Obsessive compulsive disorder
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What are the two main diagnostic features of PD?
Obsessions = recurrent, persistent thoughts, urgers, or images that are intrusive and unwanted, which the individual tried to ignore, suppress, or neutralize
Ex. Contamination, responsibility for harm or mistakes, symmetry/order, unacceptable thoughts with immoral, sexual, or violent content
Compulsions = repetitive behaviours or mental acts that are intended to prevent or reduce anxiety or distress OR to prevent a dreaded event that the person feels driven to do, either to neutralize an obsession or prevent an event, even though the behaviours or mental acts are not reasonably related to the obsession or are excessive
Ex. Decontamination, checking, repetitive routine activities, ordering and arranging, mental rituals
Do you have to have both obsessions and compulsions to qualify for an OCD diagnosis?
NO! You just need to have one or the other
But it is typically common for people to have both!
What is obsessive-compulsive personality disorder (OCPD)?
Involves personality traits such as excessive perfectionism, inflexibility, and need for control
Personality traits negatively impact relationships and functioning
What is the difference between OCD and OCPD?
OCPD:
Ego-syntonic = consistent with the person's personality and schemas (ex. "things that have to be in exactly the right order", "I have to do everything perfectly")
Focused on everyday rules, functions, order
OCD:
Ego-dystonic = not consistent with the person' personality and schemas, very upsetting (ex. thoughts about being contaminated, disturbing thoughts)
Not grounded in reality
Is OCD or OCPD more distressing and impairing?
OCD =more distressing impairing
This is because OCD is ego-dystonic / not grounded in reality
What is the sex ratio of OCD (Epidemiology)
~1:1
Women = greater comorbidity with depression + higher contamination/cleaning
Men = earlier onset age + greater comorbidity with tic and substance abuse + higher sexual/religious obsessions
*DIFFERENT FROM OTHER FEAR DISORDERS
What is the Canadian prevalence of OCD? (Epidemiology)
1-2%
*Less prevalent than other anxiety disorders
What is the age of onset for OCD? (Epidemiology)
Early 20s
*Same time frame as anxiety disorders
What is the course of OCD without treatment? (Epidemiology)
Chronic, unremitting
What is the typical response to an intrusive though for people WITHOUT OCD?
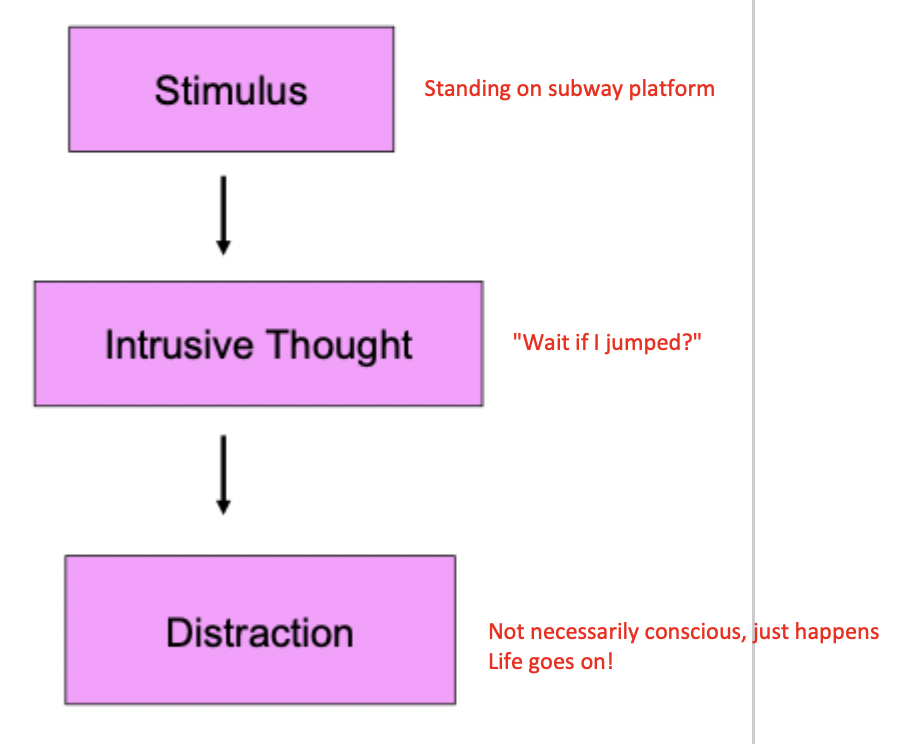
What is the cognitive-behavioural model of OCD?
