Lecture #1 - Genetics & Chromosomes
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Genes
Sections of DNA(sequence of nucleotide bases) that code for a specific protein (sequence of amino acids) and are expresssed as our phenotypes.
Alleles
Different forms of a gene- aka- different coding for a gene. For example, there are different alleles for hair genes such as curly vs straight hair.
chromosomes
packed doubled-stranded DNA that is located in the nucleus.
Made up of a double-stranded DNA + histones.
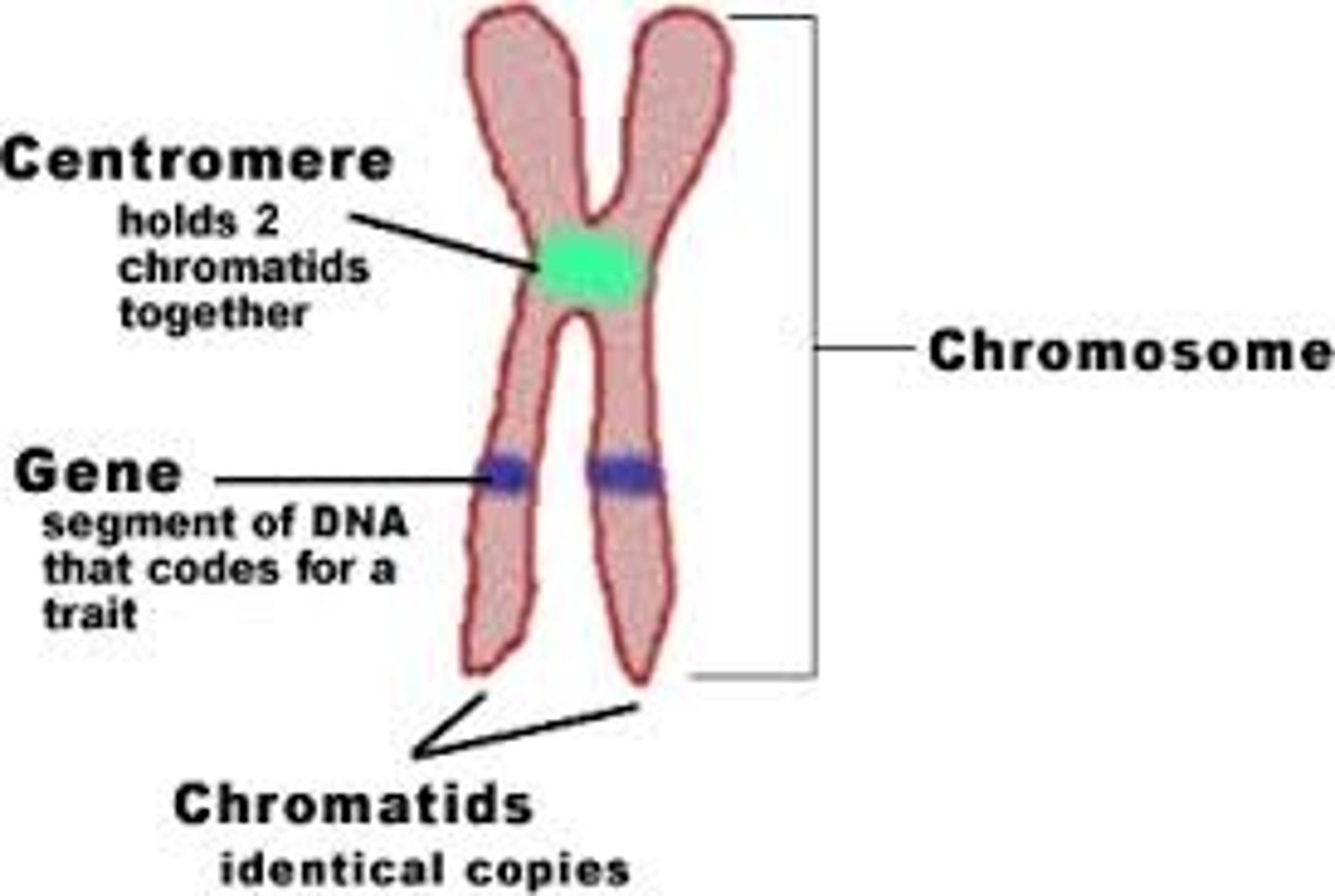
histone purpose
helps close, compactify, and organize DNA
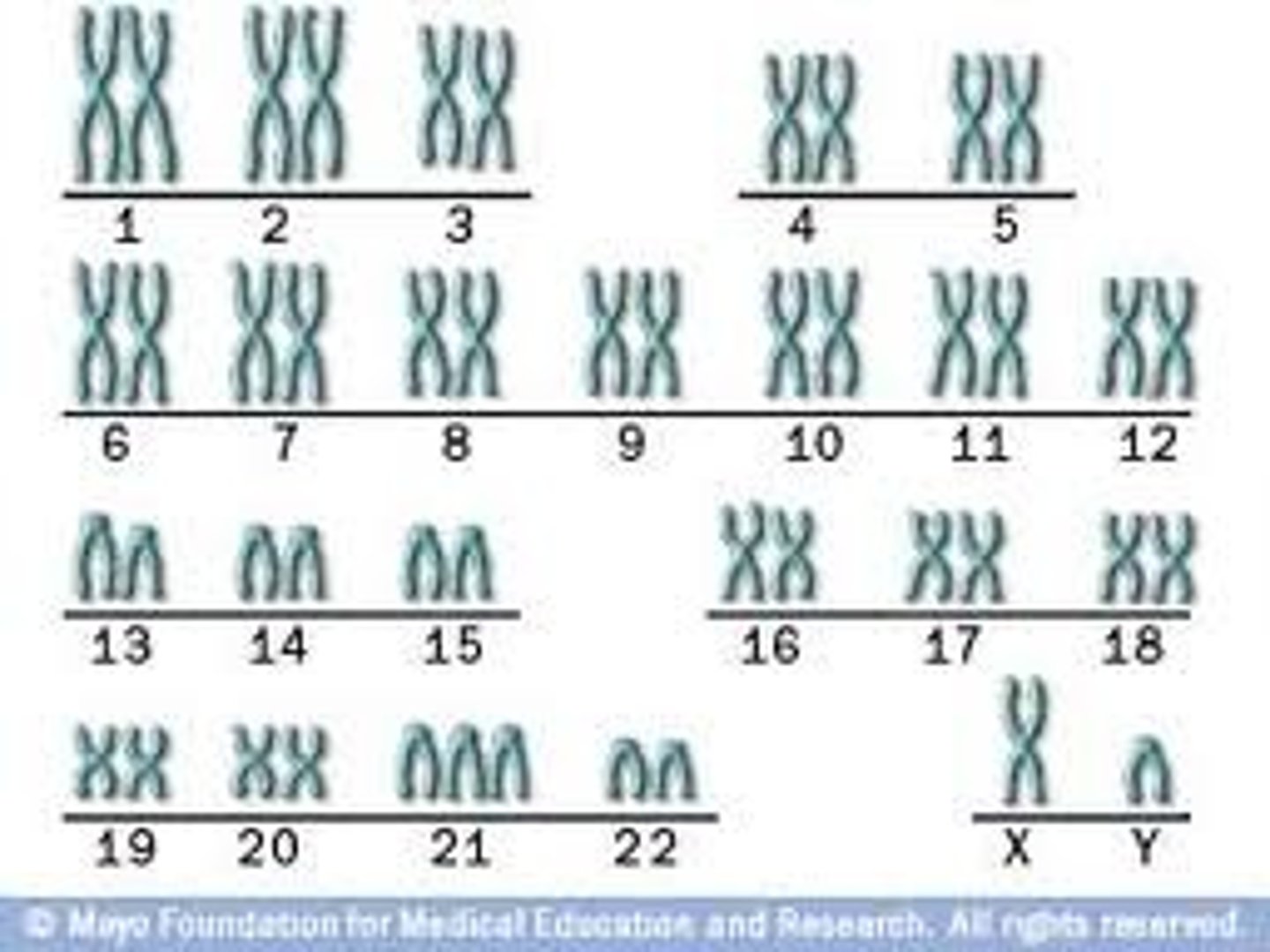
autosomes vs sex chromosomes
Autosomes = 22 pairs, 1 pair of sex chromosomes. Male = XY (determines sex of offspring). Female = XX
homologous chromosomes (homologs)
in a diploid organism, chromosomes that are similar in size, shape, and gene content
