Architectural Acoustics: Sound Absorption, Reflection, and Transmission Concepts
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What is sound absorption?
The loss of sound energy when sound waves contact an absorbent material, preventing sound from being reflected back into space.
How do sound-absorbing materials affect a space?
They create a suitable acoustic environment by reducing reverberation, which affects how sound is perceived in the space.
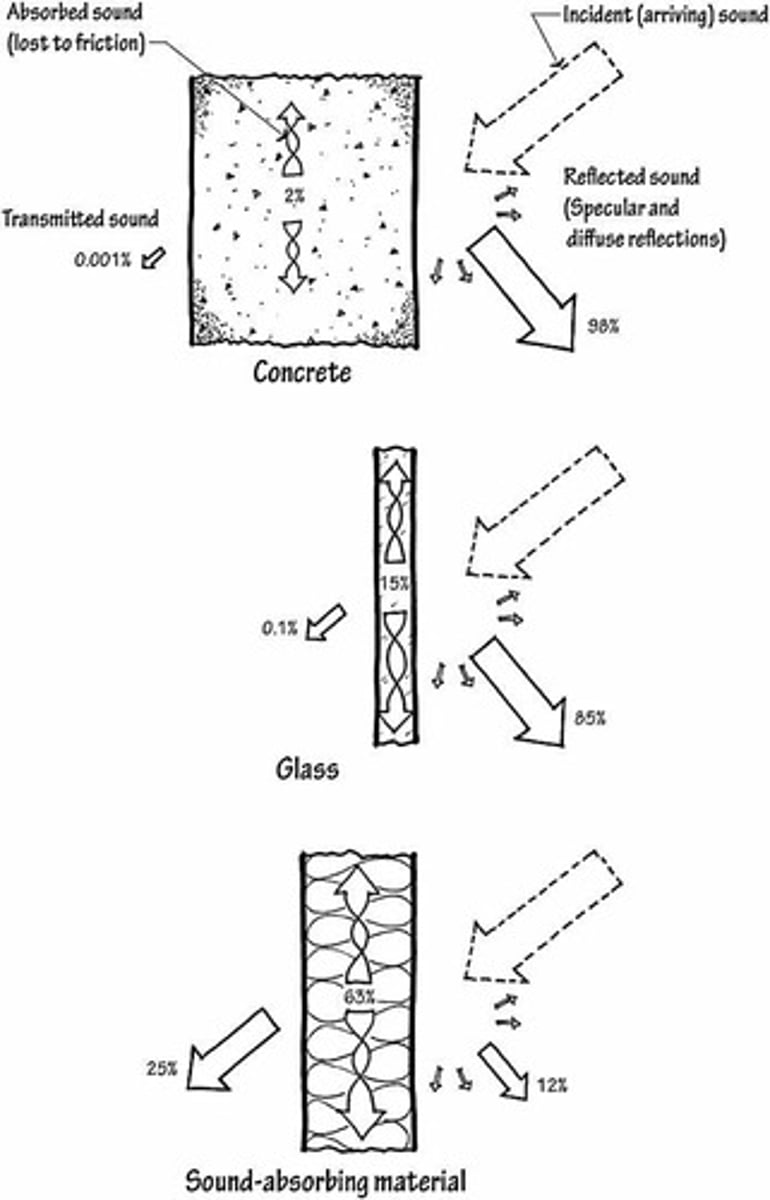
What happens to sound energy when it is absorbed by a material?
Part of the absorbed energy is transformed into heat, and part is transmitted through the material.
What is reverberation?
The persistence of sound in a space due to multiple reflections off surfaces.
Why is sound absorption important?
It lessens echo and reverberation, improving speech intelligibility and overall clarity in a room.
What is sound reflection?
The bouncing back of sound waves from a surface when they strike it.
What determines the angle of sound reflection?
The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, following the laws of reflection.
What is sound transmission?
The degree to which sound is transferred between two materials, depending on their acoustic impedance.
How can sound transmission be reduced between rooms?
By installing sound insulation materials behind walls, floors, or ceilings to prevent sound from penetrating.
What is the Sound Absorption Coefficient (SAC)?
