Chem Analyzing Data
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
A quantity that has both a number and a unit
What is a measurement?
An international system (SI) of measurement used in science
What is the Metric System?

Seven units
How many units are in the SI System?
Base units
What are the SI System units called?
Metric prefixes
What can you add to base units?
Makes it more convenient, makes it larger/smaller than the base unit
What does a metric prefix do to the base unit?
mL (mililliters), in graduated cylinder
What unit do you use for volume?
g (grams), on balance
What unit do you use for mass?
C (Celsius), in thermometer
What unit do you use for temperature?
The measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in an object
What is temperature?
m^3
Volume equation in meters
m/s
Velocity equation in meters
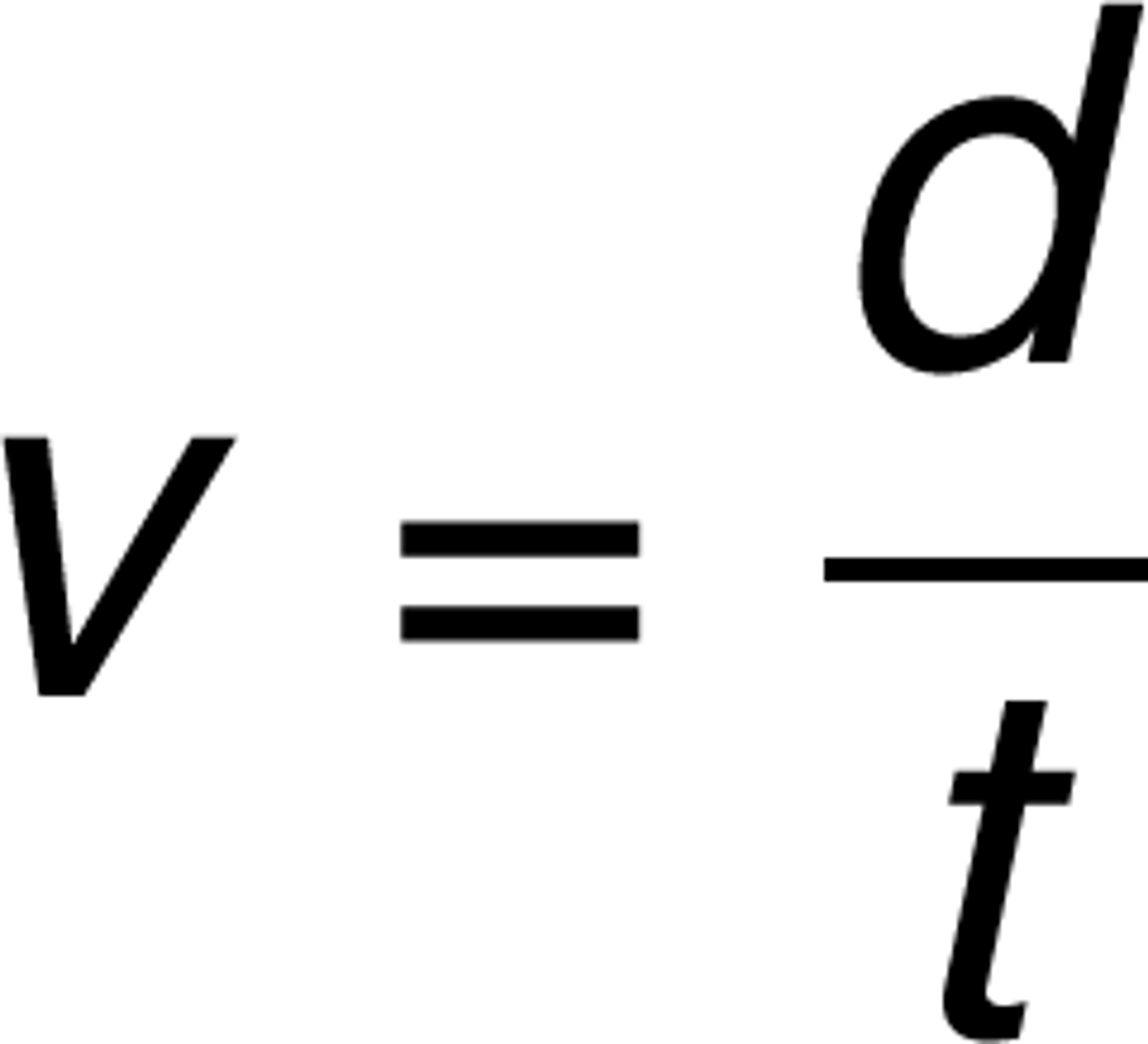
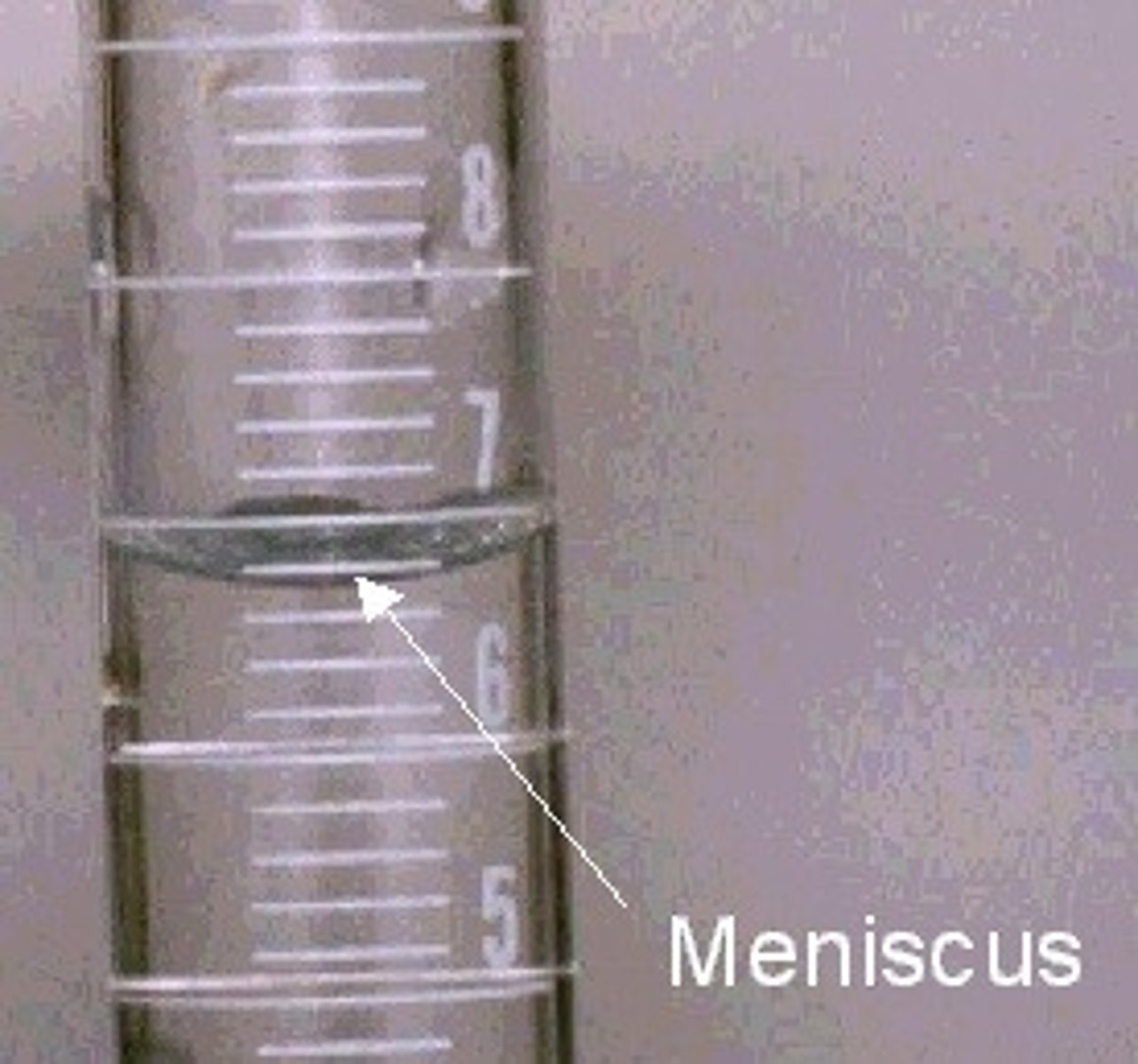
