Biology Paper 2 (HM)
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms

What do organisms compete for
Food
Water
Space
Light
CO2/O2
Mate

Interdependance
Organisms depending on each other for survival. Leads to the creation of a community.
Abiotic factors
Non living factors
Light
Temperature
Moisture
Soil pH
CO2 & O2 consentration
Biotic factors
Impact of other organisms on an ecosystem
Food
Predators/prey
Pathogens
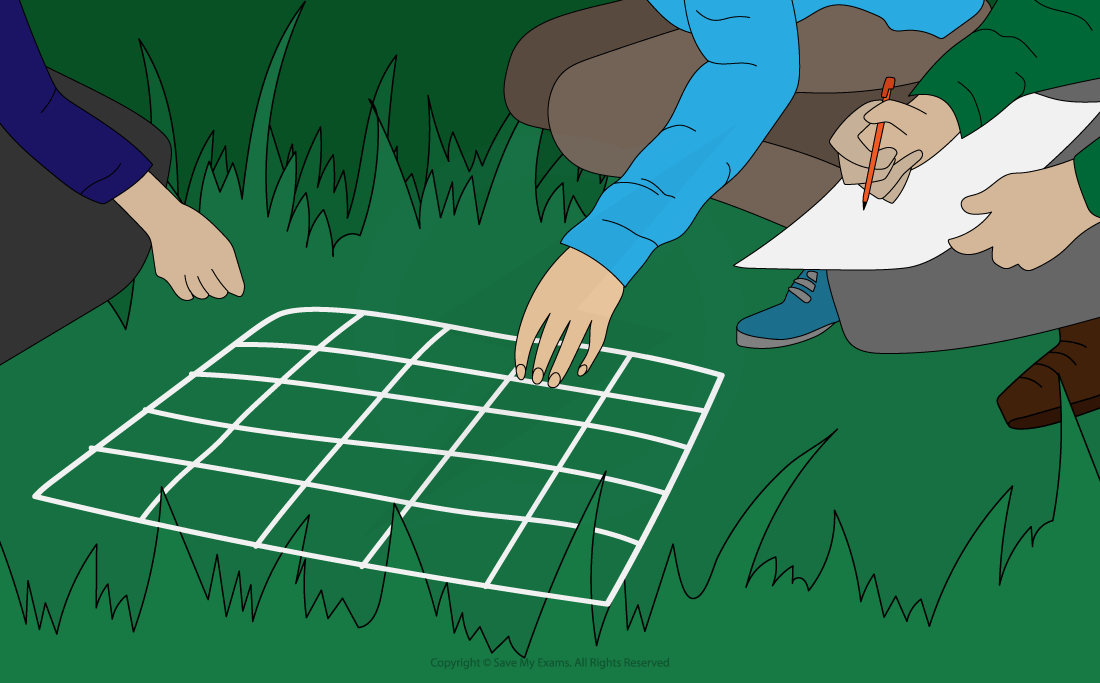
Sampling
Place QUADRAT in random positions in area (ideally 10% of area, using random number generator to choose locations)
Count number of chosen organism in each, calculate mean then multiply by total area to get estimate for population.
Moving it along a transect allows you to observe changes in population density over a distance
Food chains
Show the direction of biomass transfer between organisms

What is A?
