BIO101 Exam #3
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Virus
A tiny, nonliving particle that invades and then reproduces inside a living cell.
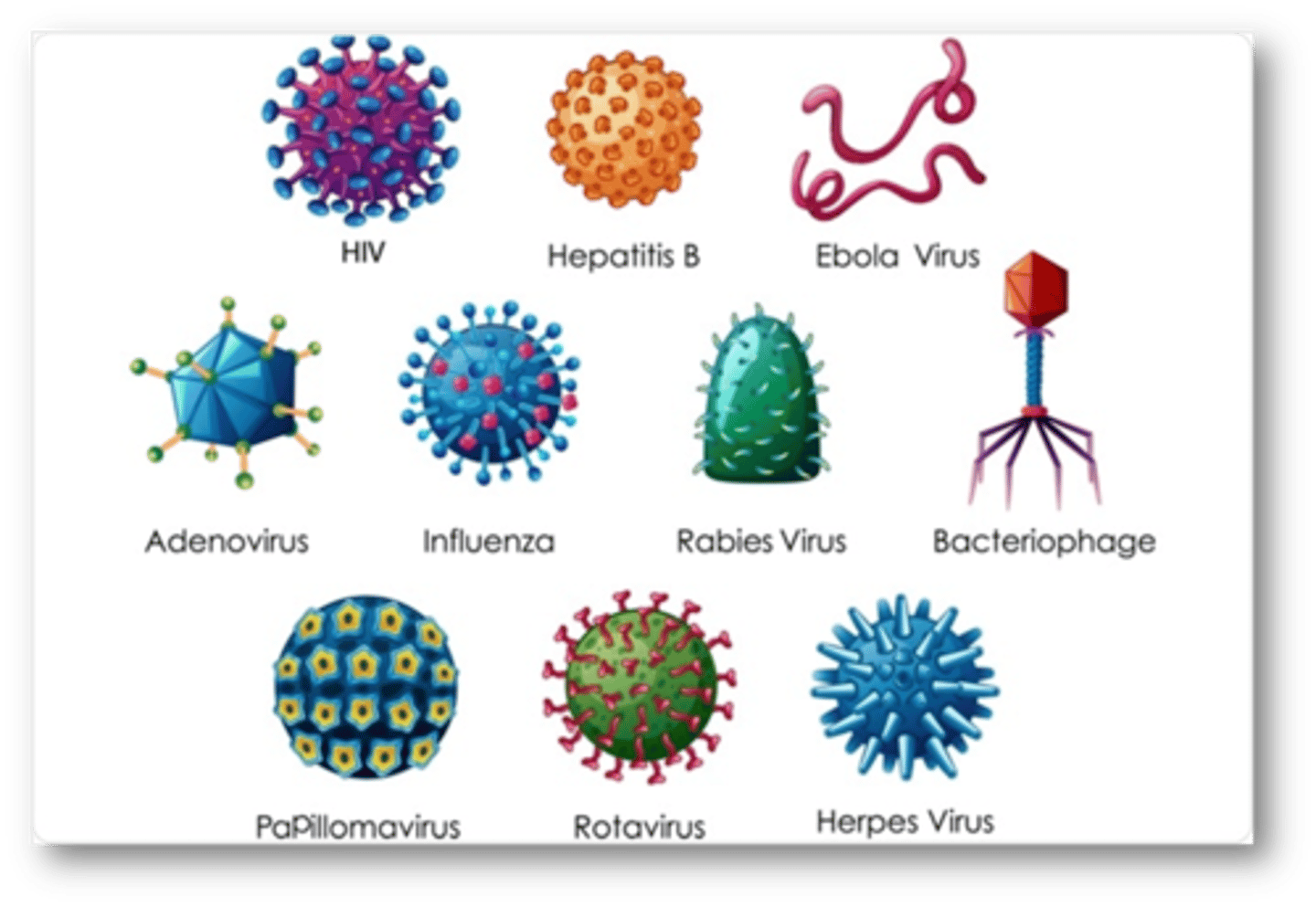
HIV
A virus that attacks and destroys the human immune system.