Measure volume at bottom of curve (meniscus)
How would you measure the volume of a liquid in a graduated cylinder?

Energy in motion, the faster the atoms are moving, the higher the temperature
What is kinetic energy?
Kelvin scale
What is the SI unit for temperature?
Kelvin = Celsius + 273
Kelvin scale equation
Water freezes at 0 and boils at 100
Celsius Scale
Celsius = Kelvin - 273
Celsius scale equation
Celsius will be used most in chemistry, Fahrenheit is not generally used in science-- hard to remember
Which measure of temperature is used most in science? Which is used least?
Combinations of base units, derived units
Other SI units can be made from ________________, called ______________
A physical property of matter defined as the amount of mass per unit volume
What is density?
density = mass/volume
Density equation
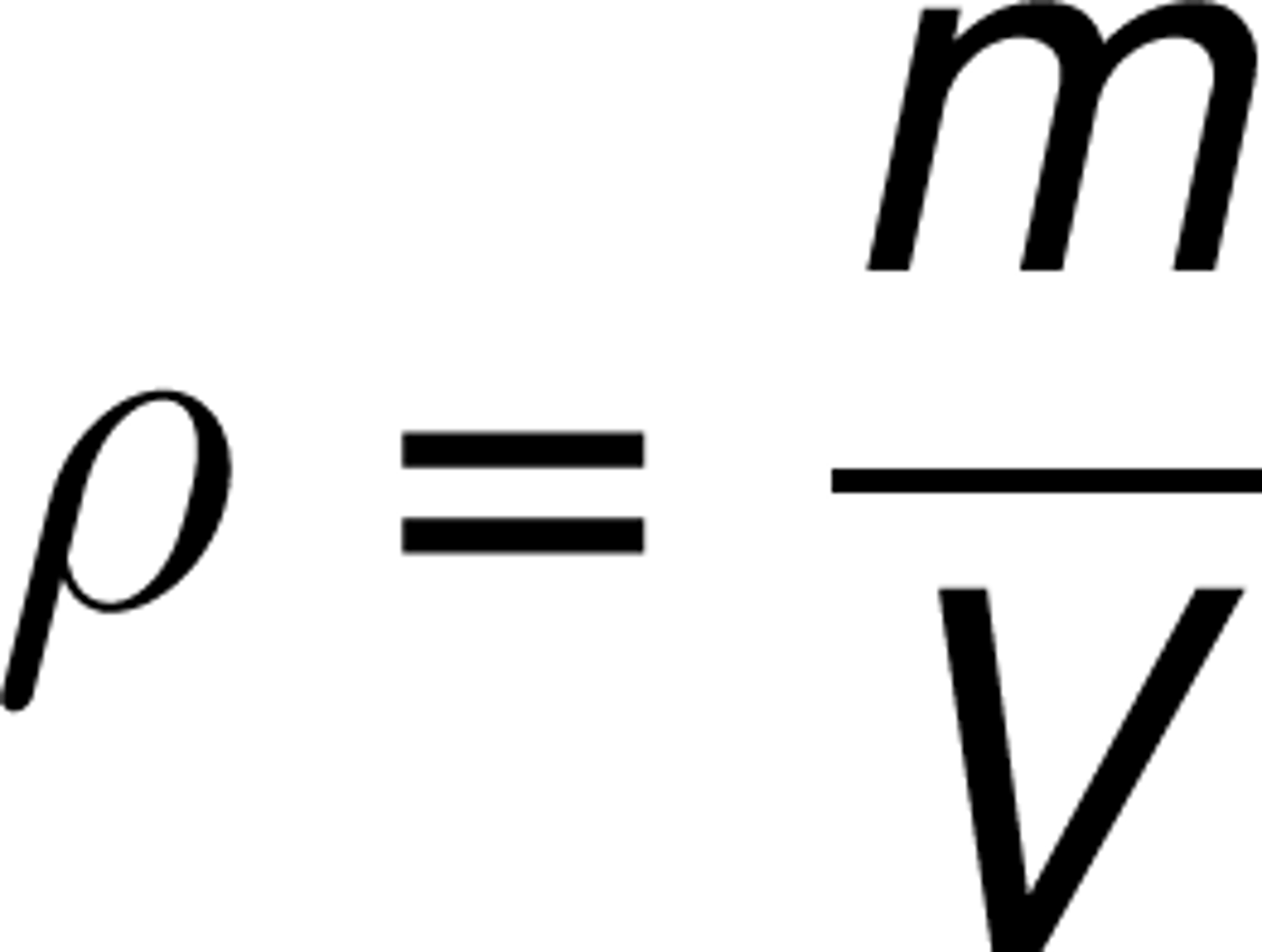
g/cm^3 for solids, g/mL for liquids and gases
What are the common units of density?
