GEOL 102 - Exam 2
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
Landslides occur on...
unstable slopes
____ ____ is usually related to the steepness of the slope and the type of material present.
Slope stability
Angle of repose
the steepest angle at which loose material will not slide down slope
Angle of repose for Fine Sand
35 degrees
Angle of repose for Coarse Sand
40 degrees
Angle of repose for Angular Pebbles
45 degrees
More Cohesive Sand
Damp Sand
Least Cohesive Sand
Water-saturated Sand
Moderately Cohesive Sand
Dry Sand
Vegetation adds...
stability
Landslides are a part of a process called ____ _______
Mass Wasting
Mass Wasting
Any down-slope movement of soil or rock under the influence of gravity:
-Landslides
-Debris flows
-Soil creep
-Rockfalls
Deadly killers
Billions in property damage
Type of material in Mass Movements
Rock
Soil
How materials move during Mass Movements
Sliding
Flowing
Falling
How fast the material moves
Slide planes: discreet failure surfaces
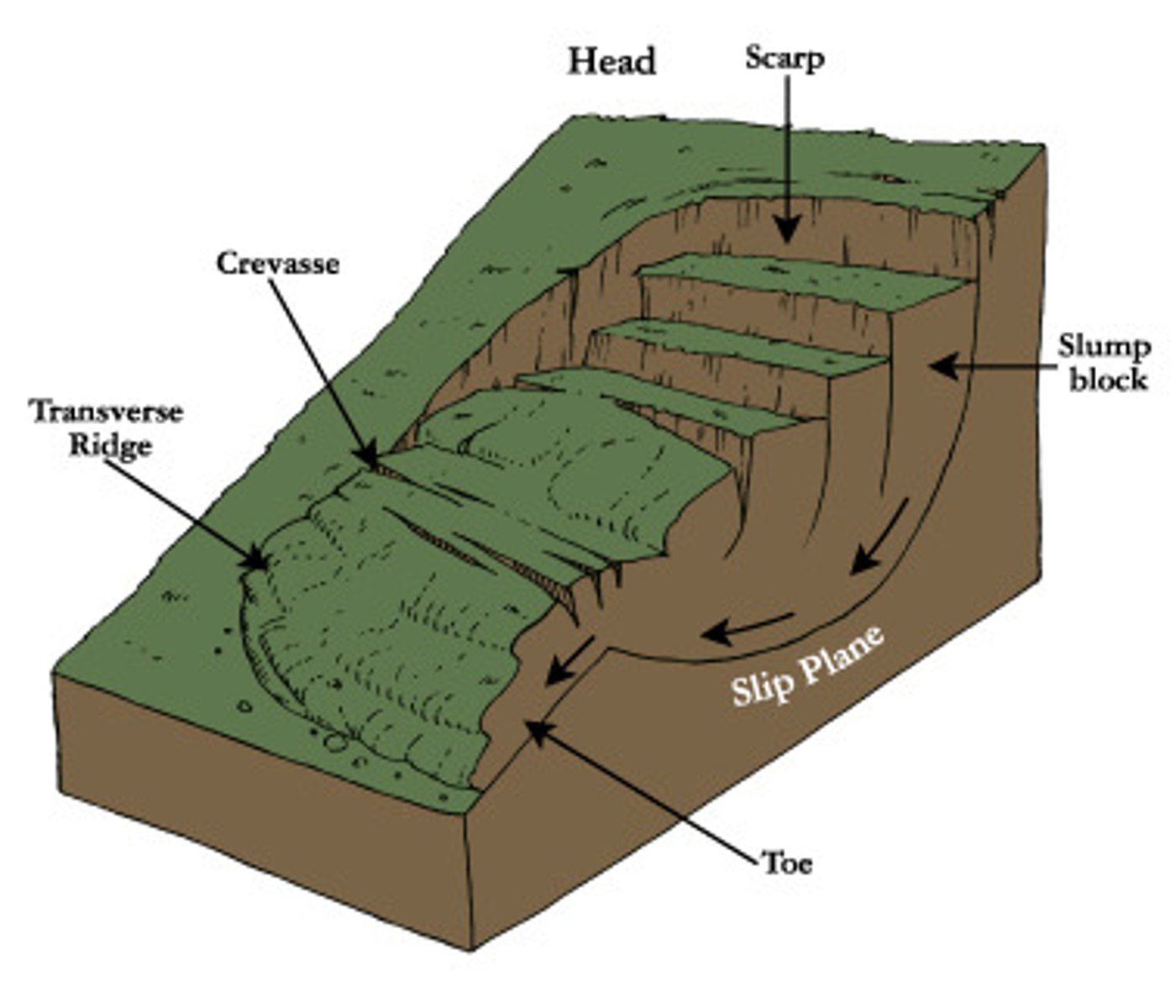
Landslide: Slump
Most common kind of landslide