Hepatitis B
inflammation of the liver caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), which is transmitted sexually or by exposure to contaminated blood or body fluids
Ebola Virus
Ebola hemorrhagic fever (immune system and blood vessels)
Adenovirus
Targets the respiratory system/common cold
Influenza
Flu virus targeting the respiratory system
Rabies Virus
Attacks the nervous system
Bacteriophage
A virus that infects bacteria
Papillomavirus
virus that causes warts and is associated with cancer
Rotavirus
Attacks the digestive system
Herpes virus
inflammatory virus of the skin
Capsid
Outer protein coat of a virus
Glycoprotein
A protein with one or more carbohydrates covalently attached to it.
Viral genes
Commonly called DNA or DNA, found inside of the virus particle.
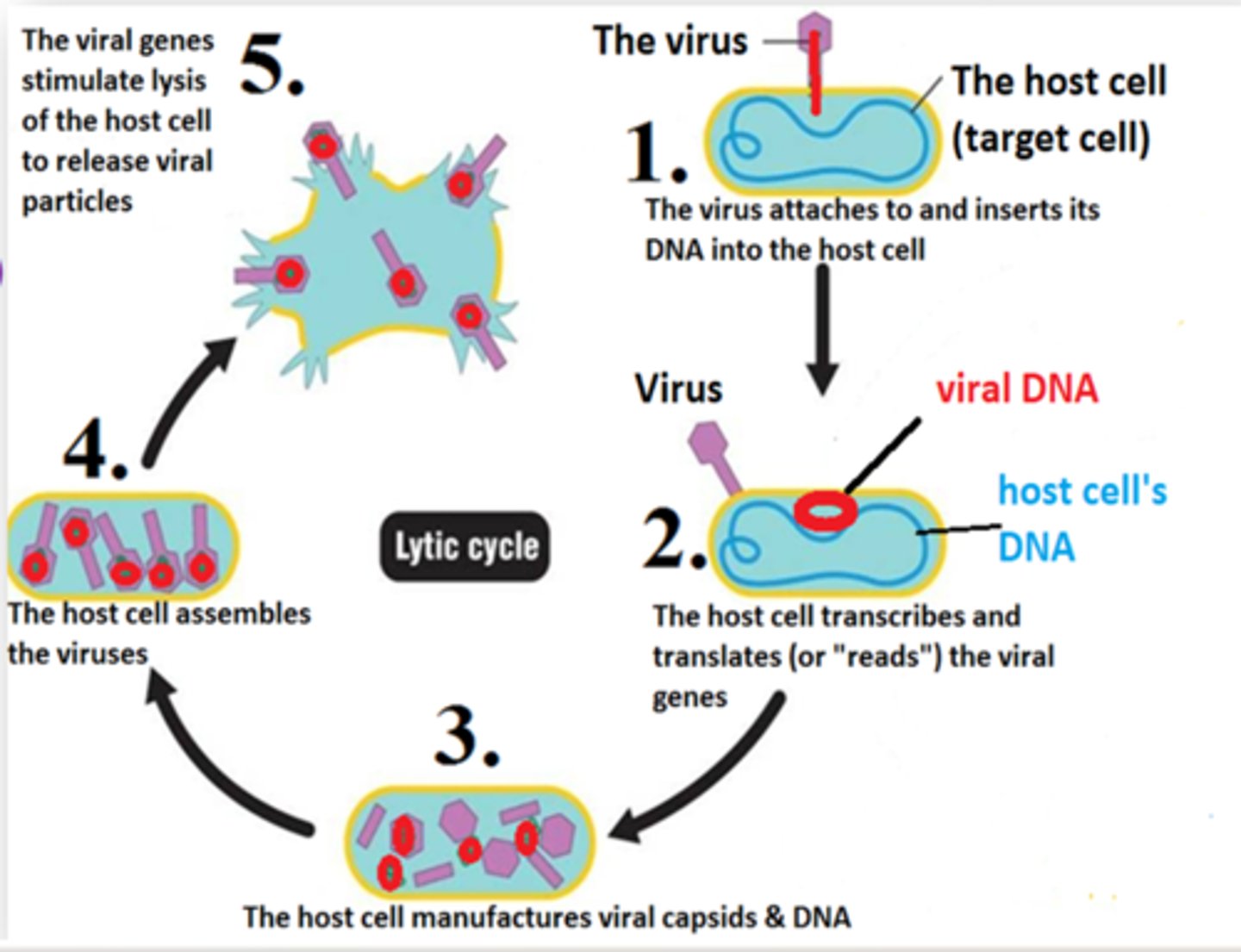
Lytic cycle
a viral reproductive cycle in which copies of a virus are made within a host cell, which then bursts open, releasing new viruses
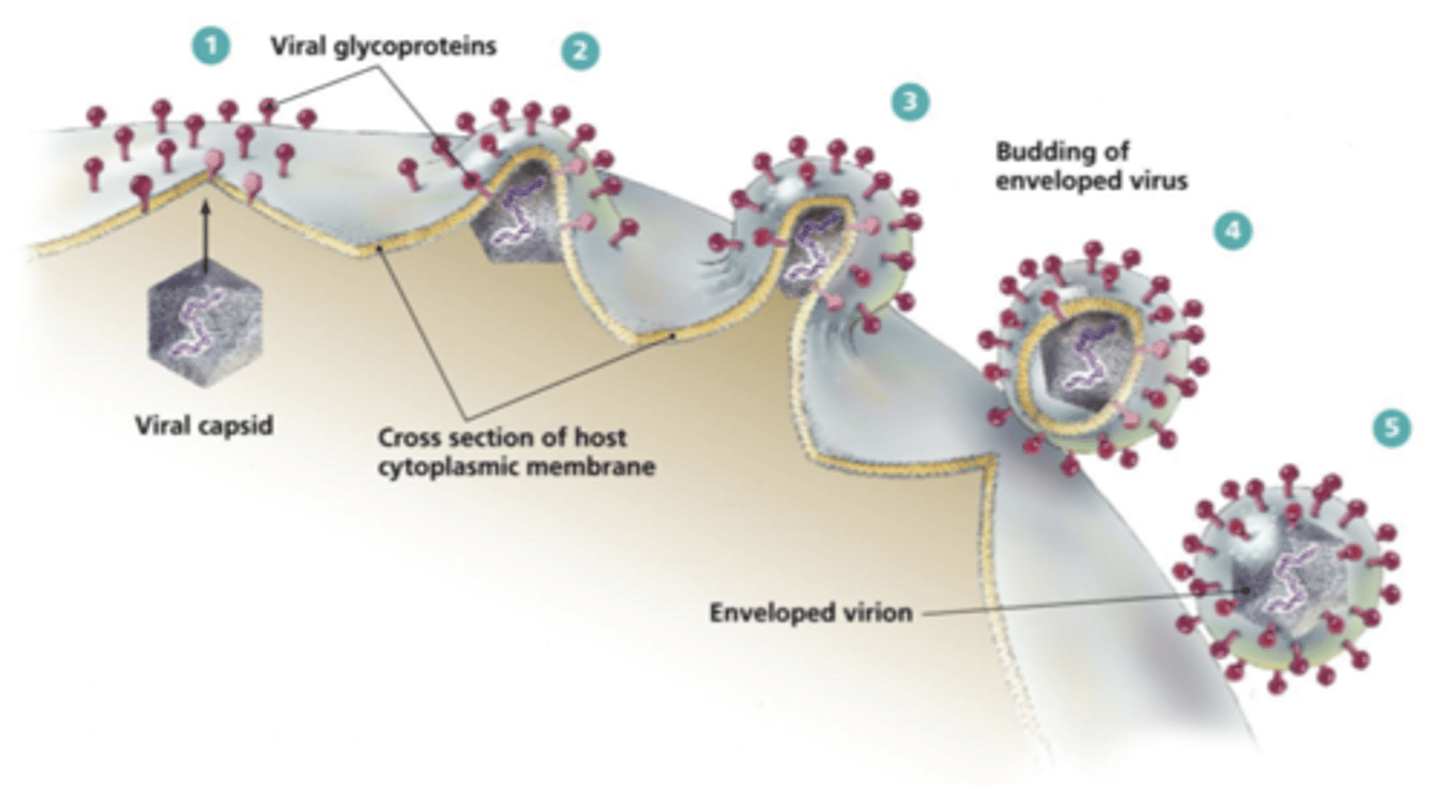
How does HPV replicate that leaves the host cell intact?