By writing all numbers known for certain and by estimating a final digit
How do you make a measurement?
Must be estimated, uncertain
A digit that ______________ is called an _____________
The certain digits and the estimated digit of a measurement together
What is a significant digit/figure
All non-zero numbers are significant
What is the first rule for significant figures?
Leading zeroes are never significant
What is the second rule for significant figures?
Zeroes between nonzero numbers are significant
What is the third rule for significant figures?
Trailing zeroes are significant only if the number contains a decimal point
What is the fourth rule for significant figures?
No, so we need to make sure our answer does not have more sigfigs than the original numbers
Do calculators know what significant figures are?
The number with the fewest sigfigs determines the number of sigfigs in the answer
What are the rules for multiplying/dividing sigfigs?
The number with the farthest left sigfig determines the number of sigfigs in the answer, exact numbers do not limit the number of sigfigs in the answer
What are the rules for adding/subtracting sigfigs?
Accuracy and precision
What are the two kinds of reliability in measurement?
How close a measurement is to the accepted value or standard
What is accuracy?
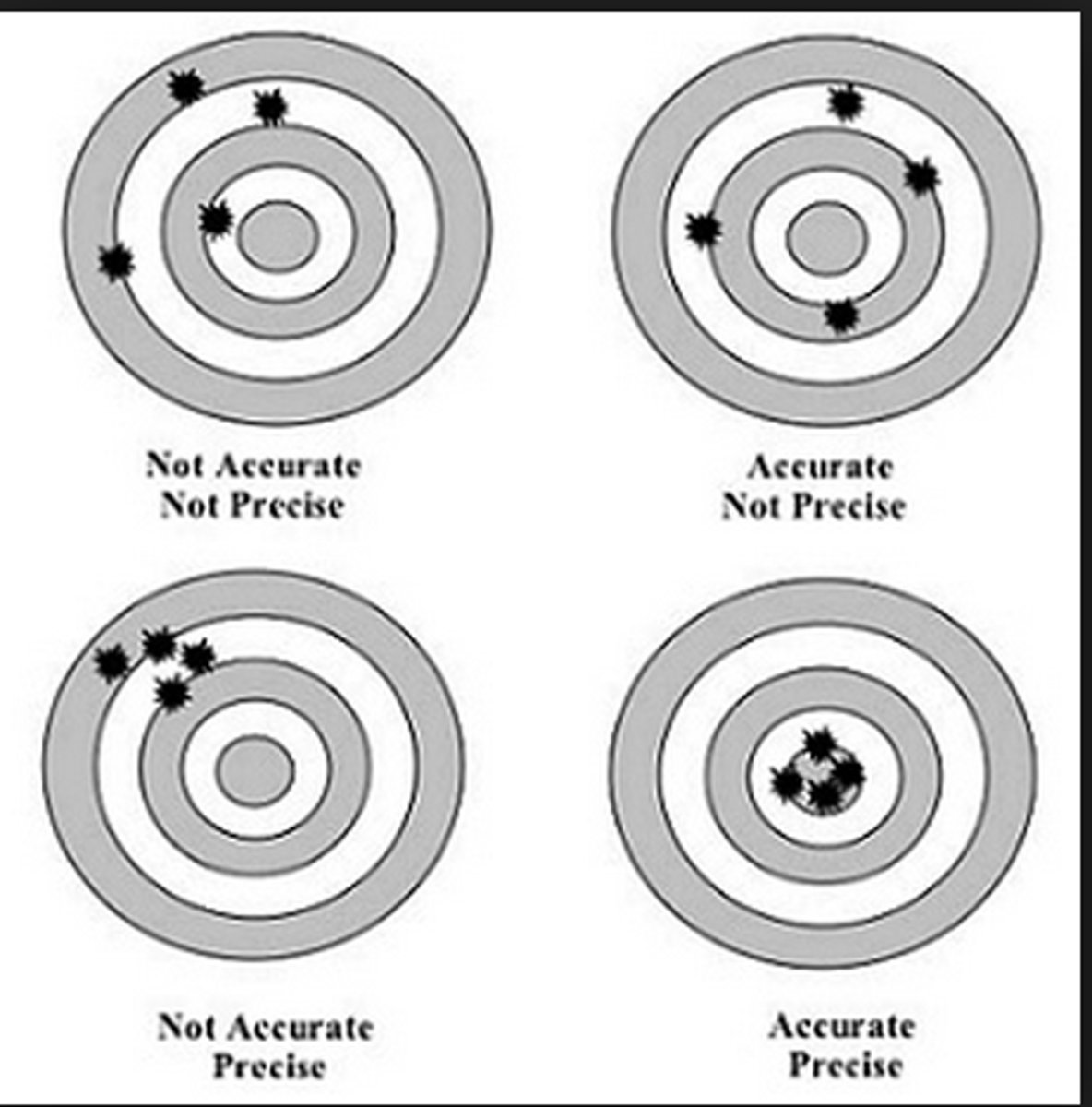
How close a series of measurements are to each other
What is precision?
