Session 1: Cell Ultrastructure
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Histology
The study of tissues
Histopathology
The study of diseased tissues
What are the four fundamental tissue types
1. Epithelial
2. Muscle
3. Nervous
4. Connective
Tissues
Functional arrangement of cells
Importance of the cell membrane
Compartmentalisation
Nucleus
• Contains genomic DNA
• Site of m-RNA transcription
• Contains the nucleolus
• Surrounded by double-membrane nuclear envelope which is continuous with the RER and is supported by network of intermediate filaments.
Nucleolus
• Site of ribosomal RNA (r-RNA) synthesis
• Initial assembly of ribosome occurs here
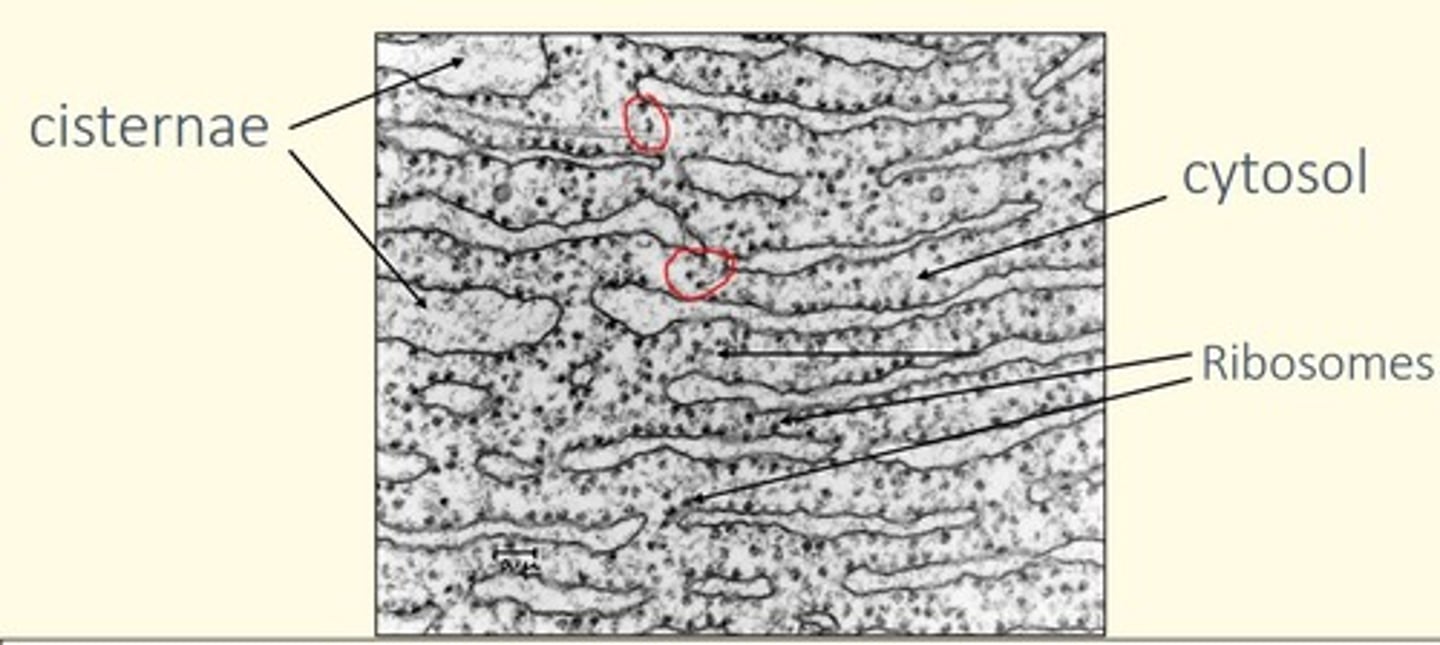
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
• Associated with ribosomes
• Site of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm
Where can an abundance of RER be found (what types of cells)?
• RER is abundant in biosynthetic cells (e.g., pancreatic acinar cells - exocrine cells)
How does RER stain with basic dyes such as haematoxylin?
• Basophilic RER stains strongly with basic dyes such as haematoxylin
Ribosomes
• Electron-dense particles (20-30 nm in diameter)
• Composed of combination of r-RNA and ~75 different proteins
• Large (60S) and small (40S) subunits associate when bound to m-RNA to catalyse protein synthesis
• Site of protein synthesis
Diameter of ribosomes
20-30nm
What are ribosomes made up of?
rRNA and proteins (~75 types)
Difference between free polyribosomes (polysomes) and membrane-bound ribosomes
• Polysomes = synthesise structural, nuclear, peroxisomal or mitochondrial proteins destined to remain INSIDE the cell
• Membrane-bound ribosomes = synthesise membrane and lysosomal proteins, and proteins destined to be secreted OUT the cell
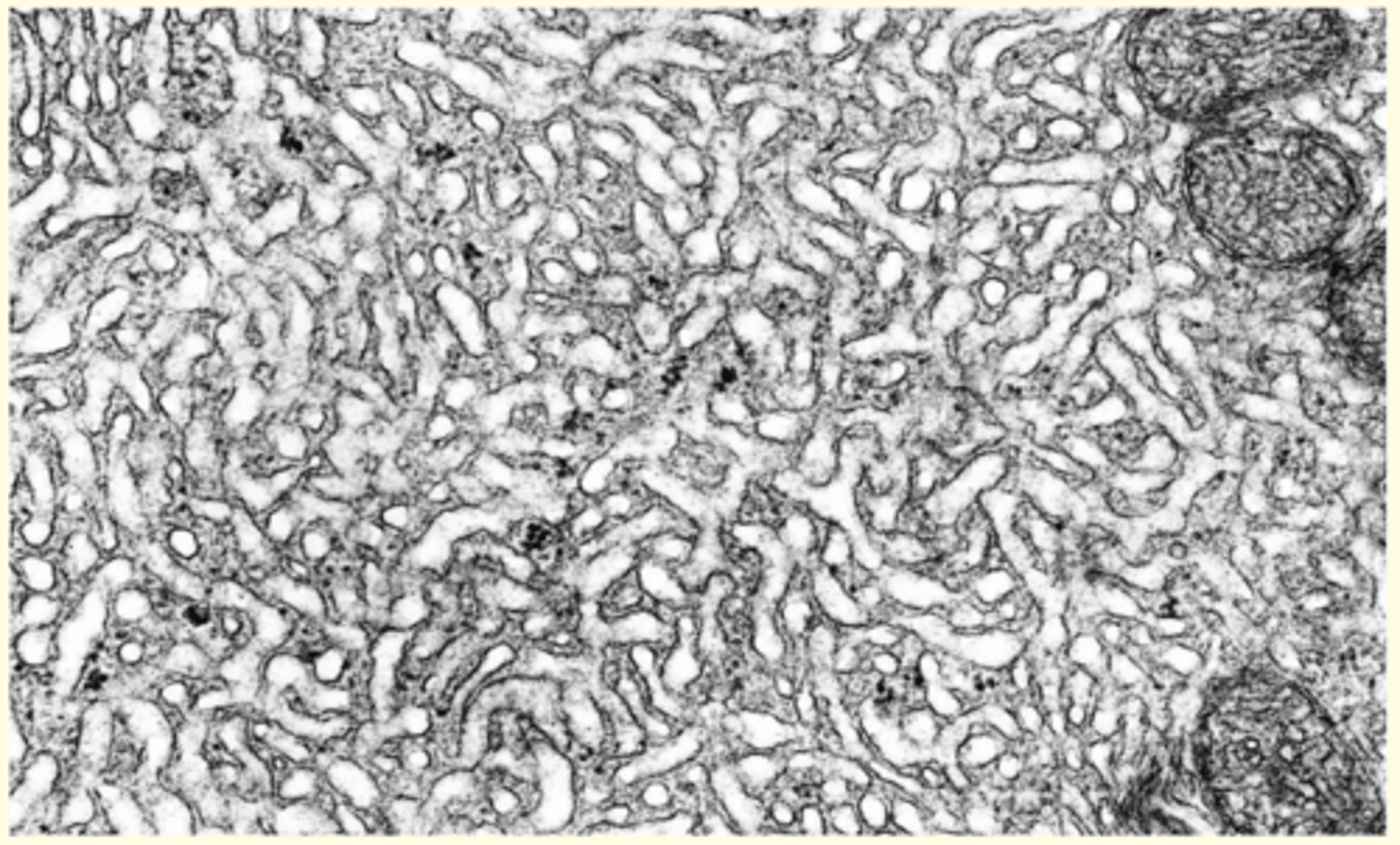
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
• Not associated with ribosomes (smooth appearance)
• Site of lipid, phospholipid and steroid synthesis
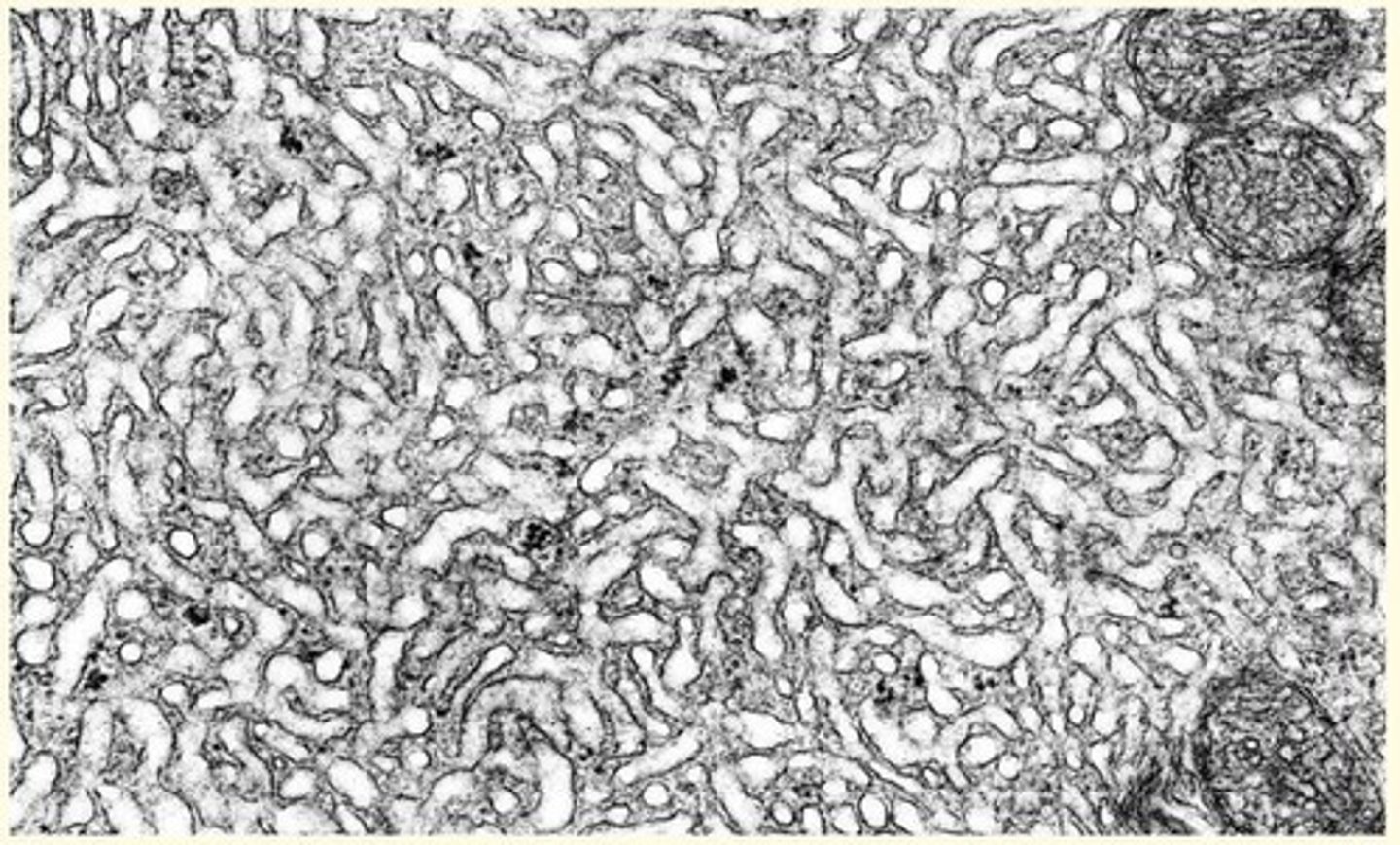
Where can an abundance of SER be found (what types of cells)?
