Criminal Justice Test 1
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Misdemenanor
A less serious crime than a felony, typically punishable by fines or a short term of imprisonment.
Felony
A serious crime that is typically punishable by imprisonment for more than one year or by death.
Jevenile Offenses
Crimes committed by individuals under the age of 18, often handled in a separate juvenile justice system.
Criminal Justice Components
The police, the courts, and corrections
What does the police component of the criminal justice system do?
The police component of the criminal justice system is responsible for enforcing laws, maintaining public order, preventing and investigating crimes, and apprehending offenders.
what does the courts component of the criminal justice system do?
The courts component of the criminal justice system adjudicates criminal cases, ensures fair trials, interprets laws, and determines the guilt or innocence of defendants.
what does the corrections component of the criminal justice system do?
The corrections component of the criminal justice system supervises offenders placed on probation or parole, manages incarceration facilities, and provides rehabilitation programs to facilitate reintegration into society.
Types of Punishment in the US
Fines, probation, intermediate punishments, imprisonment, death
Fines
monetary penalties imposed as punishment for crimes.
Probation
a court-ordered period of supervision in the community, allowing offenders to avoid incarceration while adhering to specific conditions.
Intermediate Punishments
alternative sanctions that are more restrictive than probation but less severe than imprisonment, such as house arrest or community service.
Imprisonment
the state of being confined in prison as punishment for a crime, typically involving loss of freedom and various rights.
Death
a legal penalty where an individual is executed as punishment for a crime, often reserved for the most serious offenses.
Plea Bargain (90-95%)
an agreement where a defendant pleads guilty to a lesser charge in exchange for a lighter sentence or other concessions from the prosecution.
Arrest and Booking (A SUSPECT)
the process of detaining a suspect and recording their personal information, charges, and fingerprints for legal proceedings.
Courts (A DEFENDANT)
the judicial body where legal cases are heard and decided, providing a forum for defendants to contest charges against them and seek justice.
No blea bargain = trial
If there is no plea bargain, the case proceeds to trial where both sides present their arguments and evidence before a judge or jury.
Bench Trial
A trial conducted by a judge without a jury, where the judge evaluates the evidence and makes a ruling.
Corrections (A CONVICTED OFFENDER/INMATE)
The system responsible for the punishment, rehabilitation, and reintegration of individuals who have been convicted of crimes, including incarceration and parole.
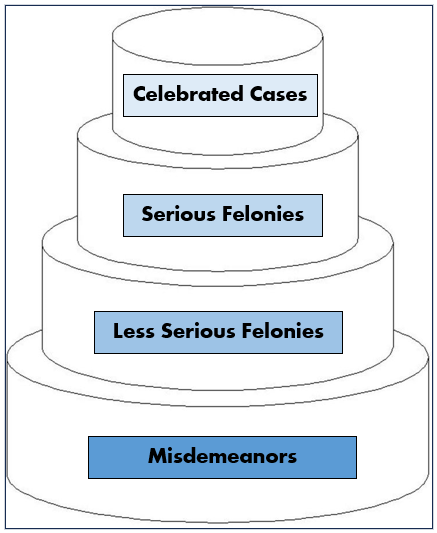
Criminal Justice Wedding Cake
A model that illustrates the different layers of the criminal justice system, highlighting the varying seriousness of cases and how they are processed through the system, often compared to a wedding cake with multiple tiers.
Goals of Criminal Justice
Retribution, Deterrence(specic deterrence/ general detterence), Incapacitation, Rehabiliation, Restoration
Retribution
A philosophy of punishment that seeks to provide a form of justice by ensuring that offenders receive a penalty proportional to the harm they caused, emphasizing moral accountability.
Deterrence ( Specific deterrence/ general deterrence)
A strategy aimed at preventing future crimes by instilling fear of punishment in offenders (specific deterrence) or the general public (general deterrence).
Incapacitation
A strategy that prevents future crimes by removing offenders from society, typically through imprisonment, to ensure they cannot commit further offenses.
Rehabilitation
A strategy focused on reforming offenders through educational, therapeutic, or vocational programs, aiming to reintegrate them into society as law-abiding citizens.
Restoration
A strategy that seeks to repair the harm caused by criminal behavior through reconciliation with victims and the community, often involving restitution and community service.
Over-Criminalization
The excessive application of criminal laws to behaviors that may not warrant such legal action, often leading to increased incarceration rates and social issues.
Victimless crimes
Crimes that do not directly harm or violate the rights of another individual, such as drug use or prostitution.
Crime Control Model
a conservative approach to criminal justice that prioritizes the swift punishment of criminals to prevent crime and protect society
Due process model
Civil cases vs. Criminal Cases