RNA & Transcriptomics 2
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
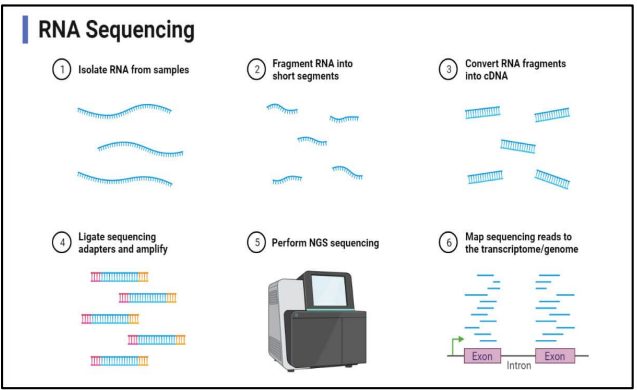
describe the steps for RNA sequencing
isolate RNA from sample
fragment RNA into short segments
convert RNA fragments into cDNA
ligate sequencing adapters & amplify
perform NGS sequencing
map sequencing reads to the transcriptome/genome
what is a gene expression profile
the “on” & “off” states of all of a cells genes
each cell type has a unique profile
genes expressed by a cell can give insight into the function & fate of the cell
what are some different types of gene expression profiles
profile distinct cell subsets (e.g. immune cells)
profile temporal changes
profile response to stimuli (infection, activation)
profile healthy vs diseased (tumours, inflamed)
how do we profile gene expression
isolate mRNA from cells
rare cells make it hard to get enough RNA
consider the question we want to answer
cell type, disease state, timing
what are some things to look for when profiling
is a gene expressed at all within the cell type?
is the gene expression level changed at all?
higher or lower
what does gene expression tell us
isolating mRNA from cells at a given time, allows us to examine which genes are transcribed at a specific time
only a snapshot of gene expression at a specific time
what controls the gene expression profile in cells
cell linage-specific expression of transcription factors
gene expression is controlled by binding of transcription factors
what is important to remember about gene expression profiling
think of it as taking the average, this means that difference between individual cells can be masked making them harder to identify
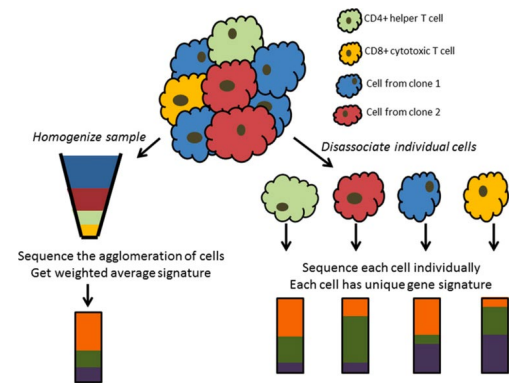
when would you use bulk or scRNA-seq
bulk RNA-seq:
cheap
used in most cases
broad analysis
scRNA-seq:
expensive
precise
what are some pros & cons of scRNA-Seq
PROS:
finely detailed map of cell population
identify rare cell types & relationships
CONS:
expensive
misses lowly expressed genes
trickly to analyze
what is some general information about cancer
progressive (cell → tumour → metastasis)
multistep process, requires multiple mutations to reach the tumour state
what 2 cell types, when mutated, can give rise to cancer
proto-oncogenes
tumor suppressor genes
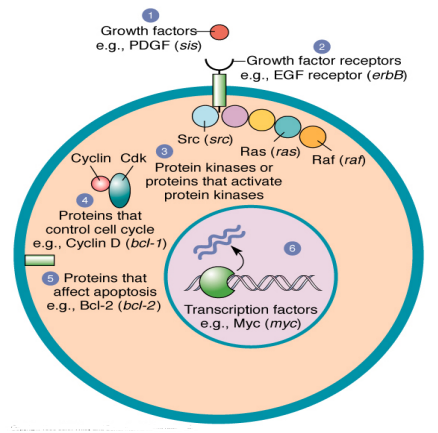
what are proto-oncogenes
a group of genes that cause normal cell to become cancerous when they are mutated
mutation are typically dominant in nature
mutated proto-oncogene = oncogene
often code for cell division, death, differentiation
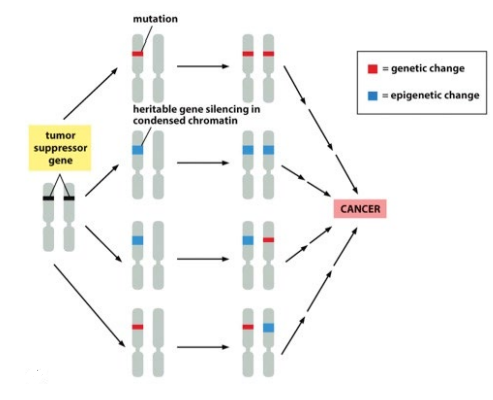
what type of proteins do tumor suppressor genes code for
cell adhesion/recognition
mutations cause cells to lose adhesion & spread
enzymes for DNA repair
mutations are more prominent
inhibit cell division
mutations causes rapid division
how can gene expression profiling identify cancer
identify whether tumor suppressor/oncogenes are lost/gained is critical
identify novel drivers of specific cancers
how can difference between tumors and normal tissue be found
comparative transcriptomics
can identify decreases/increases in certain driver genes
identifies pathways & downstream changes
what is tumor heterogeneity
due to the speed of tumor growth, different parts of the tumor can growth different mutations
hence 1 medication may only kill one part of the tumor but not the rest