-they can carry same sequence of genes(same loci) BUT they may be differen allels
-23 chromosomes from each parent from homologous chromosomes
centromeres
divides chromosome/chromatid into arms
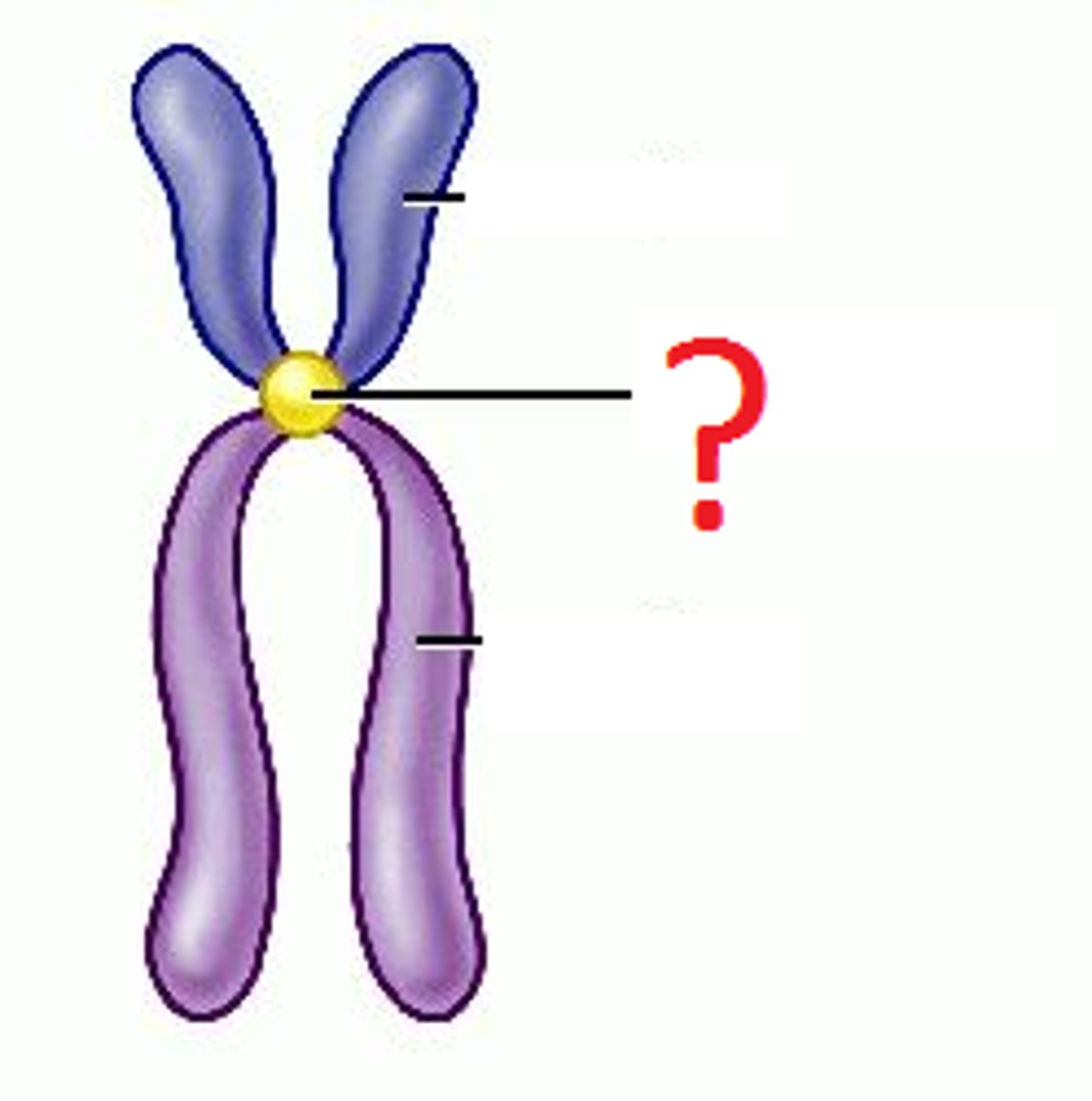
locus (loci - plural)
the physical location of a gene on a chromosome
Ploidy
number of sets of chromosomes in a cell
(how many of the same chromosomes are in the cell?)