• Liver and mammary gland = lipid biosynthesis
• Ovary, testis, adrenal gland = steroidogenesis
• Muscle = storage of calcium ions
What is the name of the structure found in endoplasmic reticulum that create a continuous intracellular compartment?
Cisternae (sacs)
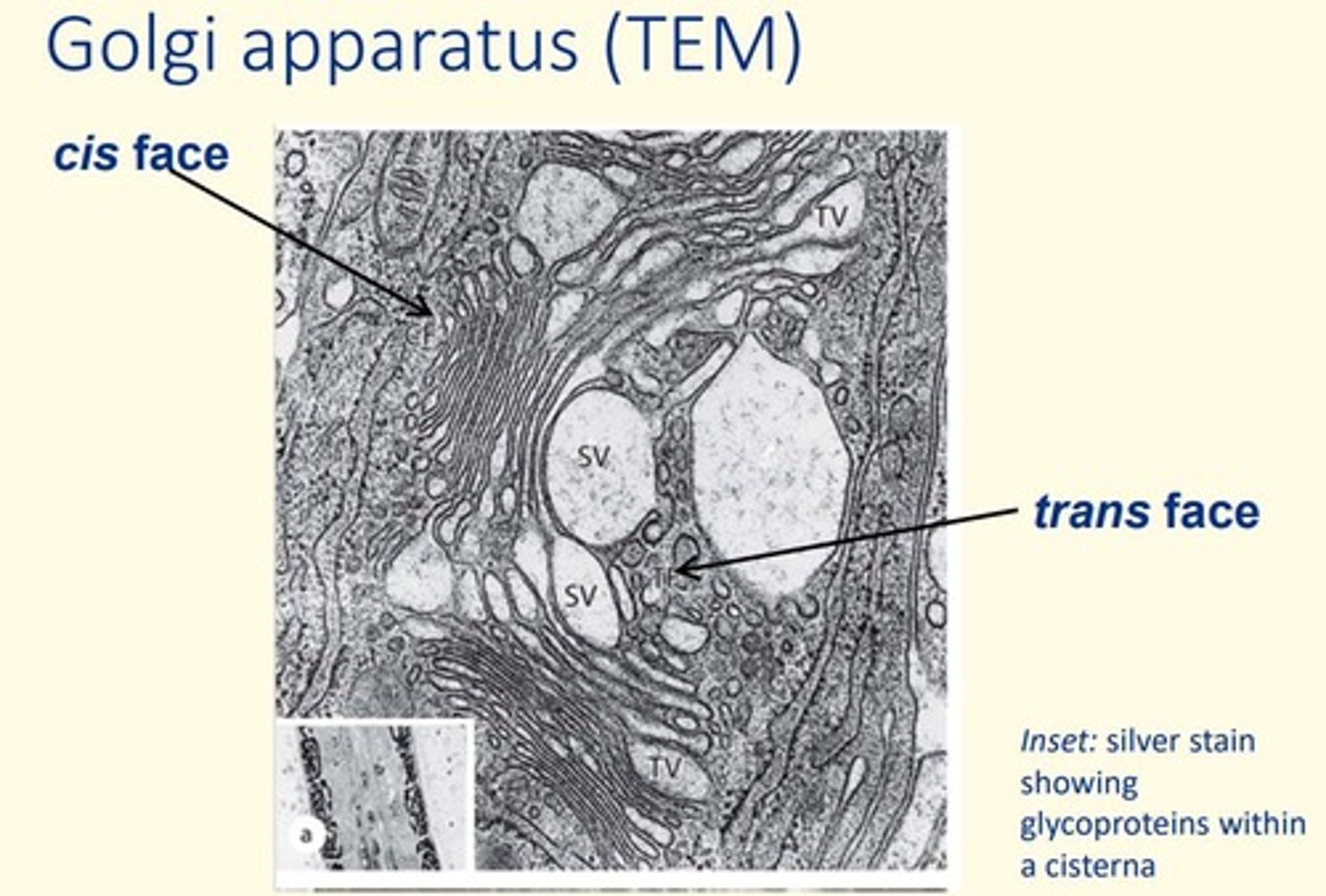
The Golgi Apparatus
• Stack of membranes in the cell that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
• 3 structural components = Cis face, medial Golgi, trans Golgi network
• Golgi vesicles tagged with specific coat protein that targets vesicles to correct compartment
What are the three functional compartments of the Golgi apparatus?
1) Nuclear-facing cis face
2) The central medial Golgi
3) The trans Golgi network
What are the five main types of vesicles found in a cell?
1) Cell surface-derived endocytic vesicles (e.g., pinocytic or phagocytotic)
2) Golgi-derived transport/secretory vesicles
3) ER-derived transport vesicles
4) Lysosomes
5) Peroxisomes
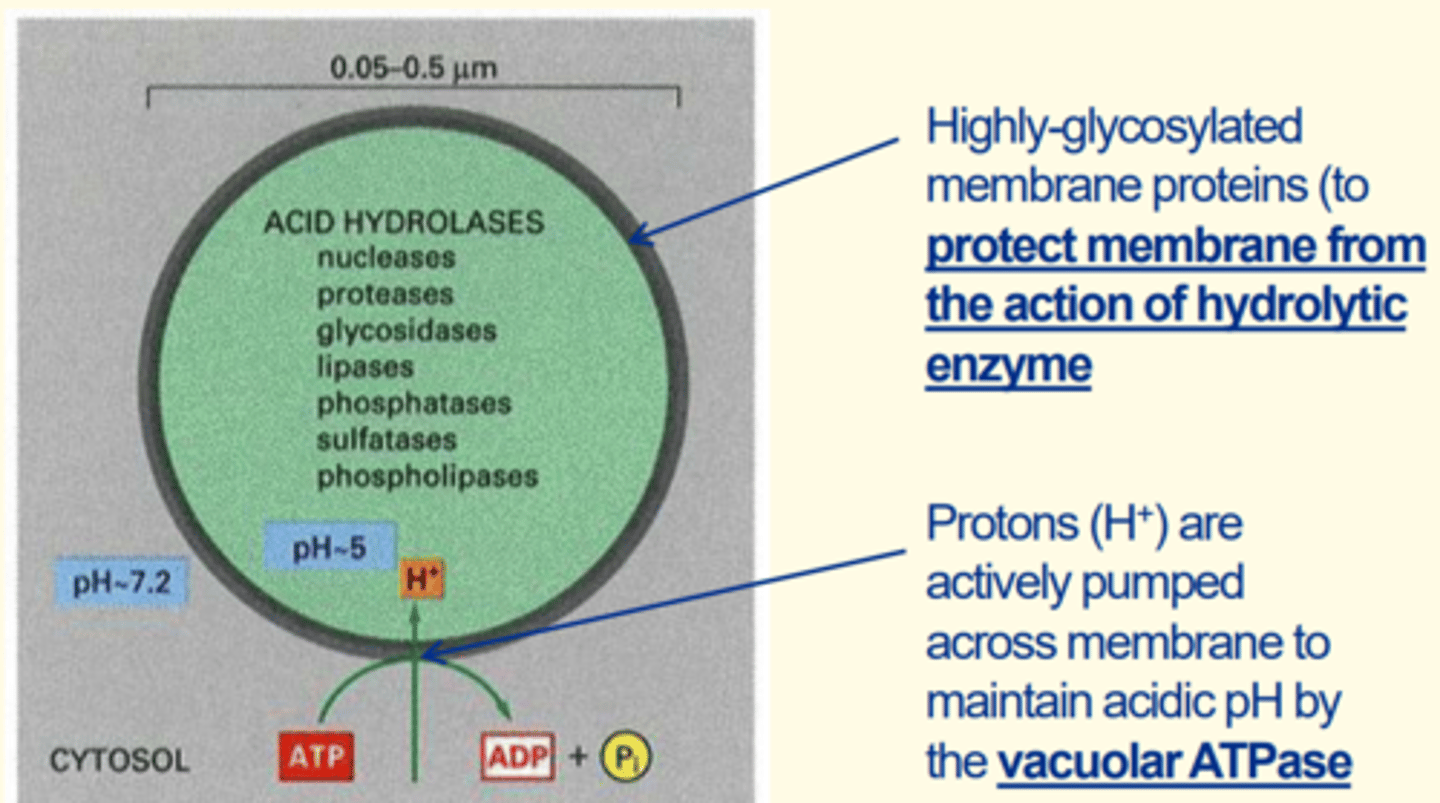
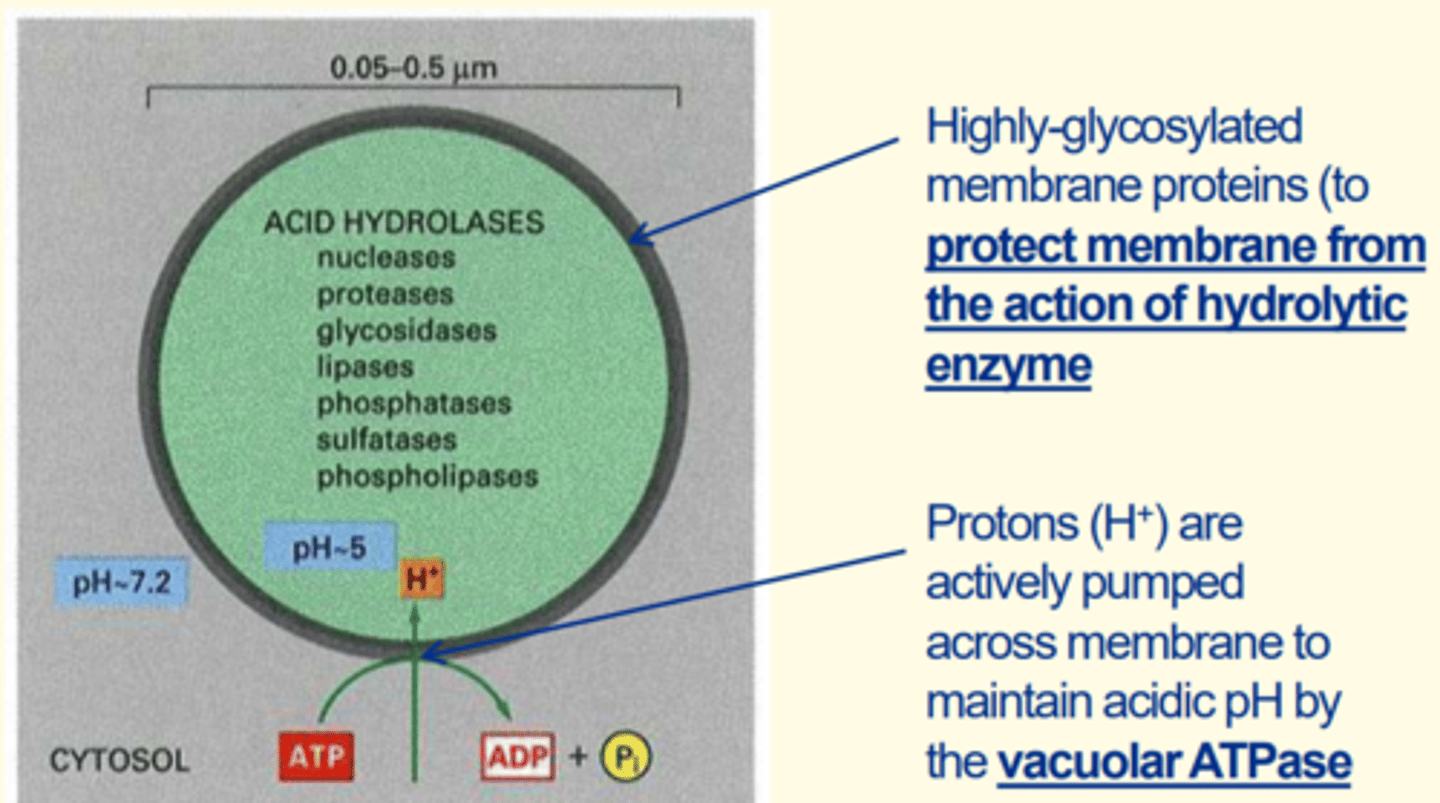
Lysosomes
• Organelle containing digestive enzymes called acid hydrolases (e.g., nucleases, lipases, phosphatases, proteases)
• Protons actively pumped across membrane to maintain acidic pH inside lysosomes via vacuolar ATPase