Producer (Produces biomass)
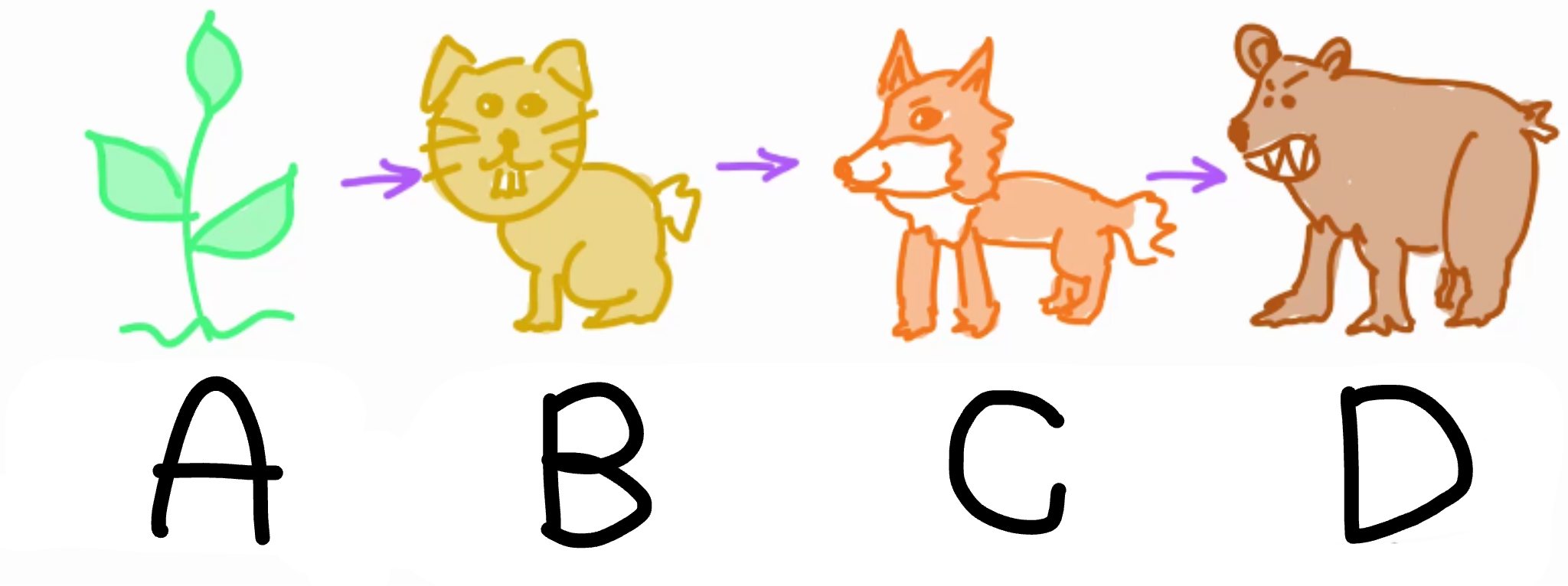
What is B?
Primary consumer(Herbivore/omnivore)
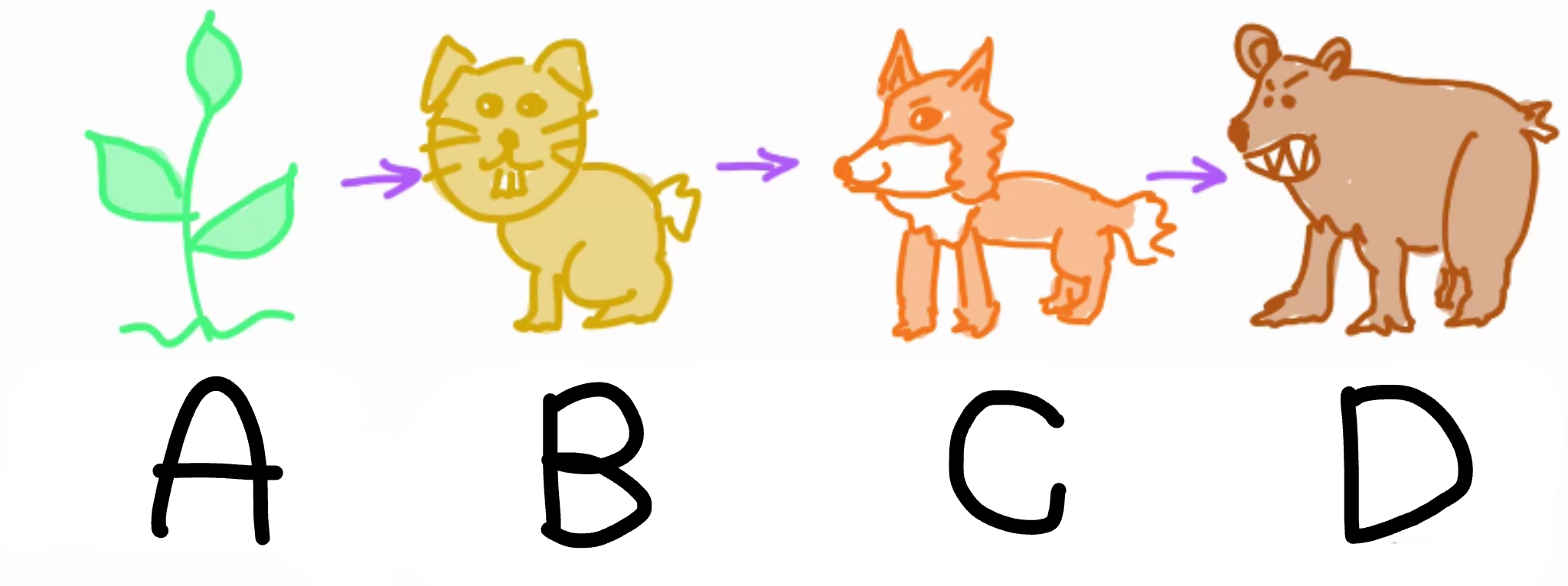
What is C?
Secondary consumer (Carnivore/omnivore)

What is D?
Tertiary consumer (Carnivore/Omnivore)

Apex predator
Always at the top of food chains
Have no natural predator
Populations fluctuate over time because …
Because food supply, predators, and competition change at different trophic levels.
When one trophic level rises or falls, the levels above and below it react.
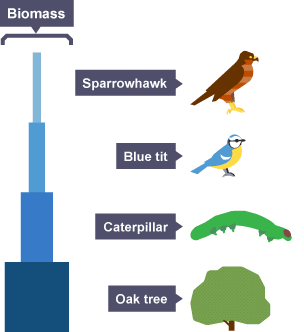
A pyramid of biomass
Indicates how much biomass is transferred between trophic levels
How much energy is lost when moving up a trophic level
10%
Why is energy lost when moving up trophic levels?
Organisms dont normally eat every part
Non-edible parts are lost to feases
Most of the nutrients that animals absorb used to release energy through respiration