Haploid
Only 1 of each chromosome in each cell
-joined sister chromatids = 1 chromosome
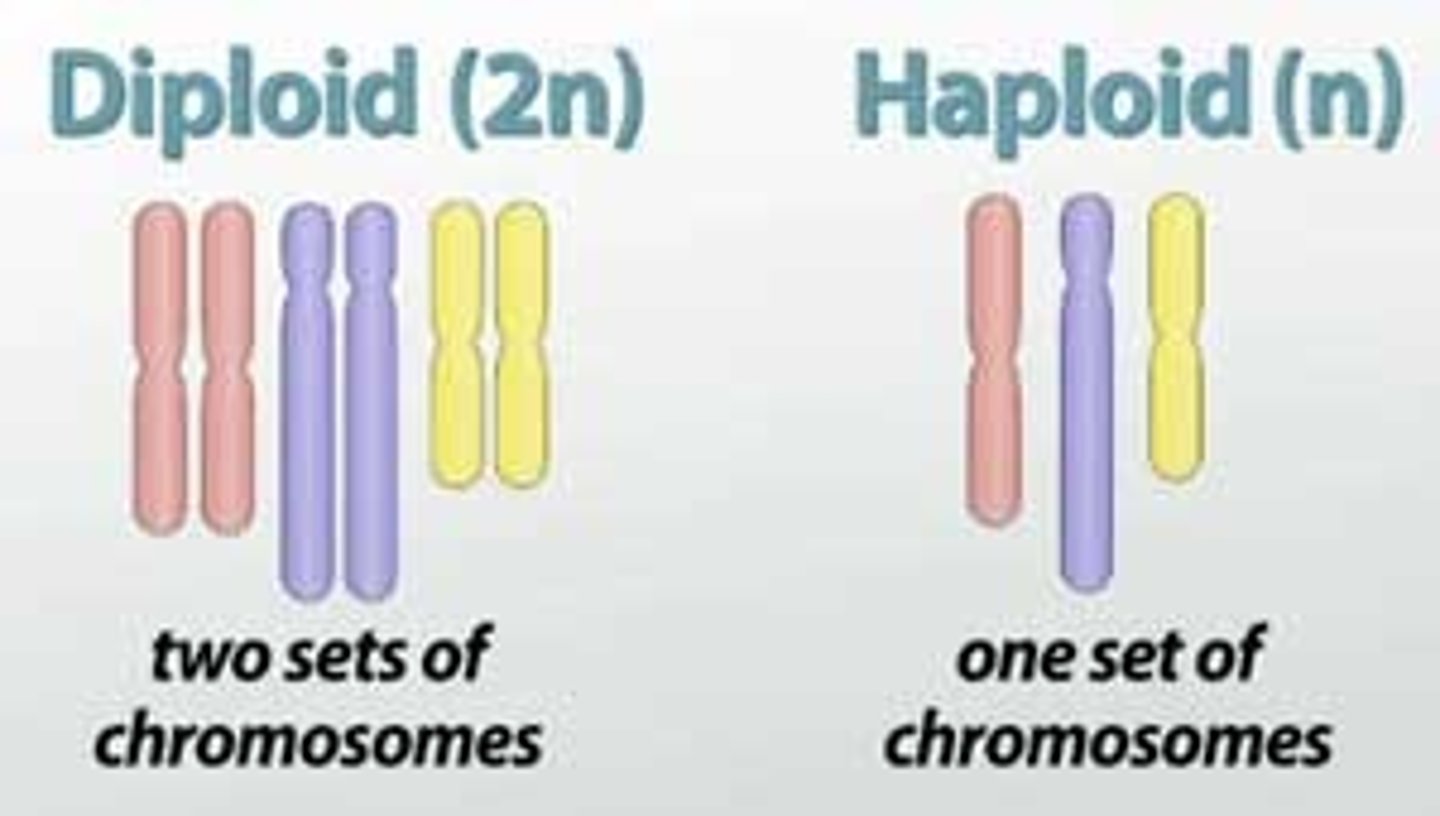
Diploid
containing two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent.