Viral shedding or budding
Why do cells have an increased risk of becoming cancerous when infected with HPV?
HPV doesn't result in the death of the host cell
Cutaneous HPV infects...
Hands and feet
Genital HPV infects...
genital regine
HPV spreads through...
skin to skin contact, vaginal, anal, or oral sex
Low-risk HPV
6 and 11, causes genital warts
High-risk HPV
16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52, 58; cancerous if left untreated
How does HPV increase cancer risk?
High-risk strains have persistent infection and may cause abnormal cell growth that increases cancer risk
HPV Cancers
throat and tonsil cancers, cervical cancer
HPV Myths
1. HPV is rare (No, it's the #1 STI in the USA)
2. If you're infected with HPV, you'd know (Most infected people are asymptomatic. Weaker immune systems may cause genital warts or cancer)
3. You must have sexual intercourse to get HPV (High frequency of HPV detection in the vagina before vaginal intercourse)
4. Only women get HPV infection (Affects both genders)
5. The HPV vaccine causes teens and preteens to become sexually active (...No.)
6. The HPV vaccine provides life-time protection (Only provides protection for certain strains for 10 years)
7. If you already have HPV, you don't need a vaccine (There are 9 different strains of HPV and it protects you from strains you haven't contracted yet)
8. HPV testing is available for both men and women (Only women thru a pap smear)
9. Females should get pap tests as soon as they're sexually active (Age 25+)
10. Females who are vaccinated do not need to be screened for cervical cancer
11. Women can stop getting screened for cervical cancer after they have kids
12. If your partner uses a condom, you cannot contract HPV (HPV transmits through skin to skin contact, not only intercourse)
13. You can figure out a time frame of when you first contracted HPV
Pap test
examination of cells taken from the cervix
Colpscopy
A follow up screening to a pap smear where a magnified glass looks at the cervix, sprays with a vinegar substance where abnormal cells can be see. The severity ranges between low grade CIN, to cervical cancer
HPV testing
Looks for the DNA high-risk HPV strains in cervical cancer
Why might it be difficult for women to see a reproductive health doctor?
Lack of health insurance/funds, embarrassment
Prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus; ex: bacteria
Eukaryotic
cells with a nucleus that are 10x larger than prokaryotes; ex: animal, plant, fungi
Resident microbes
each site has particular populations
changes over time (skin microbes gained at birth, digestive microbes through breastfeeding)
Pathogenic microbes
invade and damage the cells and tissue; disease causing
Benefits of resident microbes
Outcompete the pathogenic microbes, thus killing them, and make vitamins B & K for us
Lactobacillus
Prokaryotic bacteria
Candida
A yeast commonly found in the oral cavity, gastrointestinal tract, and female genital tract. Eukaryotic cell.
