APSC 530 Midterm
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
B. SA Node
The pacemaker cells are located in the
a. AV bundle/ Bundle of His
b. SA Node
c. AV Node
d. Perkinje’s Fiber
C. Pulmonic Valve
After blood travels to the right ventricle it then travels to the
a. RA
b. RV
c. Pulmonic Valve
d. Aortic Valve
C. Left Atrium
In fetal circulation the blood flow differs in that most blood skips which chamber of the heart
a. RA
b. RV
c. LA
d. LV
e. none of the above
C. Right and Left Atria
The base of the heart contains which 2 chambers
a. RA and RV
b. LA and LV
c. Right and left Atria
d. Right and Left Ventricles
C: no correct Answer
Matching: Braciocephalicus
a. to promote the paw
b. to flex the carpal
c. no correct answer
d. flex the elbow
e. protractor
D- Flex the elbow
Matching: Coracobrachialis
a. to promote the paw
b. to flex the carpal
c. no correct answer
d. flex the elbow
e. protractor
B: To flex the carpal
Matching: Superficial digital flexor
a. to promote the paw
b. to flex the carpal
c. no correct answer
d. flex the elbow
e. protractor
E: protractor
Matching: Pronator Quadratus
a. to promote the paw
b. to flex the carpal
c. no correct answer
d. flex the elbow
e. protractor
A: to promote the paw
Matching: Ulnaris Lateralis
a. to promote the paw
b. to flex the carpal
c. no correct answer
d. flex the elbow
e. protractor
Right Atrium= receives Oxygen poor blood from body through superior and inferior vena cava
Right Ventricle= pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs
Inferior Vena Cava= carries deoxygenated blood to RA
Left Atrium= receives oxygentaed blood from lungs
Interventricular Sulcus= marks boundary between RV and LV
Left Ventricle= Pumps oxygenated blood to the body through aorta
Pulmonary Arteries= carries deoxygenated blood to lungs for oxygenation
Superior Vena Cava= Returns deoxygenated blood to RA
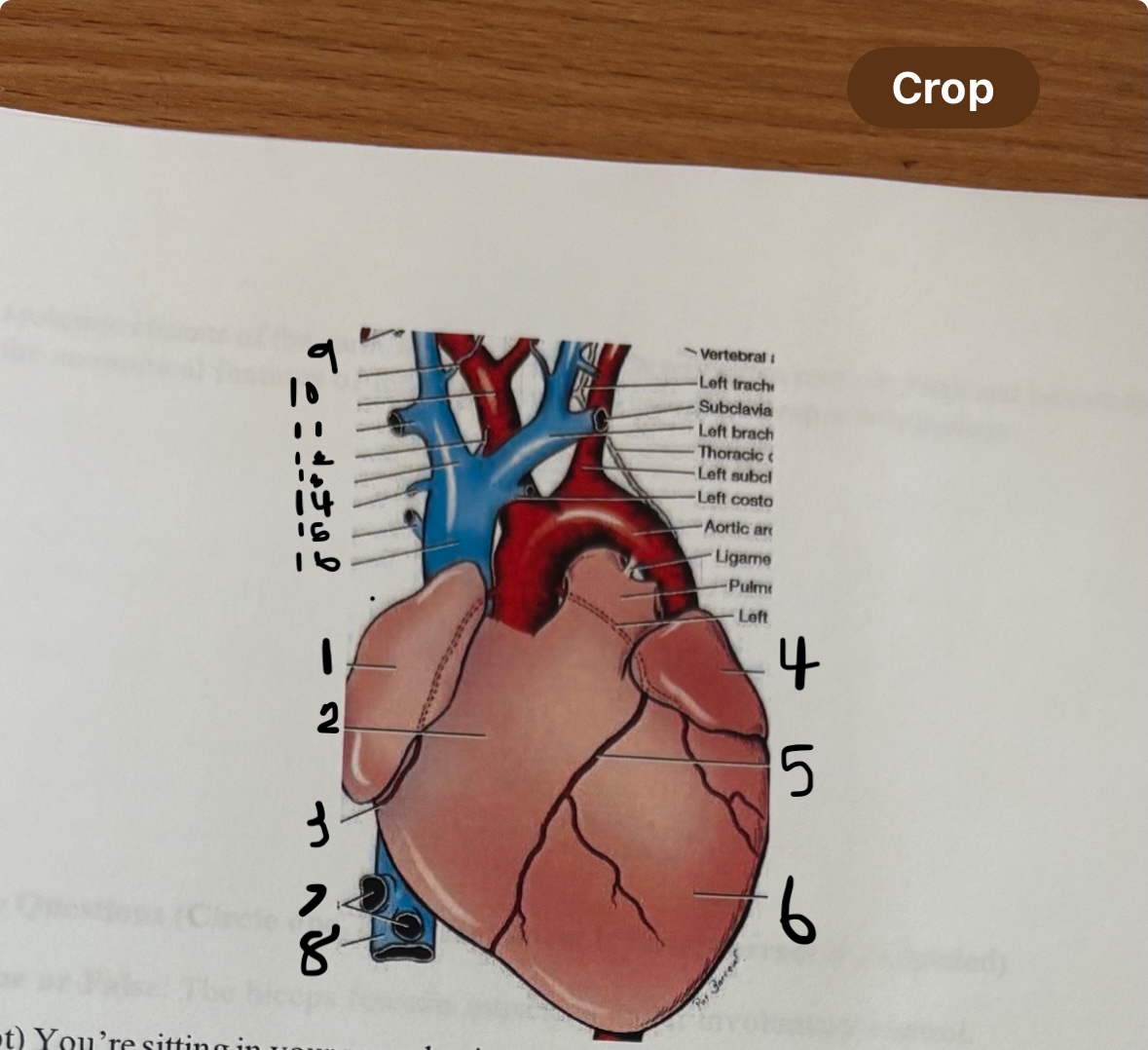
This is the front (anterior view) of the heart.
Label 1-8 of the heart and say what the function is. What view of the heart is this?
RV, LV, RA, LA, aorta/Aortic Arch, Apex, Superior Vena Cava, Pulmonary Arteries, Femoral Arteries, Femoral Veins