Spoon-shaped
Move about a center of rotation
Grow headward
Encouraged by cutting at the toe
Block glide
Blocks of land slide down together
Rock Avalanche
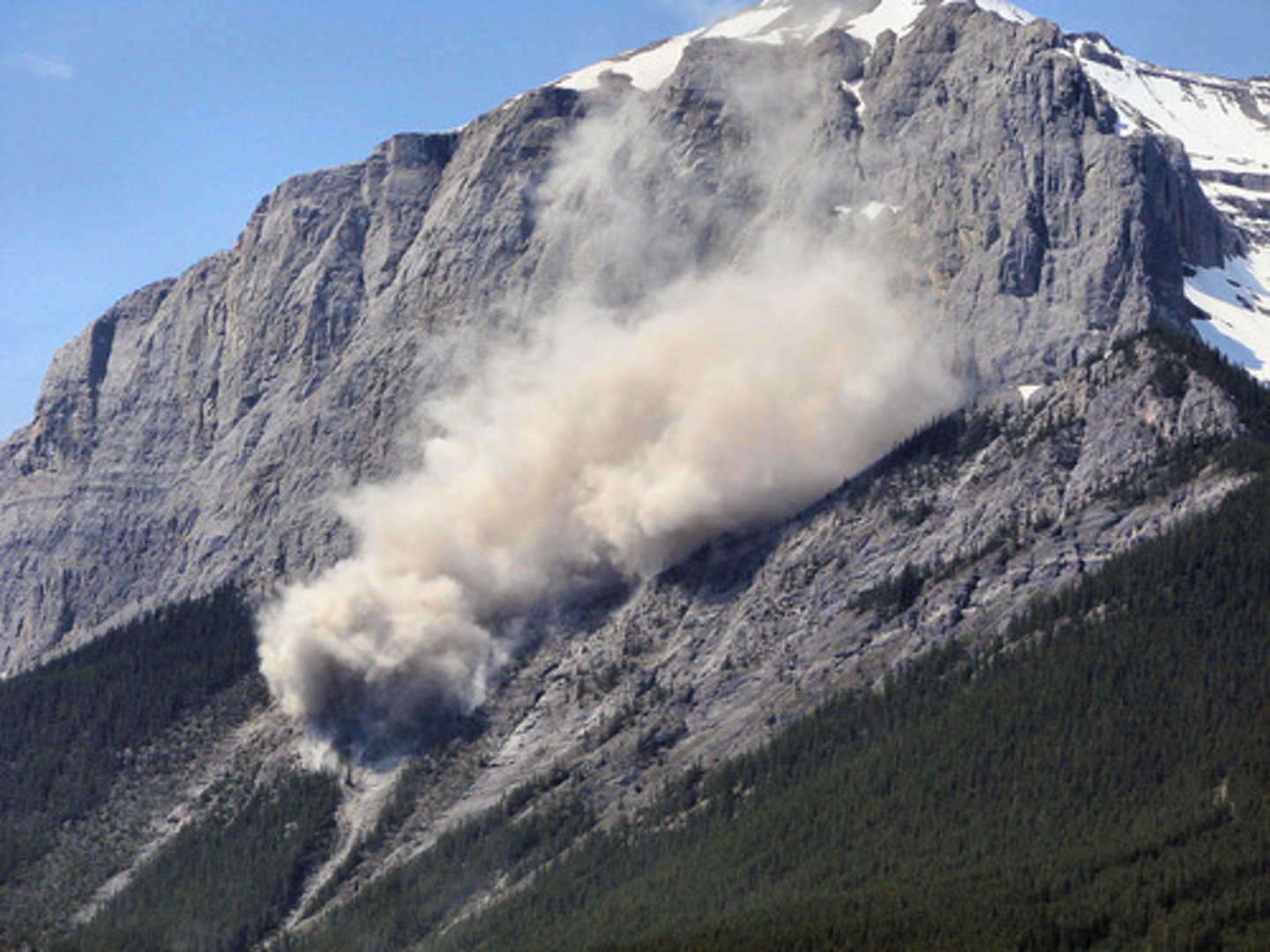

Flows
Water and air help these landslides move
Earth Flow
Rain soaked land flows down
Debris Flow
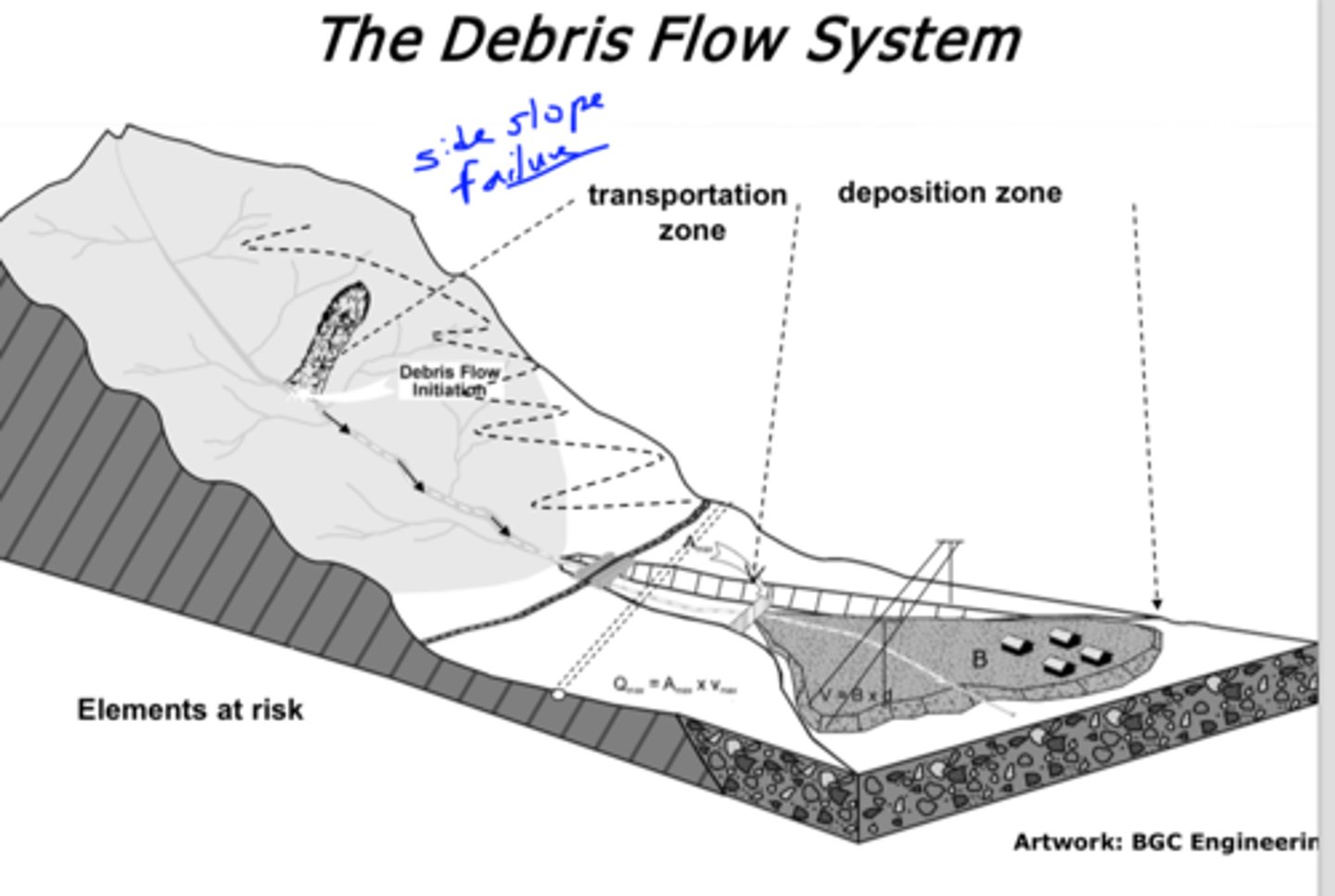
Creep
Slow (mm/year) movement downslope on steep slopes
Freeze/thaw
Wet/dry
Burrowing animals
Tree falls
Soil
-Produces food for humans
-Produces trees for lumber and paper
-Supports nearly all life
-Carrying capacity of planet depends on availability and productivity of soil
On average, it takes _____ years to make an inch of soil.
several hundred (about 500)
What is soil made of?
25% - Water
25% - Gases
45% - Mineral Matter
5% - Organic
Soil changes with...
depth
O Horizon
organic material
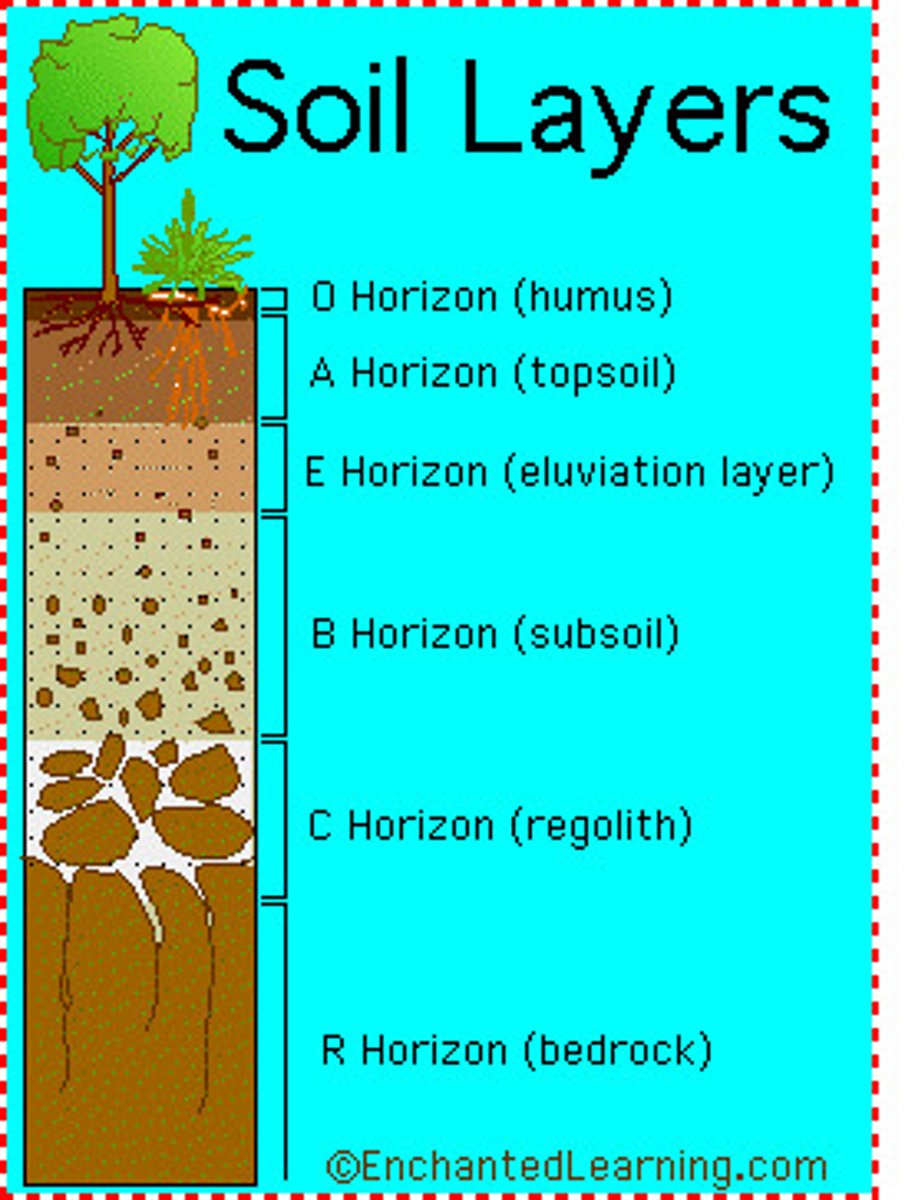
A Horizon
Rainwater and roots are active; soil aggregation
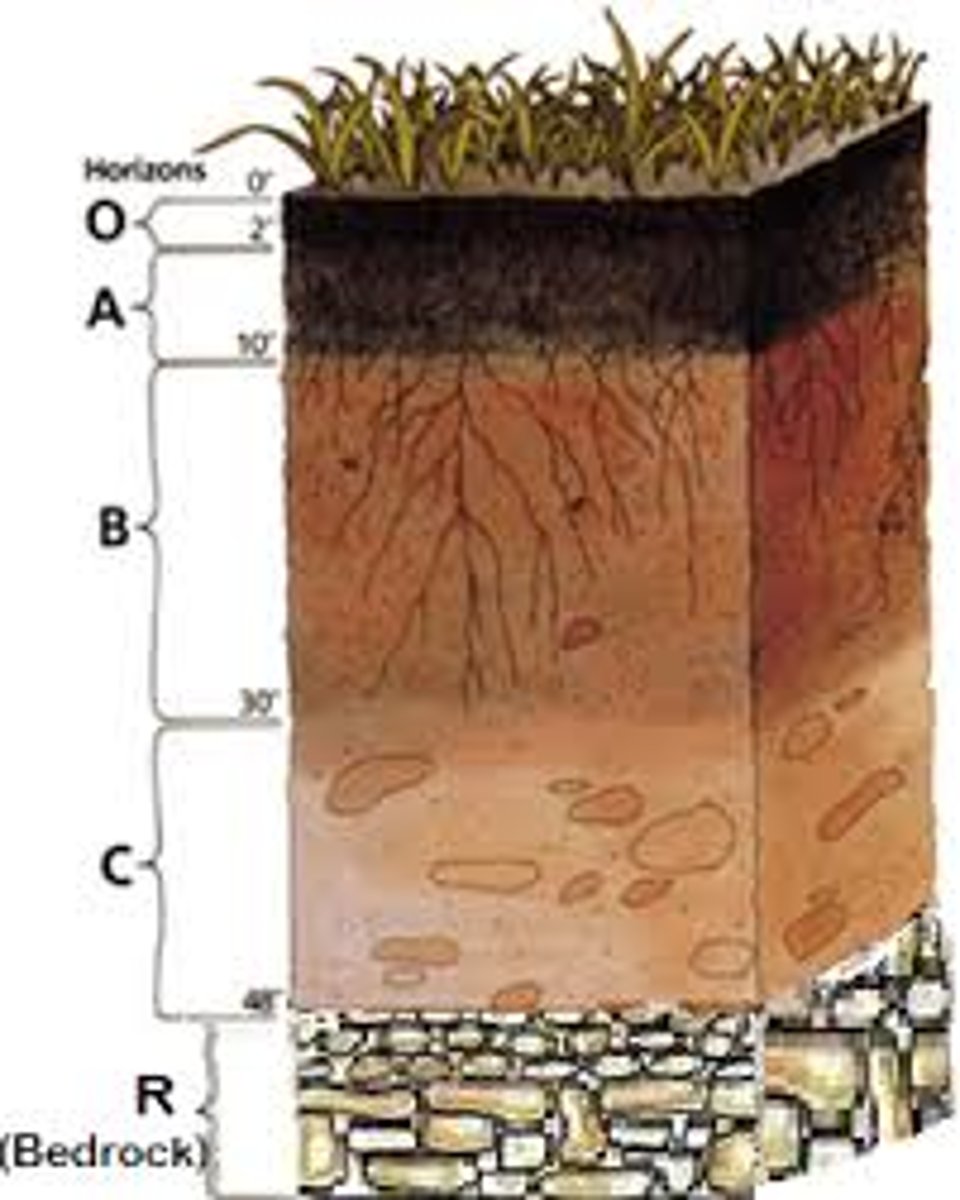
B Horizon
Zone of accumulation
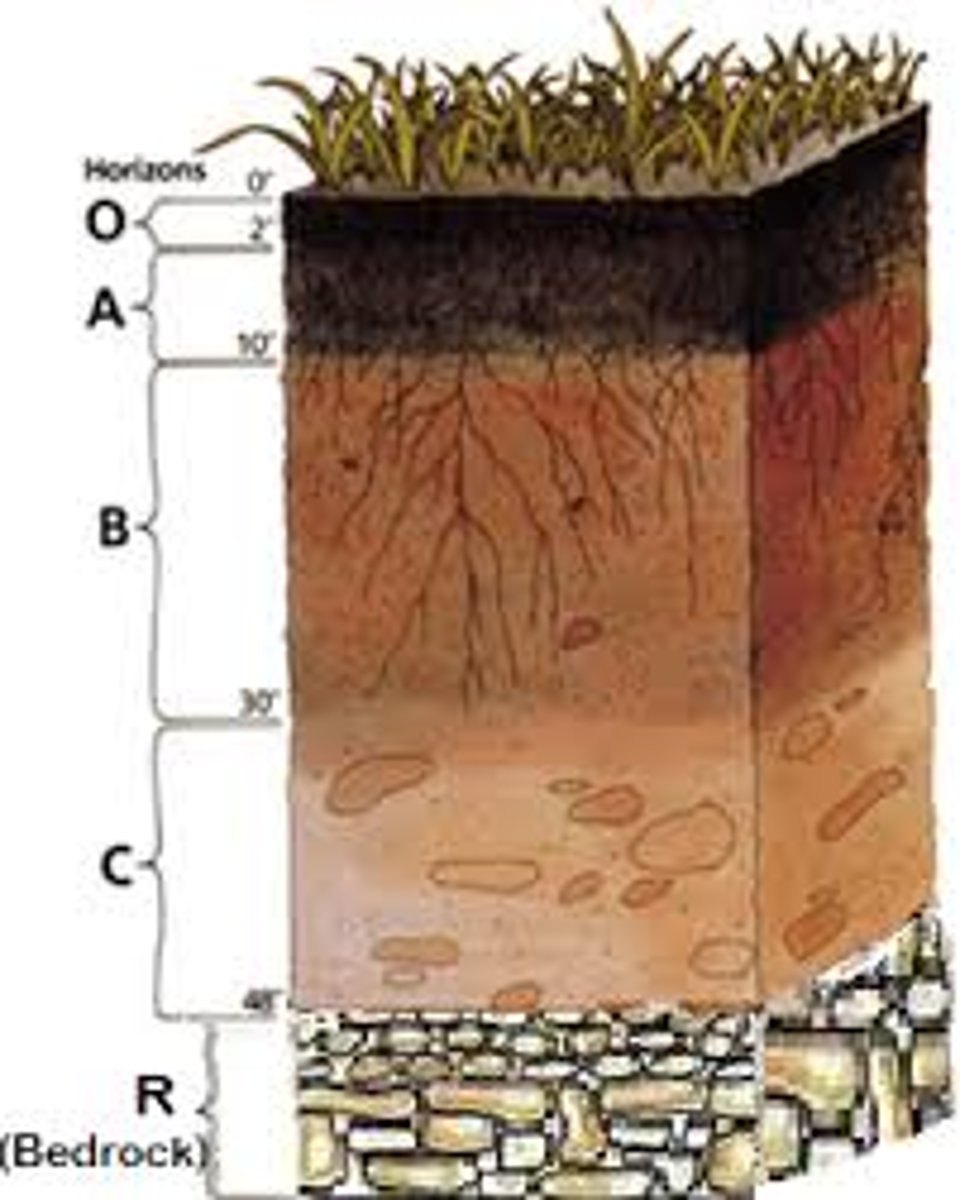
C Horizon
Rotten rock layer, rocks break down chemically and material behaves like soil still.
Soil is a product of...
weathering
Weathering
-Breakdown of rocks and minerals at and near the Earth's surface
-Physical disintegration
-Chemical decomposition
Water takes advantage of...
pre-existing fractures
in rocks
Water expands by ___% when it freezes
9
_____ is an important factor in chemical weathering
time
The type of _______ also affects the rate of chemical weathering
bedrock
Effects of Plowing
• Exposes soil to physical erosion
• Exposes organic matter to decomposition
(Some organic matter is bound by minerals that protect it from microbial decomposition. Plowing releases this, for decomposition and oxidation)
Benefits of soil
Food
Habitats
Ecosystems
Drought, extensive plowing, and high winds cause...
dust storms
Soil Loss
Huge areas have lost most productive soil
Eroded soil becomes sediment in streams
Soil loss by size
• one third of U.S. topsoil lost so far
• globally, lost area size of China and India
Eroded soil deposits sediment in streams, creating...