The ratio of absorbed sound intensity in a material to the incident sound intensity, indicating the sound-absorbing quality of a surface.
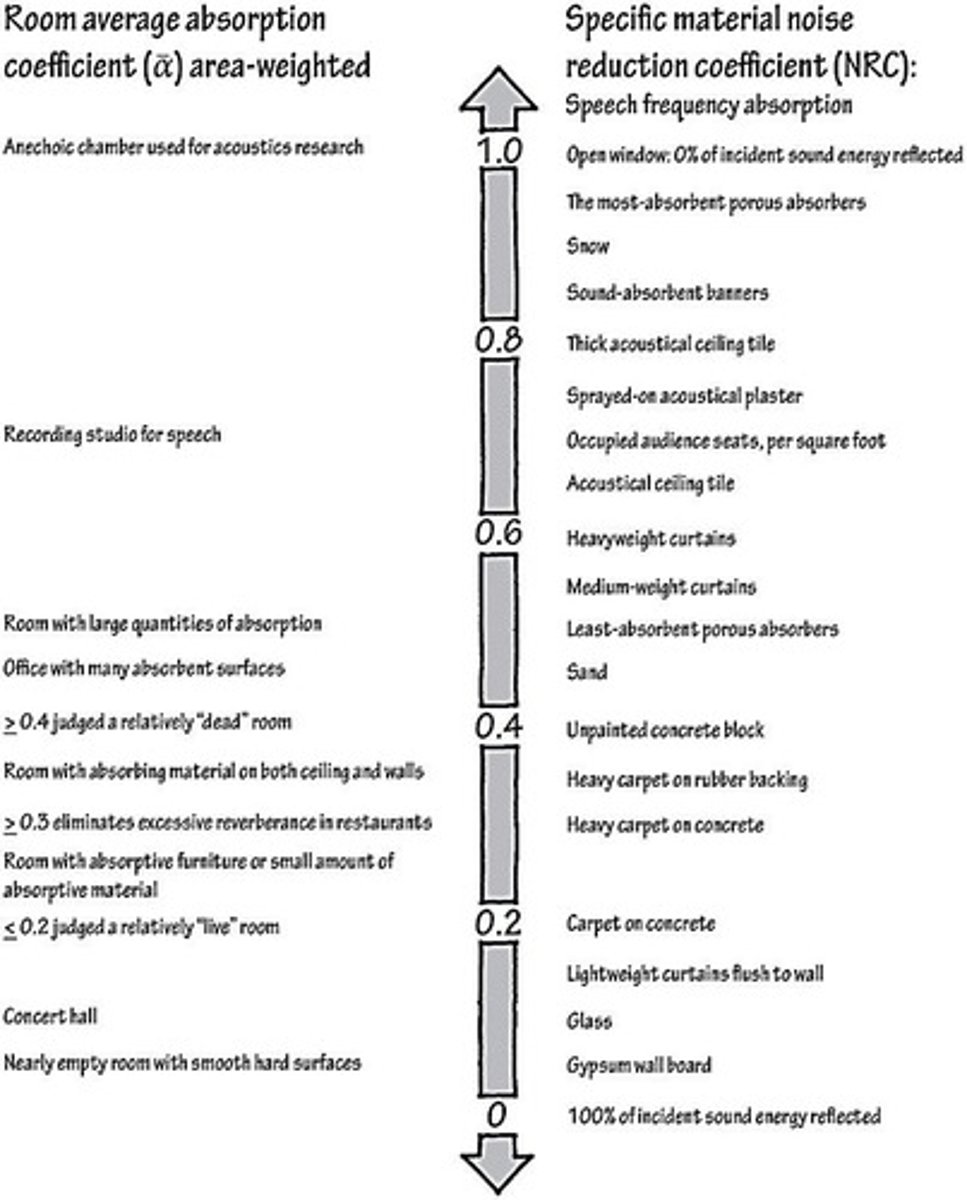
What does a SAC value of 1.0 indicate?
That no sound energy incident on that surface returns to the room, meaning it is fully absorbed.
What is the formula for total sound absorption in a room?
