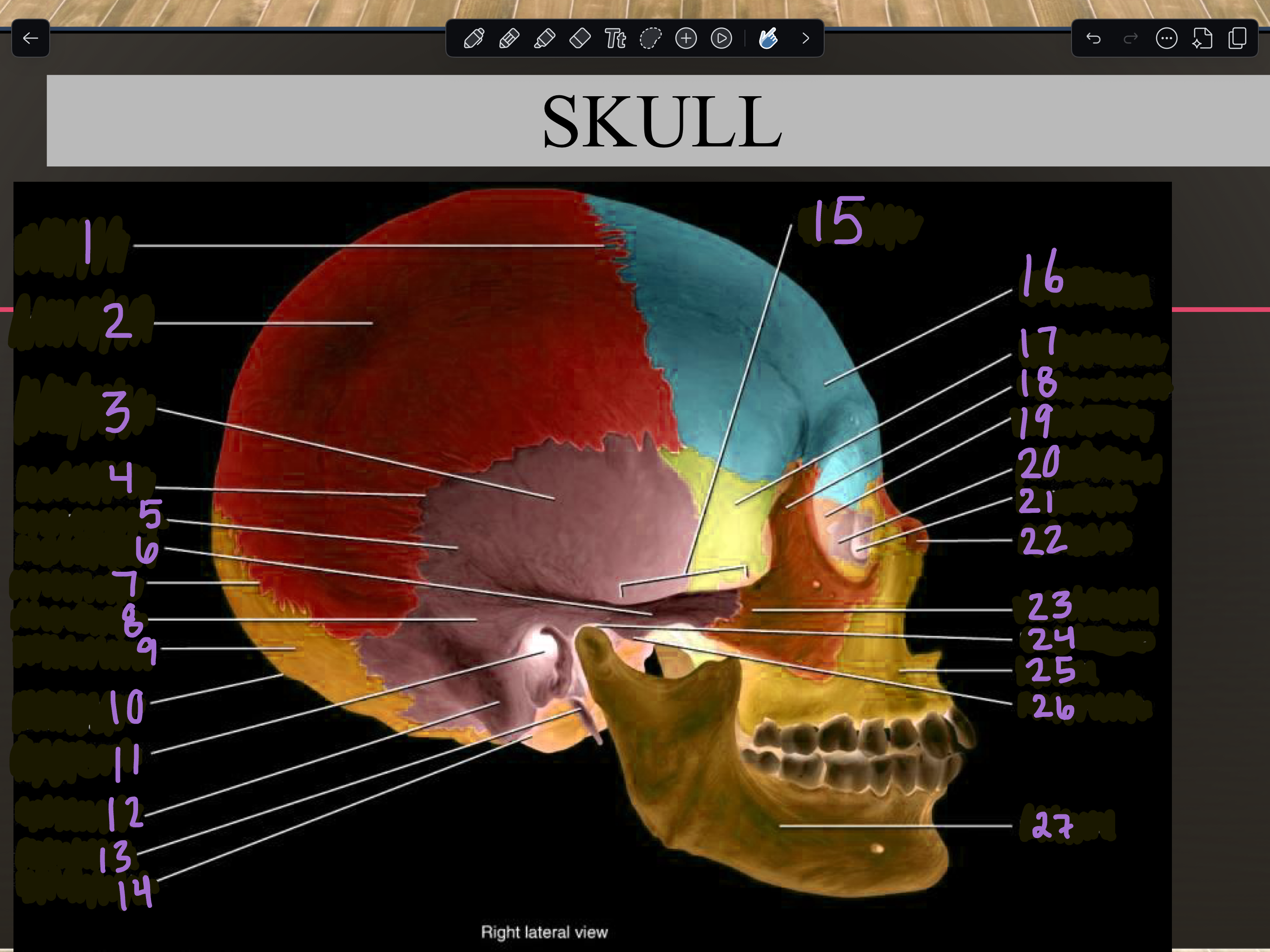
17
Sphenoid bone
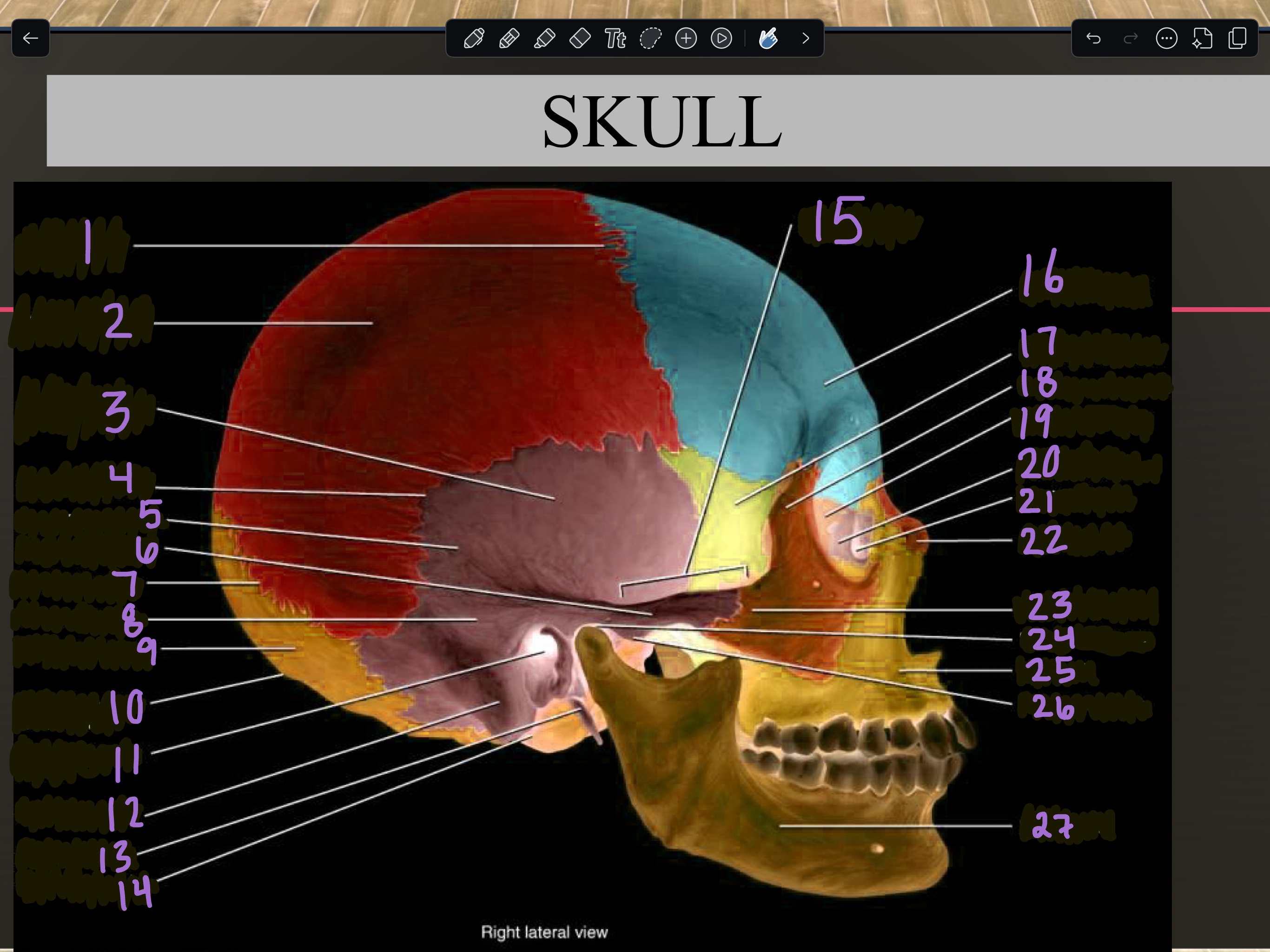
18
Zygomatic bone
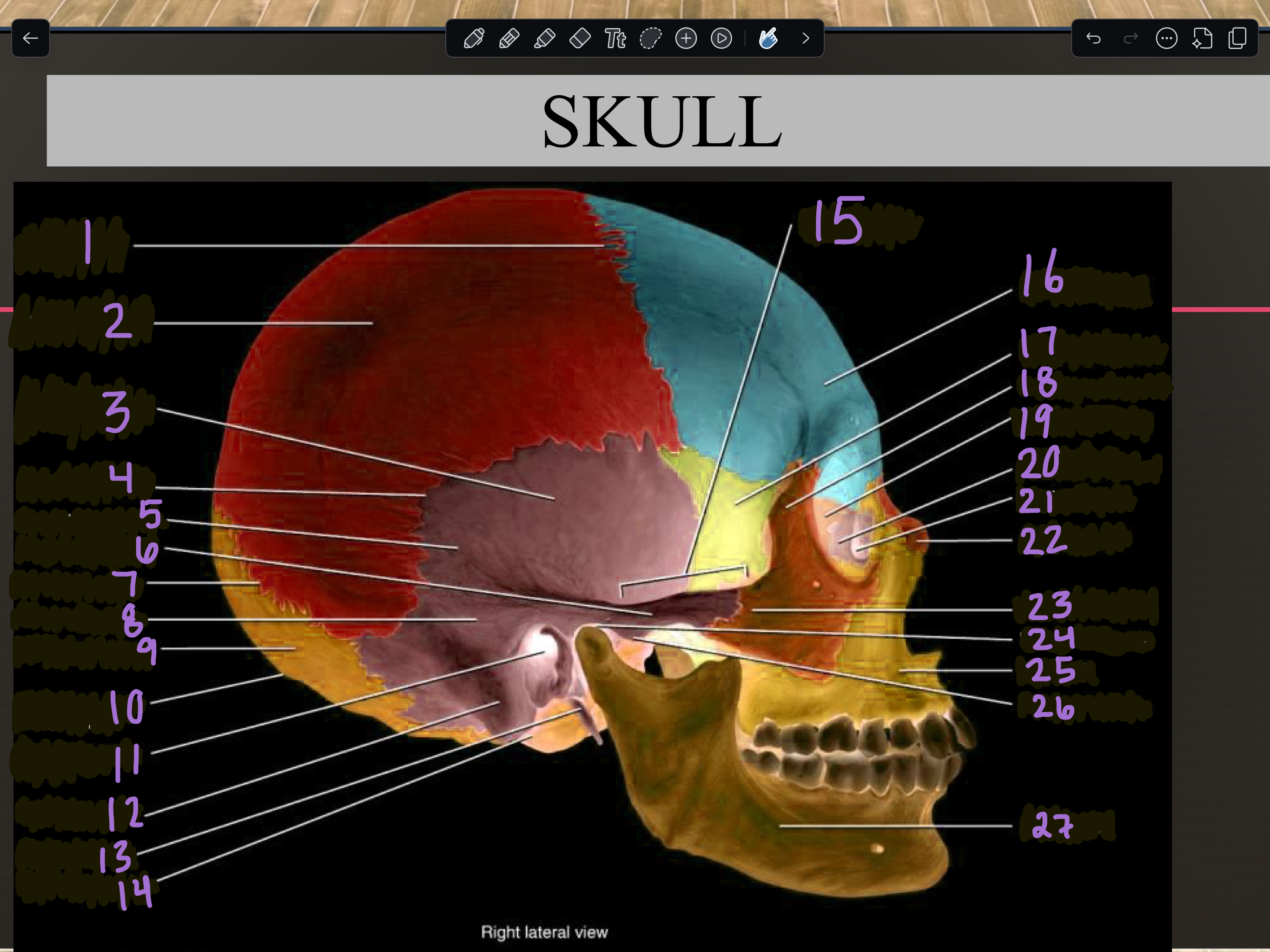
19
Ethmoid bone
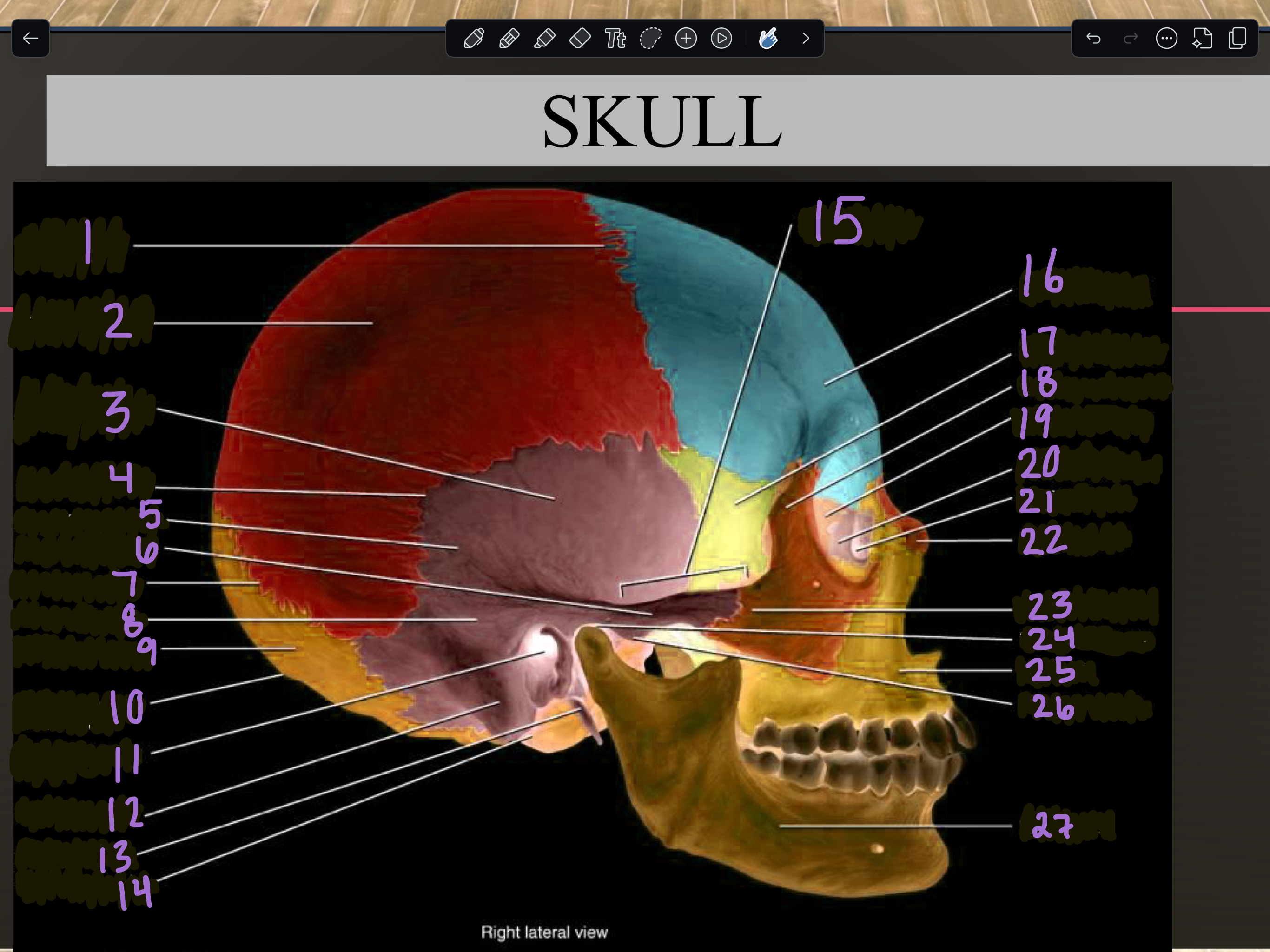
20
Lacrimal bone
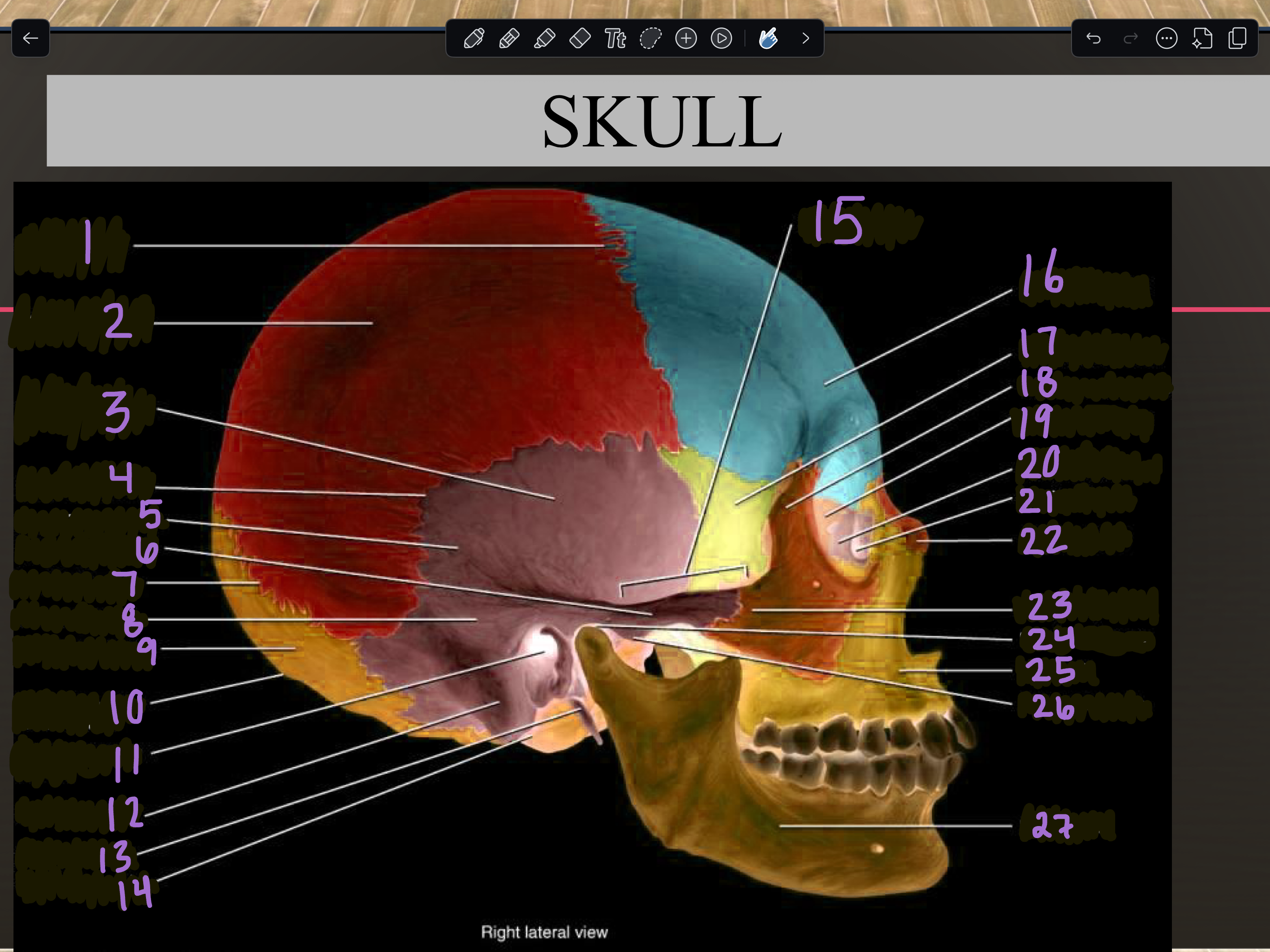
21
Lacrimal fossa
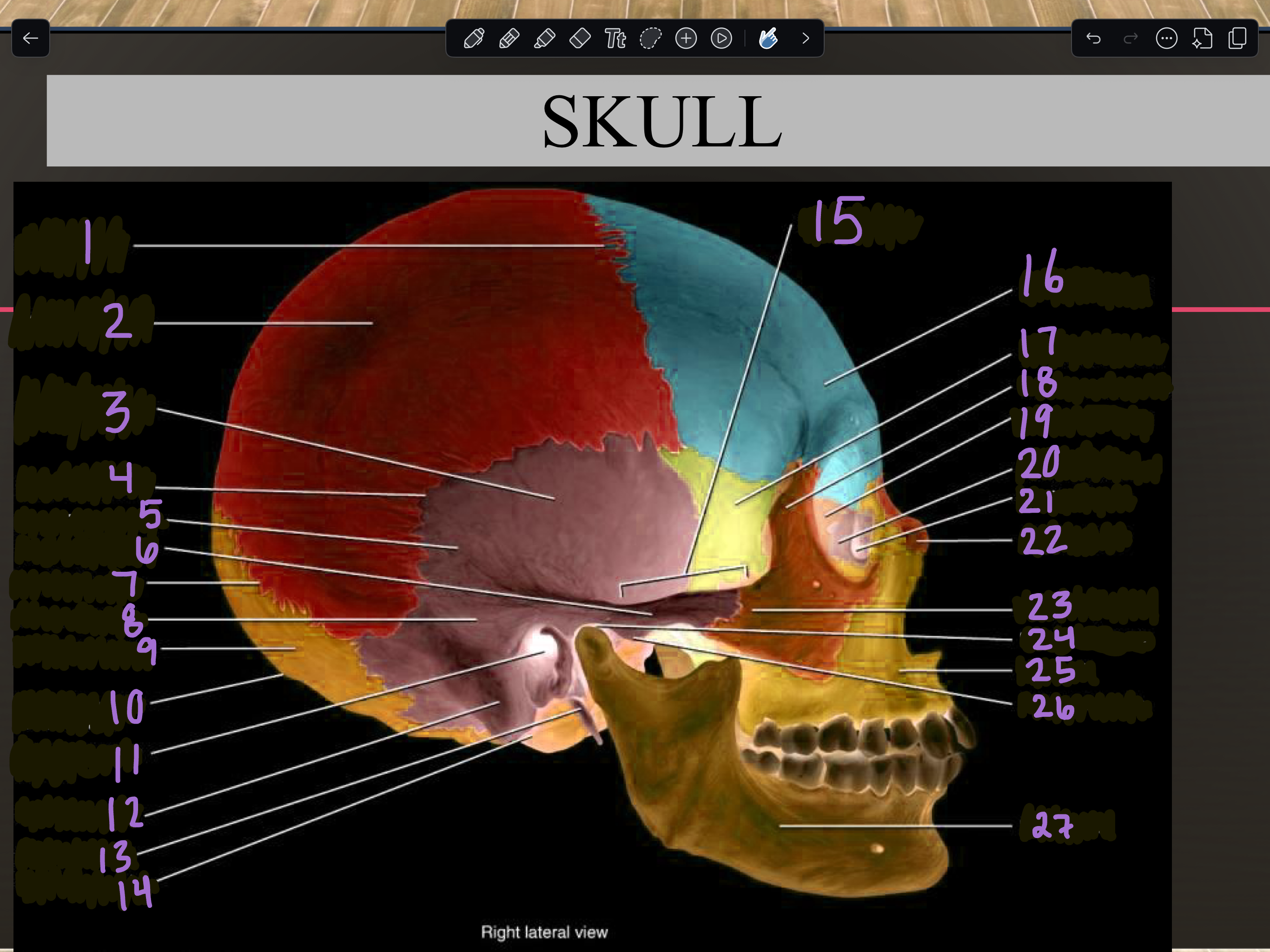
22
Nasal bone
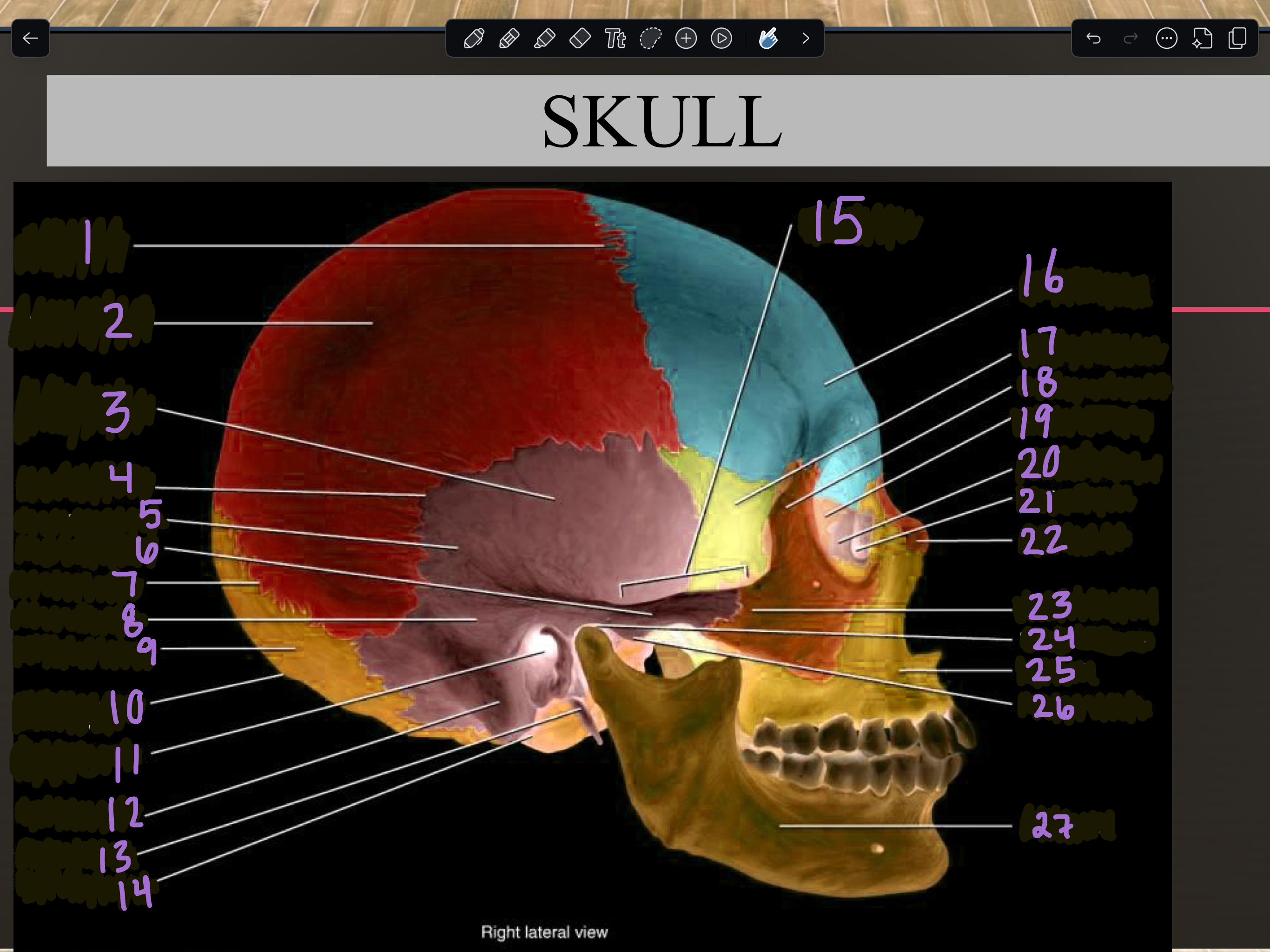
23
Temporal process
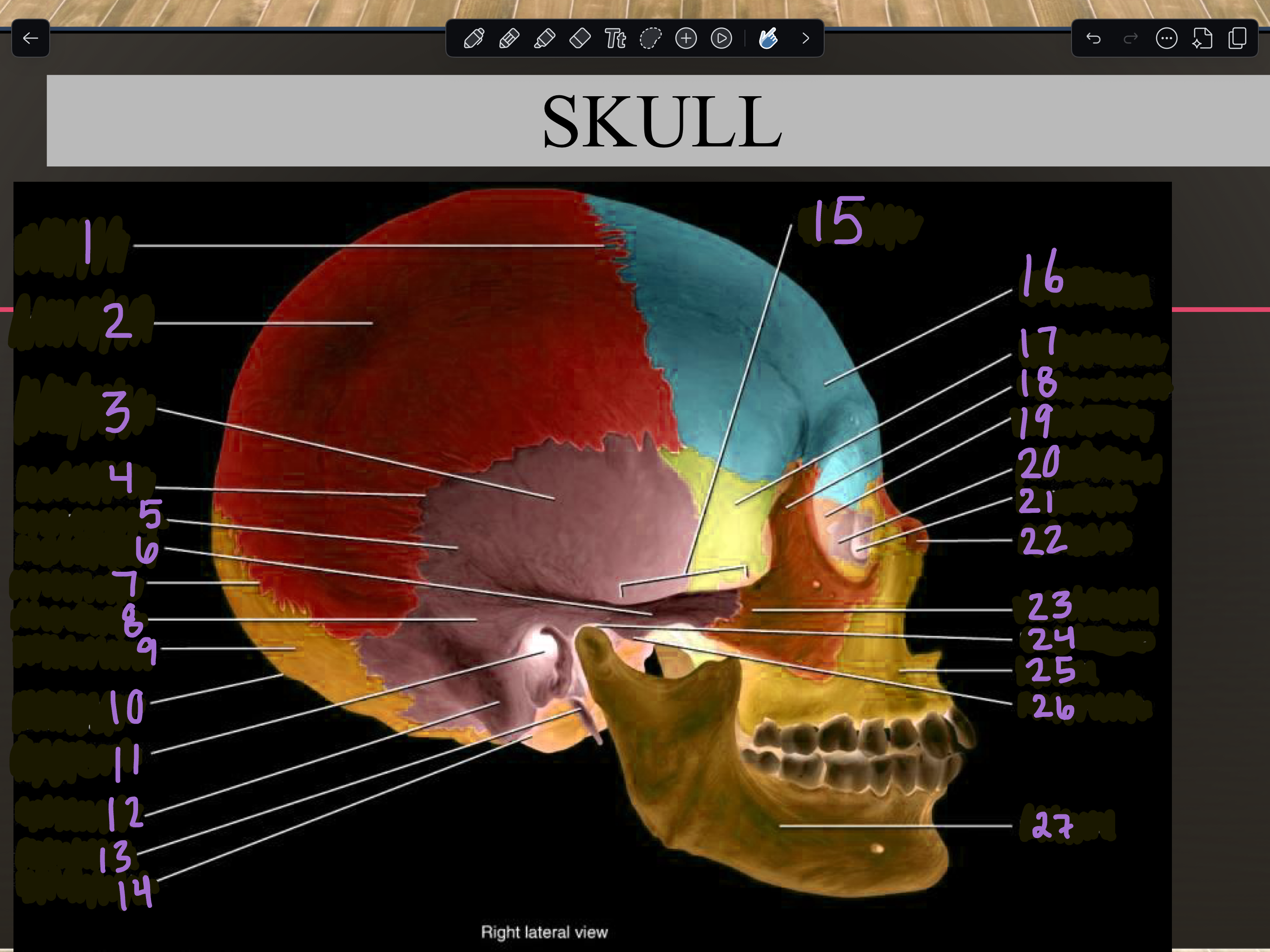
24
Mandibular fossa
