Nucleic Acid, Mutation, Chromatin, and Gene Expression
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Two Main Classes of Nucleic Acids
______ —> primarily present in the nucleus
______ —> synthesized in the nucleus and then translocated in the cytoplasm
DNA
RNA
______ are building blocks of nucleic acids
nucleotides
______ —> nucleotide without the phosphate
nucleoside
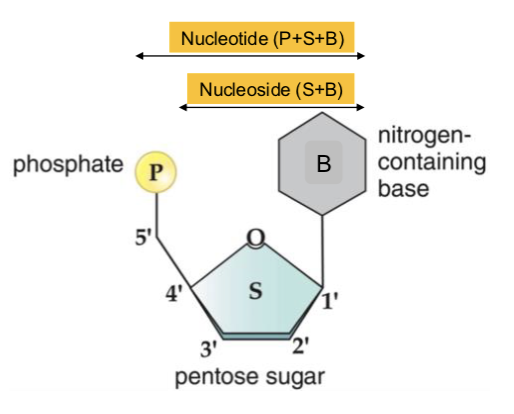
each nucleotide has 3 components…
a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
nucleic acids (DNA vs RNA) differ based on their sugar:
______ —> ribose sugar, which has a hydroxyl group (-OH) on the 2’ carbon —> more prone to hydrolysis —> LESS stable
______ —> deoxyribose sugar, which lacks that oxygen (it has -H on the 2’ carbon
RNA
DNA
Nitrogenous Bases:
______ (2 rings, larger bases)
Adenine (A)
Guanine (G)
______ (1 ring, smaller bases)
Cytosine (C)
Thymine (T) (DNA only)
Uracil (U) (RNA only, replaces T)
Purines
Pyrimidines
Base Pairing Rules
______: A ↔ T, G ↔ C
______: A ↔ U, G ↔ C
DNA
RNA
Nitrogenous bases link to the sugar backbone at the 1′ carbon through a ______ bond, forming the nucleoside structure (base + sugar) —> replacing the -OH group at this position
glycosidic
Phosphate Group
phosphate group contains one or two negatively charged ______ atom
negative charge helps in the ______ of proteins to DNA
negative charge allows DNA to remain ______ when denatured because negative charges repel themselves
oxygen
binding
straight
Nucleic Acid
alternating ______ + ______ = DNA/RNA backbone
phosphate connects the 3′ carbon of one sugar to the 5′ carbon of the next sugar —> forms two ester bonds —> ______ ______
Nucleic acids always have two ends:
5′ end = has a free ______ group
3′ end = has a free ______ group
sugar, phosphate
phosphodiester bond
phosphate
-OH
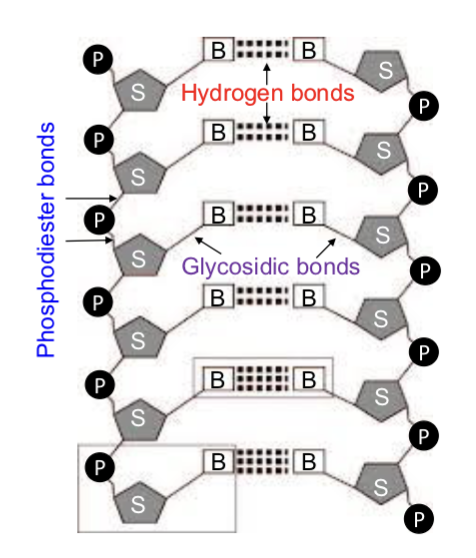
______ bonds —> between nitrogenous bases —> weakest bonds
______ bonds —> between the sugar and a base
______ bonds —> between the sugar and a phosphate
hydrogen
glycosidic
phosphodiester
DNA is double-stranded —> the ______ orientation of DNA allows for the base pairs to compliment one another
DNA is double helix —> the two helical strands are connected through ______ bonds between pairs of nucleotides
antiparallel
hydrogen
______ hydrogen bonds between G and C —> stronger DNA
______ hydrogen bonds between A and T
three
two
______ ______ —> is essential for several biological processes including DNA compaction, DNA metabolism, and likely gene expression
two types:
______ supercoiling —> more coiling —> tighter compaction
______ supercoiling —> DNA unwinds —> relaxed form
DNA supercoiling
positive
negative
______ —> enzymes that monitor and adjust DNA supercoiling by…
create temporary strand ______ in DNA
______ and ______ DNA strands
allow ______ to interact with DNA
prevent ______ supercoiling, which can damage DNA
topoisomerases
cuts
uncoil, reseal
proteins
excessive
Two Main Types of Topoisomerases
type ______ topoisomerases —> cut one strand of DNA
type ______ topoisomerases —> cut two strands of DNA
one
two
Type I Topoisomerases MOA
make a break in ______ DNA strand
pass the other strand through the ______
______ the break
Effect —> DNA winding/unwinding without ATP use.
one
break
reseal
Type II Topoisomerases MOA
Topo II binds to ______ ______.
Complex binds to ______ ______.