Lactobacillus and Candida's relationship
Antagonistic relationship. Lactobacillus keeps candida in check when the body has a yeast infection
Prokaryotic cell structure
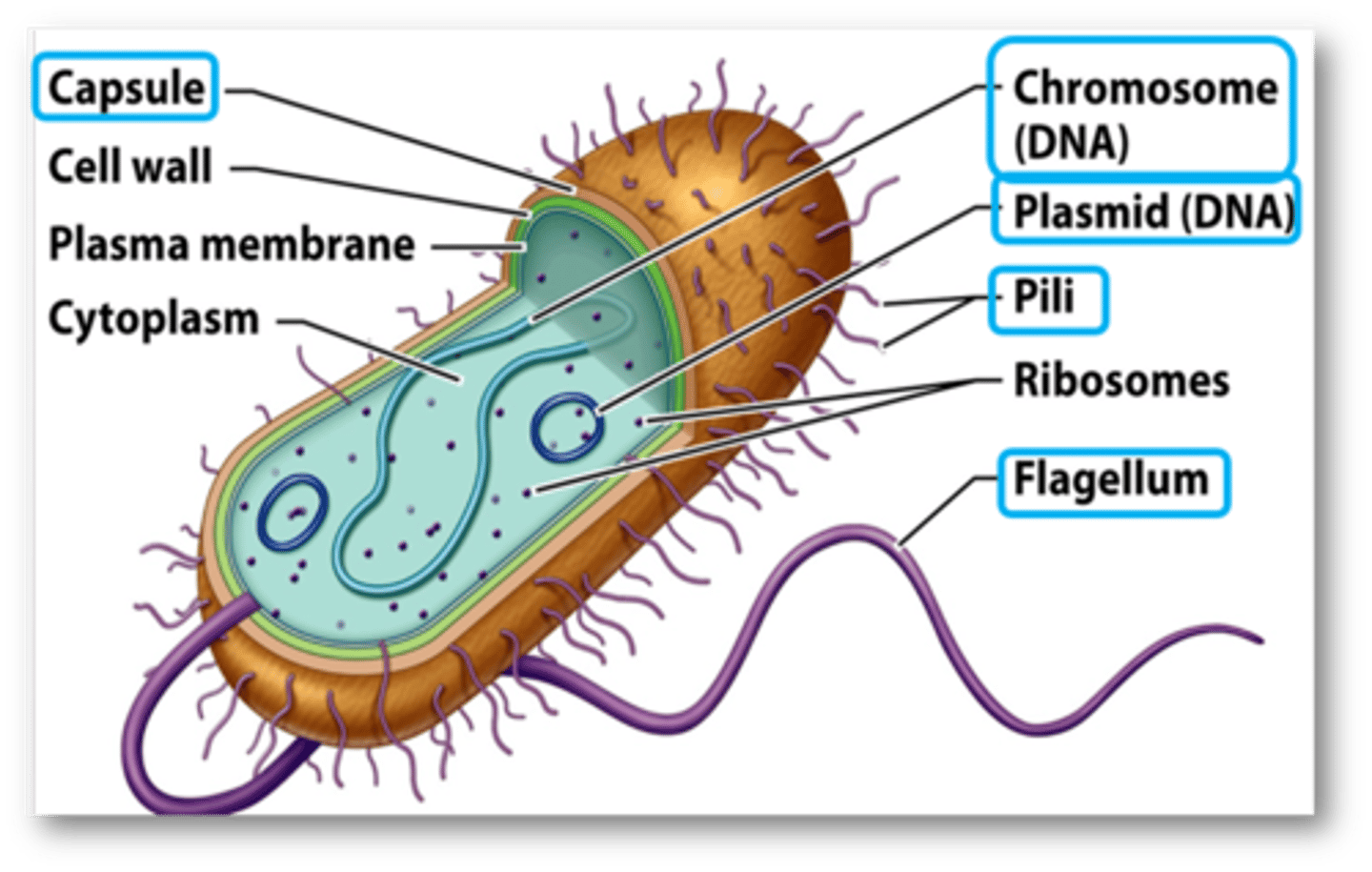
Capsule
The outermost layer of the bacterium. It prevents dehydration and allows the bacterium to escape white blood cells of your immune system
Cell wall
The middle layer of the bacterium that helps with structural support of the cell
Plasma membrane
The inner layer of the bacterium that regulates what enters and exits the cells.