• Highly glycosylated membrane proteins (to protect lysosome membrane from action of hydrolytic enzymes inside them)
• Product of the Golgi
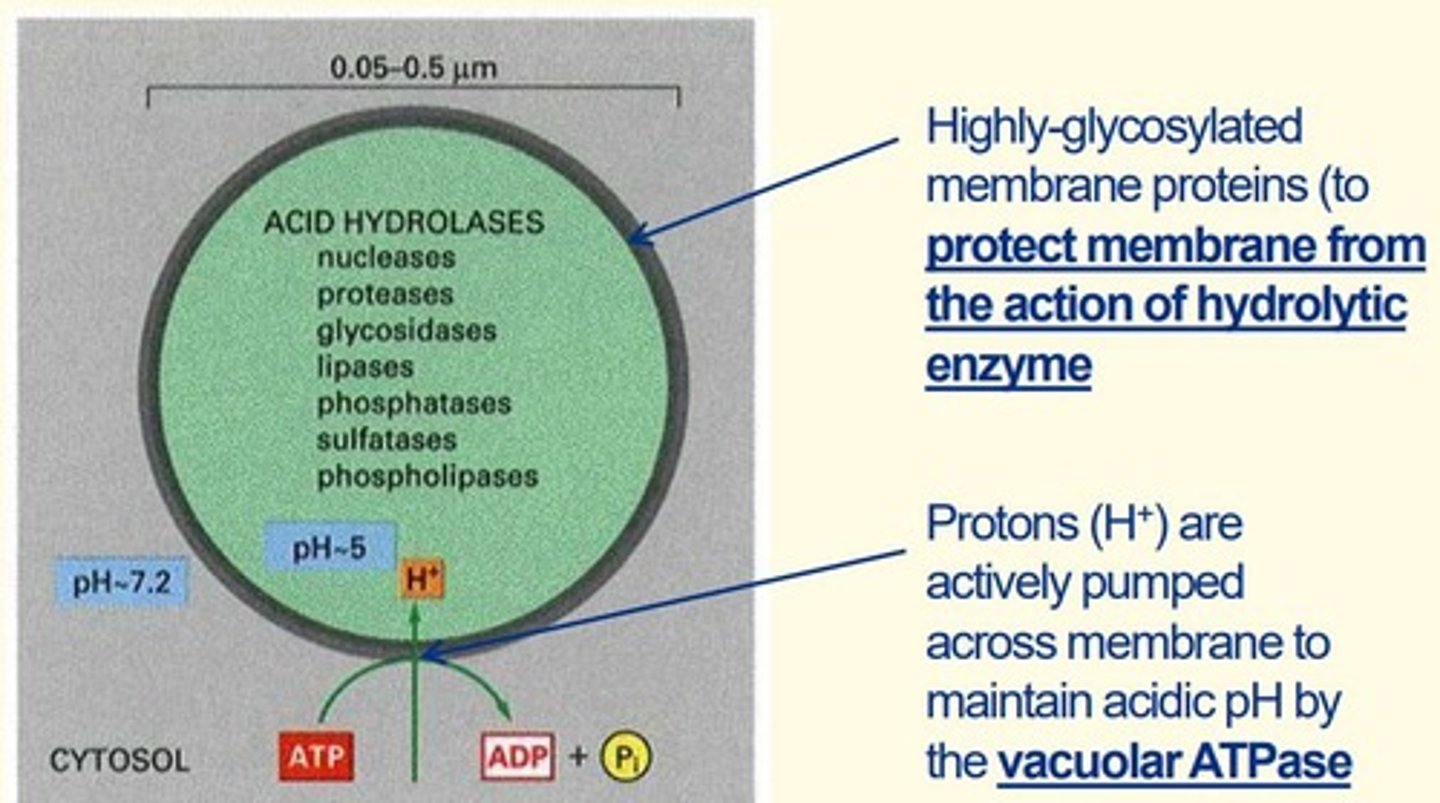
Two adaptations of the lysosome that make it efficient for its use
1) Protons actively pumped across membrane to maintain the acidic pH inside the lysosomes via vacuolar ATPase
2) Highly glycosylated membrane proteins around lysosomes to protect lysosome membrane from action of hydrolytic enzymes within them
What is the function of lysosomes
• Break down of non-functioning organelles/cellular components
• Digested products recycled
• Autophagy
Describe process of autophagy
1) Organelle engulfed by region of SER to form an autophagosome
2) Autophagosome fuses with lysosome = this forms a phagolysosome
3) Acid hydrolases (lysozymes) breakdown the organelle (autophagy) and digested products are recycled
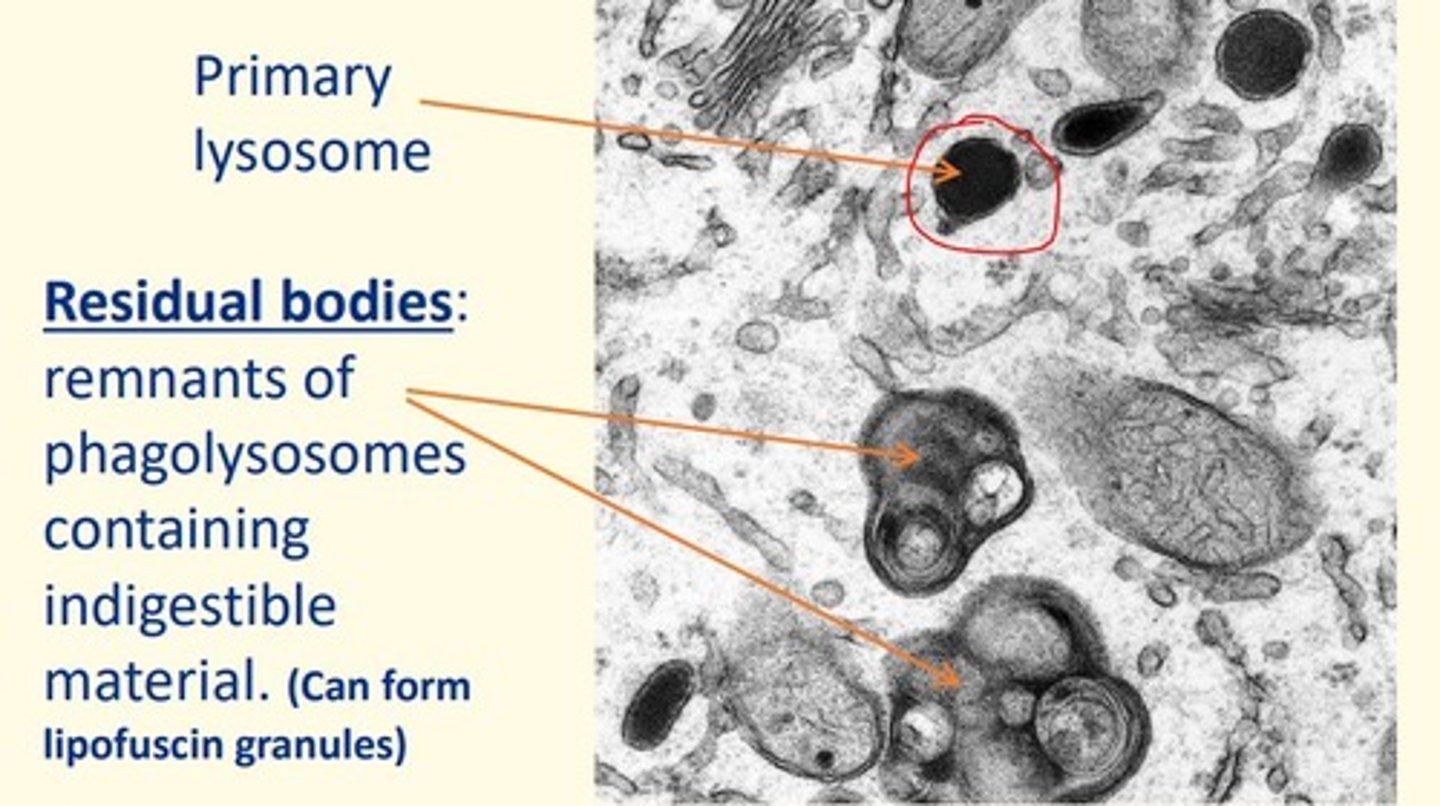
Name of structure in cells which are remnants of phagolysosomes containing indigestible material in the cell
Residual bodies
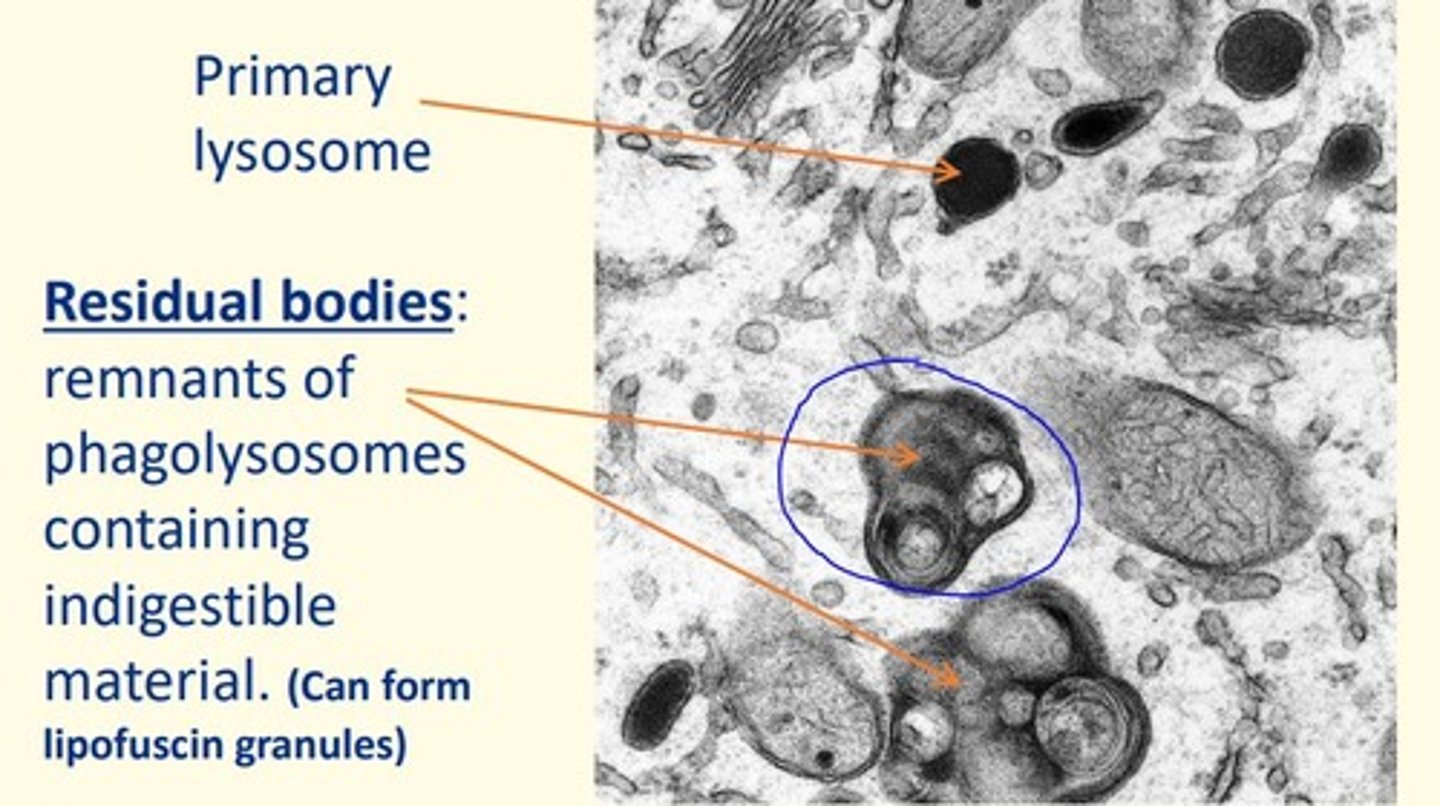
Defects in hydrolytic enzymes stored in lysosomes can lead to the accumulation of residual bodies which can lead to diseases known as...