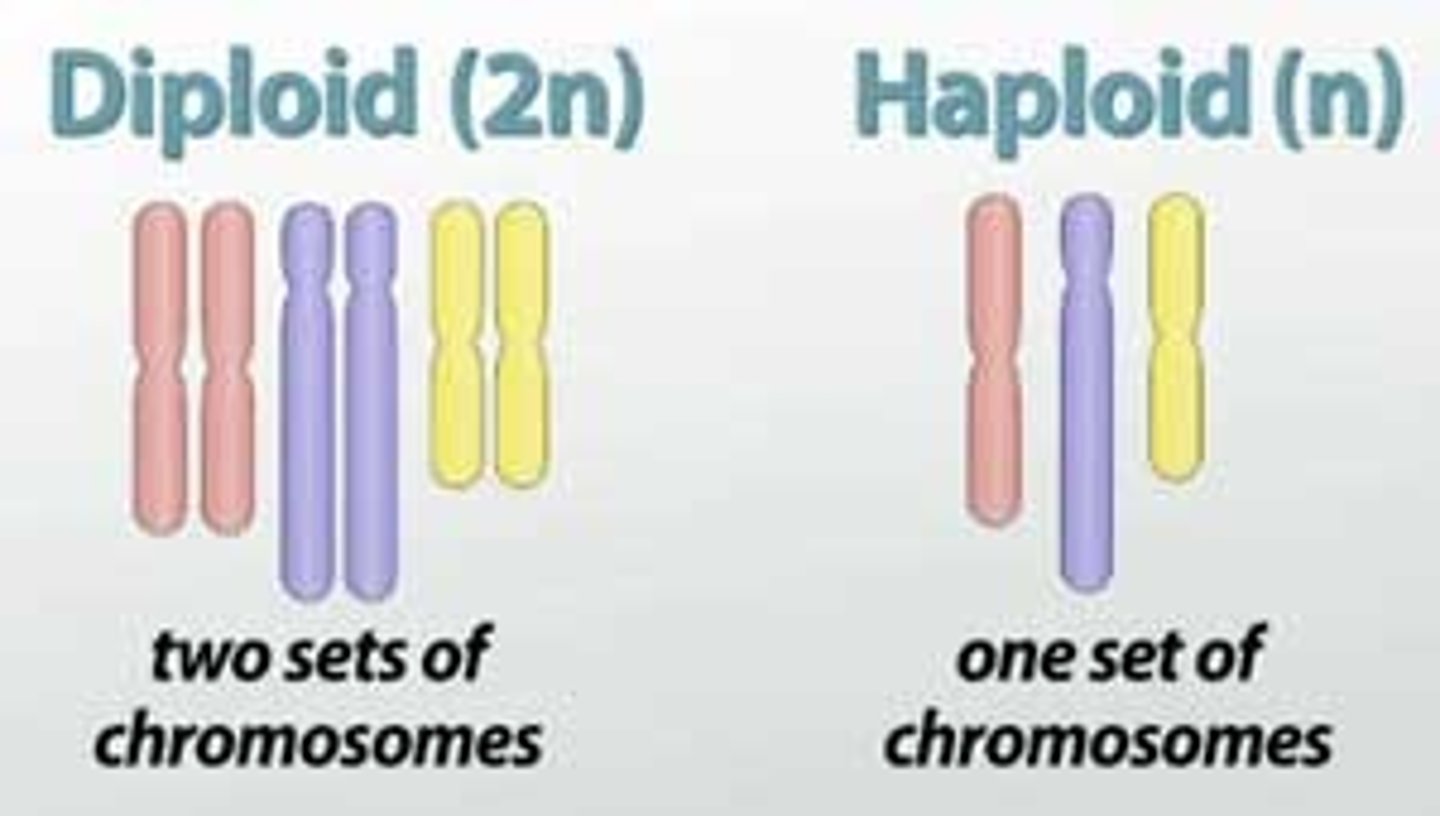
Polyploid
condition in which an organism has extra sets of chromosomes
-eg. down syndrome or different animals
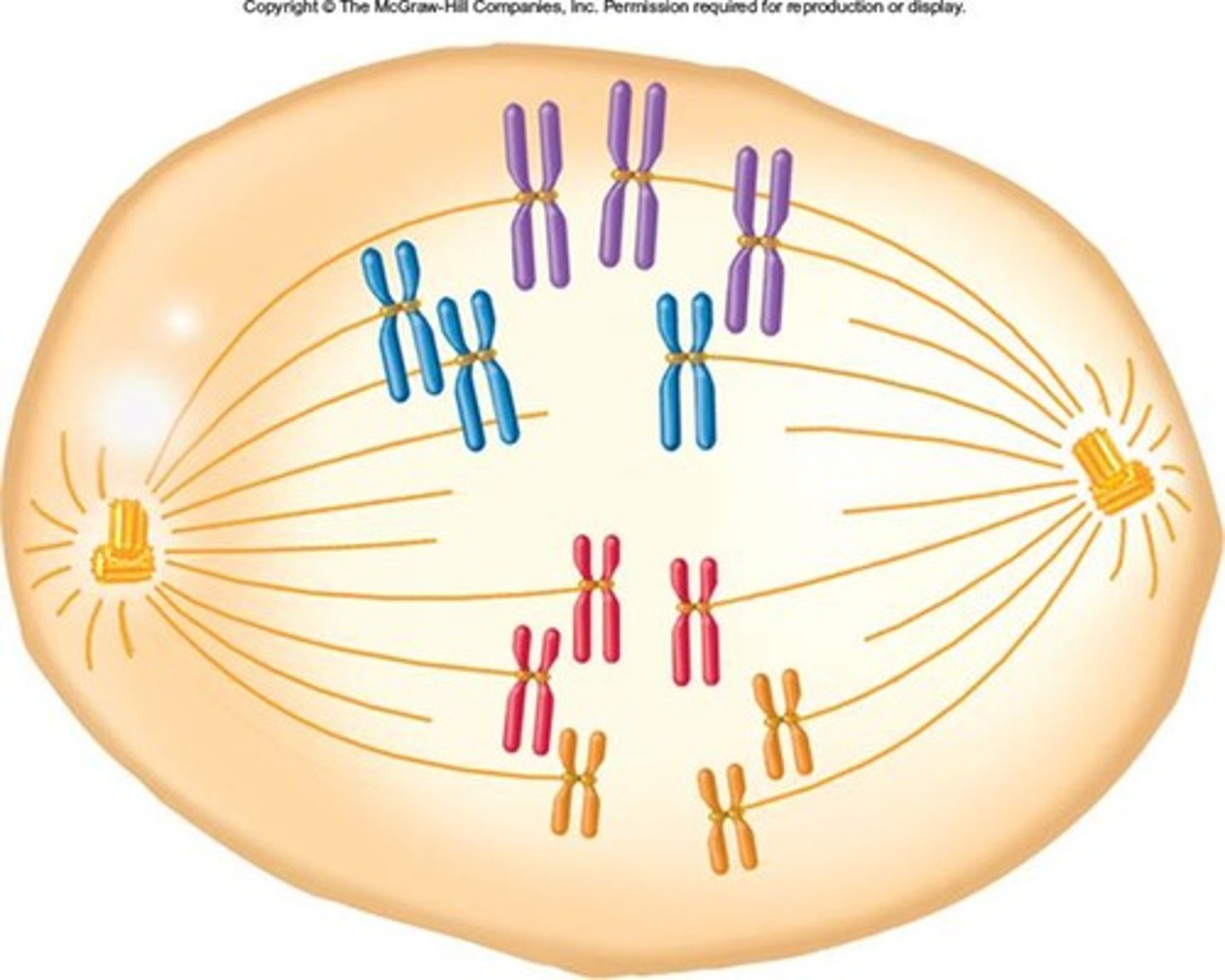
haploid number
Number of unique chromosomes in a gamate (sex cell), represented by n
