Cognition: Perception and Thinking, problem solving, judgements, & decision making
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Top-Down
Using prior knowledge to solve problems.
Bottom-Up
Having to use your senses to try and figure a puzzle out.
Cocktail party effect
Focus your hearing on one specific thing, even though noise is all around you.
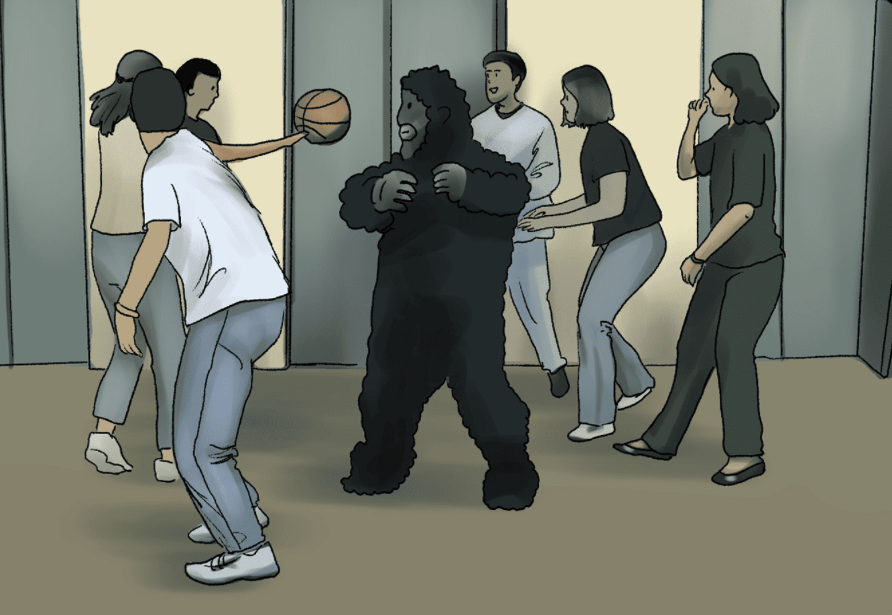