• muddies rivers
• fills reservoirs
• disrupts coastal zone
Soil Conservation
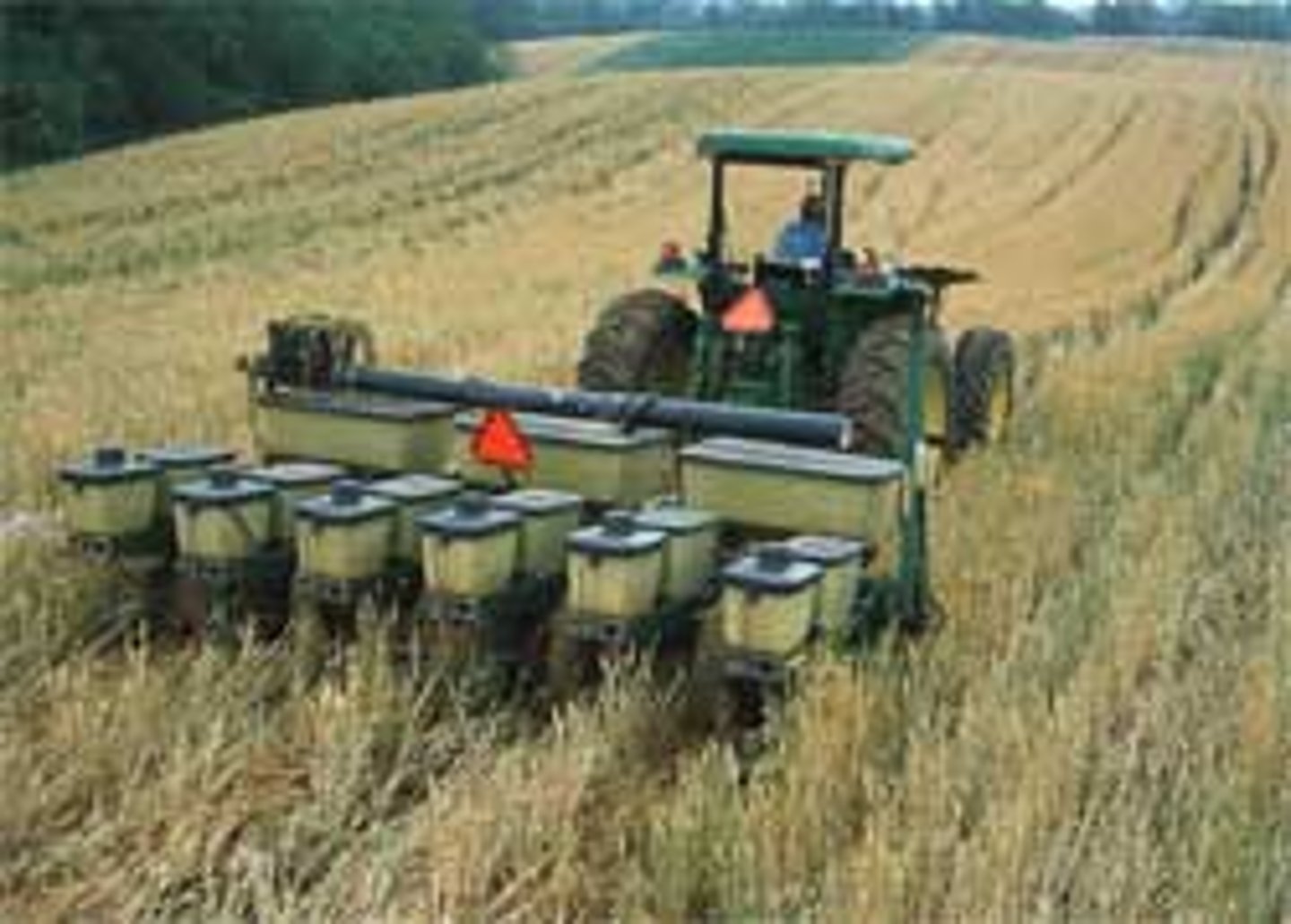
No-till agriculture
An agricultural method in which farmers do not turn the soil between seasons, used as a means of reducing erosion

"Organic" farming
Conserve soil biological activity, minimize off-farm inputs of materials and energy, forbid herbicides, pesticides, genetically modified crops or feed stocks, avoid hormones, antibiotics, and other drugs, allow animals to be outside for part of their lives, and many other "rules."
Biogeochemical Cycles
A biogeochemical cycle is the complete path a chemical takes through the four major components of Earth's system
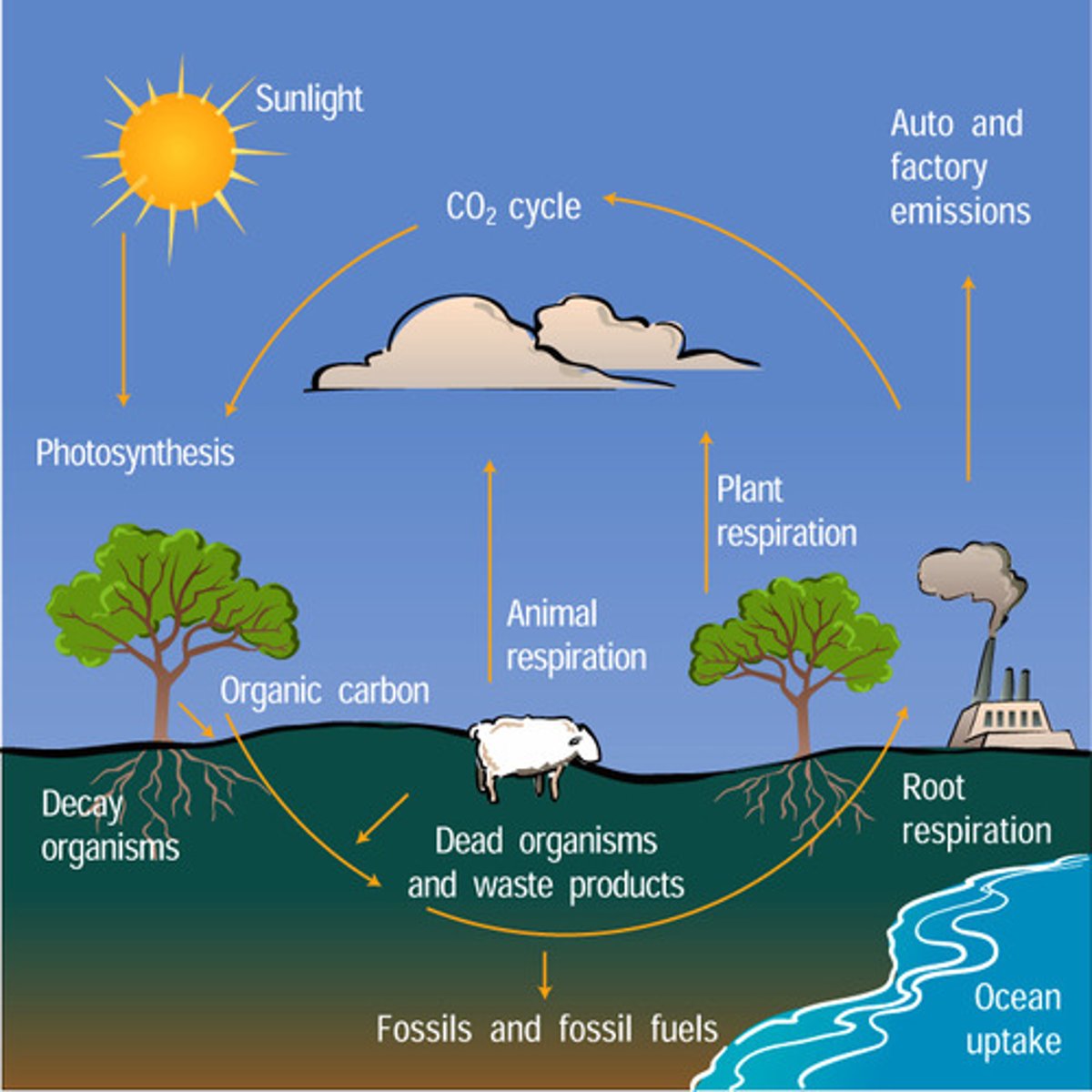
Carbon Cycle
The organic circulation of carbon from the atmosphere into organisms and back again
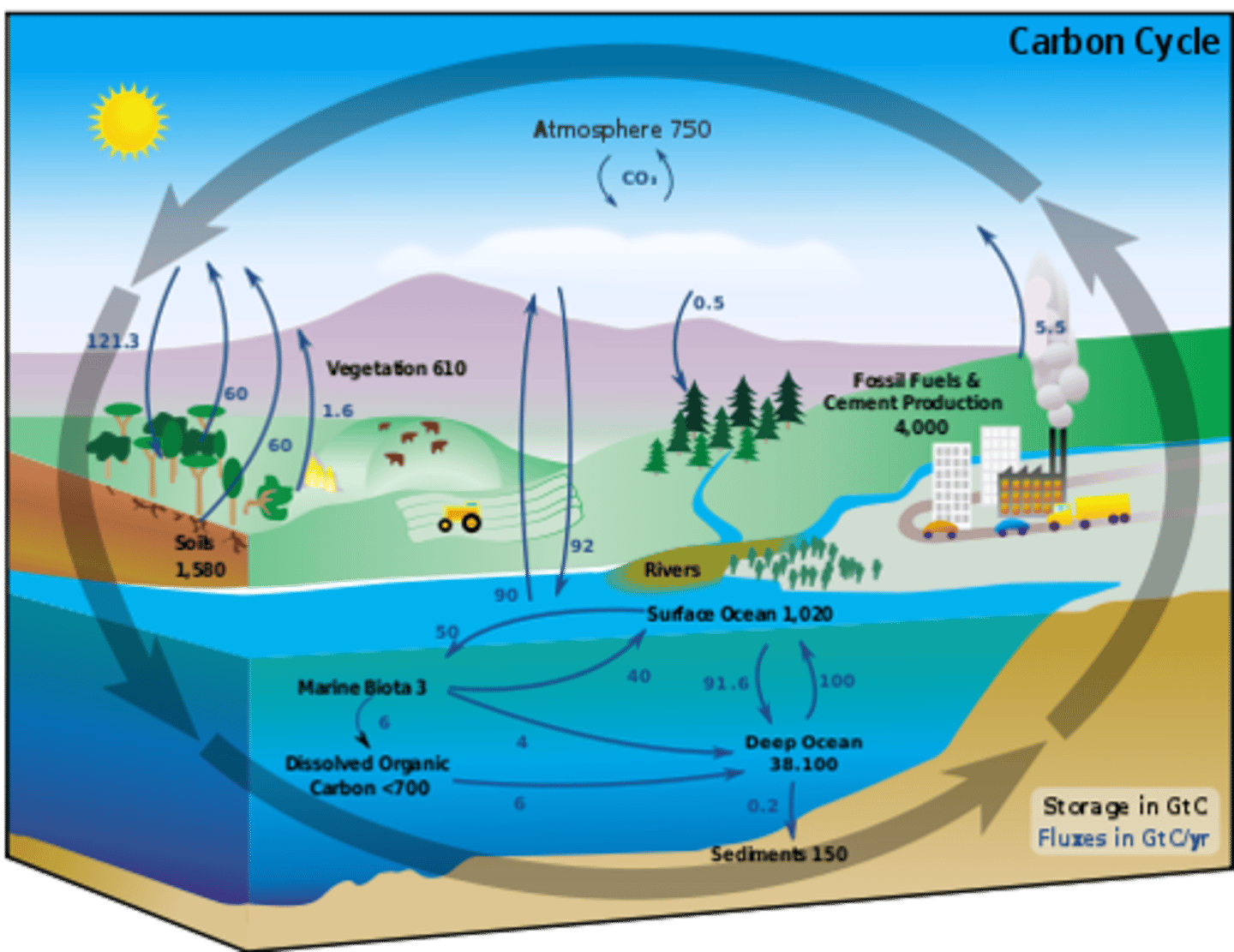
Carbon Budget
the overall exchange of carbon between the different systems on Earth. It should naturally remain balanced as carbon moves between sources and sinks.