A comparison of a measurement to its accepted value, indicates accuracy of a measurement
What is percent error?
% error = (|measured - accepted|/ accepted) x 100
Percent error equation
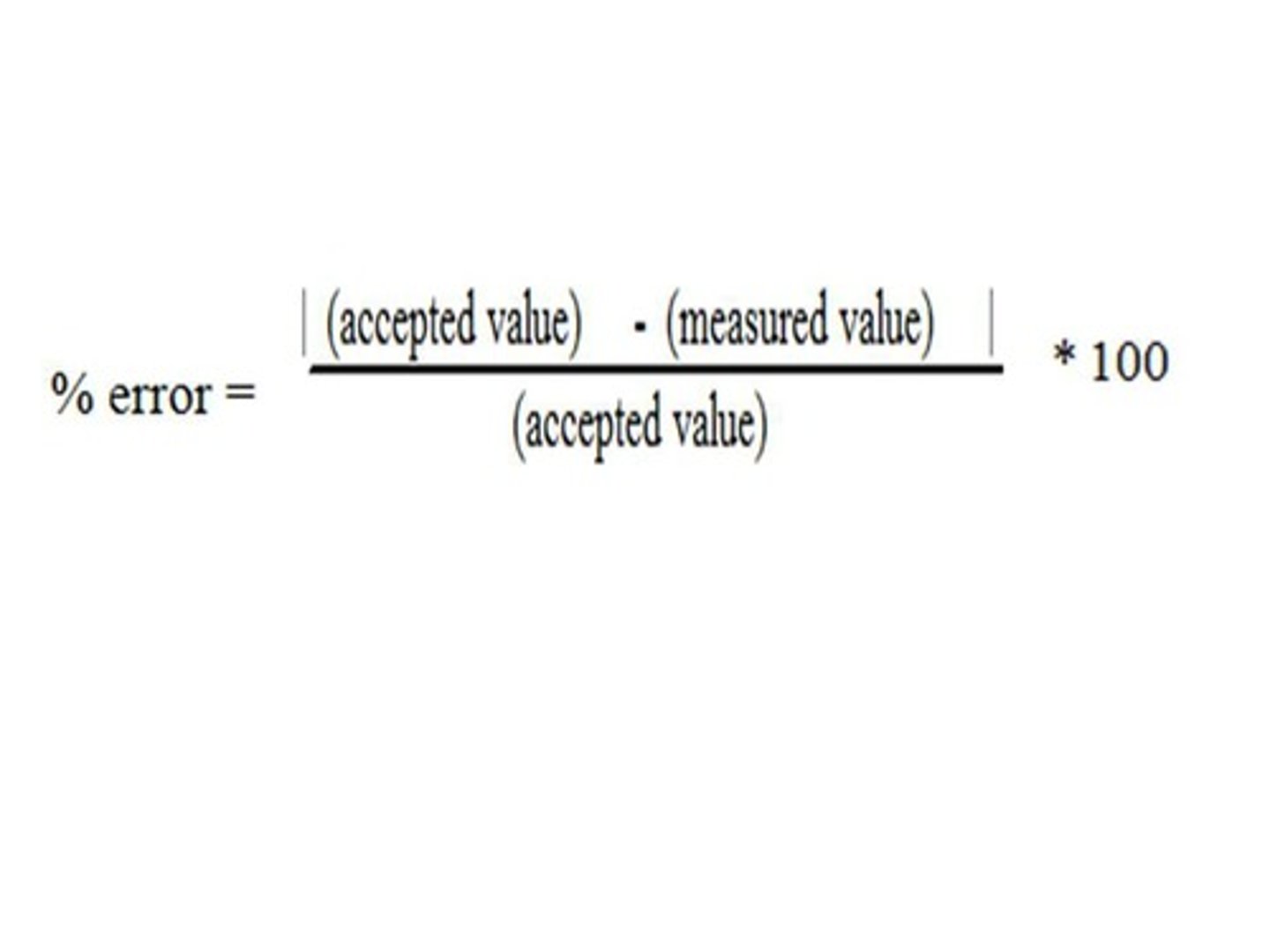
Measured = your value, accepted = actual value
What do the measured and accepted values mean?
A method of representing very large or small numbers using powers of 10
What is scientific notation?
M x 10^n
Scientific notation equation
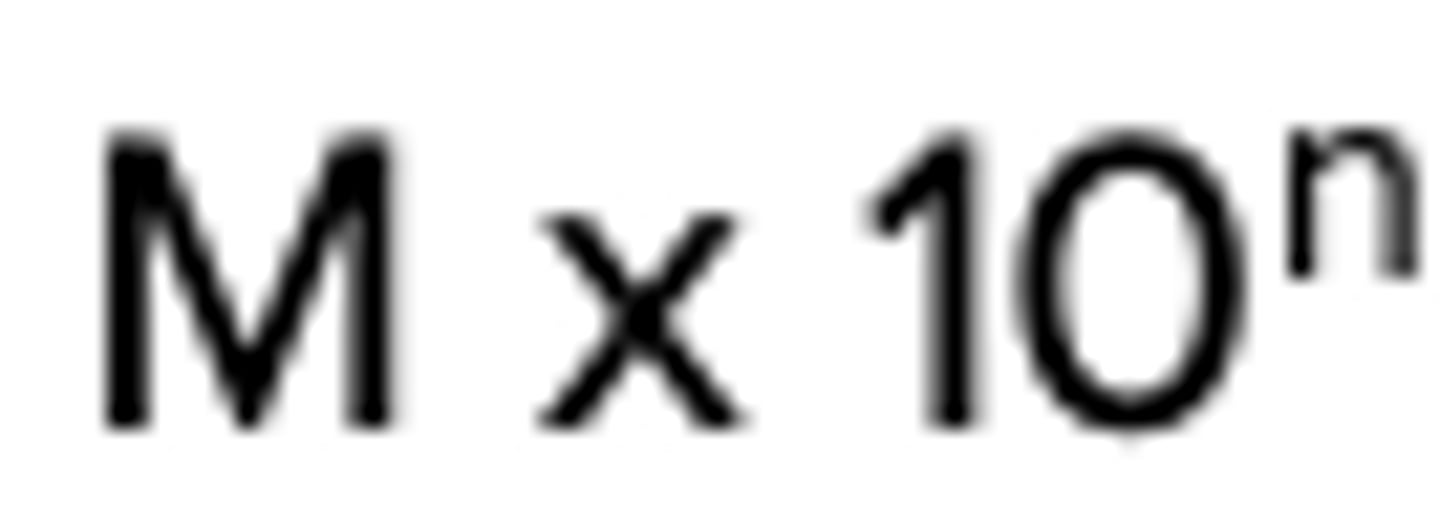
M is a number between 1 and 9.9, n is an integer, represents how many times you moved the decimal
Explain scientific notation equation
Move decimal until there's 1 digit to its left, places moved = exponent-- exponent is positive when moved left, exponent is negative when moved right
How do you convert a number into scientific notation?