How to calculate efficiency of biomass transfer (%)
100 x (Biomass transferred to next level / Biomass that was available at the previous level)

Decomposition conditions
Higher temperature and higher humidity increase the rate of decomposition.
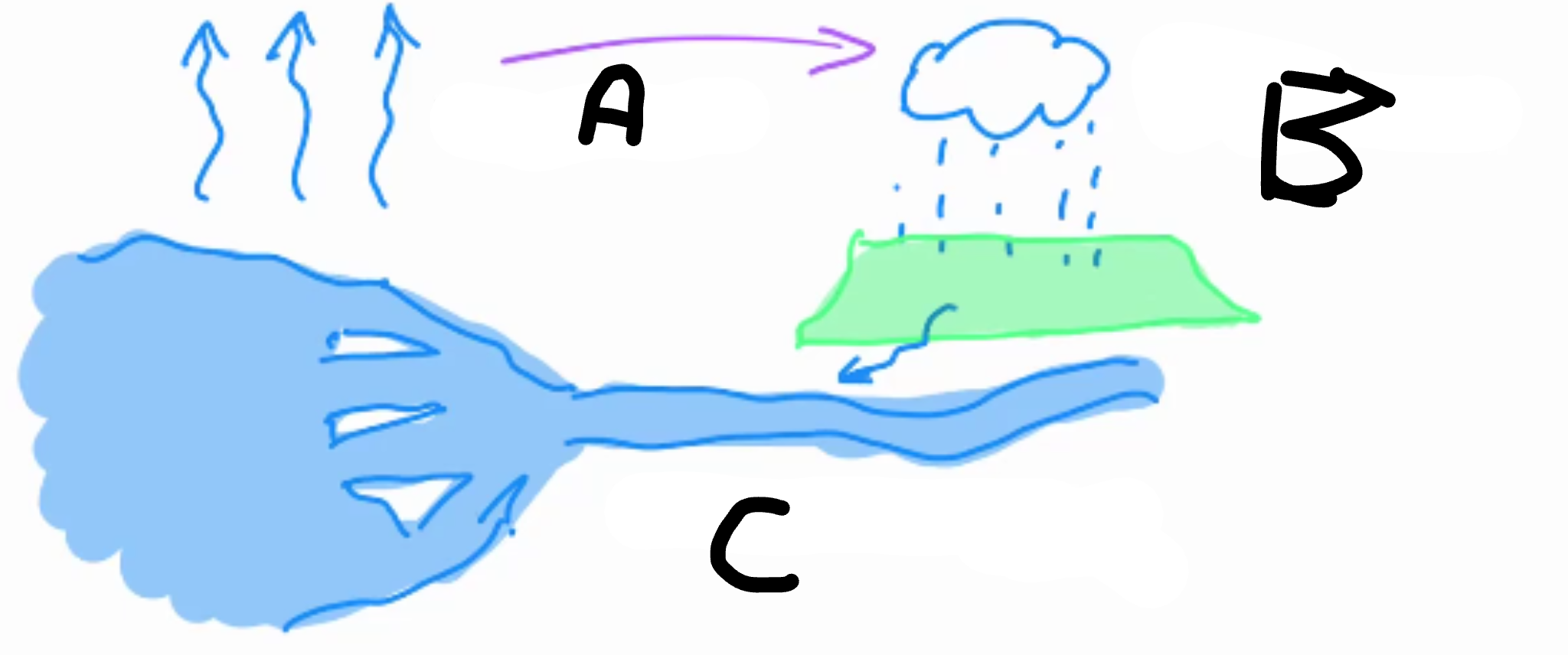
A:
Evaporation
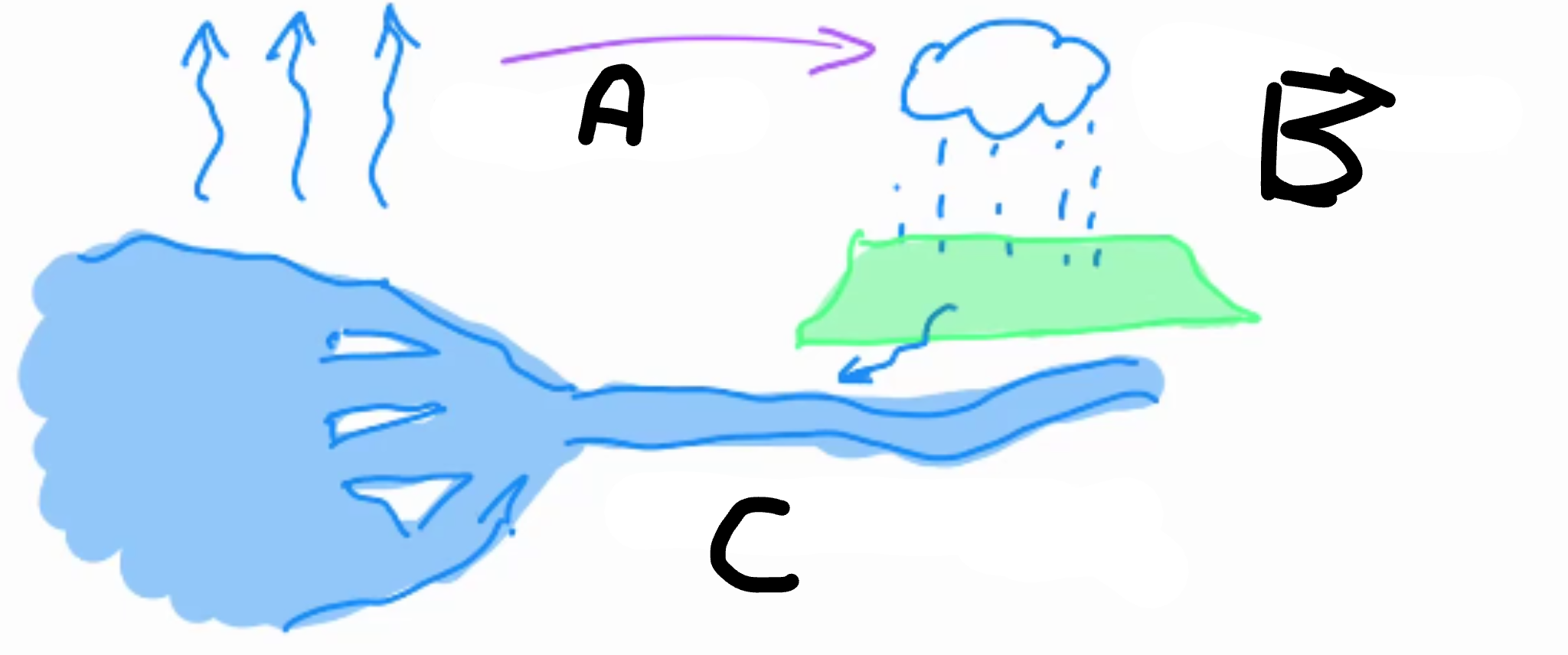
B:
Rain precipitation
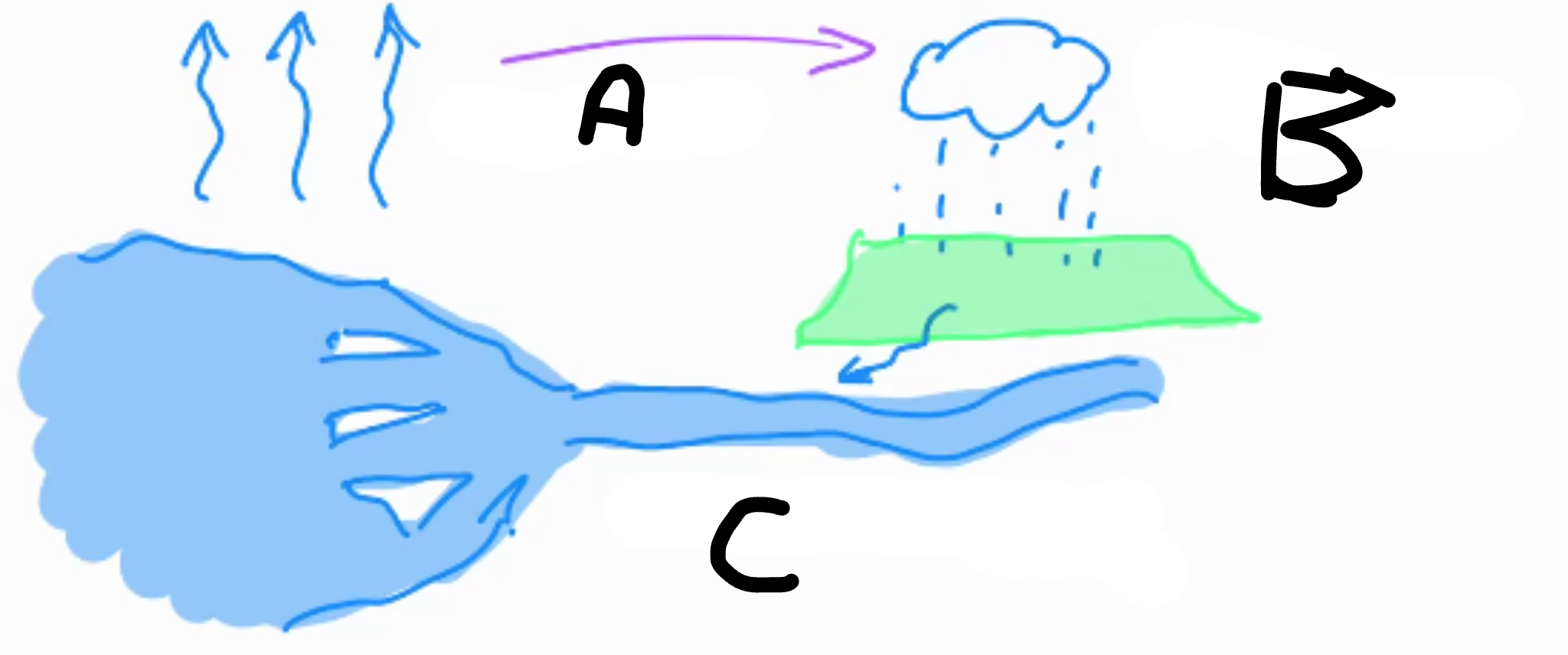
C:
Runs into rivers/sea
Biodiversity
The variety of species of organisms that exist in an ecosystem
High biodiversity creates a stable ecosystem as organisms will be be able to be dependant on greater number of species for survival
Human developement
usually results in reduced biodiversity, due to destruction of habitats
Disposing of waste in safe ways in order to reduce our impact is getting harder.
We need land to..
buildings/shelter
quarrying
farming
waste disposal
Why are peat bogs are being destroyed
To make compost
This reduces biodiversity of that ecosystem
