Biochem Exam 3
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
Michaelis–Menten model
Describes kinetics of single-substrate enzymes; ES complex forms then breaks down to product.
Bi-substrate reactions
Enzyme mechanisms that involve two substrates and two products; ~60% of known reactions.
Cleland notation
System used to symbolize substrates (A, B), products (P, Q), and enzyme forms in mechanism diagrams.
Pseudo–first-order conditions
One substrate is kept saturating so the reaction behaves as if it depends on one substrate.
Sequential reaction
Mechanism where all substrates bind before chemistry occurs and products are released.
Ordered sequential reaction
Substrates bind in a specific order; leading substrate must bind first.
Random sequential reaction
Substrates bind in any order but the EAB complex must form for chemistry.
Ping-pong reaction
One product leaves before all substrates bind; enzyme cycles between two forms (E and F).
Ping-pong hallmark
Parallel lines on a Lineweaver–Burk plot because Vmax/KM for first substrate is unaffected by second substrate.
Sequential hallmark
Intersecting lines on Lineweaver–Burk plot because Vmax and KM are affected by both substrates.
Vmax in LB plot
Equal to the inverse of the y-intercept (1/Vmax).
KM in LB plot
Equal to the negative reciprocal of the x-intercept (−1/KM).
Slope in LB plot
KM/Vmax.
Transition state
Highest-energy state; enzymes accelerate reactions by stabilizing the transition state.
Transition state analogue
Molecule resembling transition state; binds enzyme tightly and acts as a strong inhibitor.
Statins
Transition-state analogs that inhibit HMG-CoA reductase to lower cholesterol.
Protease inhibitors
Drugs that mimic transition state to inhibit HIV-1 protease.
Covalent catalysis
Enzyme forms temporary covalent bond with substrate to accelerate reaction.
Acid–base catalysis
Proton transfer from acids or bases stabilizes the transition state.
General acid catalysis
Reaction is accelerated by donation of proton in the transition state.
General base catalysis
Reaction is accelerated by abstraction of proton in the transition state.
Metal ion catalysis
Metal ions stabilize negative charges, orient substrates, or mediate redox changes.
Metalloenzyme
Enzyme with tightly bound metal ion such as Fe²⁺, Zn²⁺, Cu²⁺, Mn²⁺.
Metal-activated enzyme
Enzyme that loosely binds metal ions such as Na⁺, K⁺, Mg²⁺, Ca²⁺.
Carbonic anhydrase
Zn²⁺ enzyme that generates OH⁻ by making water more acidic.
Serine proteases
Protease family using Ser195, His57, Asp102 to catalyze peptide bond cleavage.
Catalytic triad (serine protease)
Asp polarizes His; His deprotonates Ser; Ser performs nucleophilic attack.
Oxyanion hole
Region stabilizing tetrahedral intermediate via hydrogen bonds.
Chymotrypsin cleavage site
Cleaves after aromatic residues: Phe, Tyr, Trp.
Trypsin cleavage site
Cleaves after basic residues: Lys, Arg.
Elastase cleavage site
Cleaves after small neutral residues: Ala, Gly.
Acyl-enzyme intermediate
Stable covalent intermediate formed during serine protease mechanism.
RNase A mechanism
Uses His12 as a base and His119 as an acid to hydrolyze RNA.
Enzyme regulation
Processes that alter enzyme availability or activity to control metabolism.
Regulation by synthesis
Changing rate of enzyme production (transcription/translation).
Regulation by degradation
Altering rate of enzyme breakdown to change enzyme levels.
Zymogen (proenzyme)
Inactive enzyme precursor activated by proteolysis.
Proteolysis regulation
Activation of enzyme by cleavage of peptide bonds.
Allosteric regulation
Binding of regulator at non-active site to change enzyme conformation/activity.
Allosteric effector
Molecule that binds “other site” to increase or decrease enzyme activity.
Positive effector
Shifts enzyme toward R-state, increasing activity.
Negative effector
Shifts enzyme toward T-state, decreasing activity.
Feedback inhibition
Downstream product inhibits earlier enzyme by allosteric binding.
ATCase role
Catalyzes first step in pyrimidine synthesis.
ATCase regulation
ATP activates (R-state), CTP inhibits (T-state).
Cooperativity
Sigmoidal kinetics where binding of one substrate increases affinity of others.
Hill coefficient
n>1 indicates positive cooperativity; n=1 indicates no cooperativity.
PFK committed step
Phosphorylates F6P to F1,6-BP in glycolysis.
PFK regulation
AMP activates PFK during low-energy conditions.
Covalent modification regulation
Reversible modification (often phosphorylation) changes enzyme activity.
Kinase
Enzyme that adds phosphate group to Ser, Thr, Tyr.
Phosphatase
Enzyme that removes phosphate group.
Glycogen phosphorylase
Regulated by both allostery and covalent modification.
Glycogen phosphorylase T-state
Inactive; stabilized by ATP and glucose-6-phosphate.
Glycogen phosphorylase R-state
Active; stabilized by AMP.
Monosaccharide
Basic carbohydrate unit with formula (CH₂O)n.
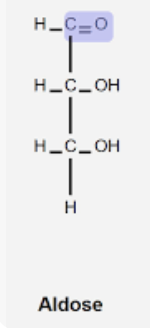
Aldose
Monosaccharide with aldehyde group.
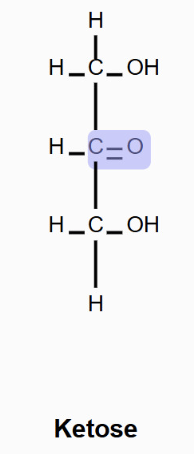
Ketose
Monosaccharide with ketone group.
