Molecular Genetics Lecture 7 - Linkage and Genetic Mapping
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What plays a huge role in discovering the functions of human genes?
linkage mapping
Alleles of two different genes do not always assort independently. True or false.
true
What is Mendel’s law of independent assortment?
alleles at one locus assort independently of alleles at another locus
What is genetic linkage?
tendency of genes that are closer to each other on a same chromosome to assort and inherit together
What are some examples of linked genes?
hair and eye colors
Allele do not assort independently if genes are
located next to each other or closer on a same chromosome (linked genes)
what is genetic linkage?
the exchange of chromosomal segments during cross over (recombination) takes place between large segments of chromosomes
What does genetic linkage lead to?
a generation of gametes with more parental alleles than recombinant alleles
crossing over is ____ likely to occur between closely linked genes than between those farther apart on a chromosome
less
recombination ______ significantly if the genes are closer to each other
decreases
what is crossing over in simple terms?
two non-sister chromatids exchange chromosomal segments
what are recombinants?
reshuffling of allele combinations between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes
what are parentals?
alleles stay the same as parents because of no crossover
what is the phenotypic ratio that occurs when there is independent assortment?
1:1:1:1
what is the phenotypic ratio that occurs when there is complete linkage (no cross over at all)?
1:1
what is the results of incomplete linkage (limited cross over)?
parental gametes are 80% and recombinant gametes are 20% of these genes
what can incomplete linkage be used to measure?
the relative genetic distance between 2 genes (genetic mapping) based on recombination frequency
what is genetic distance?
relative distance between 2 linked genes on a chromosome can be estimated using recombination frequencies
what is genetic distance measured in?
map units or centiMorgans
how do you know if two genes are linked?
recombination frequency is less than 50%
what is two-point mapping?
estimation of genetic distance between 2 linked genes
what are some cross overs that are involved with three-point mapping?
single cross over, double cross over
what is single cross over (SCO)?
single exchange of chromosomes between two loci
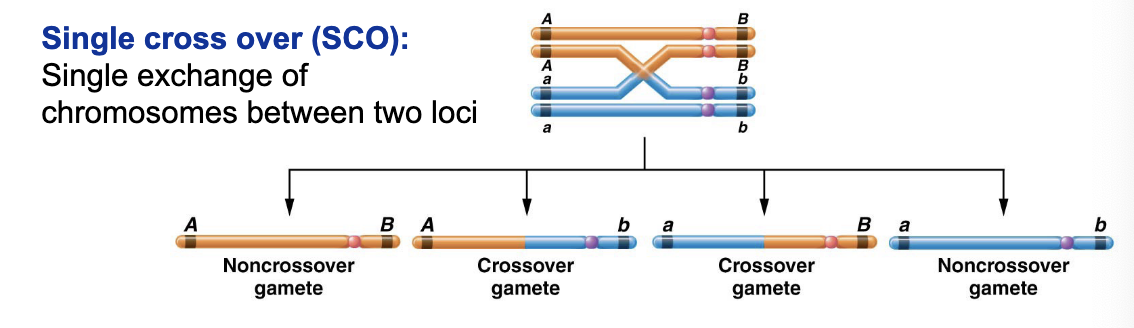
what is double cross over (DCO)?
double exchange of chromosomes between three loci
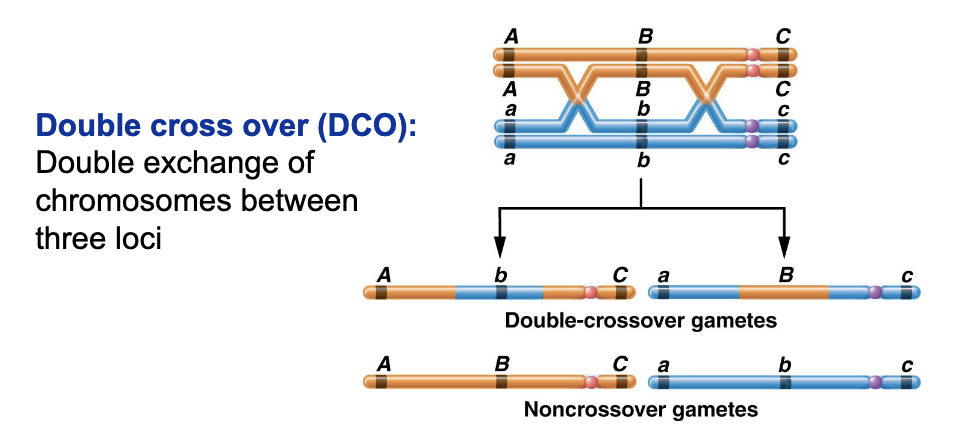
how can you identify parental offspring?
highest frequency
how can you identify SCO offspring?
intermediate frequency
how can you identify DCO offspring?
lowest frequency
what is interference?
inhibition of further crossover by crossover events in nearby region of a chromosome
if there is complete linkage, there is
no cross over at all
if there is incomplete linkage, there is
reduced cross over
what do you use to construct a genetic map?
recombination frequencies
what is a locus?
location of a gene on a chromosome
what is a cytogenetic map?
based on the visual appearance of chromosomes after staining reveals distinctive features of different chromosomes
what is a genetic map?
relative distance and positions of genes on a chromosome estimated using recombination frequencies
what is a physical map?
relative distance and positions of genes on chromosomes expressed in nucleotide base pairs
what does physical distance mean in terms of linkage and genetic mapping?
distance between 2 genes on a chromosome expressed in nucleotide base pairs (DNA sequencing)
what are some applications of genetic/linkage mapping?
linkage mapping, forward genetics, genome sequencing
what is an application of linkage mapping?
linking a phenotype to a locus (gene) on a chromosome by estimating recombination frequencies
what is an application of forward genetics
start with a defective phenotype (breast cancer) and link the phenotype to a locus (BRCA1 gene) on a chromosome
what are forward genetic screens combined with and used for?
combined with linkage mapping to identify many genes in various biological processes in various organisms
how was the breast cancer suppressor gene BRCA1 discovered by?
genetic mapping