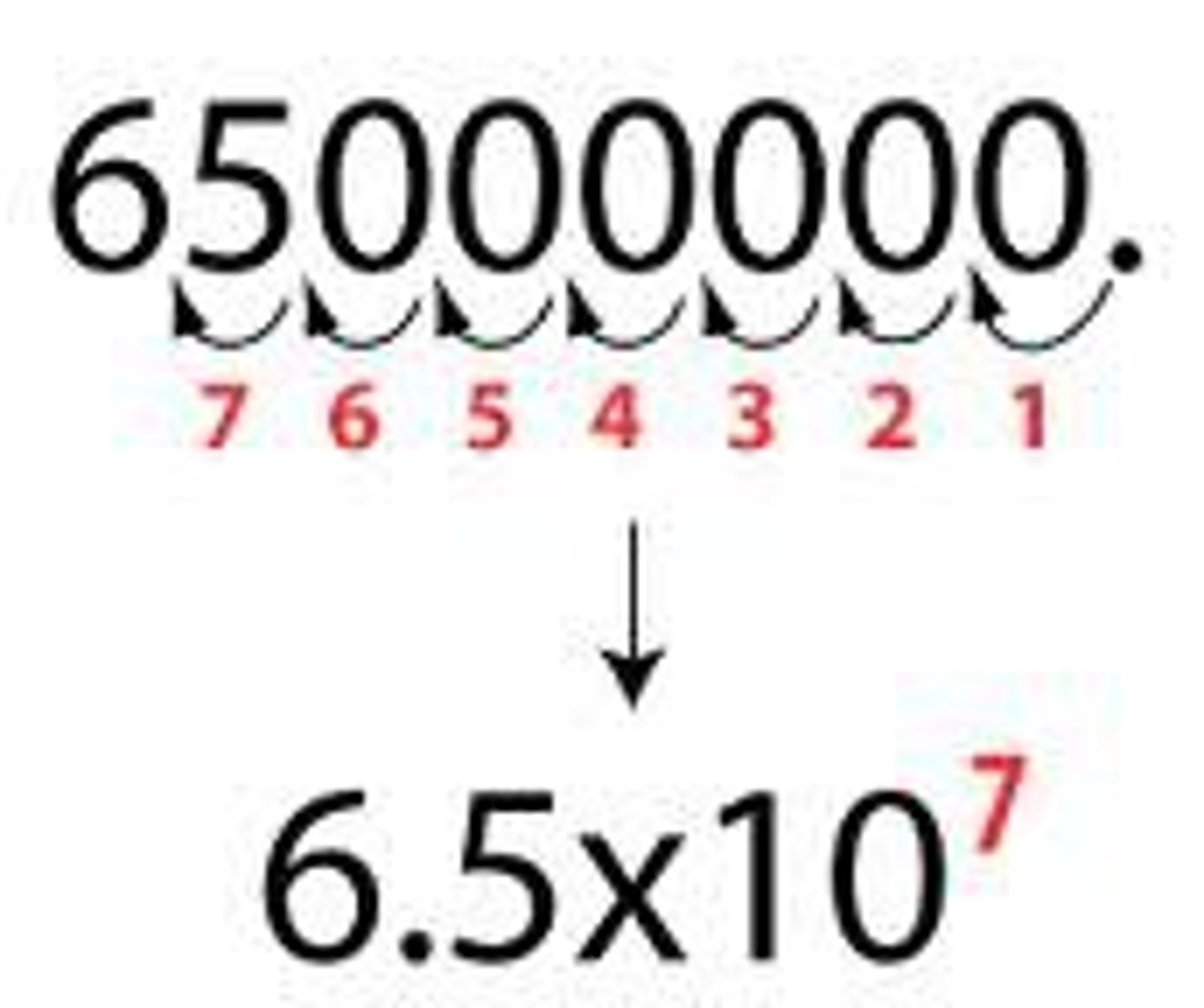
Significant figures
Only include... (scientific notation)
If the exponents are the same, add/subtract numbers in front and bring down exponent; if exponents are different, move a decimal to make them the same, then add/subtract
What are the rules for adding/subtracting scientific notation?
Multiply/divide the M values; multiplication: add exponents, division: subtract exponents
What are the rules for multiplying/dividing scientific notation?
A systematic approach to problem solving that uses conversion factors to move, or convert form one unit to another
What is dimensional analysis?