Before birth, oxygenated blood from the placenta enters the fetus through the umbilical vein and bypasses the liver via the ductus venosus to reach the heart. The blood enters the right atrium, where most of it is shunted through the foramen ovale into the left atrium, bypassing the lungs. Any remaining blood in the right ventricle is pumped into the pulmonary artery, but instead of going to the lungs, it is diverted to the aorta through the ductus arteriosus. This system ensures that oxygen-rich blood reaches the brain and body while avoiding the underdeveloped lungs.
You learn that the lungs and liver don't function fully until after birth and hence certain bypass mechanisms exist to divert the blood flow. Describe blood flow before birth
Blood starts in the right atrium, then passes through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle, which pumps it through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery to the lungs, where it picks up oxygen. Oxygenated blood returns to the left atrium via the pulmonary veins, then flows through the mitral (bicuspid) valve into the left ventricle, which pumps it through the aortic valve into the aorta to deliver oxygen to the body. After circulating through the body, oxygen-poor blood returns through the superior and inferior vena cava into the right atrium, completing the cycle. This continuous loop, called circulation, keeps the body supplied with oxygen and nutrients.
You're teaching a 5th grade class, and your assignment is to trace the path of a drop of blood in an adult, starting at the right atrium, and returning to the right atrium, through the pulmonary and systemic circuits of the CV system. Describe this route in detail and include the anatomical features of the heart involved using proper terminology. Use 4 sentences or less
True
T/F: The Z-line marks the boundary of a sarcomere
False: The filaments SLIDE PAST EACH OTHER
T/F The actin and myosin filaments change length to cause muscle contraction.
True
T/F: The H band disappears during muscle contraction
True
T/F: The motor end plate is where the nerve communicates with the muscle fiber
False: Negative
T/F: At rest the charge on the inside of the cell is positive
True
T/F: The plateau at phase 2 is due to the Fast influx of Calcium into the cell
True
T/F: Activation of the Sympathetic nervous system will increase the heart rate.
Calcium ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum when a muscle is stimulated. These calcium ions bind to troponin on the actin filaments, causing a shift that exposes binding sites for myosin. This allows the myosin heads to attach to actin and perform the power stroke, leading to muscle contraction.