Lysosomal storage disorders (LSDs)
Name two lysosomal storage disorders (LSDs)
1) Hurler syndrome
2) Tay-Sachs disease
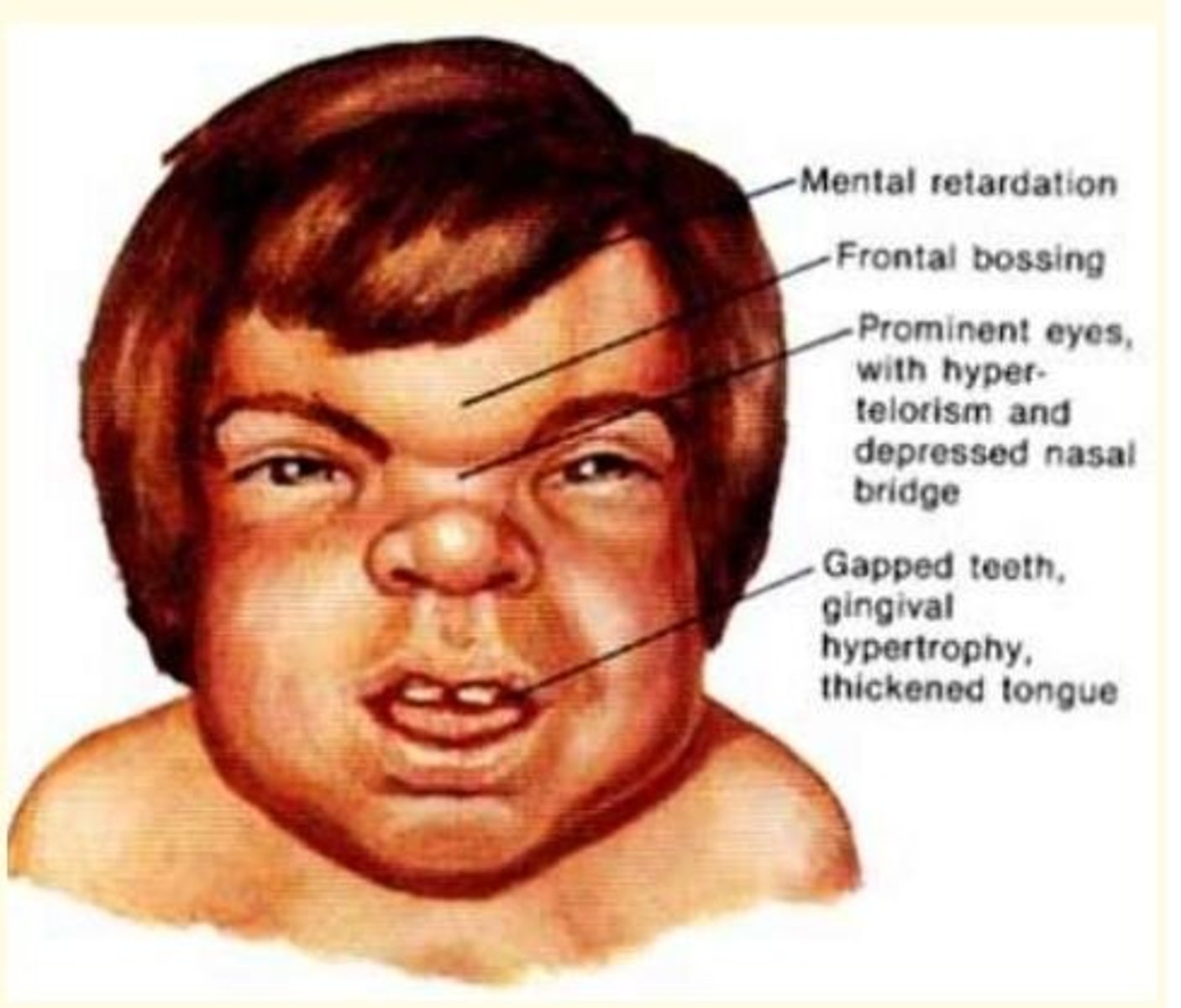
Hurler syndrome
• Lysosomal storage disorder (LSD)
• Accumulation of dermatan sulphate in lysosomes
• Mental retardation, frontal bossing, prominent eyes, hyper-telorism, depressed nasal bridge, gapped teeth, gingival hypertrophy, thickened tongue
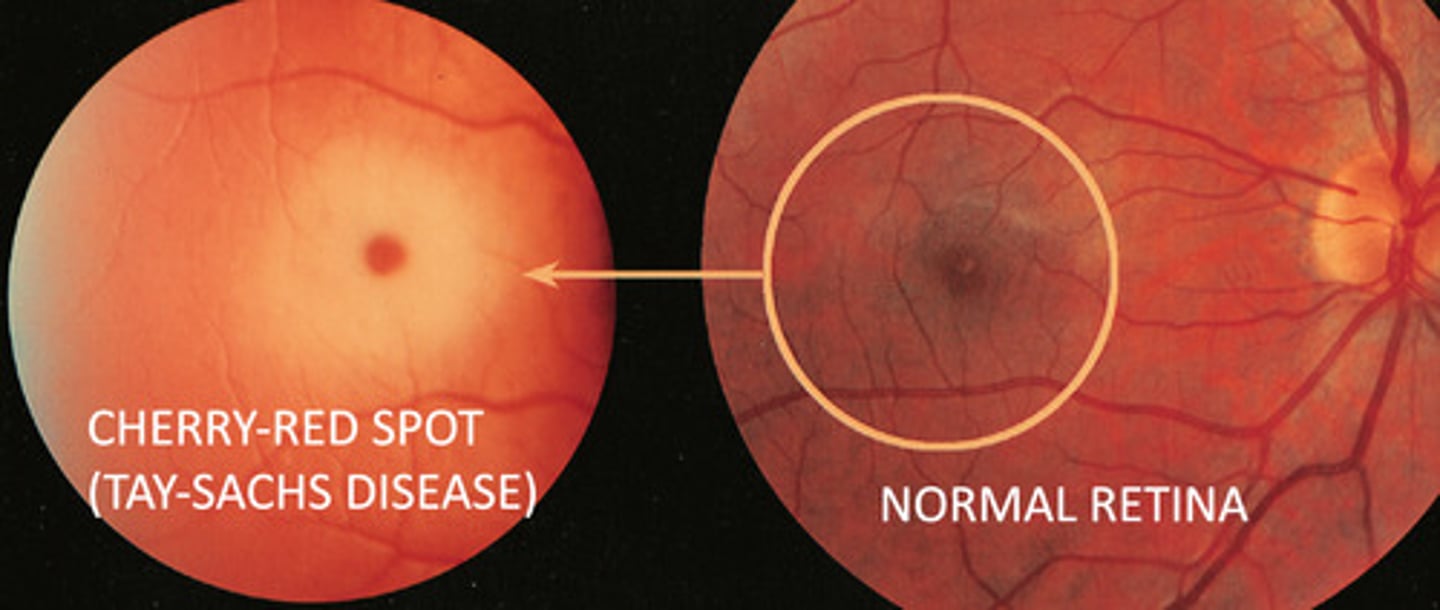
Tay-Sachs disease
• Lysosomal storage disorder (LSD)
• Lack of lysosomal enzyme β-hexosaminidase-A
• Accumulation of membrane phospholipid = GM2-ganglioside inside neurons
• Neuronal degeneration and demyelination
• Delayed development, exaggerated startle response, muscle weakness, cherry red spots in the eyes
Peroxisomes
• Small spherical membrane-bound organelles (d = 0.5-1 μm)
• Contain oxidase enzymes involved in oxidation of multiple substrates - detoxify harmful substances
• Important in β-oxidation of very long-chain fatty acids (C18 and above)
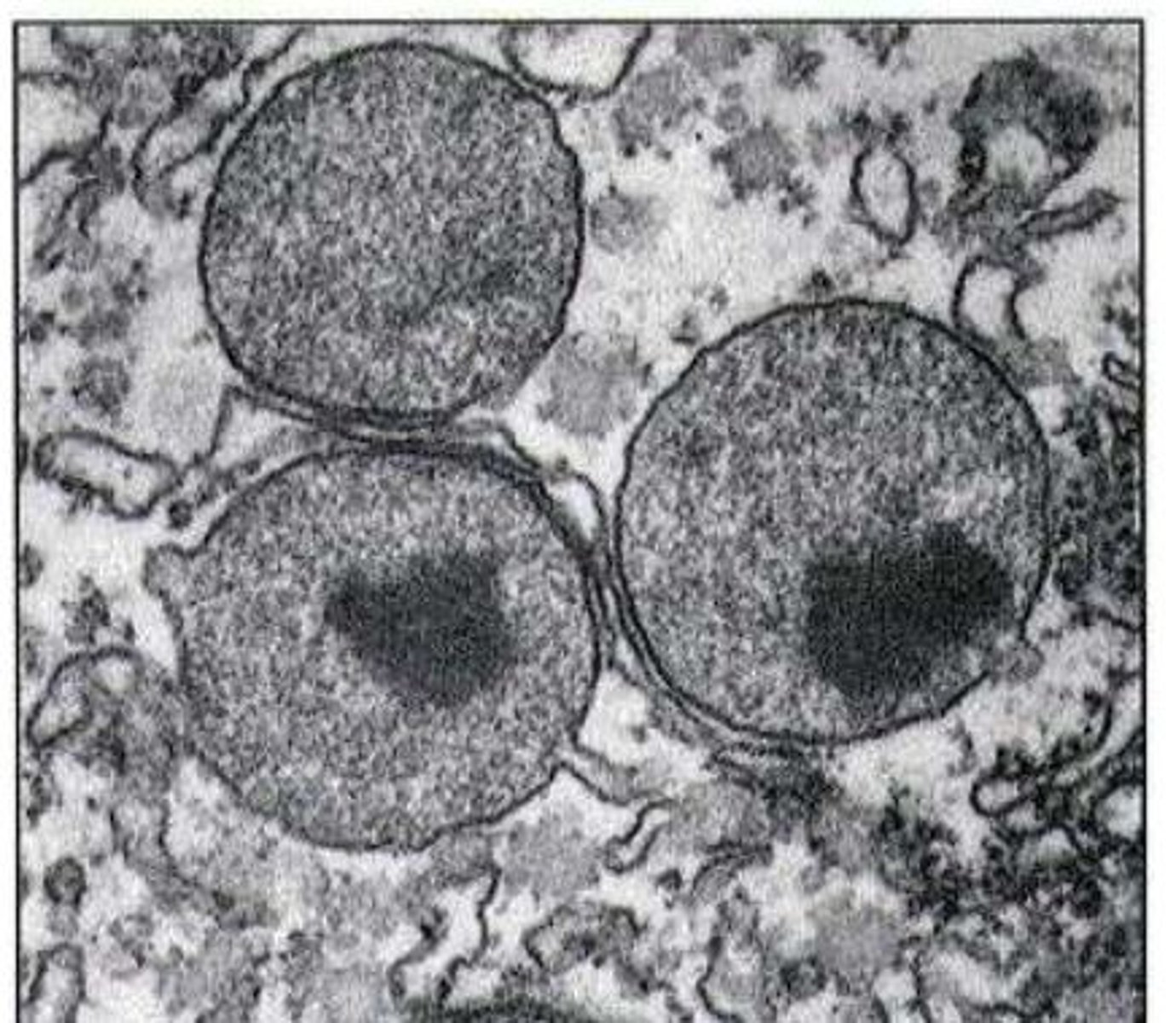
Where can abundant peroxisomes be found (what cells)?
