Different political systems
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
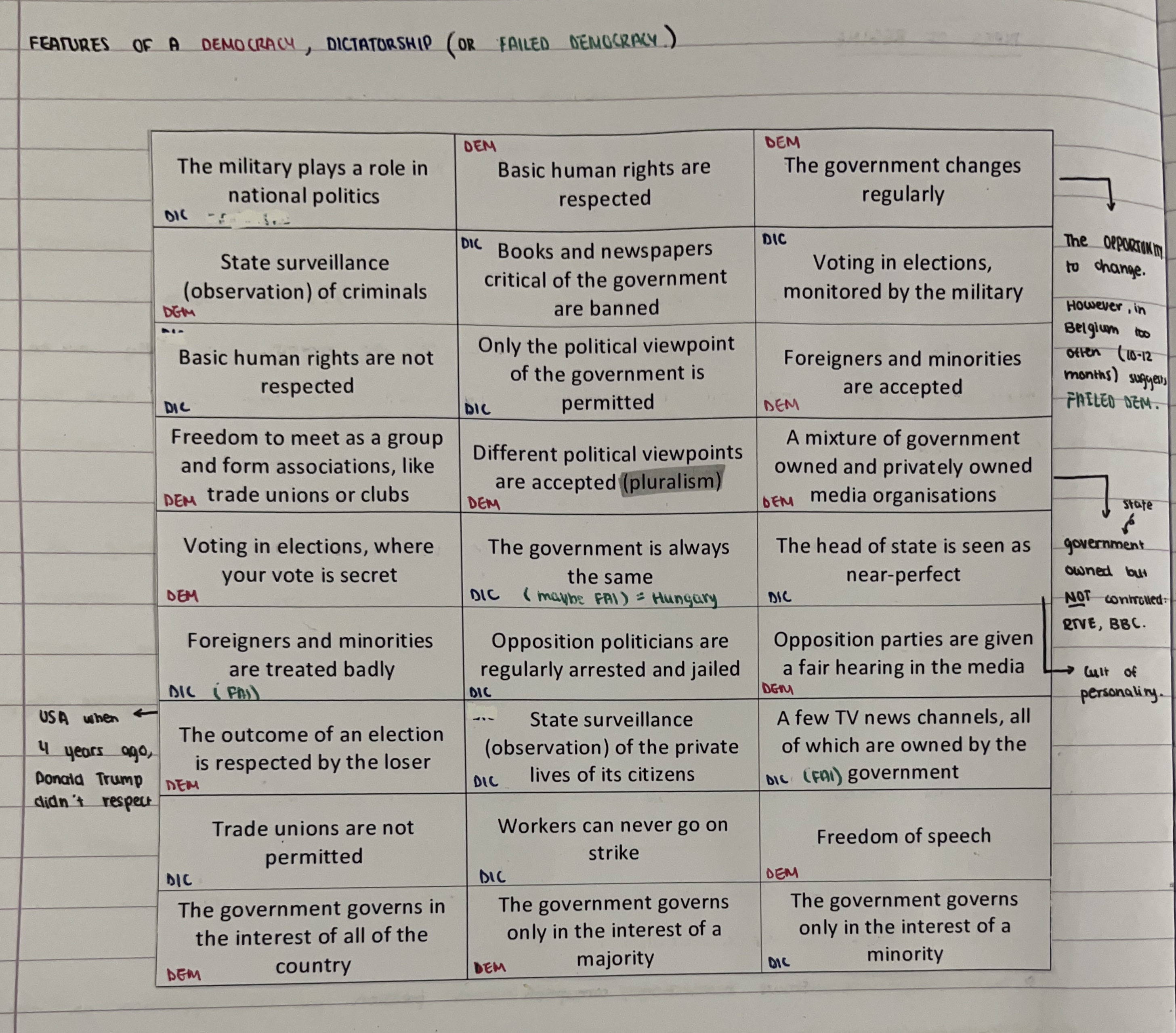
Types of regime
Full democracy, flawed democrat, hybrid regime, authoritarian regime
Full democracies
Elections are free and fair
Human rights are respected
Legal system is independent from government so will be less likely to be influenced by their power (corruption is less likely)
Pluralism (diff political viewpoints are accepted)
Examples: Sweden, Norway
Flawed democracies
Free and fair elections
People’s rights are respected
May be lack of media freedom and opposition and critics may be suppressed to some extent
(not in textbook) low levels in participation in politics and issues in the functioning of governance.
Examples: Thailand, South Africa, Suriname
Hybrid regimes
Not free and fair democracies
Might be fraud in elections, corruption and pressure put on opposition to the government
The legal system is controlled by the government
Media is not free to report on the government’s activities (= limited political knowledge)
Examples: Nepal, Guatemala, Sierra Leone
Authoritarian regimes
Run by one individual or party
Usually dictatorships or absolute monarchies
Some might have democratic institutions but have little power
People’s rights are ignored and elections can be fixed
Media and legal system are state controlled and any criticism of the government is suppressed (no freedom of speech)
Example: Burkina Faso, Myanmar, Iraq
Dictatorship, dictator
A system of government characterised by a single leader or group of leaders and little or no toleration for opposition.
A ruler with complete power over a country who is often not elected and has usually taken control by force (e.g coup).
Maybe more political instability
Examples: Egypt, Myanmar, Equatorial Guinea
Autocratic regime
A state where one person has absolute (unlimited or nearly unlimited) power. they demand that people obey completely without asking for anyone else’s opinion.
Authoritarian regimes can be ruled by one party
Totalitarian country/state
A political system where those in power have complete control and do not allow anyone to challenge them. They have a set of beliefs that it wants the people to follow.
Examples: North Korea (led by Kim Jong-un)
Oligarchy
A system of government where the people with wealth and status hold more political power.
Case study: Equatorial Guinea
How is this government not a democracy? What might it be?
Might be a dictatorship.
Elections are not free or fair
President Obiang has stayed in power for over 40 years
Accused of committing election fraud, bribery and corruption + silence opposition (threats, bribe, intimidation)
Election is not secret ballot: bribe, military present during ballot (election)
Doesn’t rule in the interest of the people
Country became major oil producer but nearly 80% of population live in poverty.
President Obiang very rich + accused of money laundering
Not using money to benefit country
Money laundering
Fraud
Corruption
The crime of moving illegal money through businesses or banks to make it look like the money was made legally.
The crime of getting money by deceiving people
Illegal, bad or dishonest behaviour, usually by people in positions of power