(ploidy #)n = total chromosomes
unreplicated vs. replicated chromosome
Unreplicated = single molecule of double-stranded DNA, aka chromatid
Replicated = 2 identical chromatids (sister chromatids) with identical DNA
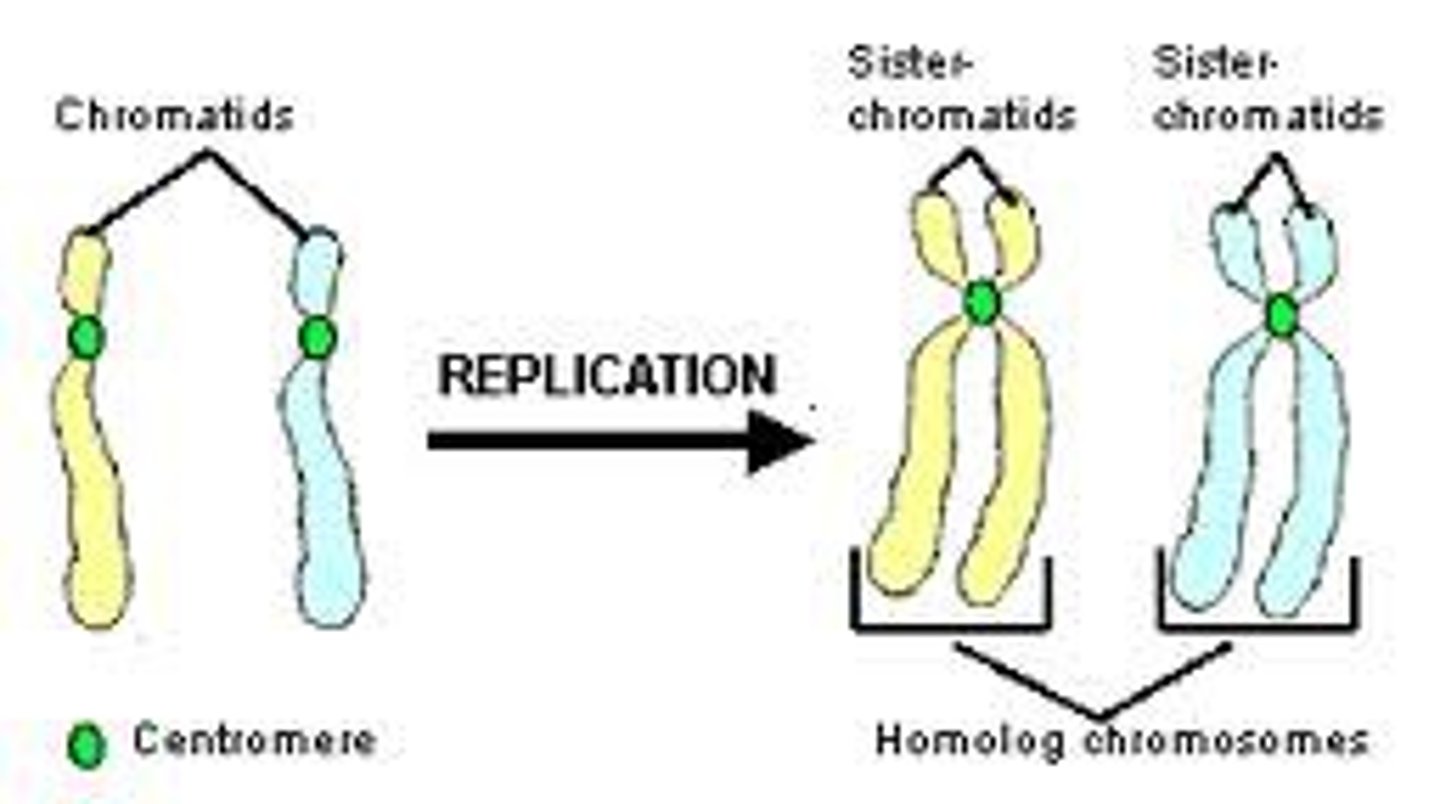