______ binds and promotes formation of the topological complex.
______ ______ of the G duplex.
______ ______ passes through the gap.
The G duplex is ______ and the bound ______ hydrolyzed.
G (gate) duplex
T (transported) duplex
ATP
Mg²⁺-dependent cleavage
re-ligated, ATP
Topoisomerase inhibitors prevent DNA repair → this leads to DNA damage → triggers ______ ______ —> utilized as anti-______ and anti-______ agents.
cell death, cancer, bacterial
mRNA
synthesized from ______ via ______
serves as the link between ______ and ______
codes for ______
______ and single-stranded RNA
a ______ cap is added at the 5’ end of pre-mRNA while mRNA is still being made
a ______ tail is added to the 3’ end of the pre-mRNA once mRNA synthesis is completed
DNA, transcription
proteins, DNA
proteins
unstable
7-methylguanosine
poly (A)
rRNA
______ RNA molecules
comprising ______% of ribosome’s mass
ensures the proper ______ of mRNA, tRNA, and ribosome during protein synthesis
stable
60
alignment
tRNA
______ RNA with extensive intramolecular base pairing
contains an ______ ______ binding site and an ______ binding site
carries the correct animo acid to the site of protein synthesis in the ______
stable
amino acid, mRNA
ribosome
Replication = DNA → ______
Why it’s essential:
—> when a cell divides, each ______ cell must receive the exact same genetic information as the parent cell.
Sequence of Events:
______ is replicated.
______ divides.
Both new daughter cells contain ______ DNA.
DNA
daughter
DNA
cellidentical
Both parental DNA strands serve as ______ for making new DNA.
______ model —> each DNA molecule has (1) 1 parental (old) strand and (2) 1 newly synthesized strand.
templates
semiconservative
Stages of DNA Replication
______ —> the DNA helix is opened up and the DNA replication proteins are positioned
______ —> synthesis of the new DNA strands
______ —> DNA synthesis is stopped
initiation
elongation
termination
DNA replication begins at the ______ of replication where two ______ ______ are formed —> DNA synthesis proceeds ______
origin, replication forks, bidirectionally
______ DNA has a single replication origin site
______ DNA has multiple origins of replication
bacterial
eukaryotic
Central Dogma
replication: DNA → DNA
transcription: DNA → RNA
translation: RNA → protein
DNA Replication —> Initiation
______ unwinds the DNA helix —> causes ______ ______ of the DNA
______ prevent the topological distortion by making temporary single-strand cuts in the DNA —> later resealed
______-______ DNA binding proteins (SSB) prevents the two original strands from re-forming a double stranded molecule
helicase, topological distortion
topoisomerase 1
single-stranded
DNA Replication —> Elongation
______ —> generates short RNA strand that binds to the single-stranded DNA to initiate DNA synthesis
DNA polymerase reads the parental strand _____, but it synthesizes the new strand ______.
Adds ______ to the growing chain by forming ______ ______ at the 3’ end.
______ strand —> continuous replication
______ strand —> discontinuous replication in short fragments —> Okazaki fragments —> later linked together with the help of ______
primase
3’ → 5’, 5’ → 3’
nucleotides, phosphodiester bonds
leading
lagging, ligase
A ______ of the template for the ______ strand places it in position for 5’ → 3’ polymerization —> enables DNA polymerase to synthesize both daughter strands simultaneously.
looping, lagging
DNA Replication Termination
Once DNA synthesis is completed, the RNA primer is removed by ______ ______
______ ______ fills the gap where the RNA primer used to be
______ ______ seals the last two nucleotides together
RNA hybridase
DNA polymerase
DNA ligase
proofreading —> ______ ______ —> if DNA polymerase detects the mis-paired deoxynucleotides —> DNA polymerase shifts backward ( ______ direction) —> removes incorrect base —> addition of correct base
exonuclease activity, 3’ → 5’
DNA Polymerase Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy
Gemcitabine —> a ______ ______ —> a “fake nucleotide” —> incorporated into replicating DNA —> inhibits ______ ______ —> stalls the ______ ______ —> cancer cells can’t divide —> leads to cell death.
