CHS Commerce B Semester 1 Exam
5.0(5)
5.0(5)
Card Sorting
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Underlined Refer to Movement of Wealth between sectors: h=household, f=firms. There's also a separate glossary set.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
1
New cards
Five Sectors of the Circular Flow Model?
Household, Firms, Financial, Government and Overseas Sectors
2
New cards
Circular Flow Model?
A model that shows the connections between the five different sectors of an economy.
3
New cards
Household Sector
It is made up of consumers, who hold economic resources such as __income (f)__, land, capital, etc. in order for the __consumption__ (f) of goods and services.
4
New cards
Firms Sector
It is made up of businesses and enterprises that use __economic resources__ (h) from households to produce __goods and services (h).__
5
New cards
financial sector
It is made up of financial institutions that act as intermediaries between the savers and borrowers in an economy. They receive the __savings (h)__ of individuals and businesses and then lend this money to others who need to borrow money for __investments (f).__
6
New cards
government sector
Refers to local, state, and federal governments who collect __taxes (t)__ and allocates that money elsewhere as __government expenditure (f).__
7
New cards
Overseas Sector
Overseas parties that trade with Australian businesses and individuals through __importing (h)__ and __exporting (f)__ goods.
\
\
8
New cards
Australian Securities and Investment Commission (ASIC)?
The commission that regulates the conduct of Australian companies, financial markets, financial services organizations (including banks, life and general insurers, and superannuation funds), and professionals who deal in and advise on investments, superannuation, insurance, deposit-taking and credit.
9
New cards
Reserve Bank of Australia
Australia’s central bank and onducts the nation's monetary policy and issues its currency. It seeks to foster financial system stability and promotes the safety and efficiency of the payments system.
10
New cards
Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC)?
A commission that regulates businesses to follow the Competition and Consumer Act and promotes competition and fair trading and regulates national infrastructure to make markets fair for everyone.
11
New cards
booms and busts of the business cycle
These are periods of high and low economic activity and make up the business cycle.
12
New cards
recession
A period for six months or longer when the economy becomes retracts and becomes smaller.
13
New cards
depression
More severe than a recession with high rates of retraction over a longer period of time.
14
New cards
contractions and expansions
The fluctuation of the business cycles between booms, recession and depression either as retractions or growths.
15
New cards
features of a contraction
Falling levels of production, Decreasing consumer spending, Rate of inflation falls, wage rates falls, lowering interest rates, unemployment rises.
16
New cards
features of an expansion
Rising levels of production, increasing consumer spending, Rising rate of inflation, Rise of wage rates, rising interest rates, unemployment falls.
17
New cards
characteristics of a recession
Low income and production, high unemployment, low inflation rate, consumer demand, business sales and profits are at a low level, unused resources, low interest rates.
18
New cards
demand
A consumer's desire to purchase goods and services and willingness to pay a specific price for them.
19
New cards
supply
refers to the quantity of a good or service that businesses are willing and able to offer for saleata given price, at a given point in time.
20
New cards
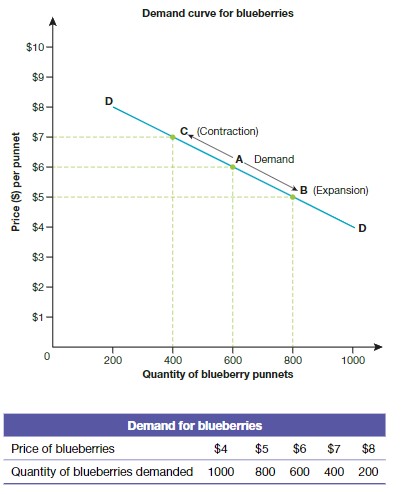
Law of Demand
The quantity of a good or service demanded varies inversely to price.
21
New cards
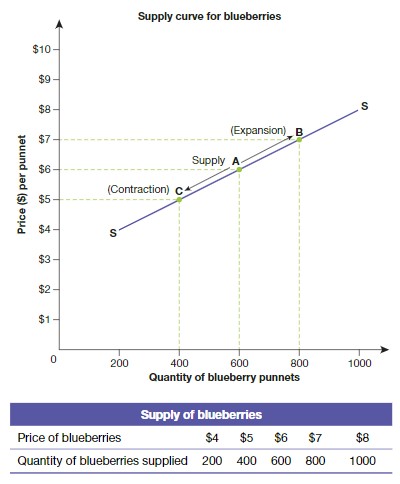
Law of Supply
The quantity of a good or service supplied varies directly with price.