Tropical Deforestation (per year)
13 Million Hectares
Percentage of water in ocean and salt lakes
97.41%
Percentage of water in ice and snow
1.984%
Percentage of water in groundwater
0.592%
Percentage of water in lakes and rivers
0.0071%
Percentage of water in soils, wetlands, and biota
0.0059%
Percentage of water in the atmosphere
0.001%
Freshwater is brought to us
by _______
the water cycle
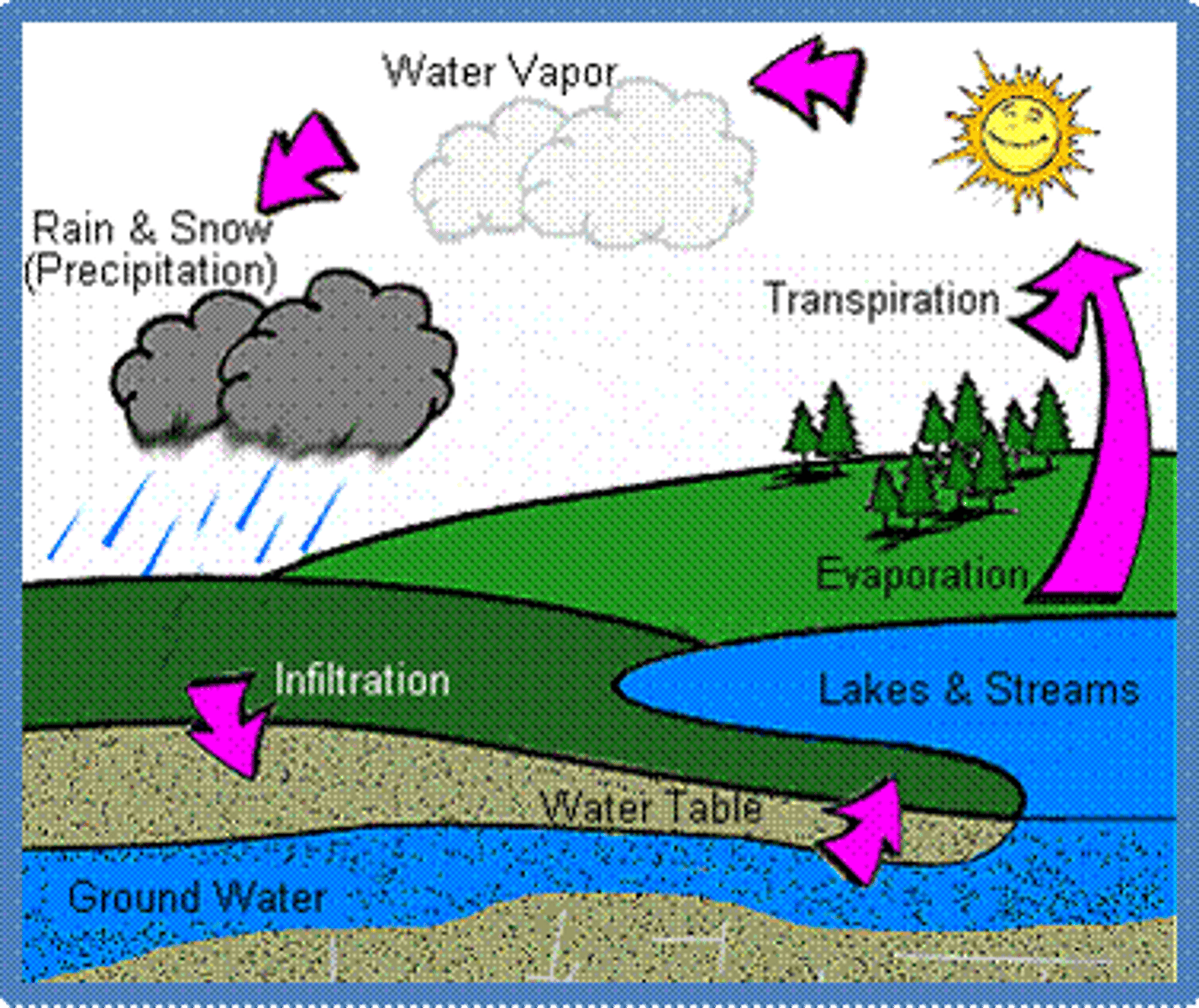
Water Cycle
-Precipitation
-Runoff
-Groundwater recharge
-Evaporation
-Evapotranspiration
---Evaporation of water
---Transpiration from plant leaves
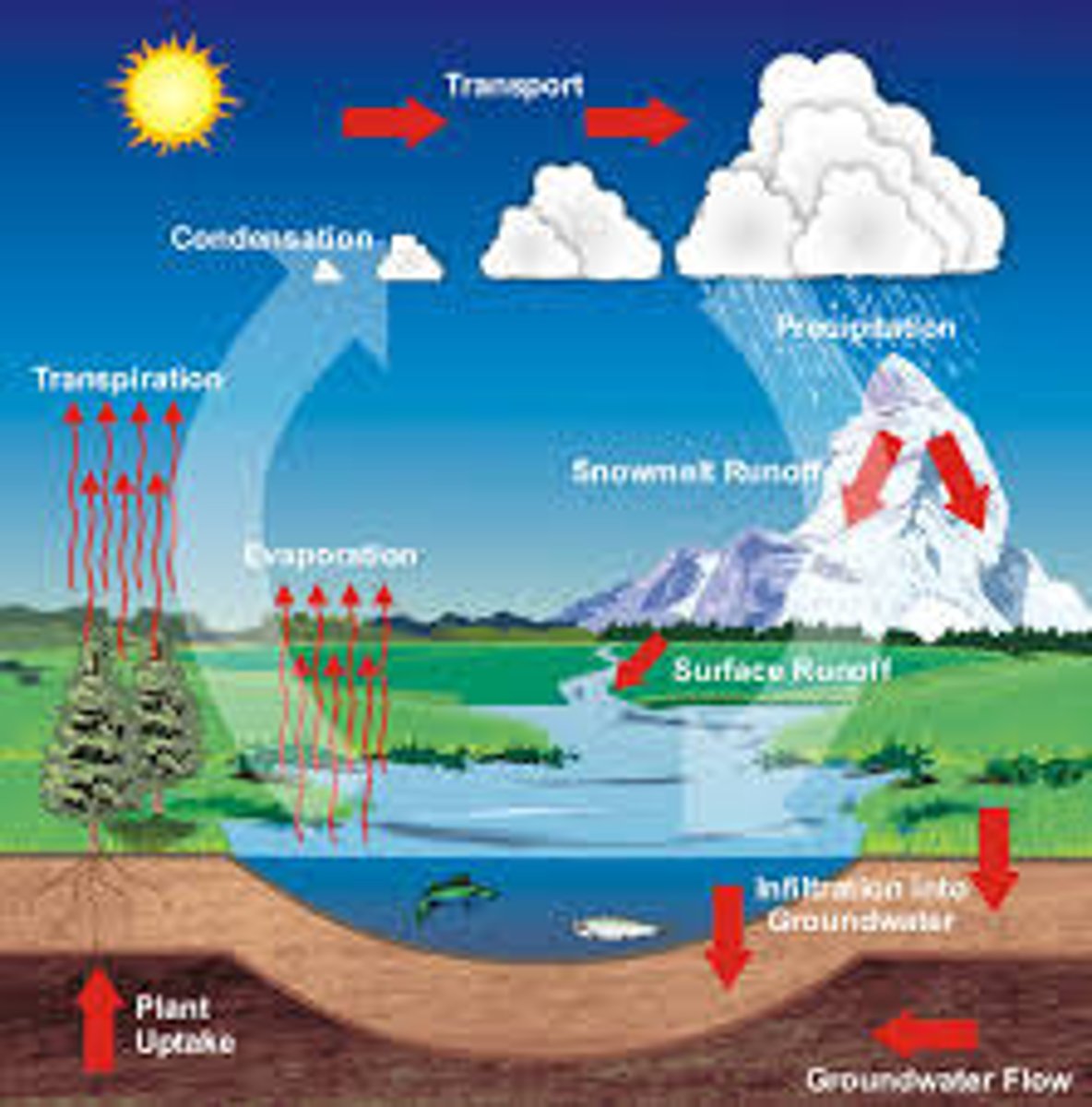
Precipitation
Any form of water that falls from clouds and reaches Earth's surface.