used to treat ______, ______, and ______ cancers
nucleoside analog, DNA polymerase, replication fork
pancreatic, lung, bladder
DNA polymerases cannot fully ______ the very ends of the chromosome —> with each replication round, a small portion of the DNA is lost at the 3’ ends —> a ______ DNA sequence is added after replication to protect the ends of chromosomes
replicate, telomere
______ is a reverse transcriptase that uses an RNA molecule as a template —> adds repetitive DNA sequence of ______ nucleotide after replication
telomerase, six
Cells with High Telomerase Activity (3)
white blood cells
stem cells
cancer cells
healthy somatic cells have very little or no telomerase activity
cells that need to proliferate have high ______ activity
______ telomerase = unlimited division potential (stem cells, immune cells, cancers)
______ telomerase = limited division capacity (normal body cells → aging)
telomerase
high
low
telomere ______ decreases with age in proliferating tissues —> progressive shortening of telomeres leads to —> (3)
length, metabolic arrest, cell death, oncogenic transformation
telomere damage or deletion leads to loss of ______ ______/______ —> characteristic feature of ______
genome integrity/stability, cancer
telomerase is significantly over expressed in 80-95% of all ______ tumors
______ —> present in green tea —> a natural telomerase inhibitor
malignant
epigallocatechin-3-gallate
______ = just the double helix
______ = DNA wrapped around structural proteins
chromatin made by ______ proteins
chromatin is further condensed to form ______
DNA
chromatin
histones
chromosomes
Chromatin exists in two forms:
______ —> loosely packed, lightly stained —> active
______ —> densely packed, darkly stained —> inactive
euchromatin
heterochromatin
Features of Mitochondrial DNA (4)
circular
lacks structural proteins
lacks telomeres
less base pairs (16,500 vs. 3.2 billion in nuclear DNA)
Gene Expression —> Two Major Steps
______ —> DNA —> mRNA in the nucleus
______ —> mRNA —> proteins in the cytoplasm
transcription
translation
Out of the 3 billion base pairs in the human genome:
______% —> genes —> proteins
______% —> non-coding DNA
2
98
Transcription Steps
______ —> RNA polymerase is positioned on the DNA of the gene that needs to be transcribed
______ —> RNA polymerase transcribes the DNA sequence of the gene into an RNA molecule
______ —> RNA polymerase is released from the DNA
initiation
elongation
termination
Transcription —> Initiation
each gene has a ______
the general ______ ______ bind to the promoter
______ ______ attaches to the transcription factors forming a transcription initiation complex
promoter
transcription factors
RNA polymerase
Transcription —> Elongation
RNA polymerase moves along one strand of DNA called the ______ strand in the ______ direction.
The strand of DNA not used as a template for transcription is called the ______ strand.
The newly synthesized mRNA has the same nucleotide sequence as the ______ strand.
template/non-coding, 3’ → 5’
non-template/coding
coding
Transcription —> Termination
not well understood in eukaryotes
RNA polymerase transcribes a ______ ______: AAUAAA —> called the ______ signal.
Once the poly-A signal is synthesized, mRNA is ______ and ______ ______ adds about ~200 adenine nucleotides to the 3’ end —> creates the poly-A tail.
consensus sequence, poly-A
cleaved, poly(A) polymerase
Precursor mRNA (pre-mRNA) in Eukaryotes
RNA transcript = ______ —> must be processed into a ______ before leaving the nucleus
a ______ is added to the 5’ end
a ______ is added to the 3’ end
pre-mRNA, mRNA
cap
poly-A tail
Processing of eukaryotic pre-mRNA: RNA splicing
Pre-mRNA has both:
______ = coding segments (kept)
______ = noncoding segments (removed)
______ —> splice out introns and combine exons via spliceosome that contains small nuclear RNAs and proteins
exons
introns
RNA splicing
______ = a set of 3 consecutive bases in mRNA that code for 1 amino acid.
read in the ______ direction of the mRNA
each codon ______ an amino acid
______ “stop” codons mark the end of a protein
______ “start” codon —> ______ —> marks the beginning of a protein
codons specify the order of amino acids in a protein from ______ (methionine) to ______
human genetic codes = ______ amino acids —> ______ codons
codon
5’ → 3’
specify
three
one, AUG
N-terminus → C-terminus
20, 64
______ RNA polymerase is a promising target for the discovery of new antimicrobial agents
bacterial
Reverse Transcription ( ______ → ______ )
RNA virus = ______ —> makes a complementary DNA ( ______ ) —> integrates into the host’s genome
______ ______ makes cDNA from RNA
^ inhibitors are a class of ______ drugs used to treat HIV infections or AIDS
RNA → DNA
retrovirus, cDNA
reverse transcriptase
antiretroviral
Ribosomes
sites in a cell in which ______ takes place
made of a large and a small subunit which come together around a mRNA molecule —> complete ribosome
ribosomes are 1/3 ______ and 2/3 ______ ______
sites for tRNA binding
____ site —> peptidyl or donor site
____ site —> aminoacyl or acceptor site
____ site —> exit site
translation
proteins, ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
P
A
E
Translation involves 3 steps…
initiation
elongation
termination
Translation —> Initiation
the initiator tRNA carrying _______ attaches to the small ribosomal subunit
the complex “walk” along the mRNA in the ____ direction to search for the start codon ______
the large ribosomal subunit joins to form ______ complex at the site of AUG on mRNA
methionine
3’, AUG
initiation
Translation —> Elongation
______-______ tRNA starts in the ______ site of the ribosome
______ then binds to ______ site
______ ______ connects amino acid to one another —> mRNA pulled onward through the ribosome by exactly one codon
methionine-carrying, P site
aminoacyl tRNA, A
peptide bonds
Translation —> Termination
happens when a ______ codon in the mRNA enters the _____ site
stop codons are recognized by ______ ______ which fit neatly into the A site of ribosome
upon termination, the ribosome is disassembled and the completed polypeptide is released
stop, A
release factors
Effects of DNA Mutations on Protein Synthesis
A different protein may form
Protein may not form at all
Less amount of protein may form
Protein production may increase
May not affect protein production