• Liver and kidney cells = where they oxidise molecules including ethanol, phenols, formic acid and formaldehyde
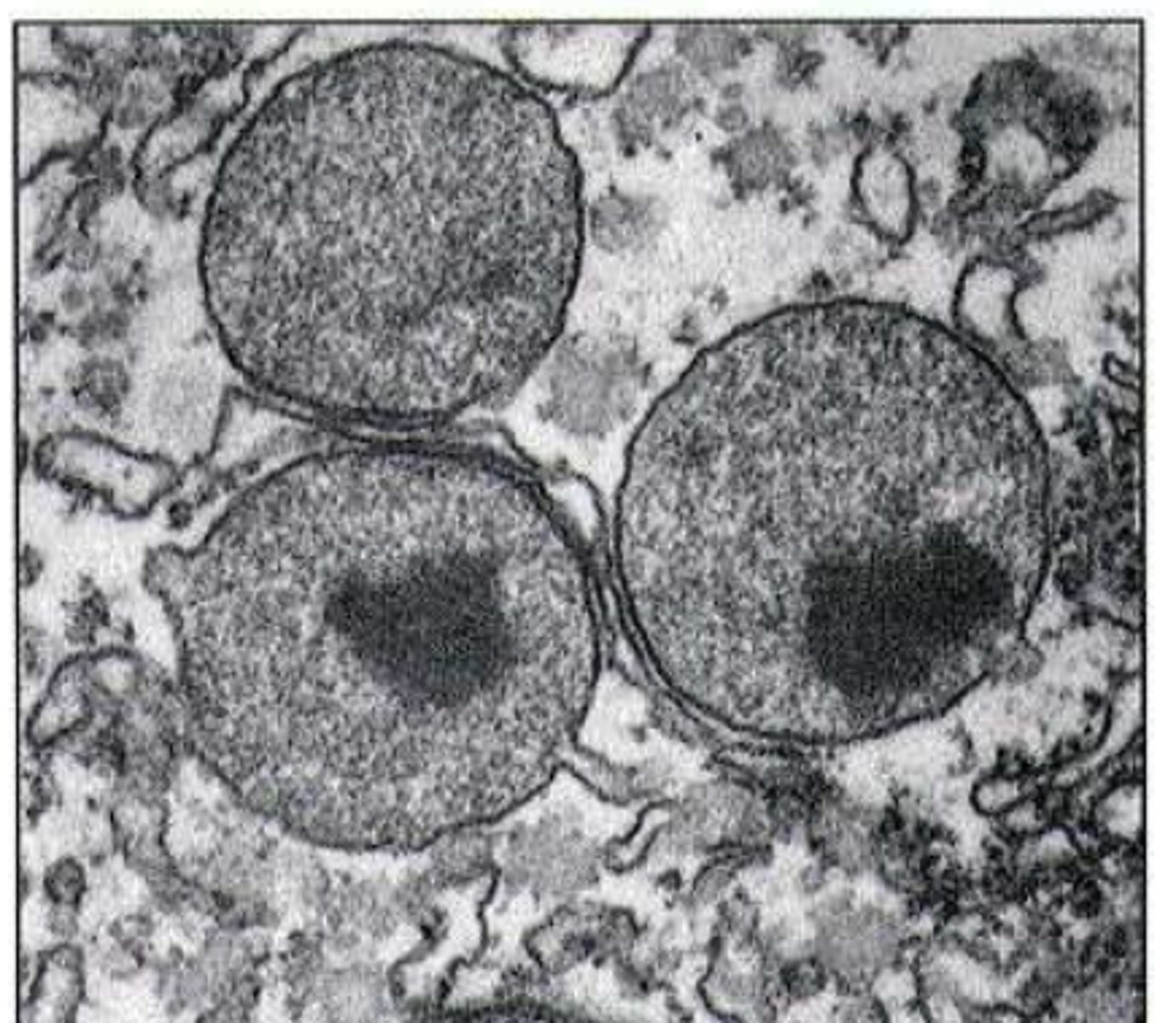
What do peroxisomes detoxify (give examples of susbtances)
• Ethanol
• Phenols
• Formic acid
• Formaldehyde
Disorder caused due to impaired β-oxidation of fatty acids within peroxisomes
Adrenoleukodystrophy
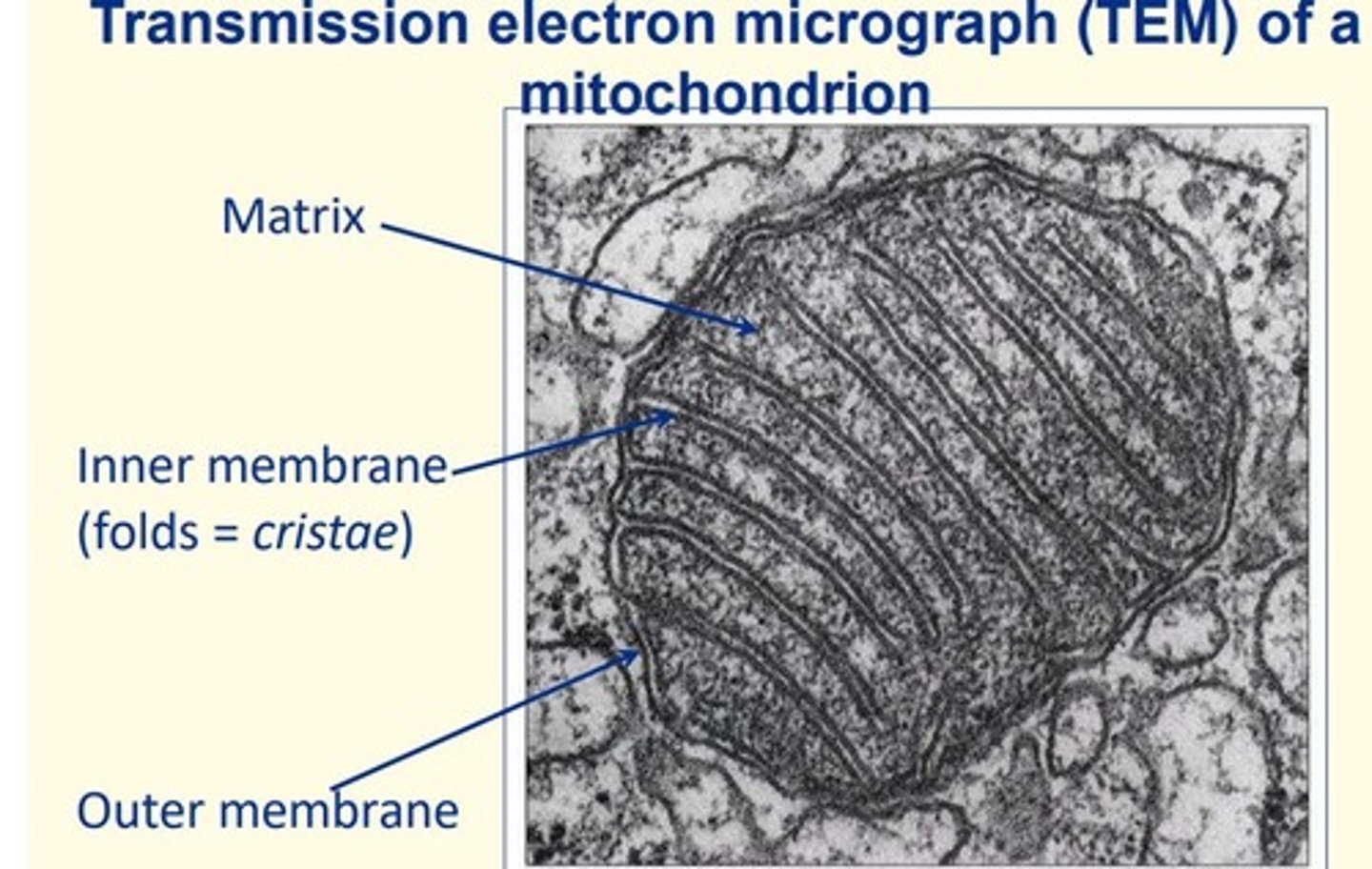
Mitochondria
• Double-membraned organelle measuring 0.5-2 µm
• Inner membrane cristae folds and inner matrix
• Site of ATP synthesis = contains enzymes for TCA cycle, oxidative phosphorylation
• Functions in = apoptosis, calcium signalling and steroidogenesis
• Contains its own circular genome encompassing 37 genes
Disorder caused by specific mutations in mitochondrial DNA (mt-DNA)
Kearns-Sayre syndrome
Examples of cells that have abundant mitochondria
Cells that have high energy requirements have abundant mitochondria
• Cardiac muscle
• Sperm flagellum (movement/motile)
The cytoskeleton is made up of...
1) Microtubules
2) Microfilaments
3) Intermediate filaments
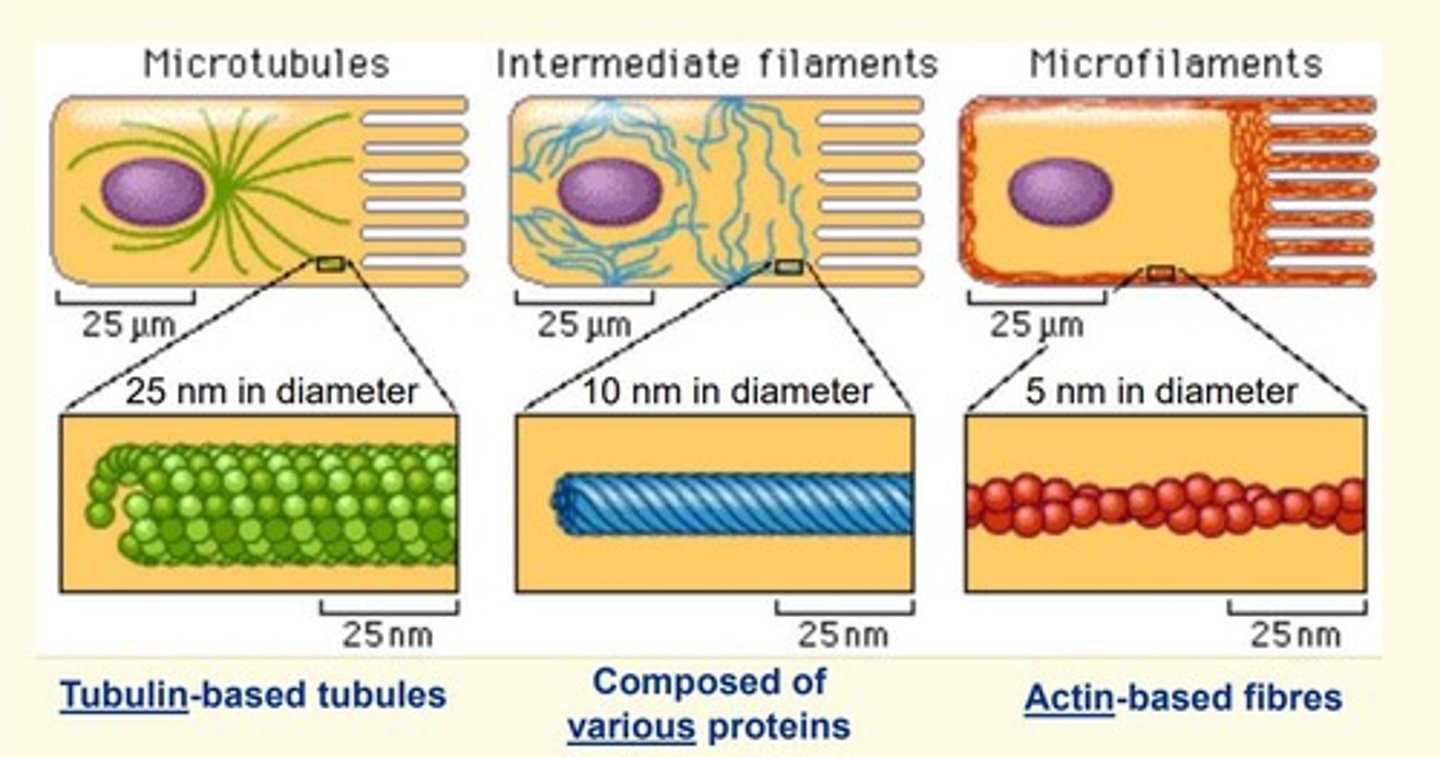
Microtubules are made of
tubulin
diameter = 25nm
Microfilaments are made of
actin
diameter = 5nm
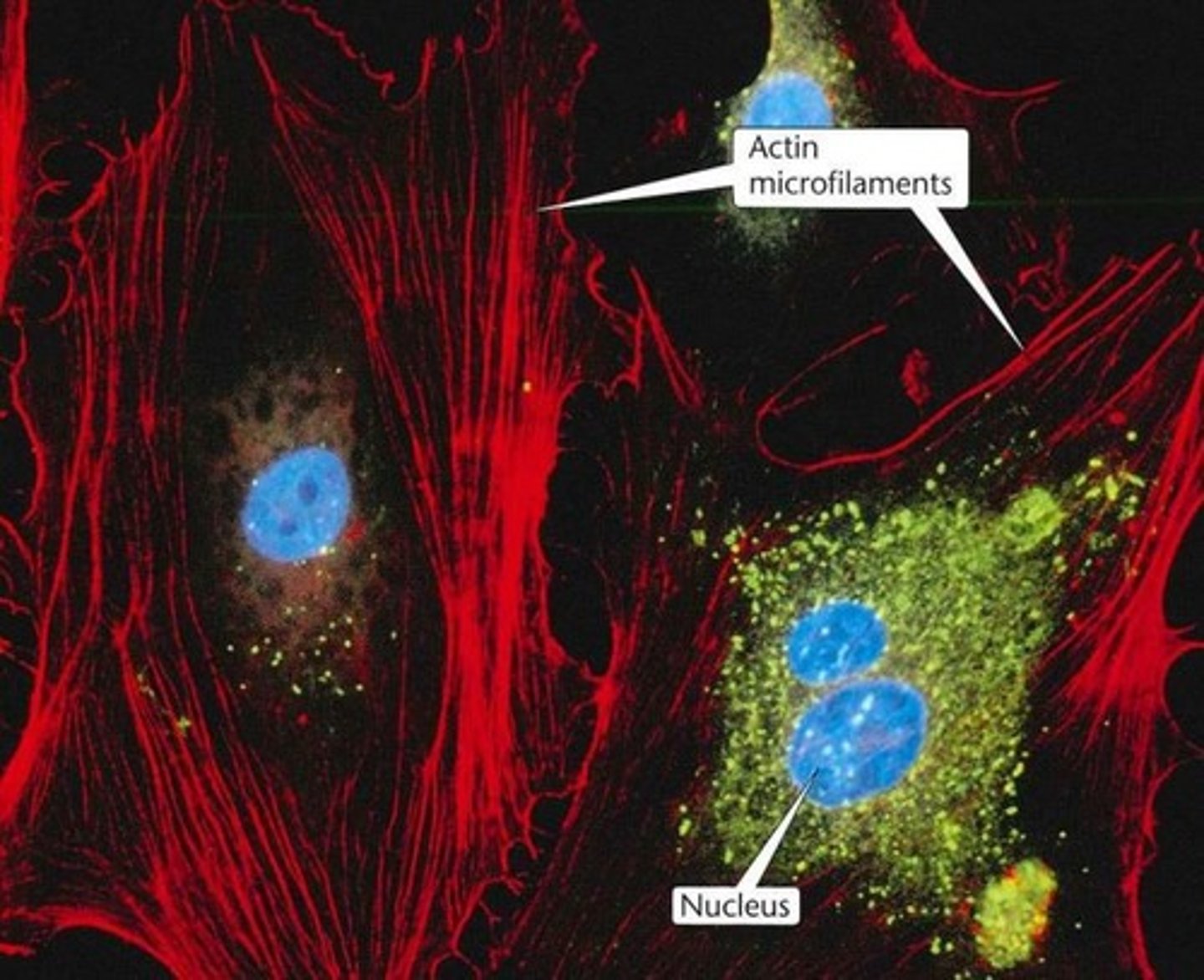
Intermediate filaments are made of
various proteins e.g., keratin
diameter = 10nm
Microfilaments
• Fine, threadlike actin-based proteins found in the cell's cytoskeleton
• 5nm diameter
• Dynamic
Filamentous actin (F-actin)
• Twisted strand composed of two rows of globular G-actin molecules to form a double helix (5nm diameter)
• Polymers of globular-actin (G-actin)
• Cortical in distribution
Each microtubule is composed of ___ protofilaments of α and β tubulin dimer subunits
13
Microtubules are ___, with GTP-powered polymerisation occurring at both ends but is more rapid at the ___ end (β end)
Microtubules are polar, with GTP-powered polymerisation occcuring at both ends but is more rapid at the + end (β end)
In cross-section, each microtubule is ___nm in diameter
25nm
What is the name of the special arrangement of microtubules in a cilium or flagellum?