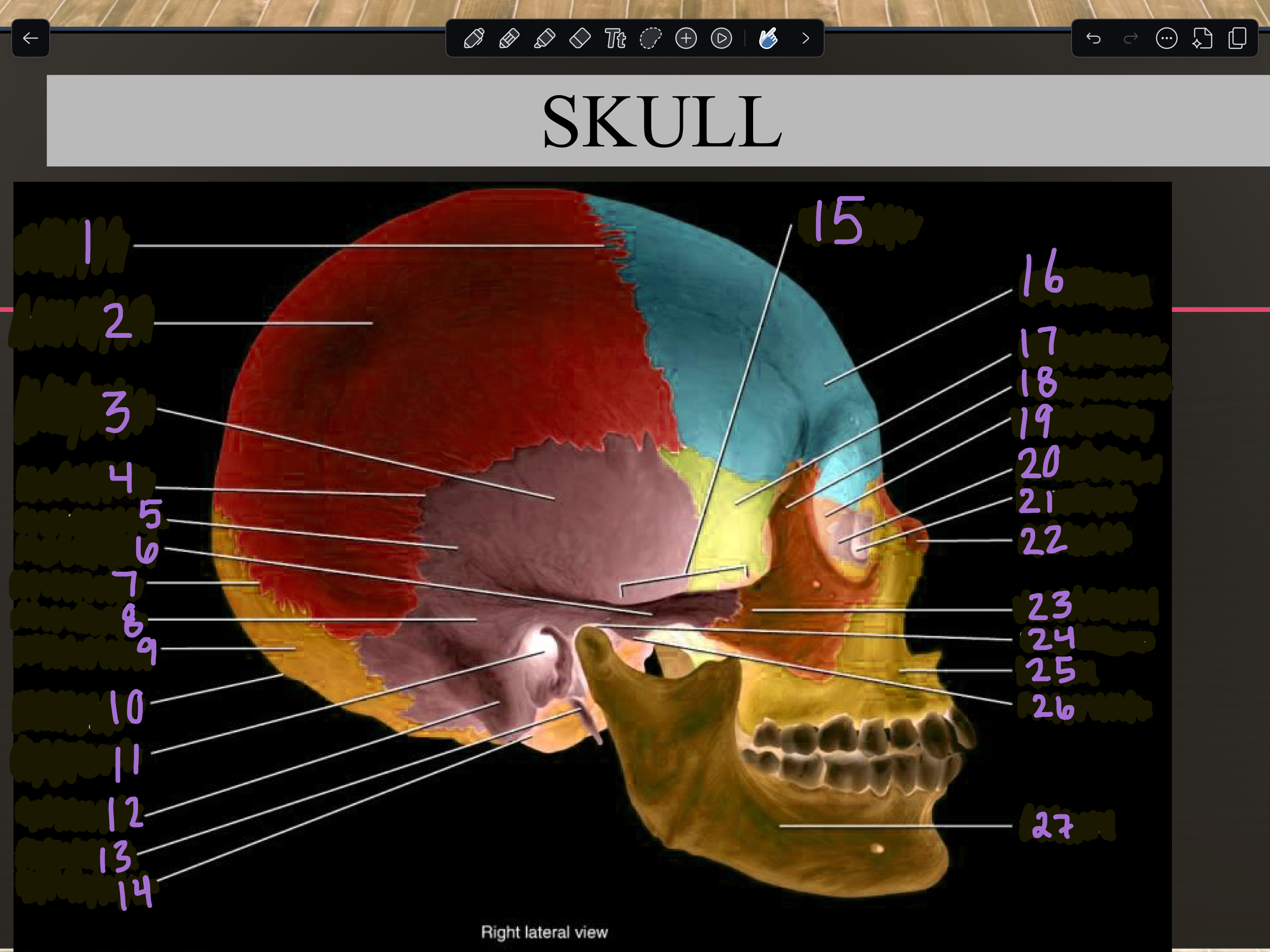
25
Maxilla
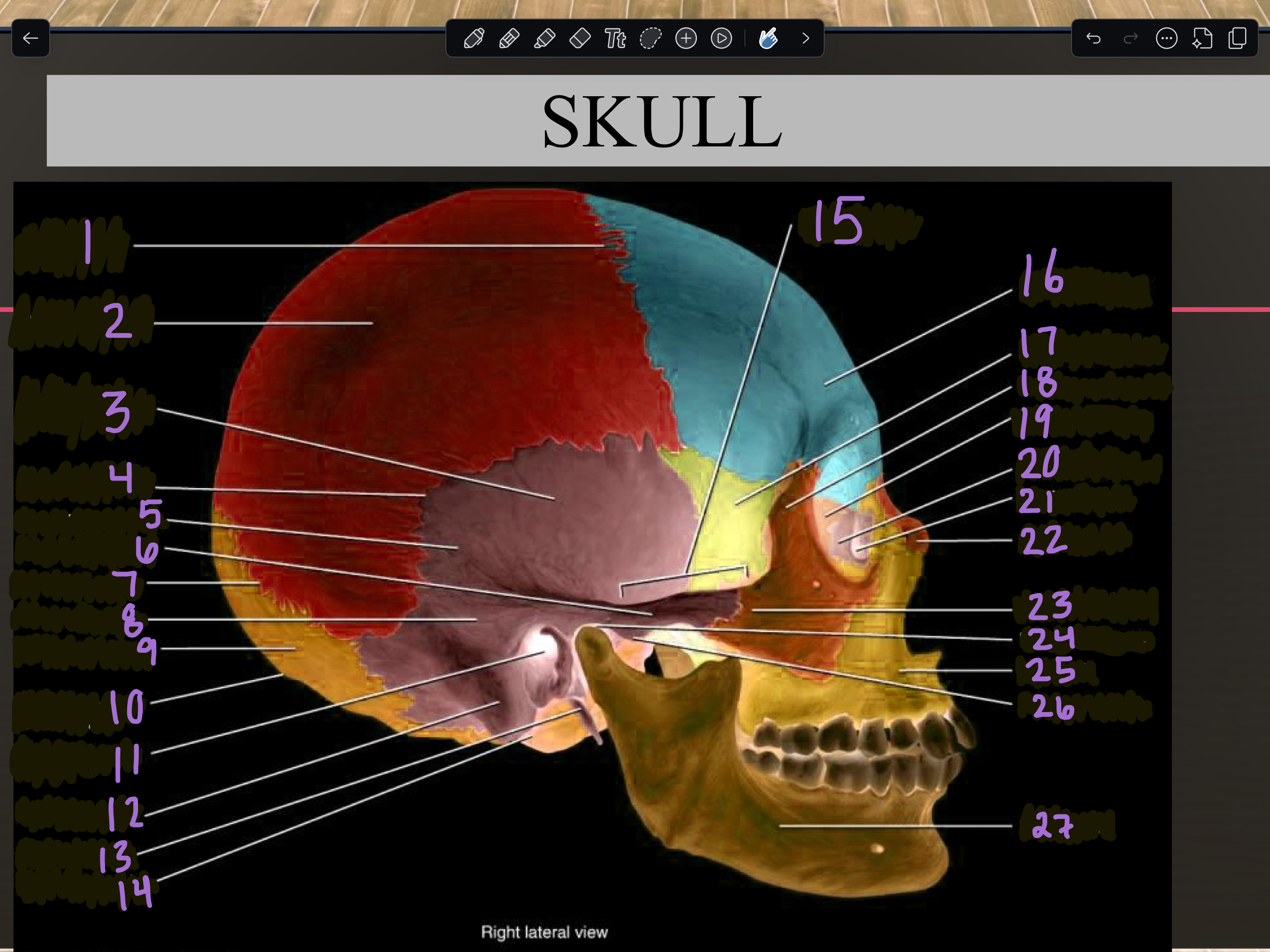
26
Articular tubercle
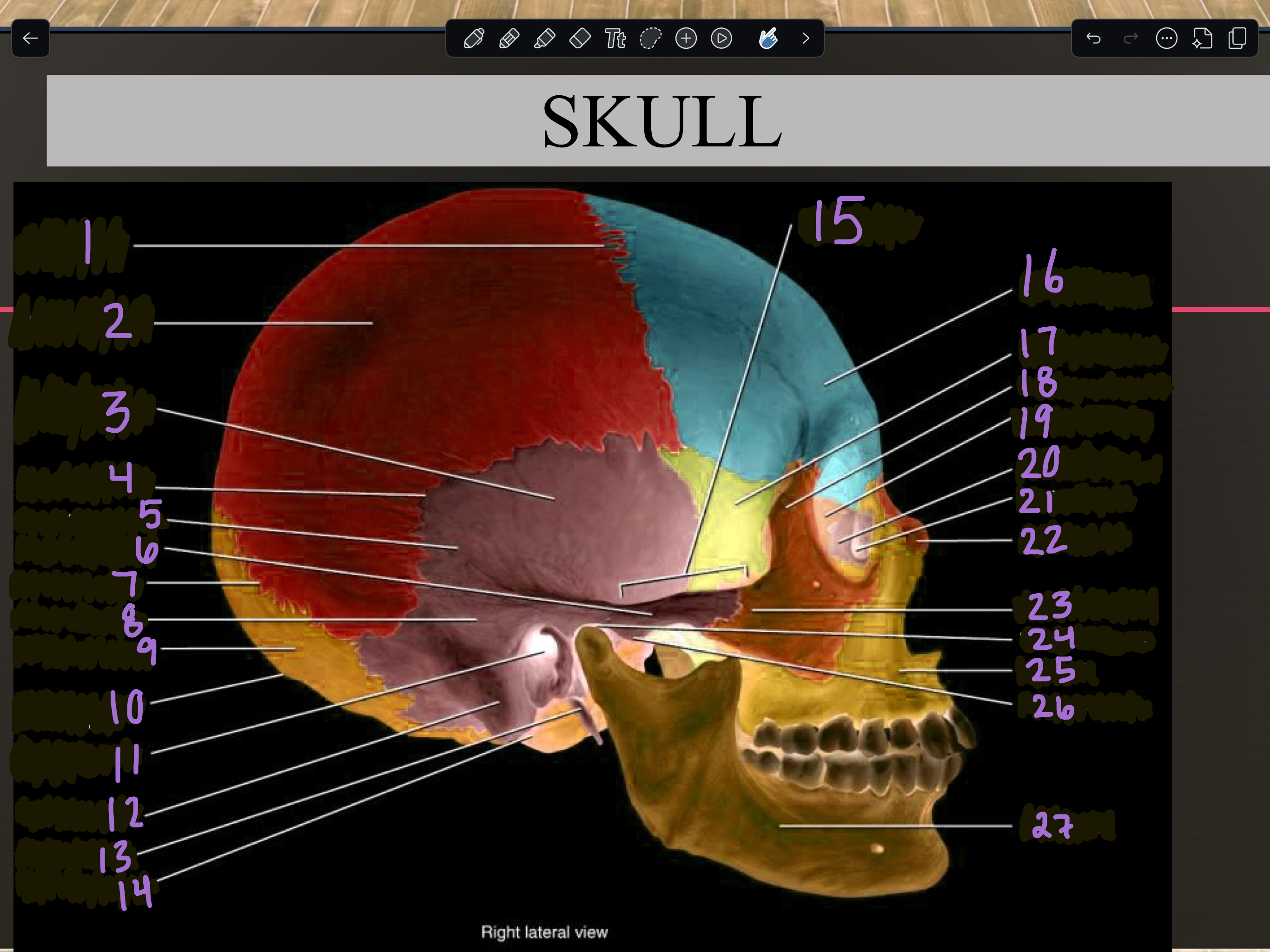
27
Mandible
How many bones does the human skull have?
22 bones
How many bones does the cranium have? List them.
8, frontal, occipital, 2 temporals, 2 parietals, sphenoid, ethmoid
How many facial bones are there? List them.
14, nasals, maxillae, zygomatics, mandible, lacrimals, palatines, inferior nasal conchae, vomer