Inattentional Blindness
Failing to see visible objects when our attention is directed elsewhere.
Change Blindness
Failing to notice changes in the environment.
Selective Attention
When there is so much going on and it’s hard to focus on one thing at a time.
Perceptual Set
A mental predisposition to perceive one thing and not another.
Schemas
Concepts that organize and interpret unfamiliar information.
Context
Not being able to recognize someone/ something in a different setting.
Motivation
Perception changes due to rewards given.
Emotions
Perception changes due to how you feel about the situation.
Figure-Ground
When we automatically separate an object (The main focus) from the background.
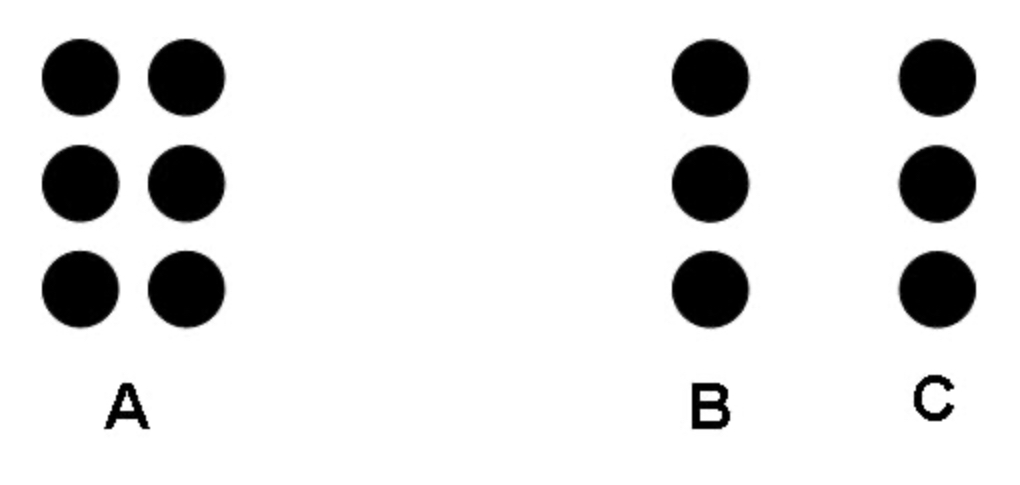
Proximity
Objects that are closer together are perceived as one group.
Continuity
Seeing smooth continuos patterns rather than broken ones.
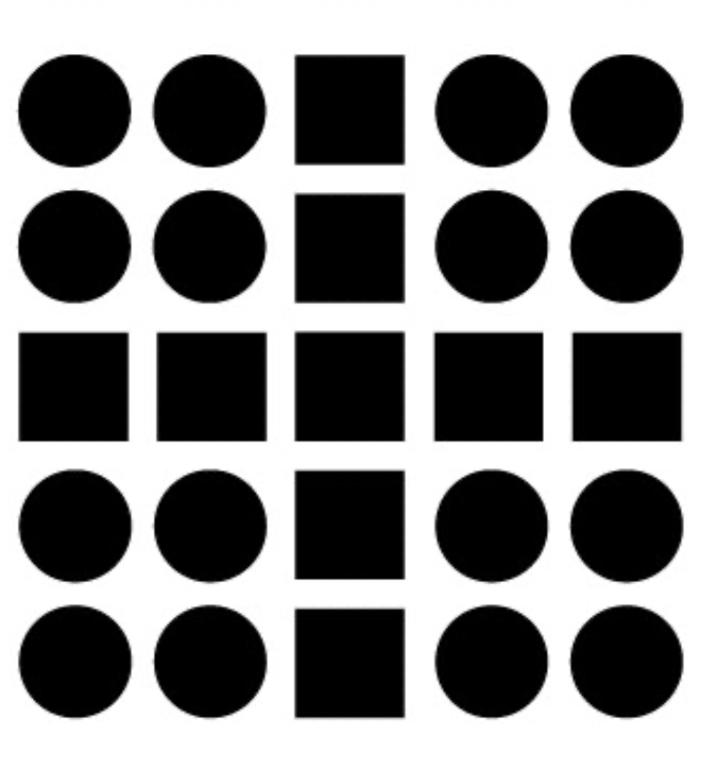
Similarity
Objects that look alike in color, shape or size are perceived as part of the same group.
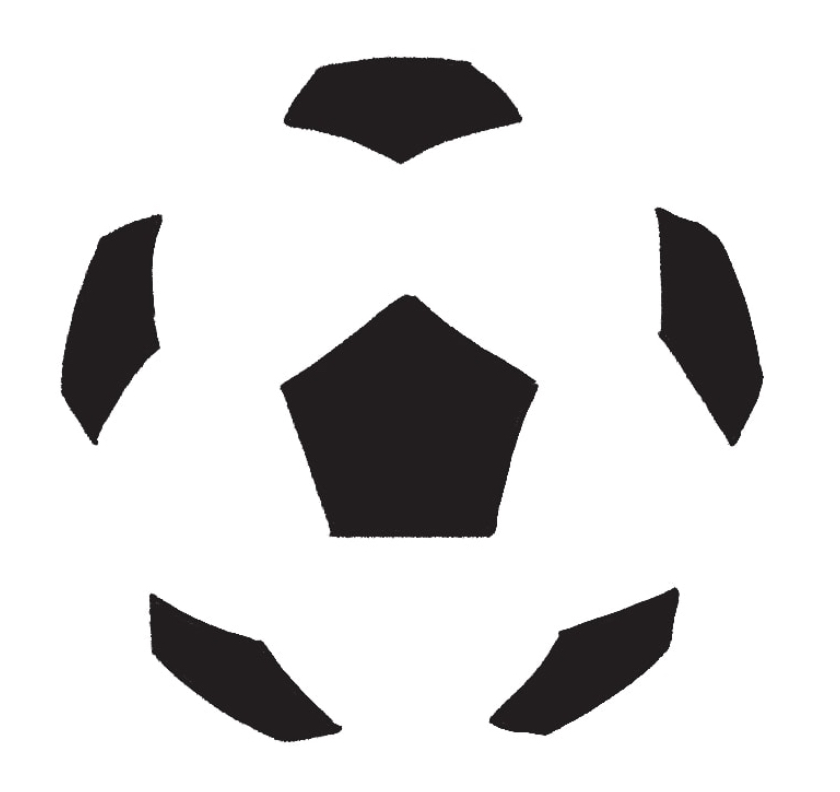