9+2 arrangement
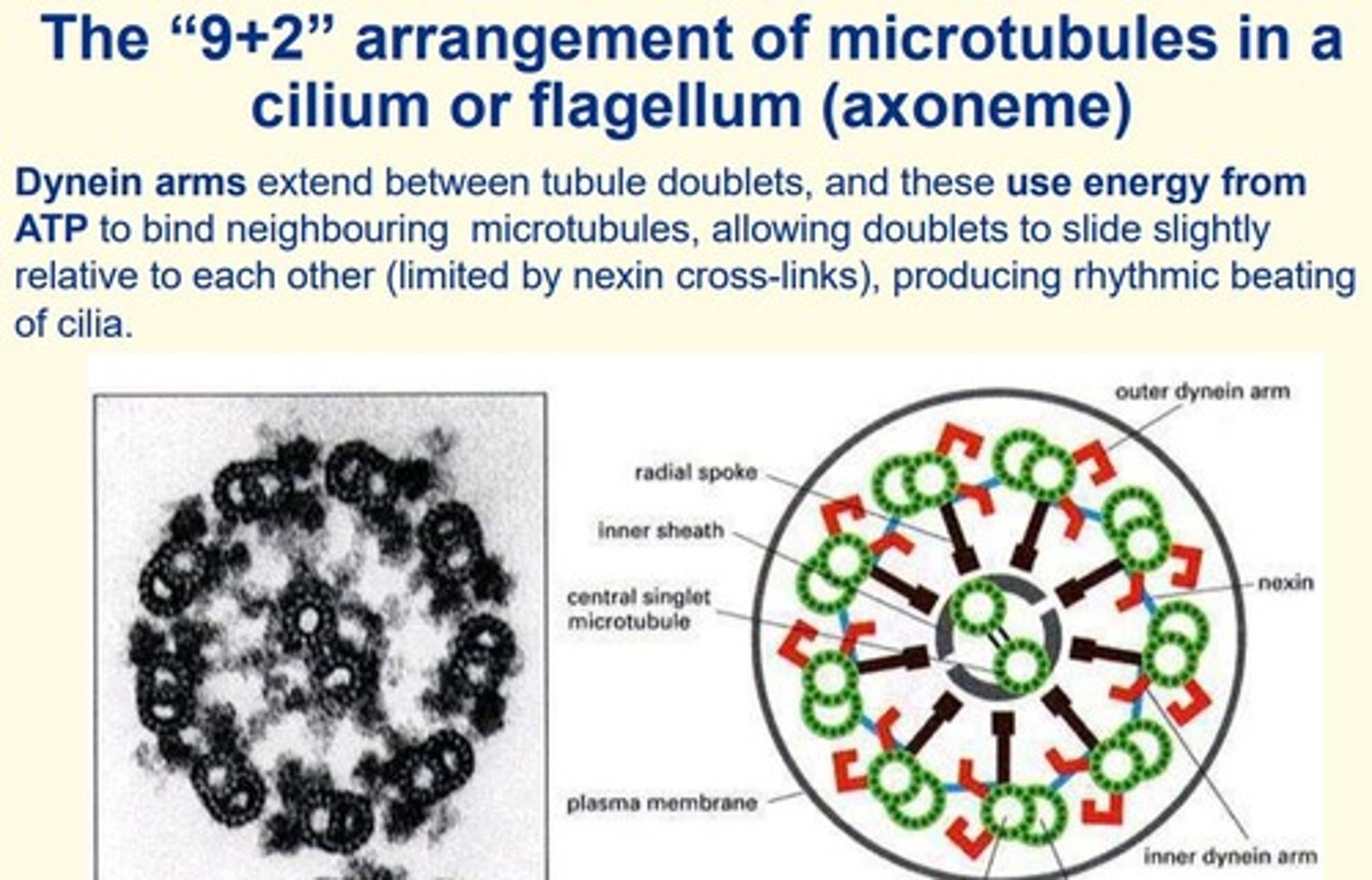
Microtubules associate with ___ to allow the movement of cilia and flagella
motor proteins
Give some other functions of microtubules in different cells
- Mitotic spindle apparatus = microtubules (cellular division)
- Allow synaptic vesicles to move along axons to axon terminals in neurons
- Form 'tracks' for organelle movement and vesicle trafficking
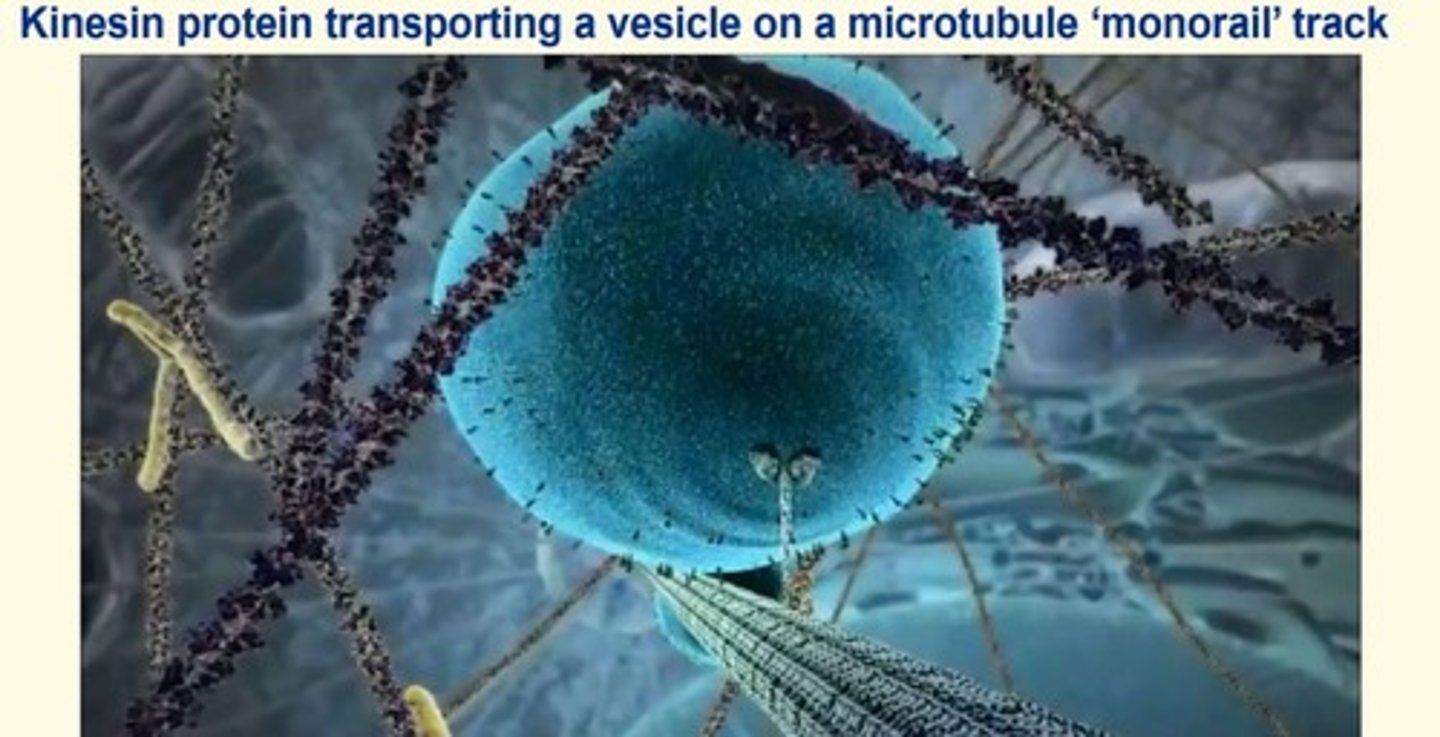
What are the names of the motor proteins that associate with microtubules to allow for organelle movement and vesicle trafficking in the cell?
- Kinesin
- Dynein
Intermediate filaments
• Threadlike proteins in the cell's cytoskeleton that are roughly twice as thick as microfilaments
• Provide structural support for cell
Give some examples of intermediate filaments in different cells and their names...
Epithelial cells = keratin
Mesenchymal cells = vimentin
Muscle cells = desmin
Mutations in the genes encoding basal keratins (e.g., K5 and K15) cause...
Skin blistering
• Due to a loss of cohesion between the basal epithelial cells and the basement membrane
Which of the following best describes the roles of the nucleolus?
a) It is a site of condensed DNA
b) It is the site of messenger RNA synthesis
c) It is the site of ribosomal RNA synthesis
d) It is the site of active DNA synthesis.
e) It is an artifact of processing
c) It is the site of ribosomal synthesis
Which of the following accurately describes the function of peroxisomes?
a) Detoxification
b) Protein synthesis
c) Destruction of non-functional proteins
d) Trafficking
e) Lipid synthesis
a) Detoxification
At which of the following anatomical sites might you expect cells to contain an abundance of SER?
Enterocytes of the gut [...]
Mammary gland [...]
Ovaries [...]
Skeletal muscle [...]
Adrenal cortex [...]
Testis [...]
Islets of Langerhans of the pancreas [...]
Thyroid gland [...]
Liver [...]
Kidney tubules [...]
