Describe the anat+funct areas of cerebrum, diencephalon, brainstem, cerebellum
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Cerebrum: Lobes
Frontal
F: personality, planning, decision making, concentration, motor control, verbal communication
Occipital
F: vision/visual area
Parietal
F: general somatosensory (touch, temp, pain, pressure)
Temporal
F: hearing and smell
Insular
F: memory and sense of taste
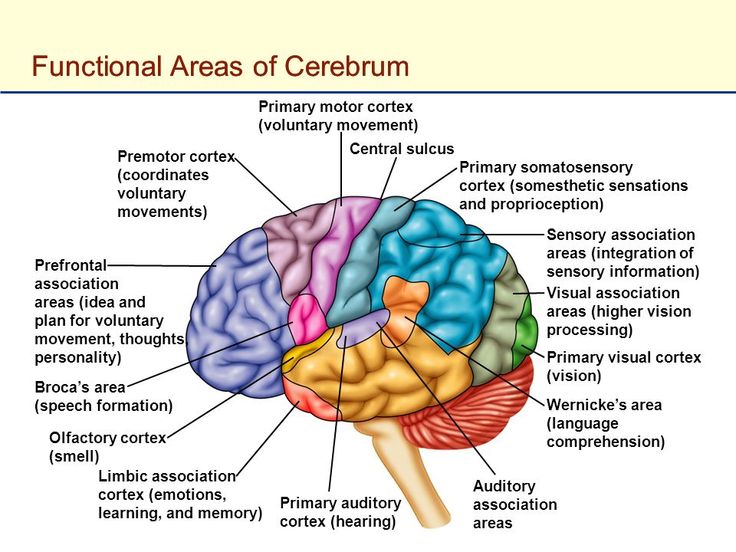
Cerebrum: Functional Motor Areas
primary motor cortex
L: precentral gyrus
F: skeletal muscle opposite side body
motor speech: Broca’s Area
inferolateral left hemisphere
muscle for vocalization
frontal eye field
L: surface middle frontal gyrus
F: regulate eye movements for reading/binocular vision
premotor cortex
L: primary motor cortex
coordinates learned, skilled activities = muscle memory
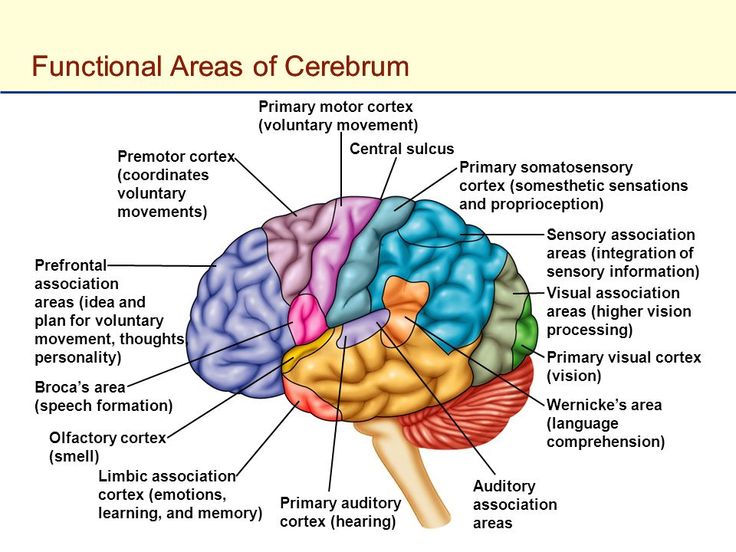
Cerebrum: Functional Sensory Areas
primary somatosensory cortex
L: post central gyrus parietal lobes
F: receive comatic sensory input proprioceptors (touch, pressure, pain, temp)
somatosensory association
L: posterior to postcentral gyrus
F: integrate touch infor = id how objects feel
primary visual cortex
L: occipital
F: receives, processes, store visual info
visual association
L: surrounds visual cortex
F: integrate + interpret color, form = id/recognition of things
primary auditory cortex
L: temporal lobe
F: integrate/interpret sounds
primary olfactory cortex
L: temporal lobe
F: receives, processes, stores odor info
primary gustatory cortex
L: insula
receives, processes, stores taste info
Cerebrum: Tracts
Assocation: connect cerebral motor regions in same hemisphere
Commissure: connection regions in different hemisphere (corpus callosum)
Projection: connect cerebral cortex to inferior brain + spinal cord
Diencephalon: Parts
epithalamus, thalamus, hypothalamus
Diencephalon: Epithalamus
L: posterior root covers 3rd ventricle
F: pineal gland: melatonin, circadian rhythm
Diencephalon: Thalamus
L: oval gray matter lateral 3rd ventrical
F: receives signals from conscious censes (not olfactory) sends to appropriate cortex, filters out distracting stimuli
Diencephalon: Hypothalamus
L: anterior inferior
F: controls ANS, body temp, sleep/wake, food intake, water intake, emotional behavior (fight/flight)
Brainstem: Parts
midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
Brainstem: Midbrain
L: superior
F: carry voluntary motor control from primary motor cortex, substantia nigra: dopamine production, visual reflex/tracking, auditory reflex
Brainstem: Pons
L: anterior
F: regulate skm associated with breathing, sound localization, sensory and motor
Brainstem: Medulla Oblongata
L: inferior brainstem
F: autonomic functions: BV diameter, HR, breathing, coughing, sneezing, swallowing, vomiting, salivating, hiccupping
Cerebellum
3 parts
- cerebellar cortext: outer gray
- arbor vitae: inner white “tree of life”
- deep cerebellar nuclei: gray
F: fine tunes motor movements, muscle memory, regulates involuntary/voluntary motor pathways, maintains equilibrium and balance
Motor and Sensory Homunculus
distorted proportions of body reflect amount of cortext dedicated
sensory: large portion to lips, fingers, genitals
motor: large portion to hands and face
Cerebral lateralization
hemisphere have different functions
L = categorical, language, and analysis (logical)
R = representational, visuospatial relationships, imagination, comparison of senses (creative)