In simple terms and in 3 sentences or less, describe the role of calcium ions in muscle contraction
Actin= thin protein filaments; extend toward the center; filaments consist of tropomyosin
Myosin= thick filaments makes force for contraction
Tropomyosin= block binding sites on actin at rest
Troponin= has affinity for calcium ions and allows myosin to bind to actin
What are the major proteins involved in skeletal muscle contraction and in 1 sentence what are their roles
According to Huxley's Sliding Filament Theory, what happens when calcium binds to troponin? Use simple terms and explain this in 1 sentence
When calcium binds to troponin, it causes a shift in the tropomyosin protein, which exposes binding sites on actin, allowing myosin to attach and initiate muscle contraction.
Tendon
Give an example of a muscle attachment (HINT: PAFT)
Bursae
This is filled with fluid to help decrease friction in joints
Rhomboideus
Trapezius
Deep Pectoral
Superficial Pectoral
Name 4 extrinsic muscles (HINT: 2 shapes)
Infraspinatus
Supraspinatus
Teres Major
Teres Minor
Name 4 intrinsic muscles of the shoulder
The electrical impulse in the heart starts at the SA node (sinoatrial node), which is the heart’s natural pacemaker, causing the atria to contract. The impulse then travels to the AV node (atrioventricular node), where it is delayed briefly to allow the ventricles to fill with blood. After the delay, the impulse moves down the AV bundle (bundle of His) and branches into the Purkinje fibers, which spread the impulse through the ventricles, causing them to contract. This coordinated electrical pathway ensures that the heart beats in a regular, synchronized rhythm.
In 4 sentences or less and in simple terms, describe conduction of the heart, including the sequence in which impulses are transmitted. Your answer should include the follwoing: SA node, Purkinje fibers, AV node and AV bundle.
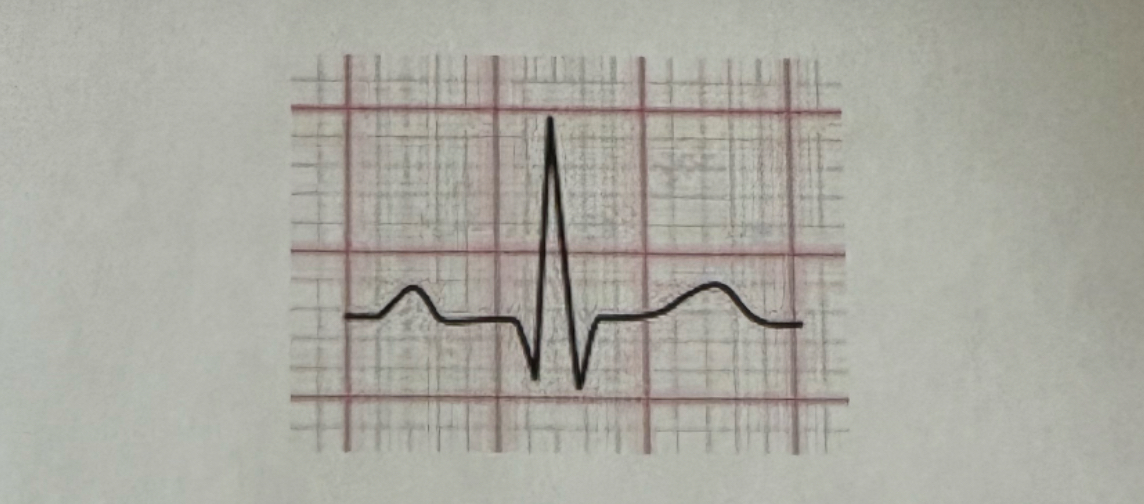
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). It’s important bc. it reads the electric currents generated by the heart as it contracts and relaxes which gives us insight into the heart’s rhythm and overall function and condition of the heart.
What’s the name of the graph that depicts the electrical current of the heart and why is it important?
The specific waveform shown suggests it could be from a lead such as Lead II, which typically involves placing one electrode on the right arm and another on the left leg, with a grounding electrode on the right leg.
Briefly describe placement of the lead used in the procedure that generates the image shown.