Enterocytes of the gut No
Mammary gland Yes
Ovaries Yes
Skeletal muscle Yes
Adrenal cortex Yes
Testis Yes
Islets of Langerhans of the pancreas No
Thyroid gland No
Liver Yes
Kidney tubules No
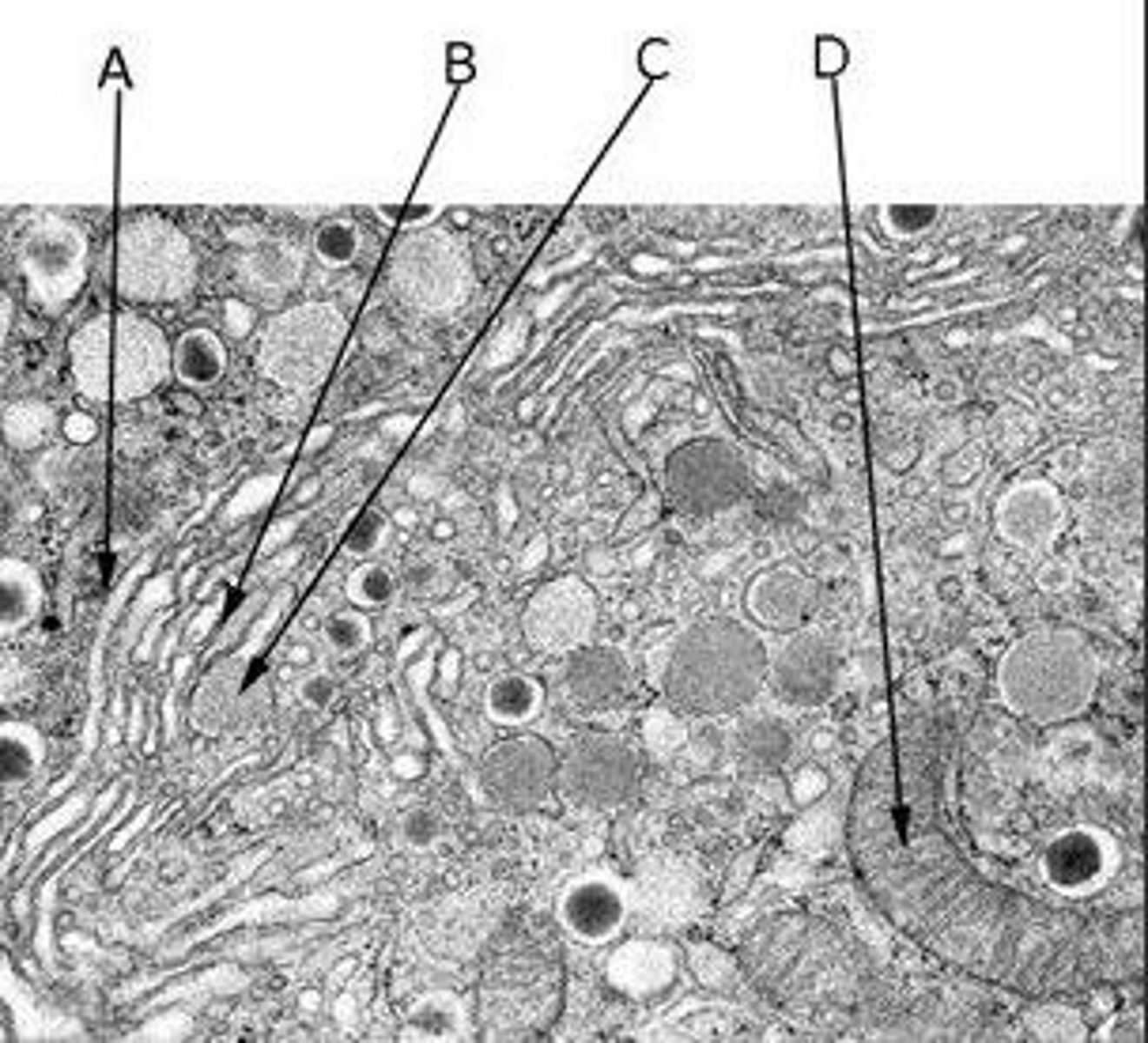
Identify the features in the following diagram showing Golgi body profiles in an islet cell of the pancreas
A Golgi body's cis face
A vesicle budding from the trans face of a Golgi body
A Golgi body's trans face
A mitochondrion
A) A Golgi body's cis face
B) A Golgi body's trans face
C) A vesicle budding from the trans face of a Golgi body
D) A mitochondrion
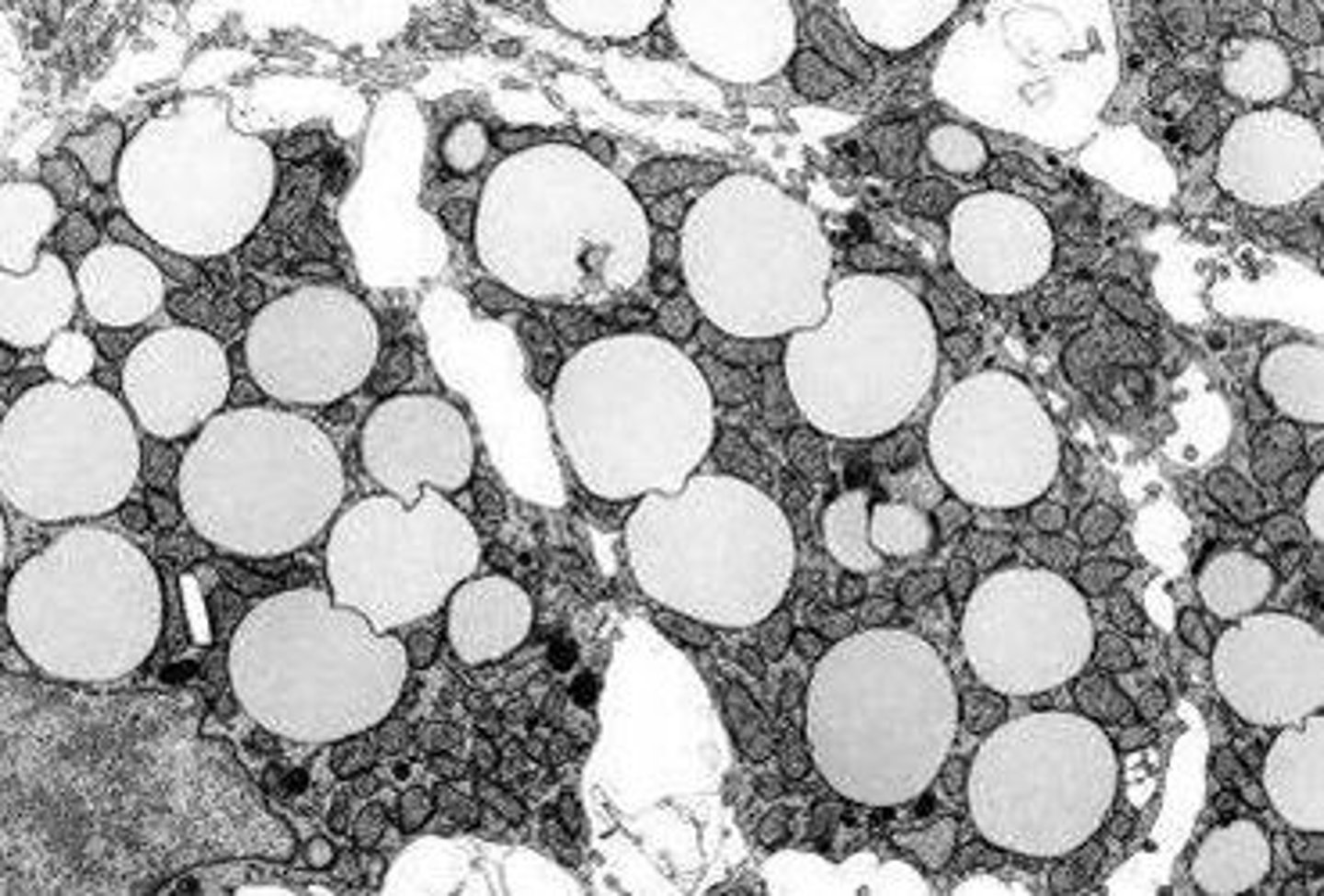
The roughly spherical inclusions in the electron micrograph shown below are not membrane-bound, and are common in adipocytes and steroidogenic cells. What are they?
a. Lipid droplets
b. Endosomes
c. Secretory vesicles
d. Lysosomes
e. Peroxisomes
a) Lipid droplets
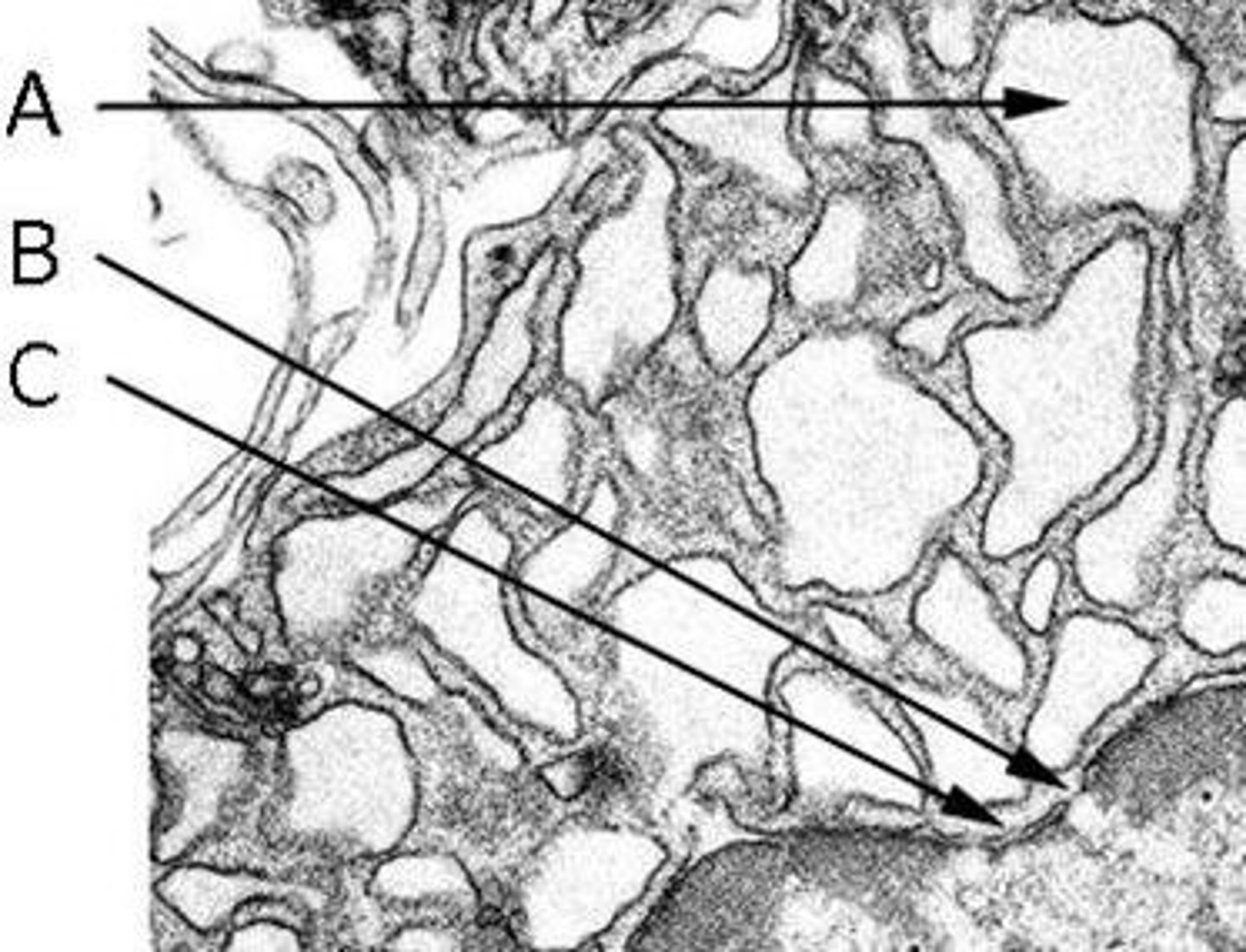
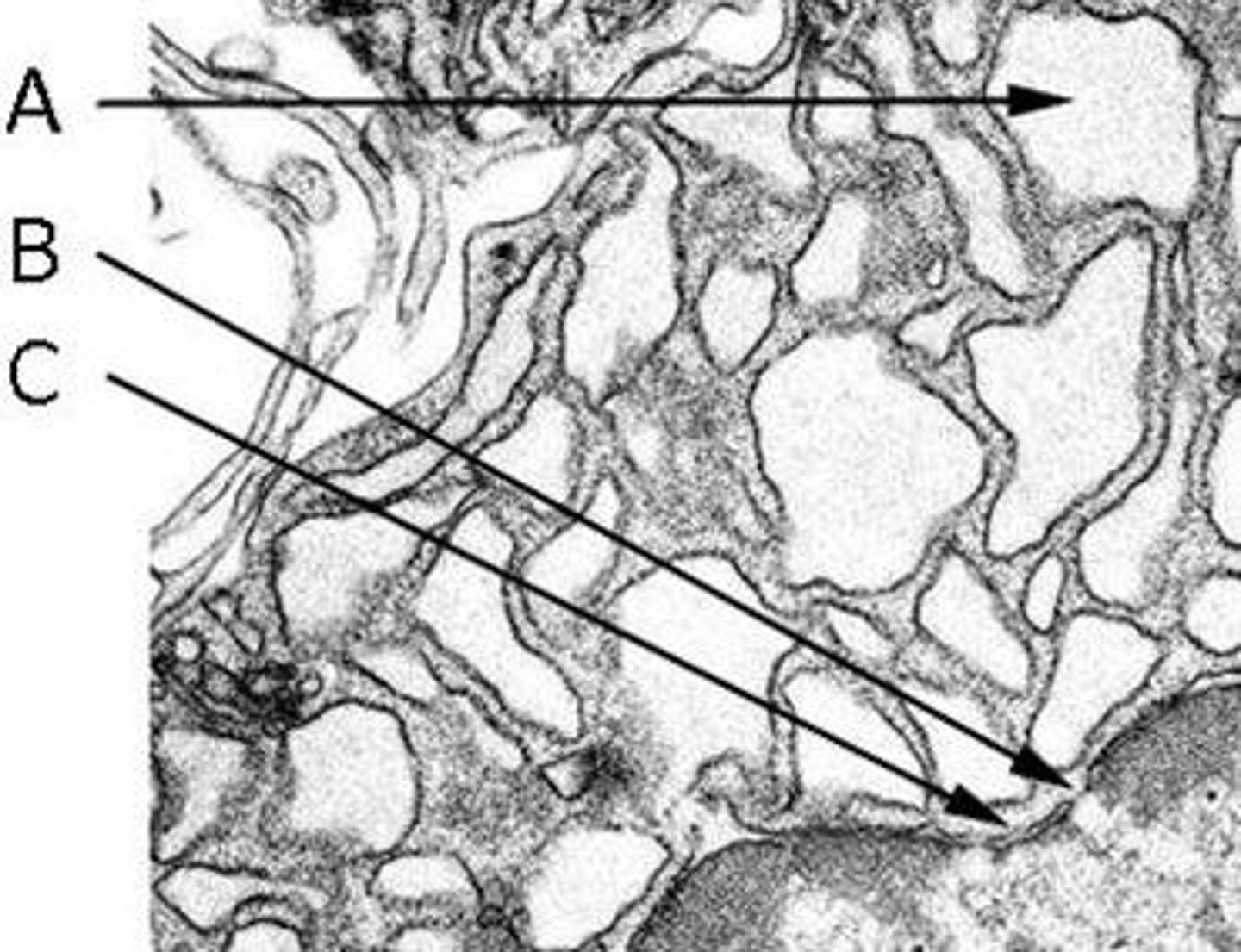
Identify the features in the following TEM image of RER in a plasma cell
The double membrane of the nuclear envelope
The intracisternal space of the RER
A nuclear pore
A) The intracisternal space of the RER