22
New cards
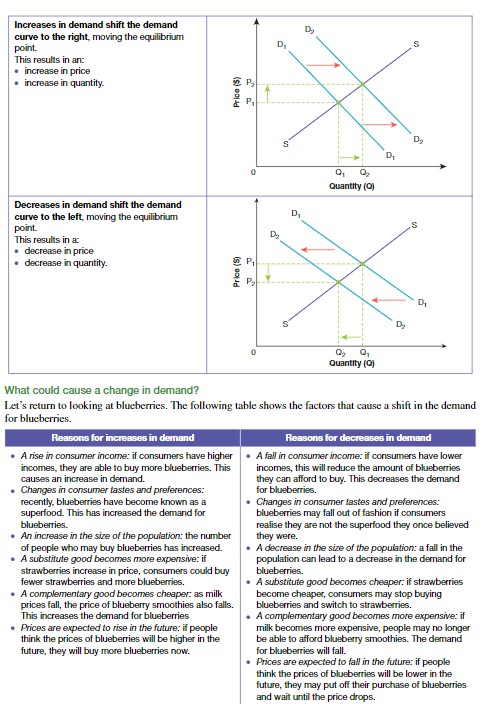
Factors that cause a change in demand
Consumer income, consumer preferences, size of population, substitute goods, complementary goods, expected future price
23
New cards
market equillibrium
The point at which buyers and sellers agree on a price and exchange the good or service for money.
24
New cards
market
A situation where buyers and sellers come together to exchange goods and services.
25
New cards
types of markets
Retail (shops), Labour (Hiring Signs), Financial (Banks) and Stock (ASX)
26
New cards
Reasons Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people Traded
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people traded to improve their standard of living by obtaining items that were not available in their area.
27
New cards
Trade Routes of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people created exchange routes that follow rivers, or multiple watering holes. These routes often intersected with multiple people taking in different sections of the route.
28
New cards
Items Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people traded
Before European settlement, Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people traded many valuables such as shells, pearls and special stones. They were used to ornaments and jewellery. They also traded ochres for paint and decorations, tools, ceremonial items and foods such as fish, crab, turtle, eggs and yams. Besides goods, they also traded rituals, chants, ceremonies, ideas and words (literally).
29
New cards
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Cultural Knowledge in the Economy
There have been many Indigenous enterprises and businesses established in recent times. They mainly consist on arts and craft, cultural tourism, land management, finance, mining and Indigenous education.
30
New cards
Reasons for Government Intervention in the Market?
Environmental Degradation, Conservation of Natural Resources, Socio-politically Offensive
31
New cards
Types of Businesses
Online, On-demand, Micro, Small, Medium, Large, Global, Government, Not-for-Profit and Offshore Businesses
32
New cards
Online Business
A business which runs some or all of its business using the internet.
33
New cards
On-Demand Businesses
Businesses that use technology to maximize consumer convenience. (Uber Eats)
34
New cards
micro business
a business with fewer than five employees.
35
New cards
small business
business with 5 to 19 employees.
36
New cards
medium business
business with 20 to 199 employees.w
37
New cards
large business
business with 200 or more employees.
38
New cards
global business/transnational corporation(TNC)
a large company that has branches in many different countries.
39
New cards
Offshore Business
A business that utilises other countries regulations by creating a branch to take advantage of cheaper production costs.
40
New cards
government businesses
government-owned and operated. They provide essential community services such as health, education, roads and welfare.
41
New cards
Not-for-Profit Business
A business provides services to the community and does not earn a profit for its owners. All of the money earned from donations or running the business must go back into the services the business is providing to the community. Typically, most not-for-profit businesses receive tax concessions, meaning they do not pay as much tax as other types of businesses.
42
New cards
Globalisation
the process by which the world is becoming increasingly interconnected as a result of increased trade and cultural exchange.
43
New cards
positives of globalisation
Expanded markets, cheaper materials, access to labour
44
New cards
negatives of globalisation
Increased competition, cheaper imported products, environmental and social issues.
45
New cards
Innovation of Technology
technology has increased efficiency and lowered the production costs for businesses, while globalisation has allowed businesses to sell their products worldwide and get their products produced in other economies, but has increased competition.
46
New cards
corporate social responsibility
When businesses consider the interests of stakeholders, society and the environment when making economic and business decisions.\\
47
New cards
benefits of having an ethical business
Corporate social responsibility is good business — customers eventually find out which businesses are acting responsibly, and which are not. Customers can react and stop buying a business’s product if they learn that the business is exploiting employees, accepting bribes or polluting the environment. At the same time, customers will reward socially responsible businesses by purchasing more of their products. Acting in a socially responsible way may cost money in the short term, but in the long run it turns out to be in the company’s own interest.
48
New cards
innovation
Either adding a new product to an existing product line, or significantly improving an existing product or process the process of creating a new or significantly improved product, service or process (way of doing something.
49
New cards
entrepreneur
A person who is willing to take a risk and has the qualities required to turn an idea into a successful businessC
50
New cards
Causes of the Great Depression
Stock Market Crash of 1929, Banks Failing with $7 Billion Worth of Assets, Extremely Low Consumer Confidence, Collapse of World Trrade and Collapse of Money Supply
51
New cards
Injections
Putting money into the economy
52
New cards
Leakages
Taking money out of the economy or unutilised money (savings)