Closure
Filling in the gaps to create a complete object.
Connectedness
Objects that are visually linked by lines, shapes, or colors are seen as a single unit.
Visual Cliff
A laboratory device for testing depth perception, especially in infants and young animals.
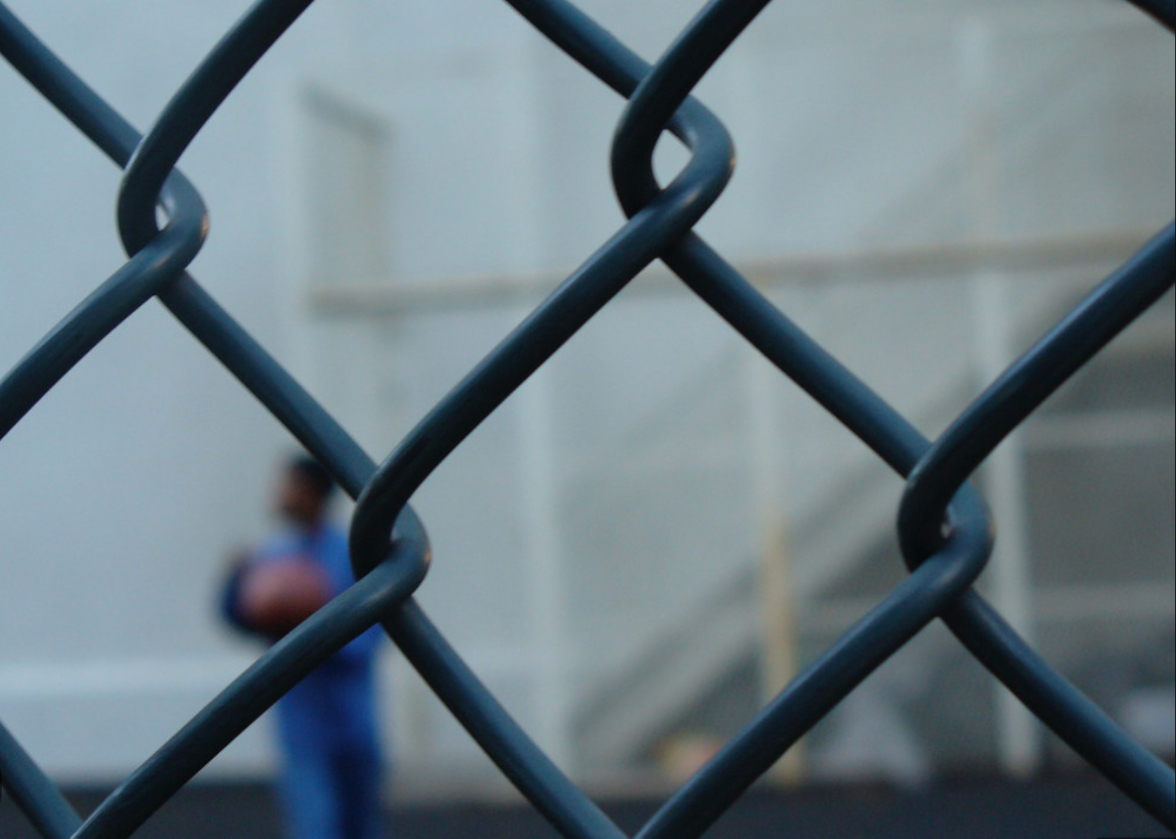

Relative Clarity
That objects closer up appear more clear than objects further away.
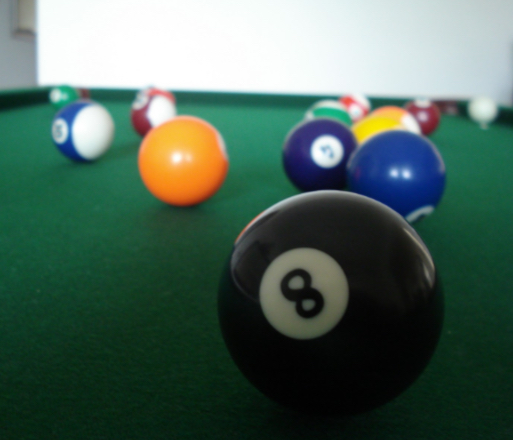