Triose
Three-carbon sugar.
Pentose
Five-carbon sugar.
Hexose
Six-carbon sugar.
Fischer projection
2D representation for showing chiral center configurations.
D-sugar
OH on right of chiral carbon furthest from carbonyl.
L-sugar
OH on left of chiral carbon furthest from carbonyl.
Epimer
Sugars differing at one chiral center (e.g., glucose/mannose).
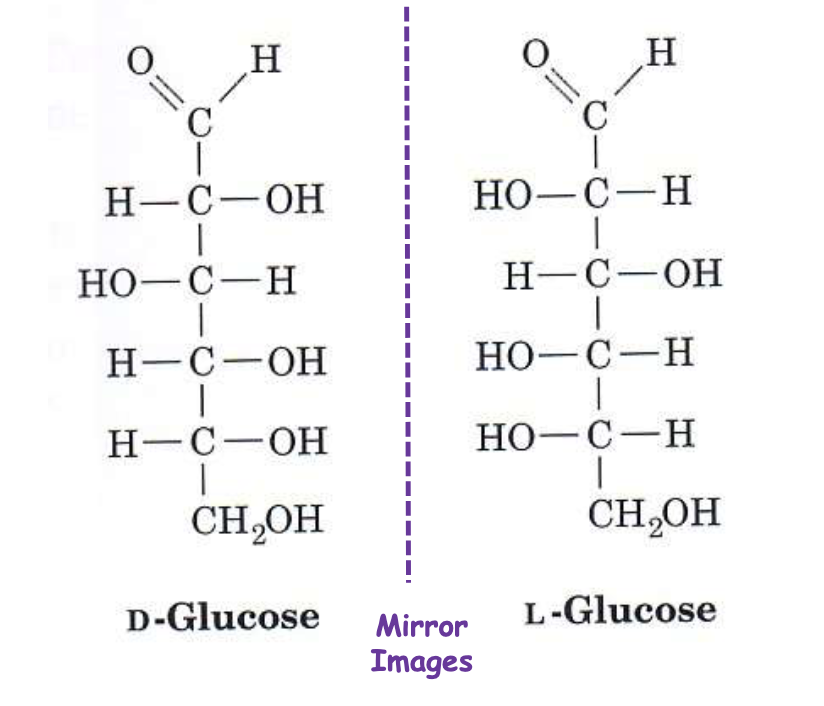
Enantiomers
Mirror-image stereoisomers (D-glucose vs L-glucose).
Anomer
Isomers differing at anomeric carbon (α vs β).
Anomeric carbon
Carbonyl carbon that becomes chiral during ring closure.
Hemiacetal
Formed when aldehyde reacts with alcohol during cyclization.
Hemiketal
Formed when ketone reacts with alcohol during cyclization.
Pyranose
6-membered sugar ring.
Furanose
5-membered sugar ring.
β-D-glucose
Ring form where anomeric OH is up.
α-D-glucose
Ring form where anomeric OH is down.
Reducing sugar
Has free anomeric carbon that can open to aldehyde.
Lactose
Disaccharide of galactose + glucose via β(1→4) linkage.
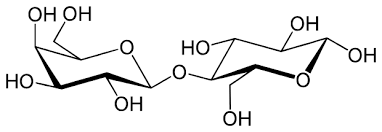
Sucrose
Disaccharide of glucose + fructose via α(1→2)β linkage; non-reducing.
Cellulose
β(1→4) glucose polymer; structural component in plants.
Chitin
β(1→4) polymer of N-acetylglucosamine; exoskeletons and fungi.
Starch
Mixture of amylose and amylopectin; plant storage polysaccharide.
Amylose
α(1→4) glucose polymer; unbranched.
Amylopectin
α(1→4) with α(1→6) branches.
Glycogen
Highly branched animal storage polysaccharide.
Sugar acid
Oxidized sugar (e.g., glucuronic acid).
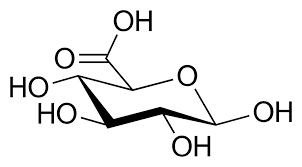
Sugar alcohol
Reduced sugar (e.g., sorbitol).
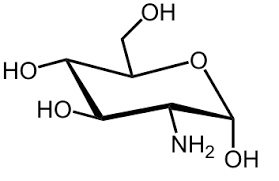
Amino sugar
Sugar containing NH₂ instead of OH (e.g., glucosamine).
Fatty acid
Long-chain carboxylic acid; building block of lipids.
Saturated fatty acid
No double bonds; higher melting point.
Unsaturated fatty acid
Contains double bonds; lower melting point.
Polyunsaturated fatty acid
Two or more double bonds.
Omega-3 fatty acid
Double bond three carbons from methyl end.
Triacylglycerol
Three fatty acids esterified to glycerol; energy storage.
Glycerophospholipid
Membrane lipid with glycerol backbone, two FAs, phosphate head group.
Sphingolipid
Lipid with sphingosine backbone; important in membranes.
Ceramide
Sphingosine + fatty acid via amide bond.
Sphingomyelin
Sphingolipid with phosphocholine head group; found in myelin sheath.
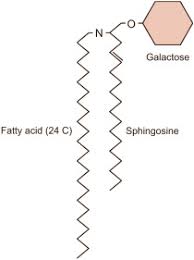
Cerebroside
Ceramide with one sugar head group.
Ganglioside
Ceramide with 3+ sugars including sialic acid.
Steroid
Lipid with four fused rings; cholesterol is major example.
Cholesterol
Precursor for steroid hormones; modulates membrane fluidity.