Chapter 5, Lesson 5: Cellular Junctions, Glands, and Membranes
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 5, Lesson 5 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Ninth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Cell junctions
The connections between two cells; they are usually anchored with each other or the matrix for communication, strength, and transfer
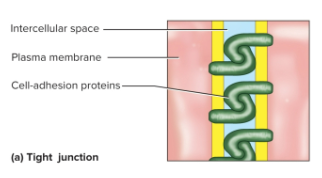
Tight junction
A zipper-like, interlocking linkage between cells by trans membrane adhesion proteins
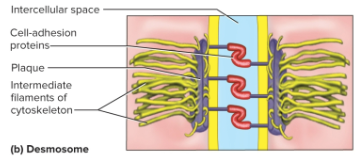
Desmosome
A Velcro-like patch that holds cells together and resists mechanical stress, has hook-shaped proteins with more space in between
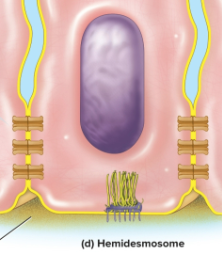
Hemidesmosome
A half-desmosome that anchors basal cells of an epithelium to the basement membrane
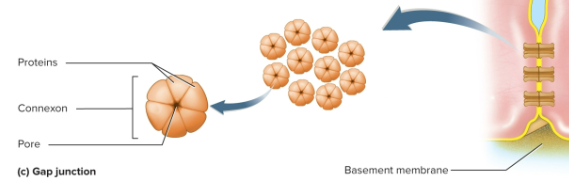
Gap junction
Junction formed by orange-like connexons, these transfer substances like a bridge and are located in cardiac and smooth muscle as well as the embryo, lens, and cornea
Connexon
Six trrans membrane proteins arranged like segments around a water-filled pore
Gland
A cell or organ that secretes substances for use in the body or releases them
Secretion
Keeping a product useful to the body
Excretion
Removing a product not useful to the body (waste products)
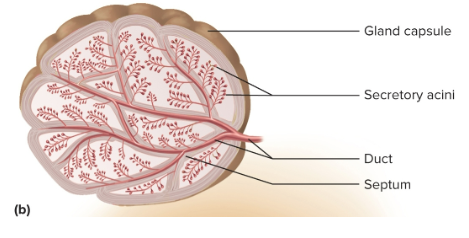
Exocrine glands
Glands that maintain their contact with the surface of the epithelium via a duct
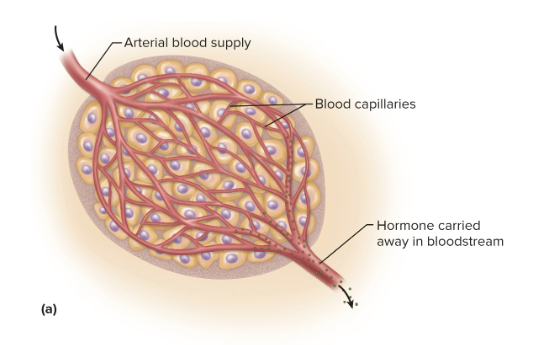
Endocrine glands
Glands that have no ducts or contact with the outside, they secrete hormones directly into the blood
Hormones
Chemical messengers that stimulate cells elsewhere in the body
Unicellular glands
Found in an epithelium that is predominantly non-secretory; can be endocrine or exocrine