A = a1s1 + a2s2 + a3s3 + ..., where A is total absorption, ai is the SAC of surface i, and si is the area of surface i.
What is the significance of sound insulation?
It controls sound transmission between rooms, enhancing privacy and reducing noise pollution.
What is the effect of too much sound absorption in a space?
It can make the music sound flat and require performers to work harder to maintain sound quality.
What materials are commonly used for sound absorption?
Materials like carpets, curtains, and acoustic panels are used to absorb sound energy.
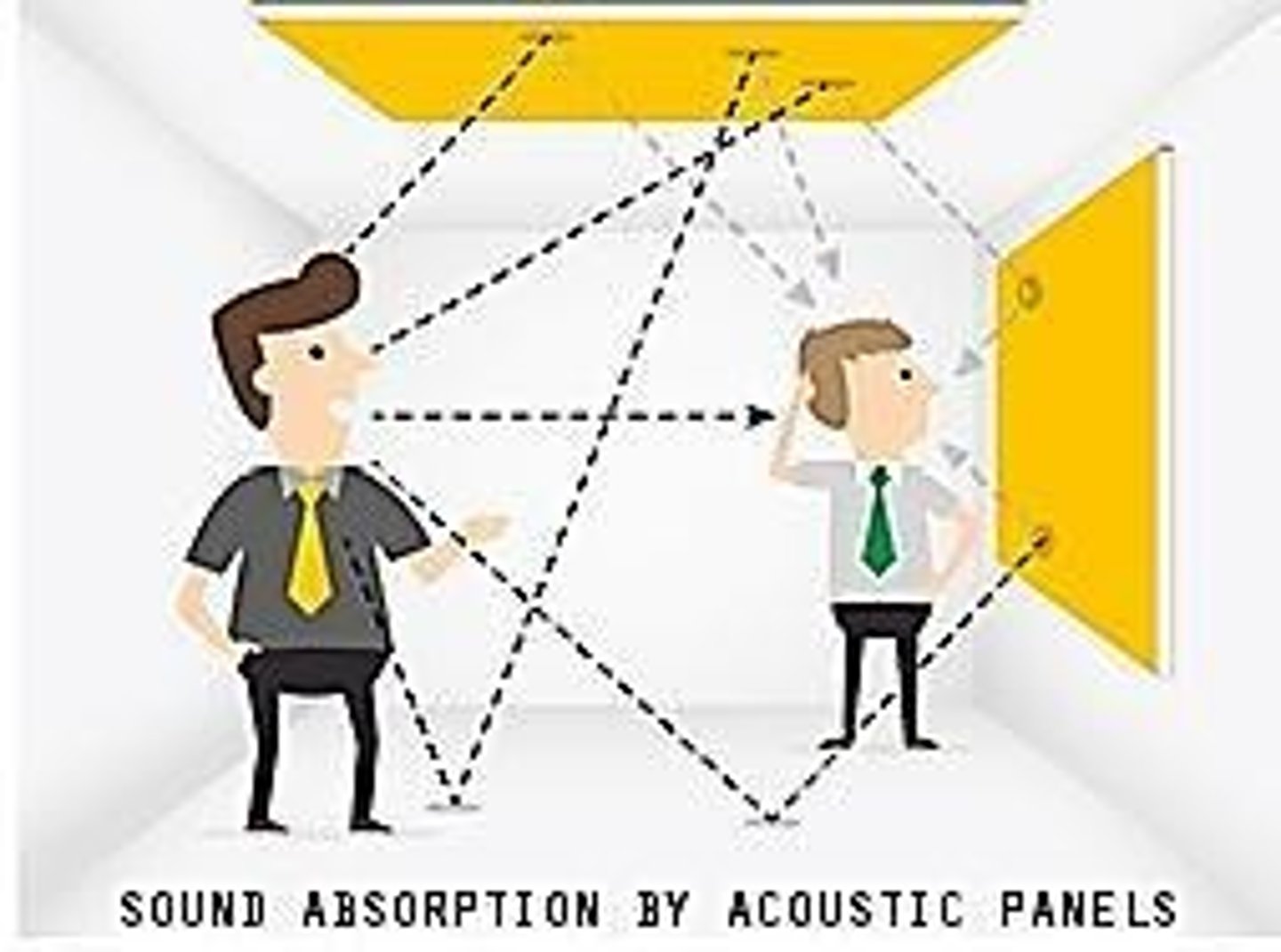

What is the relationship between sound absorption and room acoustics?