B) A nuclear pore
C) The double membrane of the nuclear envelope
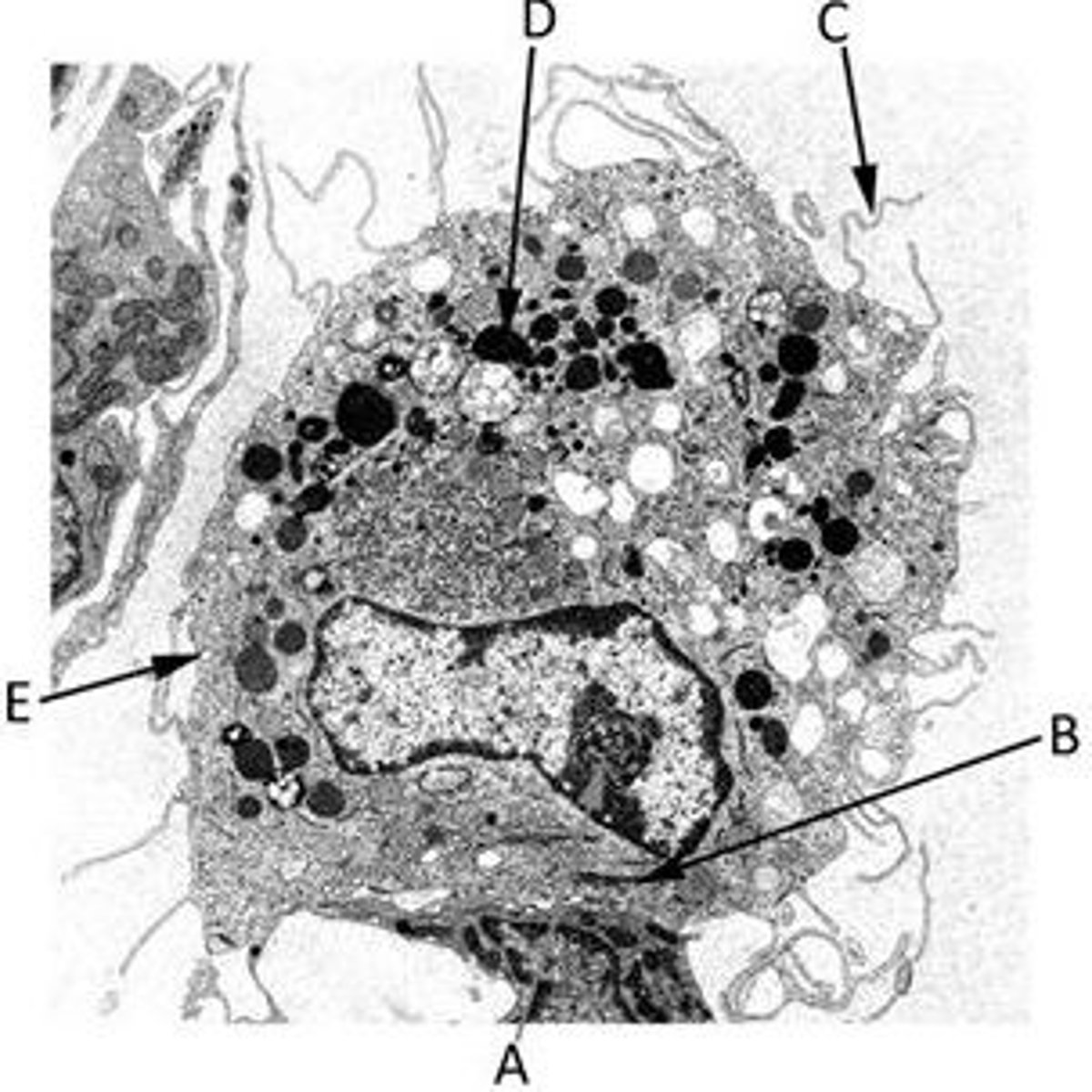
Match the label with the most appropriate description in the following TEM of a macrophage.
A nucleolus
A pinocytotic vesicle
A cytoplasmic extension (a pseudopod)
A lysosome
A Golgi body
A) A nucleolus
B) A Golgi body
C) A cytoplasmic extension (a pseudopod)
D) A lysosome
E) A pinocytic vesicle
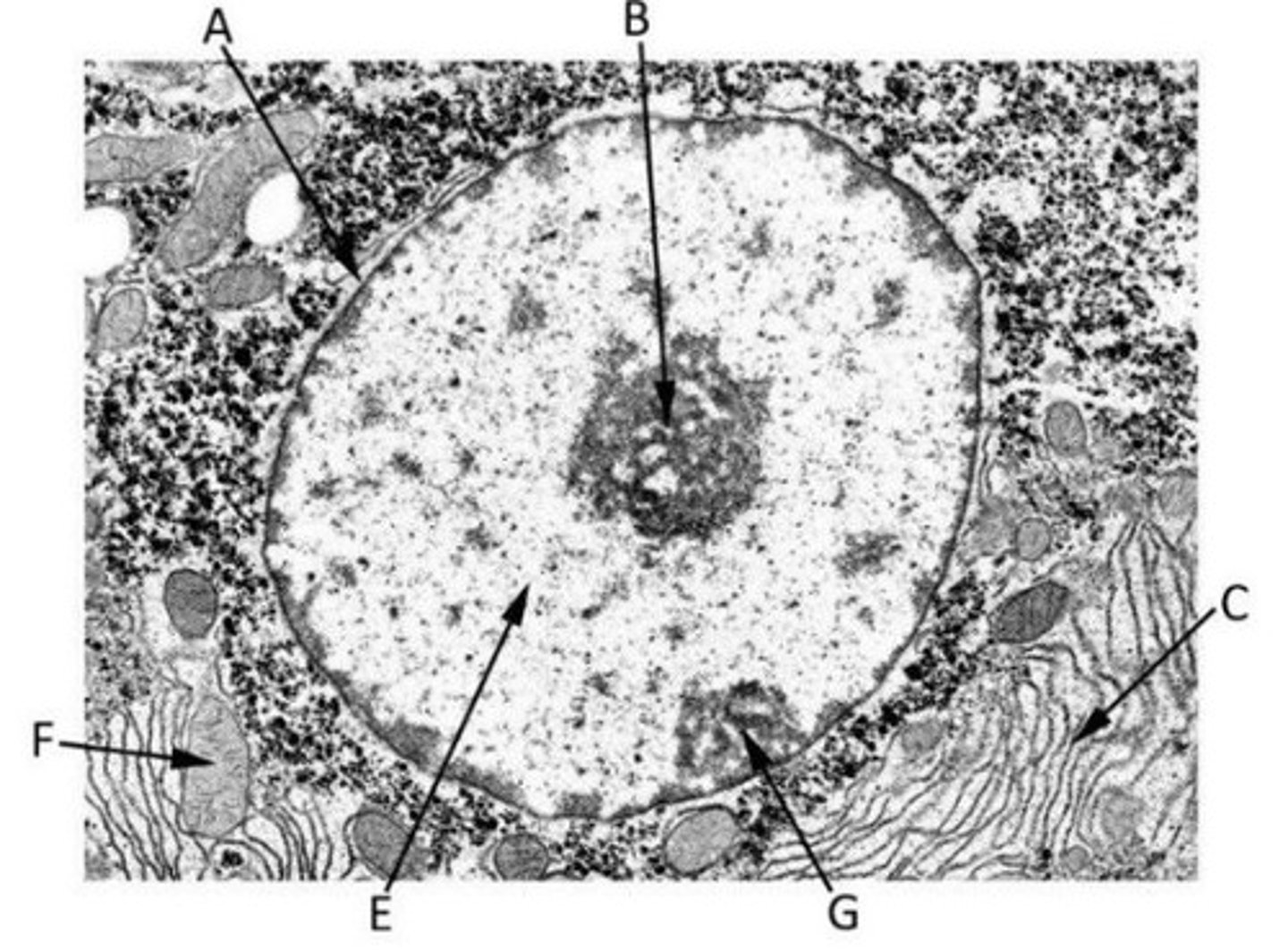
Identify the featurees in this TEM image of a nucleus
A) Nuclear envelope
B) Nucleolus
C) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
E) Euchromatin
F) Mitochondrion
G) Heterochromatin
Pseudopodia extended by macrophages are important in the sensing and capture of prey. The dynamic assembly of which cytoskeletal component allows the movement of pseudopodia?
a) Intermediate filaments
b) Microfilaments
c) Myosin filaments
d) Microtubules
b) Microfilaments
Identify the features in the following TEM image of RER in a plasma cell.
The double membrane of the nuclear envelope
The intracisternal space of the RER
A nuclear pore
A. The intracisternal space of the RER
B. A nuclear pore
C. The double membrane of the nuclear envelope