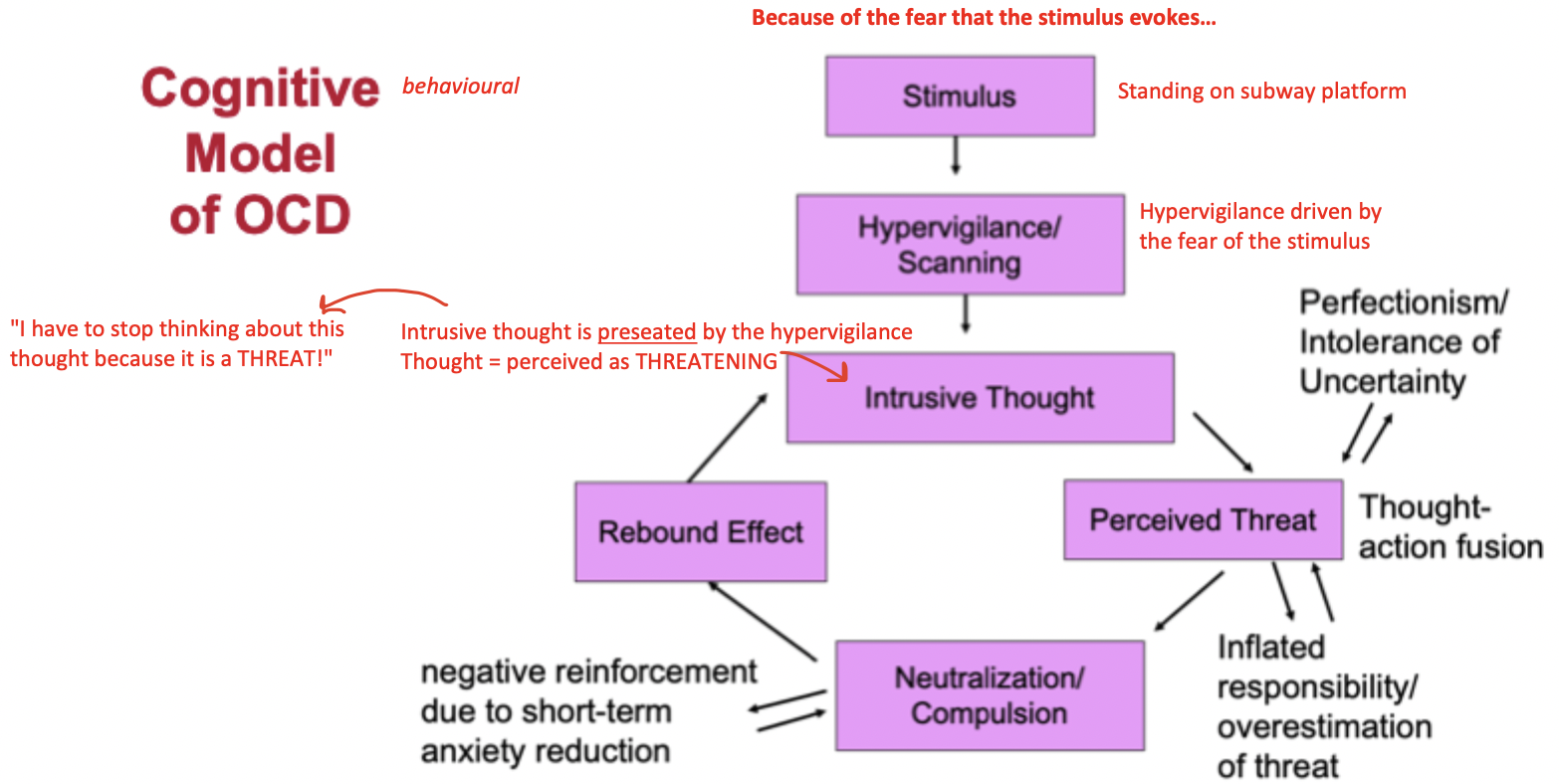
Inflated responsibility (dysfunctional belief in OCD)
Belief that one has the power to cause and/or the duty to prevent negative outcomes
Ex. Client who though they had killed children
Overestimation of threat (dysfunctional belief in OCD)
Belief that negative events are likely and unmanageable
Ex. "If I go to the mall, I am going to have a panic attack and horrible things will happen. If those things happen, I wont be able to cope…"
*This is common to other anxiety disorders
Exaggeration of the importance of thoughts (dysfunctional belief in OCD)
Thought-action fusion = belief that the mere presence of a thought indicates that this thought has occurred
Ex. The mere prescence of a thought about killing children meant to the client that they had actually killed children (thought = proof)
Obsessive thoughts are a major trigger of OCD
*KEY FEATURE OF OCD
Need to control thoughts (dysfunctional belief in OCD)
Belief that complete control over thoughts is necessary and possible
Ex. "I need to be able to control everything that goes on in our mind" not normal…
Perfectionism (dysfunctional belief in OCD)
Belief that mistakes and imperfections are detrimental
Uncertainty (dysfunctional belief in OCD)
Belief that it is necessary and possible to be 100% certain that negative outcomes will not occur
Not being able to live with any doubt
Ex. "I have to go back home multiple times to check that I turned off the oven"
*KEY FEATURE OF OCD
What are the consequences of neutralization/compulsion in OCD?
Paradoxical increase in thought frequency
The more you try to get rid of a thought = the more it comes back
Hypervigilance to thought triggers
Neutral stimuli included in attentional focus
Constantly scanning environment
Terminates exposure to thought
Prevents new learning
Negative mood increases the future salience and accessibility of the thought
We are biased to remember negative things when we feel down
What is exposure and response prevention (ERP)?
Exposure to obsessive stimulus (thought) + prevention of compulsive response (behaviour)
Involves…
Habituation to obsessional distress (sitting in the discomfort)
Learning that the feared outcomes are less likely / less severe than anticipated (learning there is nothing inherently dangerous about the thoughts)
Eventual extinction of obsessional anxiety over time
Example of ERP exercise for contamination (obsession) + washing (compulsion)