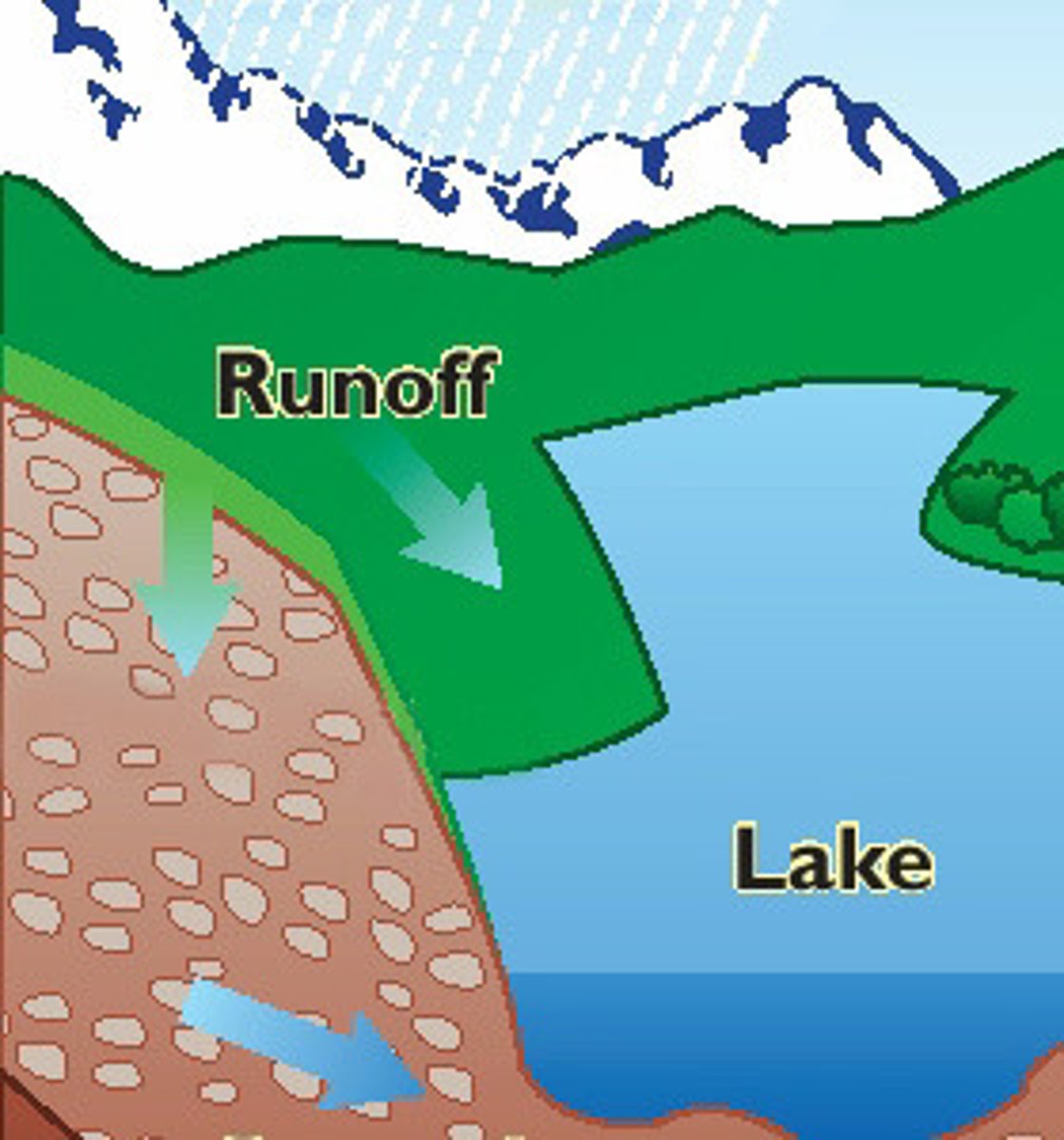
Runoff
Water that flows over the ground surface rather than soaking into the ground
Groundwater recharge
A process by which water percolates through the soil and works its way into an aquifer.
Evaporation
Liquid to gas

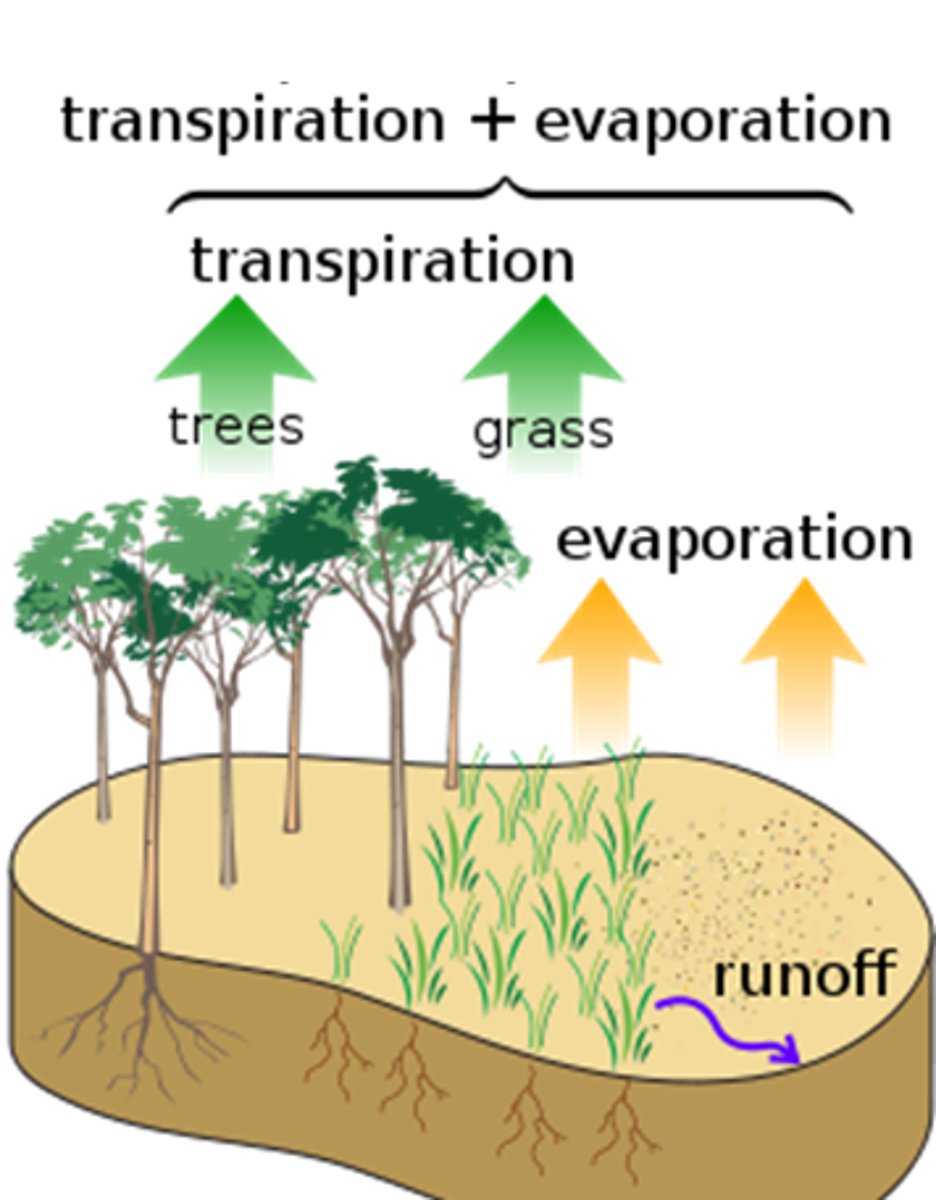
Evapotranspiration
The evaporation of water from soil plus the transpiration of water from plants.