Relative Size
When two objects of the same size look different becuase one is further away than the other.
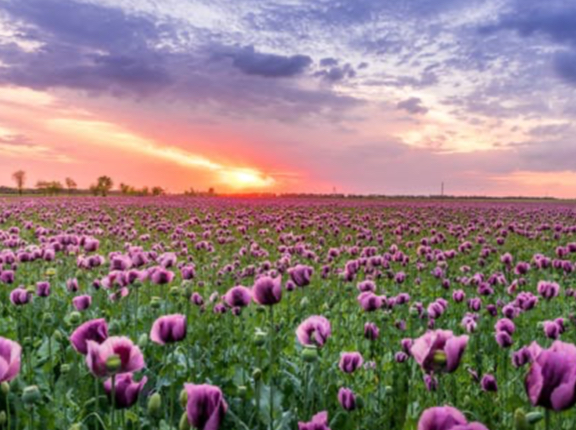

Texture Gradient
Objects closer show more detail and textured and objects further away appear less detailed and smoother.
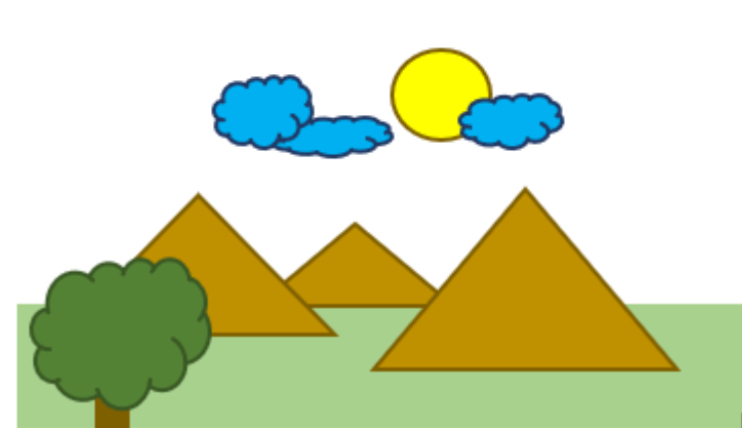

Interposition
When one object blocks another so it appears closer and the object blocked looks further.

Linear perspective
Parallel lines appear to meet as they get further away from our line of vision.
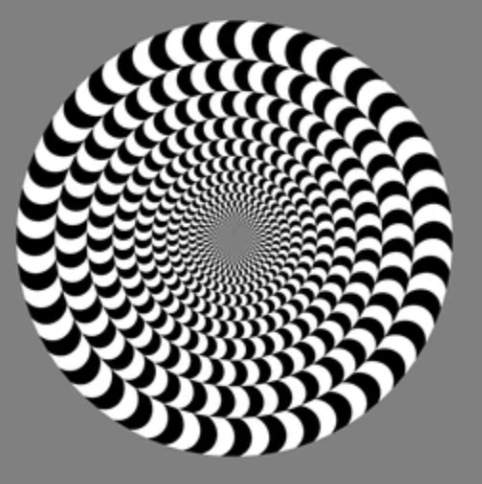

Apparent Movement
The illusion of movement that happens when stationary images or lights are shown quickly.
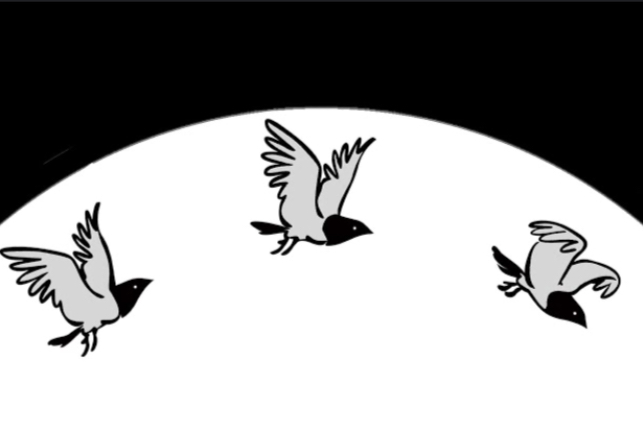