Burning peat releases CO2 (Global warming)
Deforestation
Reduce biodiversity
Usually to create farmland
Animal and plant reproduction (Type)
Animals - Sexually
Plants - Sexually & Asexually
Asexual reproduction process uses …
mitosis meaning offspring will be identical
Sexual reproduction advantage
Offspring can become become better (Adaption)
Asexual advantage
only 1 organism needed to reproduce
Genome
entire genetic code of an organism
DNA
double helix polymer that stores genetic code
Gene
portion of DNA that codes for a protein
Genotype
an organism specific genetic code
Phenotype
Physical characteristics expressed by the genetic code
Inheritance
Characteristics are shaped by the types and quantities of proteins produced.
Most characteristics are the result of multiple genes interacting.
Different versions of the same gene are known as alleles.
Some characteristics are controlled by a single gene.
Dominant alleles
expressed even when genotype contains a RECESSIVE allele
There must be no dominant allele in order for a recessive allele to be expressed in the phenotype.
Male/Female chromosome
Men - XY
Women - XX
Variation is a result of
genetic and environmental factors
Darwin’s theory of evolution
Random mutations results in variation
Some organisms better adapted to environment
These compete ('survival of the fittest')
Those better adapted are more likely to survive; over time these desirable characteristics are more pronounced.
LAMARCK'S THEORY OF EVOLUTION
Mutations/adaptations are a result of environment affecting characteristics inherited by offspring; not random.
How is ANTIBIOTIC-RESISTANT BACTERIA used as evidence for Darwinian evolution
If not all bacteria killed, those most resistant will reproduce. This is why you must complete the full course of antibiotics.
Selective breeding
Breeding organisms that have desired characteristics to produce offspring in which they are more pronounced
Species
A group of organisms that are capable of producing fertile offspring
Genetic engineering
The INSERTION of a GENE into an ORGANISM'S GENOME so it SYNTHESISES a specific PROTEIN to achieve a DESIRED CHARACTERISTIC.
Genetic engineering process
Desired gene is cut from another organisms DNA using restriction enzymes, leaving it with sticky ends
Gene inserted into a vector (e.g bacteria plasmid)
Vector inserts gene into cells of another organism early in development
Organism develops with desired characteristics
Cloning
Producing genetically identical organisms
You can clone plants using cuttings or tissue cultures
Cells from fertilisation can be separated to produce identical offspring
Cloning process
Nucleus taken from skin cell of organism to be cloned
Nucleus inserted into an egg cell
Electric shock causes cell to split and develop
Developing cells inserted into surrogate mother