Ribosomes
Produces protein for the bacteria
Cytoplasm
The fluid and space found outside the nucleus
Chromosomal DNA
Contains basic genes that allow bacteria to survive and carry about basic life functions
Plasmid DNA
Not all bacteria will have this. Plasmids are pieces of DNA bacteria absorb from their environment or get from other bacteria. May provide bacteria with a certain advantage, like the ability to be resistant to antibiotics
Pili
protein structures that allow bacteria to attach to surfaces that they want to infect
Flagella
Help bacteria move to search for food and resources, or to escape from white blood cells trying to hunt them down
Biofilm
Polysaccharide sheath shielding a community of bacteria. Large communities can produce biofilms that protect the bacteria from destruction
ex: dental plaque and growths inside cathers
Benefits of forming biofilms for bacteria
1. Get protection from the polysaccharide sheath
2. In communities, bacteria can communicate when food and resources are high (stimulates growth). When food is low bacteria growth is slowed down.
Endotoxins
Inside the second layer (cell wall)
Benefits of releasing endotoxins for bacteria
Endotoxins are used to damage host cells and to trigger symptoms that can cause the host to transmit the disease
(symptoms of fever, coughing, chills)
Exotoxins
Endospores
Endospores are used by anthrax bacteria. Produced by bacteria that will die due to limiting circumstances (severe weather, lack of resources). The dormant (inactive) version of the bacterium that are left behind when the bacteria dies. Can survive any extreme condition.
Bacillus
Meningitis
Inflammation of the meninges (a set of 3 tissue layers the cover the brain) caused by cocci (circular) bacteria that affect the nervous system.
Transmitted through coughing, sneezing, sharing utensils & drinks, kissing, living in close quarters. The olfactory nerve in the nasal cavity connect directly to the brain.
Symptoms include severe headaches, sudden high fever, stiff neck/body aches, fatigue, confusion, loss of balance and motor skills
Diagnosed thru lumbar puncture (spinal tap) to access cerebrospinal fluid.
Antibiotic treatment.
Anthrax
A bacilli (pill-shaped) bacteria caused by spore-forming bacteria used as biological warfare.
Transmission types and their symptoms:
1. Cutaneous exposure: large sore on skin with necrosis (dead tissue), w/ a topical treatment
2. Inhalation: death of suffocation
3. Ingestion: Bleeding in digestive system (2 & 3: I.V. treatment)
Diagnosed thru test of the presence of the bacterium in a blood, respiratory secretions (ie mucus), and a skin swab. Antibiotics used to kill the bacteria.
Lyme Disease
A spirochete bacterial disease spread by the black legged tick.
Transmitted by tick bites. They release an anesthetic that numbs the skin and anticoagulant that prevents blood from clogging.
Symptoms are a circular, bullseye rash
Diagnosed through blood test or lumbar puncture
Antibiotic treatment
Syphilis
A sexually transmitted bacterial disease caused by spirochete (spiral-shaped) bacteria
Transmitted thru direct contact with a syphilitic sore during oral, vaginal and anal sex, from mother to child during pregnancy
Primary syphilis: a chancre sore going away in 4-6 weeks
Secondary syphilis: body wide rash ranging from days to months
Tertiary syphilis: Heart and nervous system affected
Diagnosed thru blood test
Antibiotic treatment
Antibiotics
Medications and drugs that used to kill bacteria; significantly reduces the number of bacteria and then allows your immune system to fight the remaining germs
Antibiotic resistance
When some antibiotics are no longer effective in killing bacteria; the bacteria survives in the presence of the antibiotic
How do bacteria get the plasmid DNA needed to help the bacteria resist antibiotics?
Transformation and Conjugation
Transformation
Form plasmid by connecting DNA fragments that enter the bacteria cell
Conjugation
A temporary union of two organisms for the purpose of plasmid DNA transfer
Three strategies bacteria uses to become resistant to antibiotics
1. Plasmid has information to protect itself and destroys the drug with protein #1
2. Efflux pump removes the antibiotic from the cell
3. Decrease uptake, doesn't allow the antibiotic to work