Which are the two movable skull bones?
Mandible and auditory ossicles
What is the cranium
Section that holds the brain
Forehead
Frontal bone
Cranial bones attached to membranes called _________
-Stabilizes position of the brain
-outer surface provides large areas for muscle attachment that allows head movement or facial expressions
Meninges
Top of the skull
Parietal bones
Back of the skull
Occipital bone
Side of the skull
temporal bones
Base of the cranium, holds up large portion of the brain
Sphenoid bone
Roof of the nasal canal
Ethmoid bone
Layers that surround and protect the brain and spinal cord
Meninges
Meninges tough fibrous outer layer “tough mother’’
Dura mater
-Meninges middle layer; cobweb like layer
-subarachnoid space is below it, containing cerebrospinal fluid
Arachnoid mater
Meninges delicate inner layer that closely adhered to the surface of the brain in the spinal cord
Pia mater
Vertical fold (extension) of the dura mater that divides cerebral hemispheres and keeps them in place
Falx cerebri
Horizontal fold (extension) of dura mater that separates the cerebrum and the cerebellum; protect the brain stem
Tentorium cerebelli
Vertical fold (extension) of dura mater that divides the two hemispheres of the cerebellum; separates and stabilizes the two cerebellar hemispheres
Falx cerebelli
-Consists of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata
-produces automatic behaviors necessary for survival
-provides a pathway for tracts running between higher and lower neural centers
Brainstem
What does the brain stem consist of?
The midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata
Where is the brain stem located?
Between cerebrum and spinal cord
how long is each region of the brain stem?
about 1 inch
Many cranial nerves enter here
Brainstem
-Nerve fibers that travel down through the midbrain and pons into the medulla oblongata
-Carry signals from your brain to your body for crossing over movement control
-on anterior surface of medulla oblongata
Pyramids
-Controls eye movement; plays a role in coordination, alertness, and smooth voluntary movements
-Uppermost part of the brain stem
Midbrain
-located between the midbrain (midbrain is above) and the medulla oblongata
-responsible for breathing and signal relay
-relay center for motor/sensory pathways; connects cerebrum and cerebellum
Pons
-lowest part of the brain stem
-responsible for involuntary functions such as heart rate, sneezing, blood pressure, breathing, vomiting
Medulla
-Network of interconnected neurons that spans the brain stem
-brain stem command center; arousal, sleep, pain, and muscle tone
Reticular formation
What makes the left carotid artery different than the right carotid artery?
It comes directly off the aorta