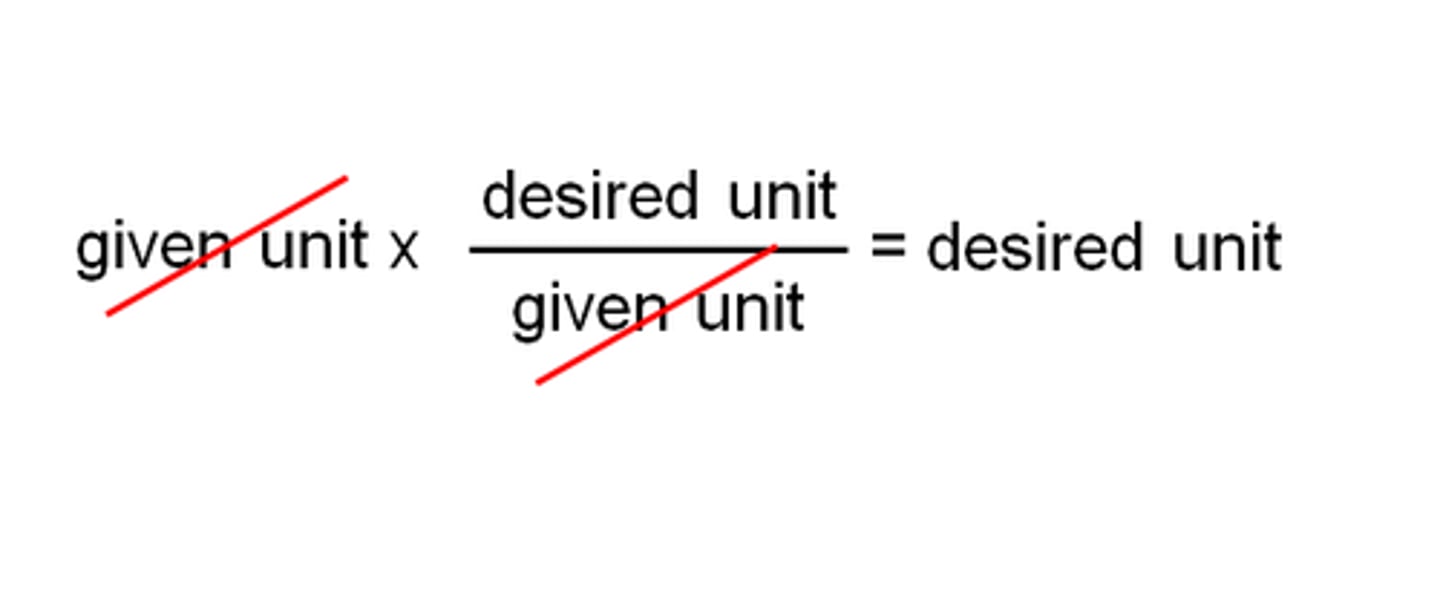
A ratio of equivalent values having different units
What is a conversion factor?
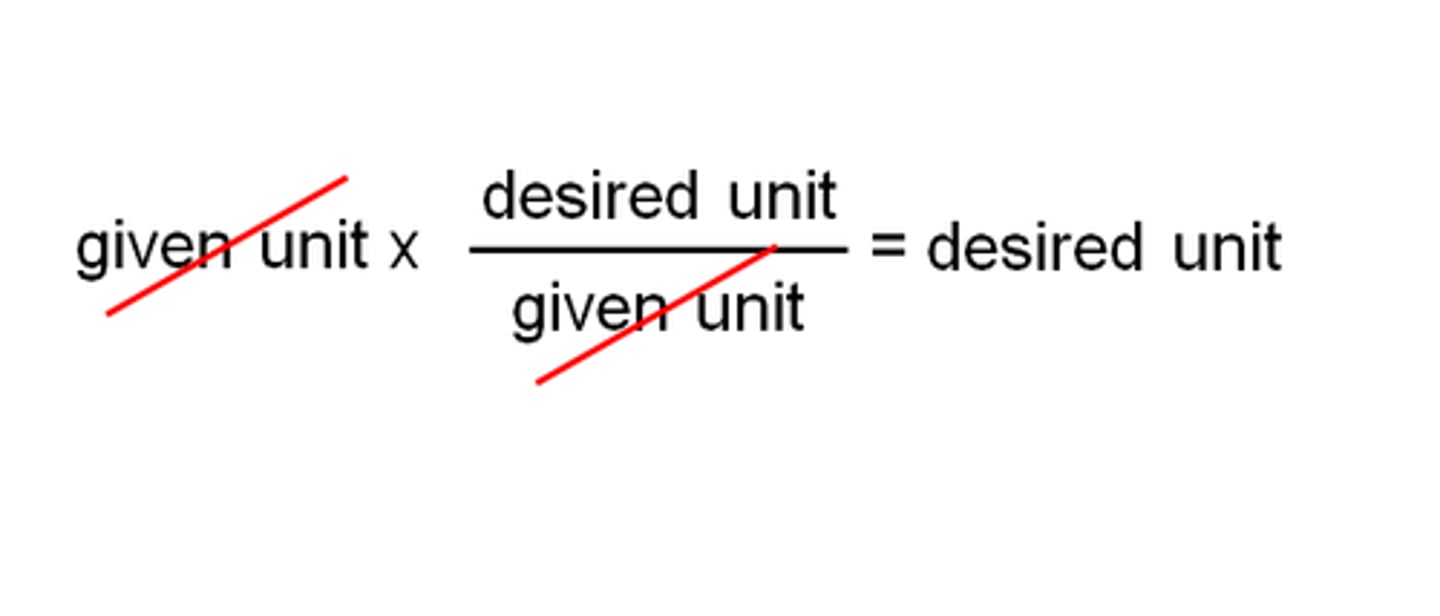
It must cancel one unit and introduce a new one; all units except desired unit must cancel
What are the two things a conversion factor used in dimensional analysis must accomplish?
A visual display of data that makes trends easier to see than in a table
What is graphing?
Circle/pie graph, bar graph, line graph
What are different types of graphs?