Sound absorption directly impacts the acoustics of a room by controlling echo and clarity.
What is a practical example of sound absorption in a performance space?
Using sound-absorbing materials in an auditorium to enhance the quality of music and speech.
What is the role of surface roughness in sound reflection?
Rough surfaces can scatter sound waves, affecting how sound is reflected in a space.
What is the purpose of creating a cavity between adjoining spaces?
To reduce sound transmission by filling it with heavy insulation to prevent sound from penetrating.
How does sound behave in a medium?
Sound waves can be absorbed, reflected, or transmitted depending on the properties of the medium they encounter.
What are some common sound-absorbing materials?
Acoustic panels, foam, carpets, and curtains are examples of materials that absorb sound.
What is the impact of sound transmission on privacy?
High sound transmission can lead to a lack of privacy between rooms, making conversations audible.
How does sound absorption improve speech intelligibility?
By reducing background noise and echo, making it easier to understand spoken words.
What is the effect of sound insulation on building design?
It requires careful planning and installation to effectively reduce sound transmission in a building.
What is the importance of measuring sound absorption in a room?
To ensure the acoustic design meets the intended use and enhances the overall sound experience.
What is the formula to calculate the average absorption in a room?
a_avg absorption = (a1 s1 + a2 s2 + a3 * s3 + ...) / (s1 + s2 + s3 + ...)
What does the term 'Room Constant' refer to?
The result of the absorption coefficients of the surfaces, including the total surface area.
What is the significance of an absorption coefficient greater than 0.50?
Materials with an absorption coefficient greater than 0.50 are considered sound-absorbent.
What characterizes materials with lower sound absorption values?
They are typically smooth, dense, and massive.
What is the effect of replacing gypsum board with a porous absorber in a room?
It can increase the total absorption significantly, as shown by increasing from 0.043 to 0.186 sabins.
What does NRC stand for in acoustics?
Noise Reduction Coefficient.
How is the NRC calculated?
NRC = (a250 + a500 + a1000 + a2000) / 4, where a250, a500, etc., are absorption coefficients at respective frequencies.
What does an NRC of 0 indicate?
Perfect reflection of sound.
What does an NRC of 1 indicate?
Perfect absorption of sound.
What factors contribute to higher sound absorption values?
More porous materials, less smooth surfaces, and lighter weight.
What is the impact of sound dampening on speech intelligibility?
Effective sound dampening positively impacts speech intelligibility and clarity.
What is the average absorption coefficient for a room with 100 sq ft of wood floor and 500 sq ft of gypsum board?
The average absorption coefficient measures 0.043.
What happens to sound absorption when adding more surfaces in a room?
It typically increases the total absorption value.
What is the relationship between surface area and sound absorption coefficients?
Each absorption coefficient is multiplied by its corresponding surface area to calculate total absorption.
What is the effect of vertical elements on sound transfer in a space?
They help cut down sound energy transfer between different spaces.
What materials are characterized by high sound absorption values?
Materials that are more porous, less smooth, and have lower mass.
What is the role of acoustic panels in sound management?
They absorb disturbing sounds, leading to a quieter environment and improved focus.
How does the thickness of a material affect its sound absorption properties?
Thicker materials tend to be more porous and can provide better sound absorption.
What is the relationship between sound pressure levels in two rooms with different sound sources?
The difference in sound pressure levels is described as the difference in sound levels between any two points along the path of sound propagation.
What is the purpose of calculating the average absorption at specific frequencies?
To determine how effective a material is at absorbing sound at those frequencies.
What is the impact of sound absorption on collaborative workspaces?
It fosters focus and enhances effective collaboration.
What happens when you replace sound-reflective materials with sound-absorbent ones?
It can significantly improve the acoustic environment by reducing echo and noise levels.