Most fresh water is...
groundwater
Ground water
-Most in pore spaces and fractures
-Hydrogeologists are better than dowsers at locating sites for wells
-40% of public water supplies
-Important for irrigation
Helps maintain streamflows

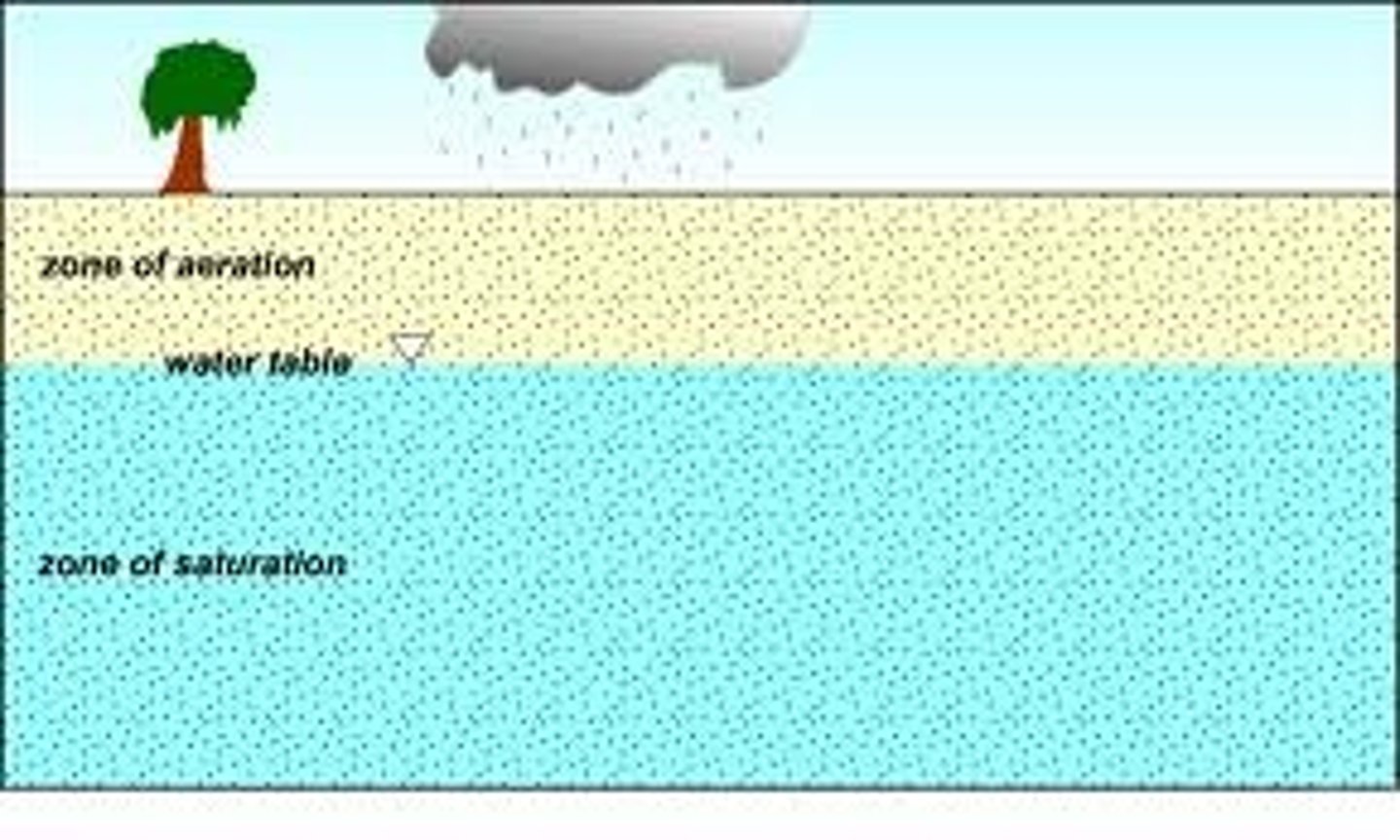
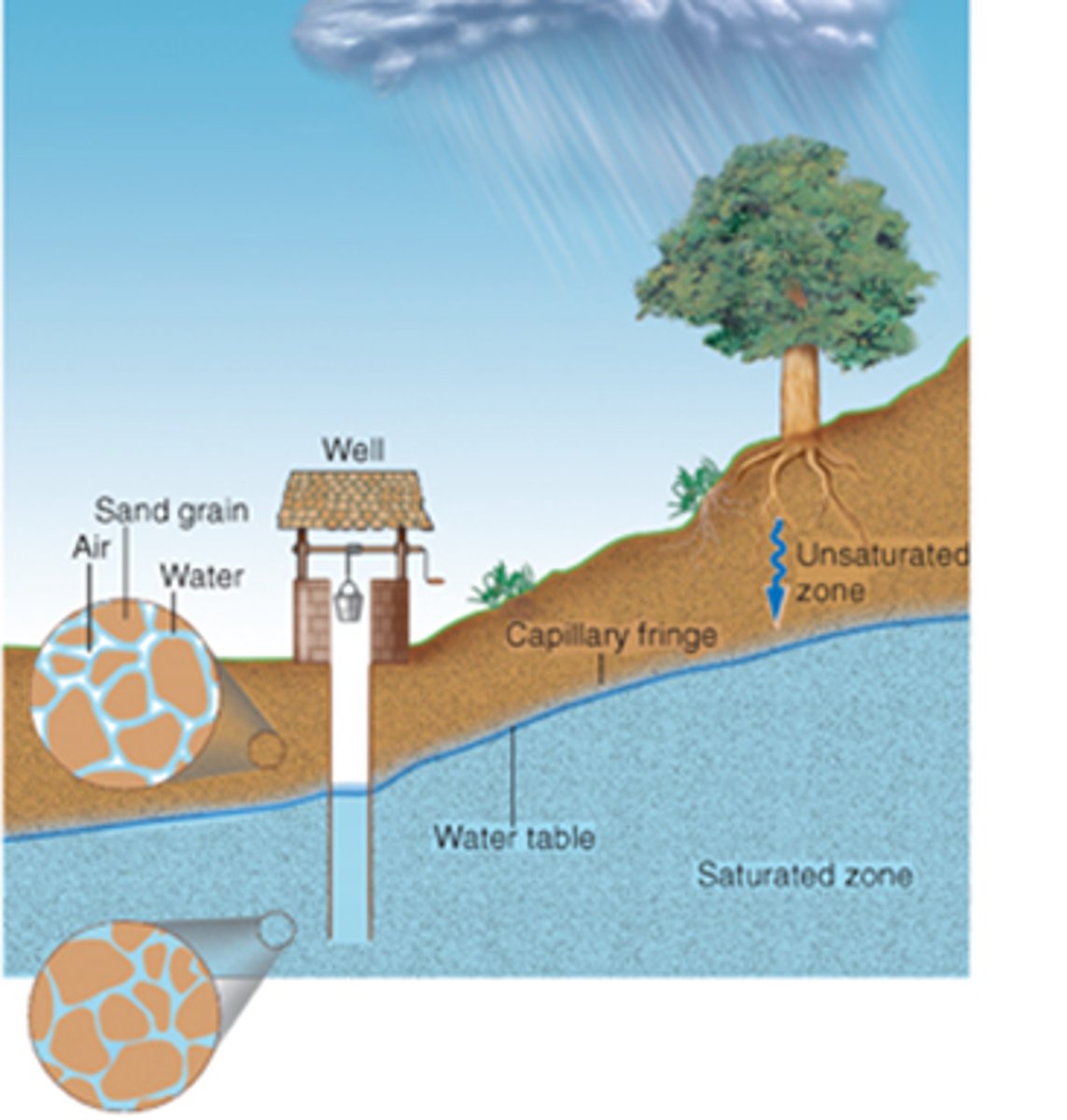
Zone of saturation
The lower zone where water accumilates between small rock particles.