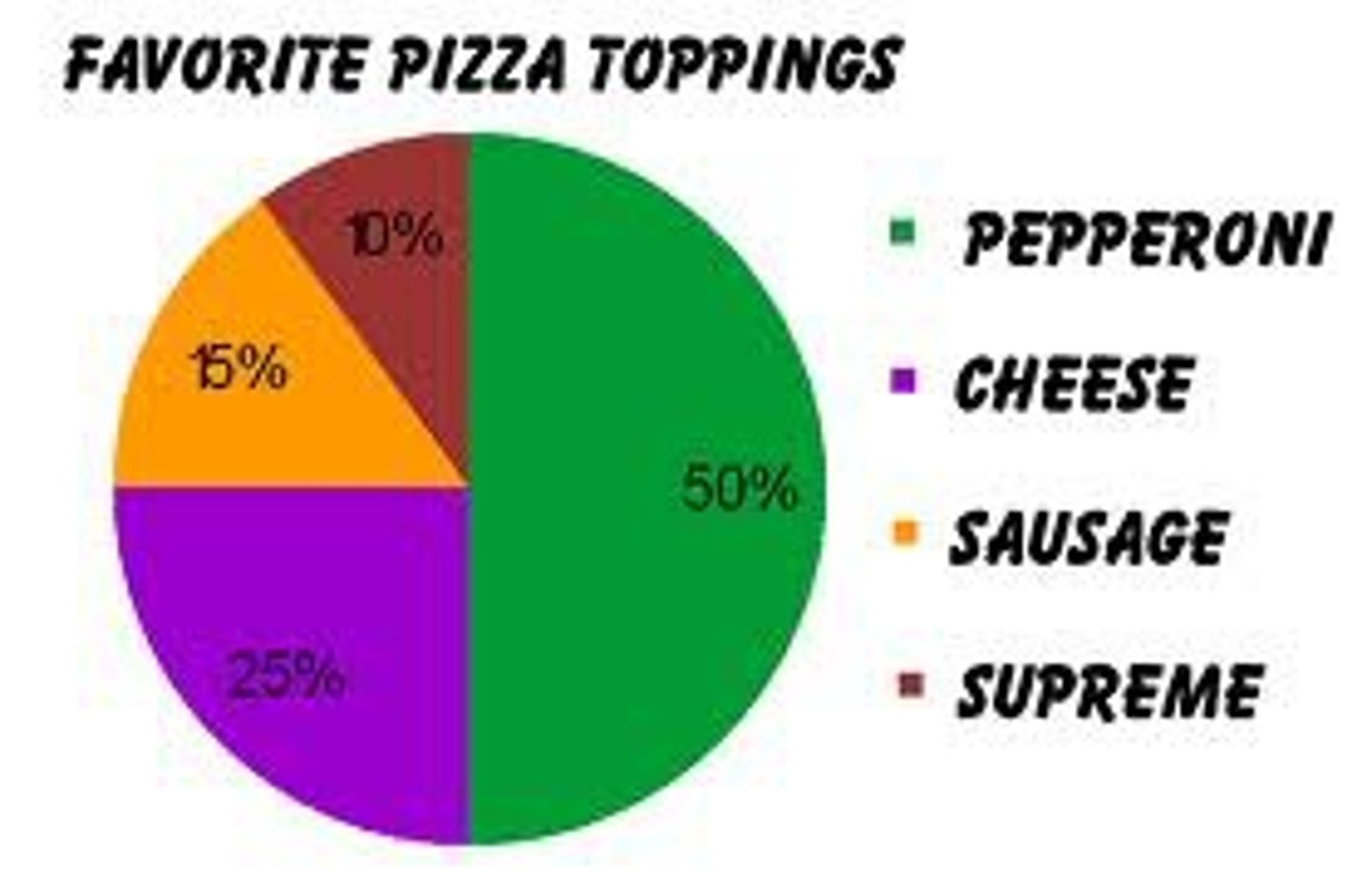
Aka pie chart, has wedges that visually represent percentages of a fixed whole
What is a circle/pie graph?
Often used to show how a quantity varies across categories
What is a bar graph?
Independent variables are plotted on x-axis and dependent variables are plotted on y-axis
What is a line graph?
Label the axis, use quantities and also proper units
What is the first step to creating a graph?
Choose a range that includes all the results of the data
What is the second step to creating a graph?
Calibrate the axis
What is the third step to creating a graph?
Give the graph a title
What is the fourth step to creating a graph?