Capsule
The connective tissue covering of the exocrine gland
Septa (trabeculae)
Extensions of a capsule that divide into compartments
Stroma
The connective tissue framework of the gland; supports and organizes glandular tissue
Parenchyma
Cells that perform both the tasks of synthesis and secretion
Classification of glands
By duct (simple and unbranched, or compound and branched) or by gland shape (tubular with narrow secretory portion, acinar with multiple secretory cells, or tubuloacinar with both characteristics)
Serous glands
Produce thin, watery secretions (perspiration, milk, tears, digestive juices)
Mucous glands
Produce glocyoprotin, mucin, to absorb water from mucous
Mixed glands
Contain both serous and mucous cell types and produces a mixture
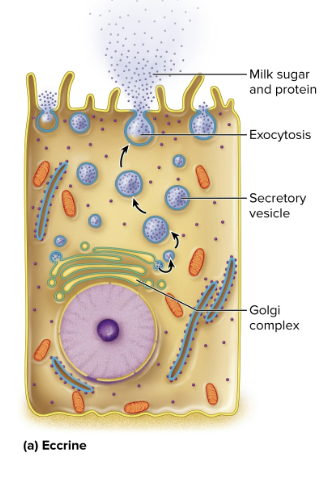
Eccrine glands
Uses vesicles that release secretion by exocytosis, like tears, the pancreas, etc

Apocrine glands
A liquid droplet covered by the membrane and cytoplasm from the cell surface; used to make milk
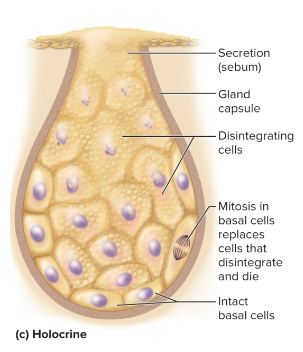
Holocrine secretion
Cells accumulate a product until they disintegrate, secretes cell fragments and substances
Membranes
Only epithelial, only connective or a mix of epithelial, connective, and muscular tissues
Cutaneous membrane
The skin (the largest membrane in the body), made up of stratified squamous epithelium on connective tissue
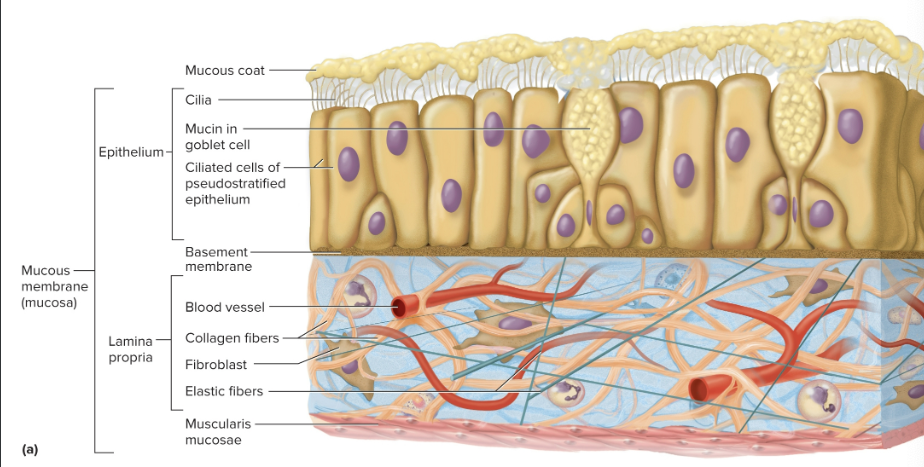
Mucous membrane
Lines passages that open to the external environment (like the digestive tract); absorbs, secretes, and protects often with goblet cells
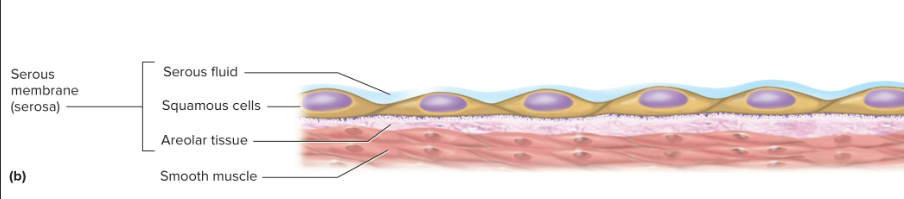
Serous membrane
Internal membranes of simple squamous epithelium on areolar tissue; produces serous fluid that arises from blood and lines organs and body cavities (endothelium to the heart, mesothelium on cavities)