homologous chromosomes vs. sister chromatids
Homologous = same length/size/centromere but DIFFERENT ALLELES
sister = same length/size/centrmere with EXACT SAME ALLELES (DNA)
number of DNA molecules vs chromosome number
1 chromosome = 2 DNA molecules
ploidy versus haploid number
Ploidy = How many replicates of unique chromosomes
Haploid = How many uniques chromosomes
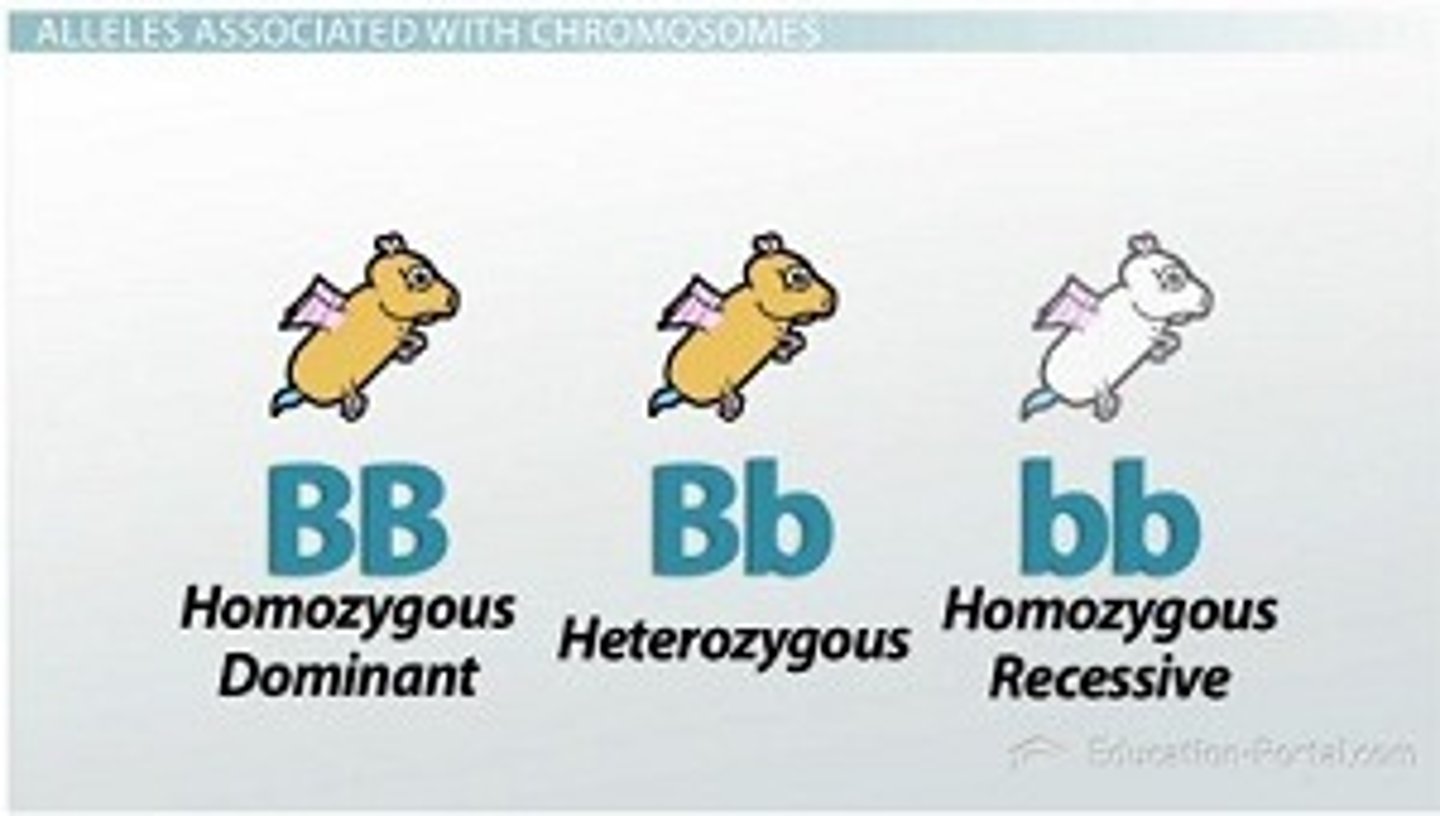
Heterozygous vs. Homozygous
Heterozygous - Two different alleles (Aa)
Homozygous - Two same alleles (AA or aa)