Use a smooth line to connect points
What is the fifth step to creating a graph?
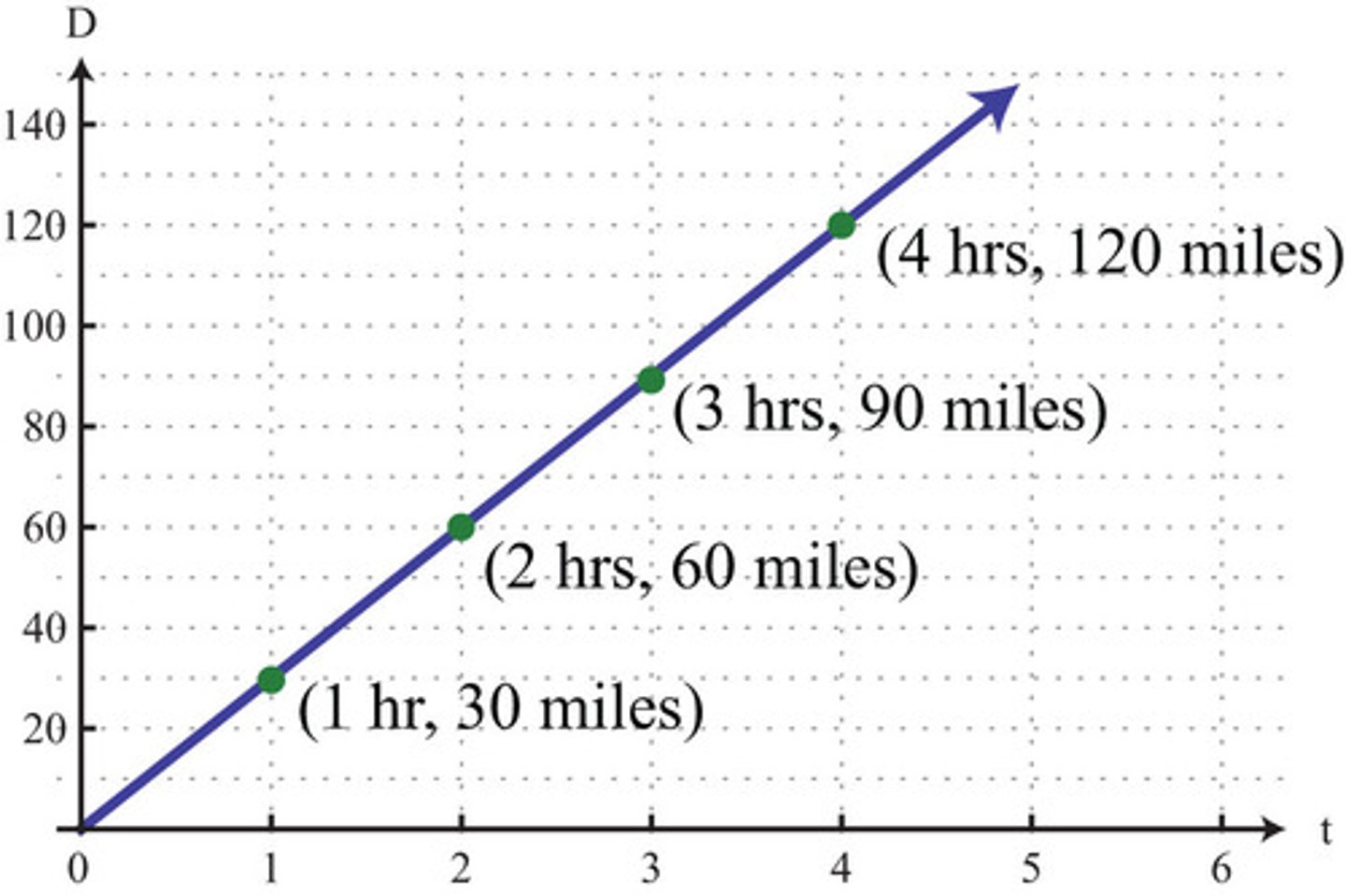
Directly proportional and inversely proportional
What are the two different kind of proportional relationships between variables?
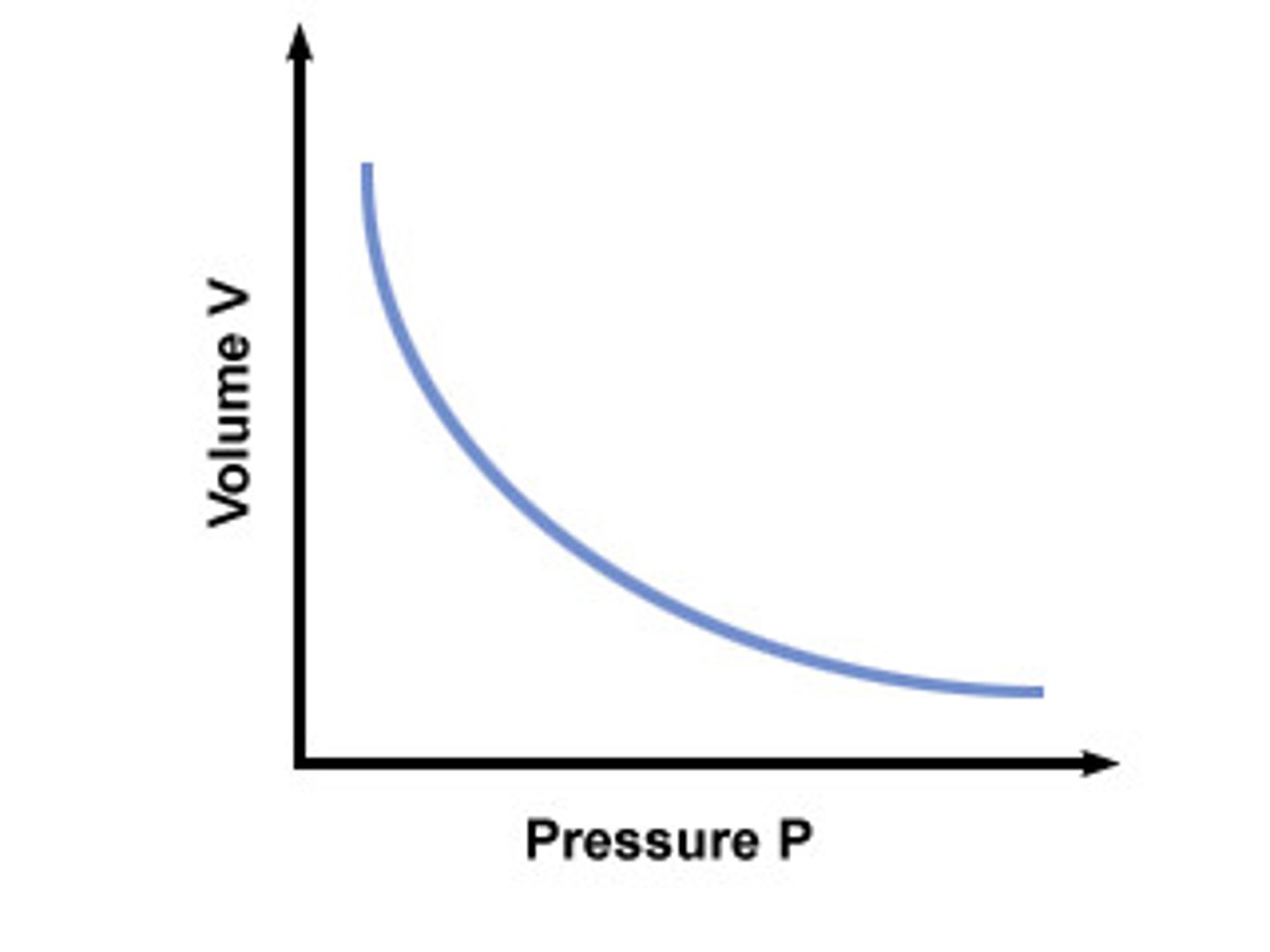
As one variable increases, other decreases; as one variable decreases, other increases; hyperbola on graph
What does it mean when two variables are inversely proportional?
As one variable increases, other also increases; as one variable decreases, other also decreases; straight line on graph
What does it mean when two variables are directly proportional?