Get client to repot a plant (get their hands dirty and sit there without washing them)
Clinician asks them about their SUDS level throughout the exercise
Example of ERP exercise for breaking the mechanism (obsession) + checking (compulsion)
Get client to visit the thing they thought they broke and then make them walk away (do not let them go back )
Example of ERP exercise for responsibility for harm (obsession) + checking (compulsion)
Get client to go for increasingly long walks / periods of time before they can check the news
(specific example tailored to the person who thought that they killed children)
Example of ERP exercise for immoral thoughts (obsession) + mental rituals (compulsion)
VERY HARD TO TREAT!
Have convos with client about what ego-dystonic thoughts are (thoughts as just being thoughts and nothing more)
*More psychoeducation-focused!
Example of ERP exercise for hoarding
Get client to throw things away
Unique subtype of OCD
*Different than simply liking to keep things(behaviour is on a continuum, the extreme would be impaired functioning and distress when throwing things away or health and safety concerns due to hoarding/crowded spaces)
Equifinality
Different pathways or starting conditions can lead to the same final outcome or developmental state
What medications are used to treat OCD?
SSRIs and SRIs
NOTE: few patients achieve minimal symptoms with SSRIs or SRIs alone…
Treating OCD with medication alone is not the gold standard… you are missing that vital exposure and response prevention
What is done for OCD partial responders?
In partial responders (individuals whose OCD symptoms do not fully go away with their first medication alone), treatment response is improved through augmentation ("adding") with a low-dose anti-psychotic medication (risperidone, aripiprazole)
What is the efficacy of ERP augmentation vs. Risperidone augmentation (low-dose anti-psychotic)? (Foa et al., 2015)
Study details:
Participants (OCD patients) received a therapeutic does (enough to have a clinical effect) of an SRI medication
Acute phase = patients randomized to received 8 weeks of
Risperidone augmentation (low-dose anti-psychotic med)
Exposure and response prevention augmentation
Maintenance phase = back to ongoing SRI treatment for 6 months
Study findings:
ERP augmentation lead to significantly reduced symptoms + participants were better able to maintain their gains over time