Stroboscopic effect
A type of apparent motion created when slightly different images are flashed quickly to make it seem it’s moving.
Phi Phenomenon
The illusion of movement when two or more lights blink on and off in sequence, making it look like a single light moving between them.
Auto kinetic effect
The illusion that a stationary point of light in a room is moving.
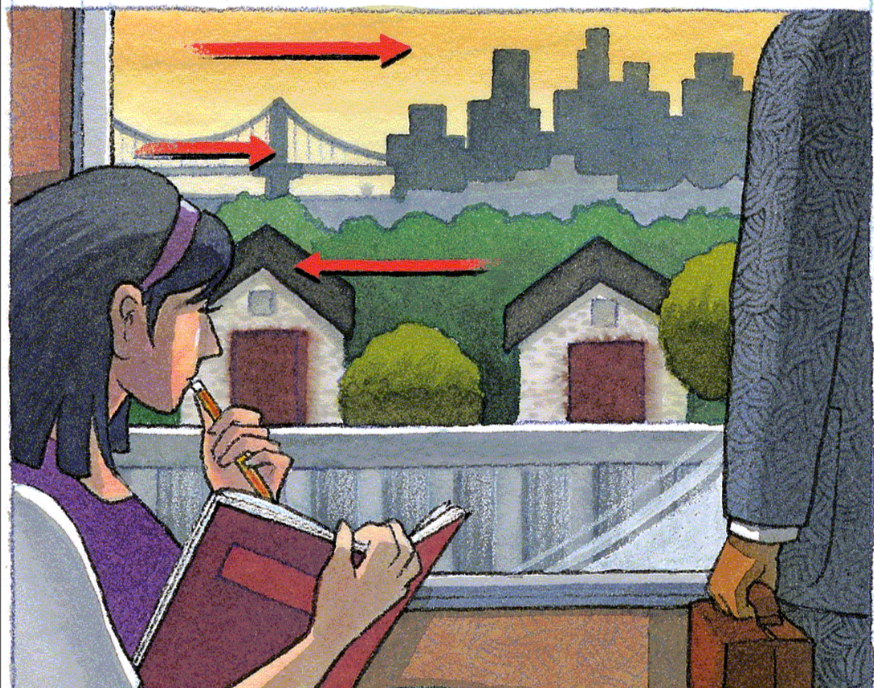
Relative Motion
A monocular depth where objects closer to you seem to move faster and in the opposite direction across your field of vision than objects farther away that move in the same direction as you.
Prototypes
Best example of a category. Enhances memo And recall.
Schemas
Places where new information is organized to provide a framework for understanding future experiences.
Assimilation
Taking new information and fitting it into an already existing schema. SS= Same Schema
Accommodation
When a new schema needs to be made in order to fit in new information. CC= Change or create
Creativity
The ability to produce new and original ideas, etc… combining existing knowledge in unique ways.
Convergent Thinking
Narrow the available problems to determine the single best solution. Down to one answer.
Divergent Thinking
Expanding the number of possible problem solutions. As many possibilities.
5 components of creativity
Expertise
Imaginative thinking skills
Venturesome personality
Intrinsic motivation
Creative environment
Executive functions
Mental skills that help us plan, organize, make decisions, focus attention, etc…
Algorithms
Step by step strategies for solving a problem, methodically leading to a specific solution. Always guarantied an answer
Heuristics
Step-saving thinking strategy or principle which generates a solution quickly. Short cut
Insights
A sudden realization that leads to a solution. Prior knowledge.
Confirmation bias
Searching for information that supports our preconceptions and to ignore or distort contradictory evidence.
Fixation
Inability to see a problem from a new perspective.
Mental set
Approaching a problem in a way that had been successful in the past.
Functional Fixedness
Tendency to think of things only in terms of their usual functions.
Intuition
Effortless, immediate, automatic feelings or thoughts.
Representative heuristics
Estimating the likelihood of events in terms of how well they seem to represent or match prototypes.
Gambler’s Fallacy
Thinking the probability of an outcome changes based on previous events.
Availability heuristics
Estimating the likelihood of events based on their availability in memory.
Overconfidence
Tendency to be more confident then correct.
Sunk-Cost fallacy
Reluctant to abandoning a strategy when abandonment would be more beneficial.
Belief Preserverance
Clinging to one’s initial conceptions after they have proven wrong.
Framing/Wording Effects
How an issue is worded can affect decisions and judgment.
Priming
Activation, often unconsciously, of certain associations, thus predisposing one’s perception, memory, or response.