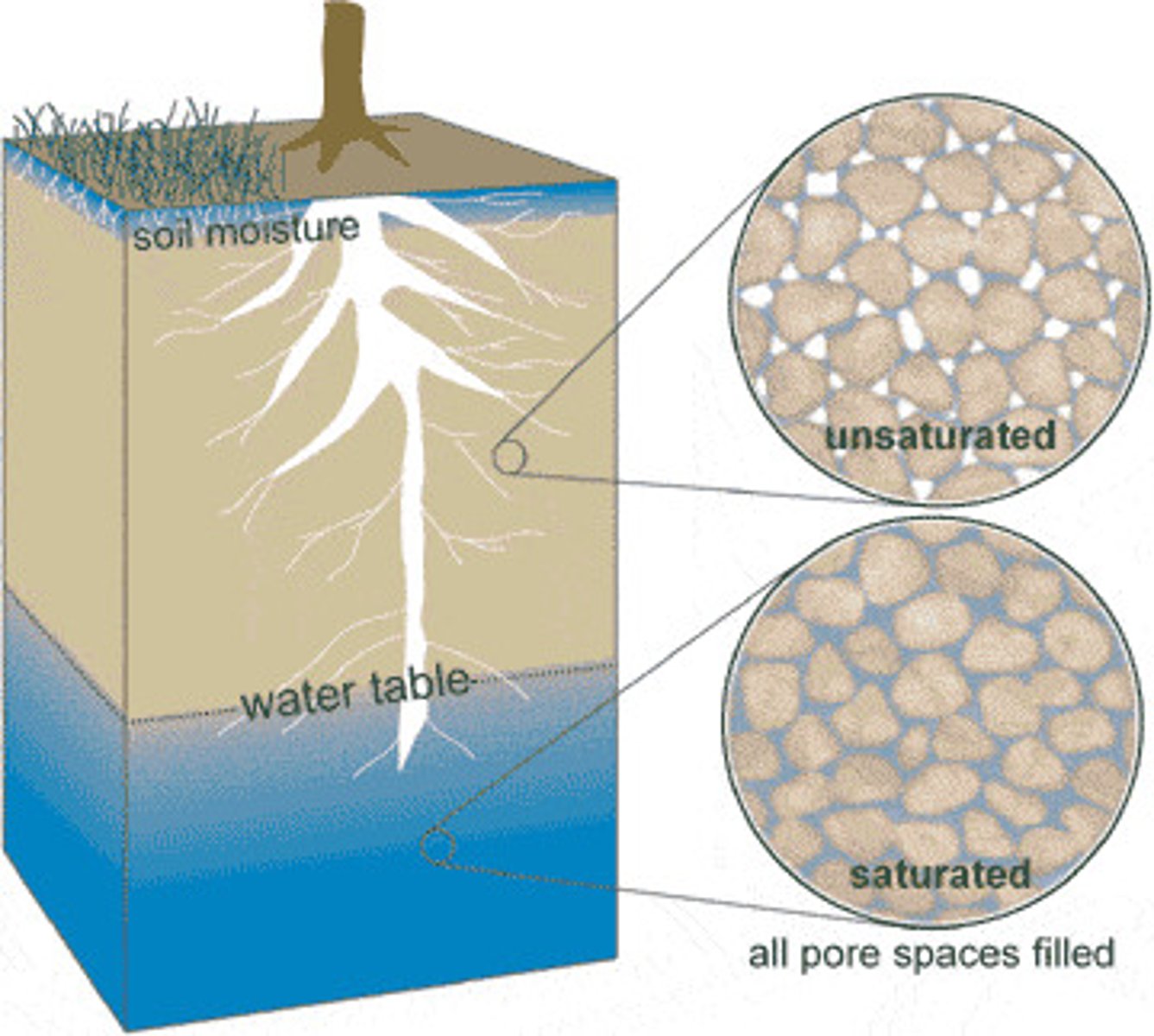
Zone of aeration
The upper zone which usually isn't completely filled with water, but with rocks and soil too. ( Is about Ground water)
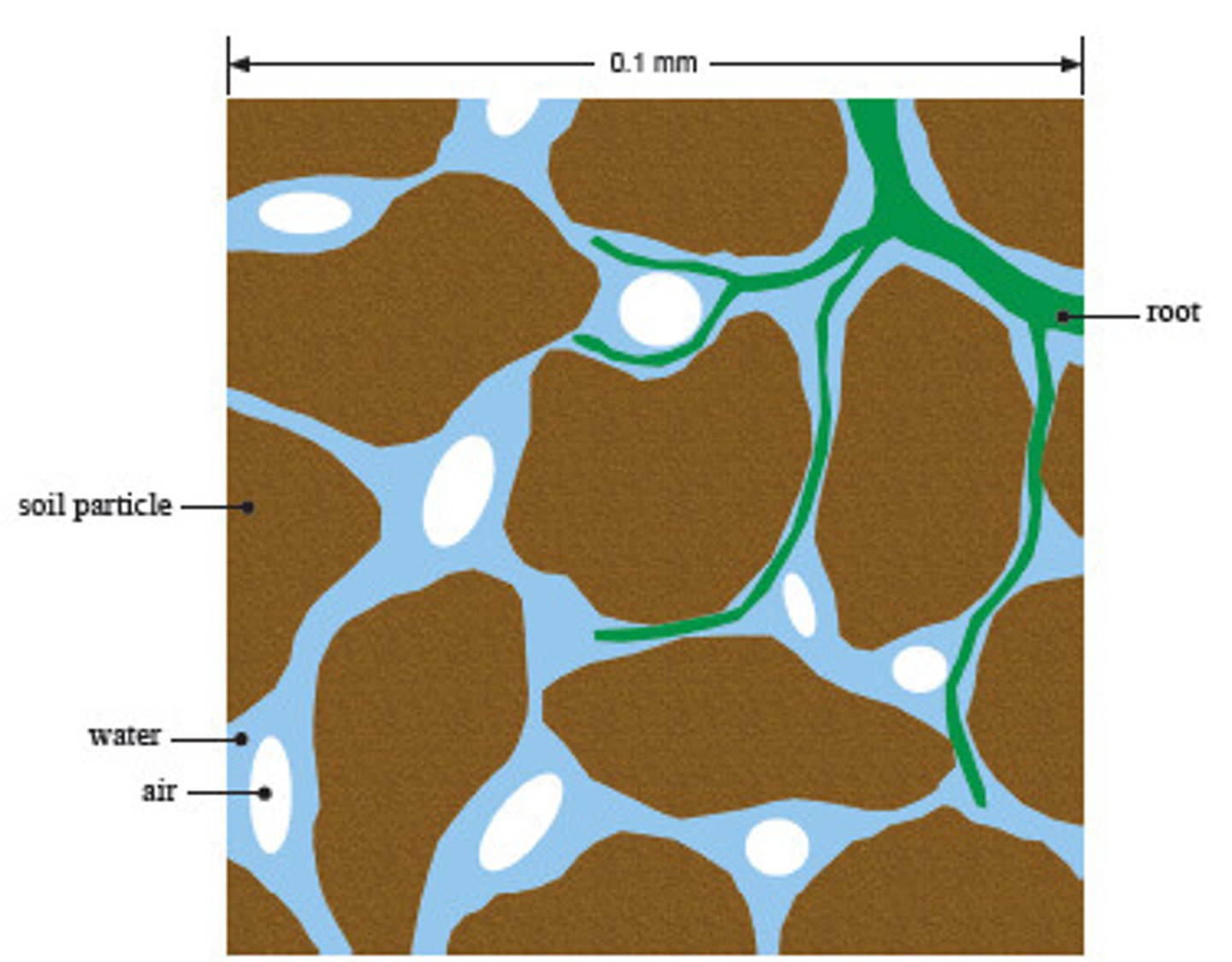
Pore space
The space between soil particles
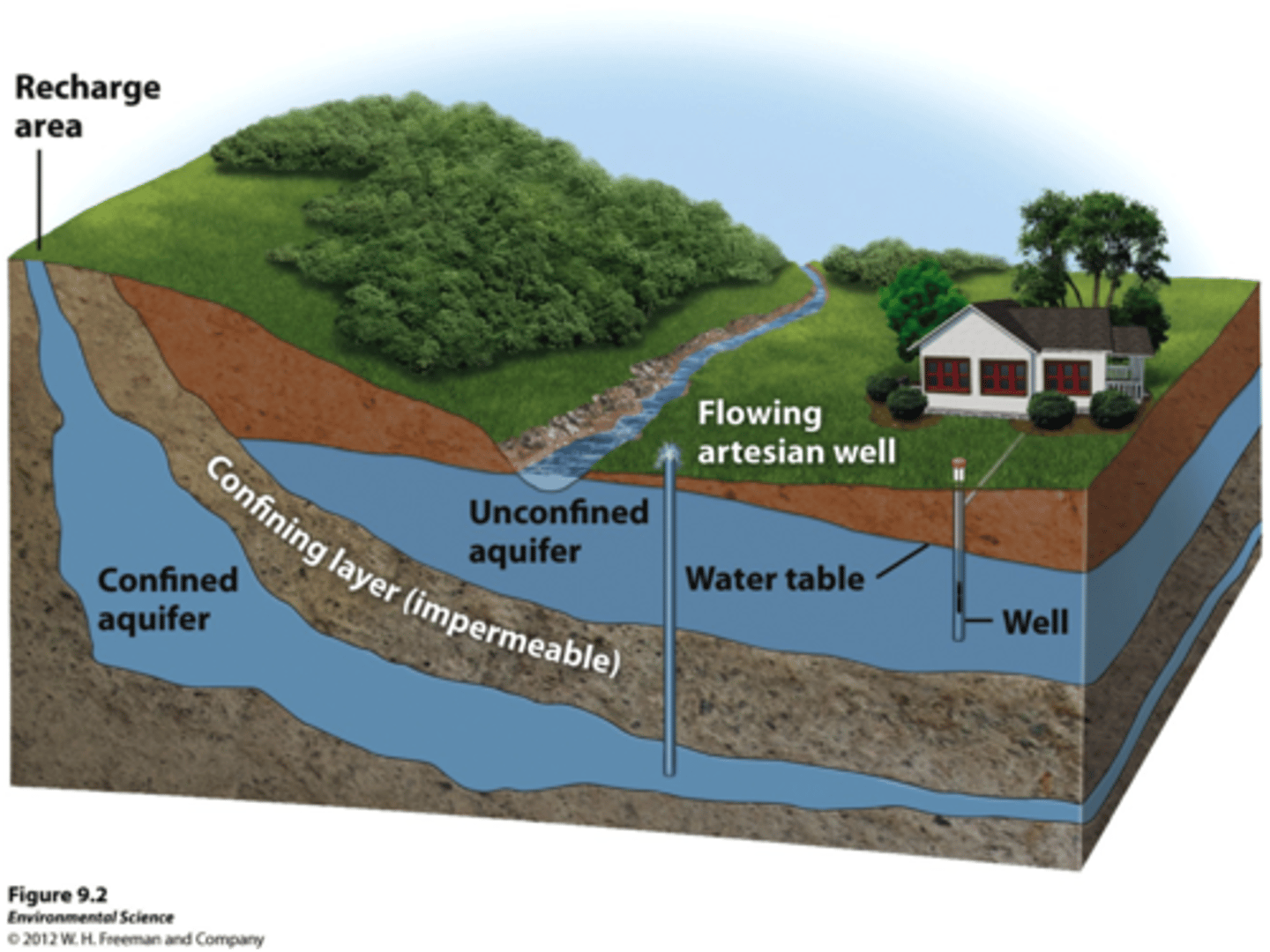
Infiltration ground water
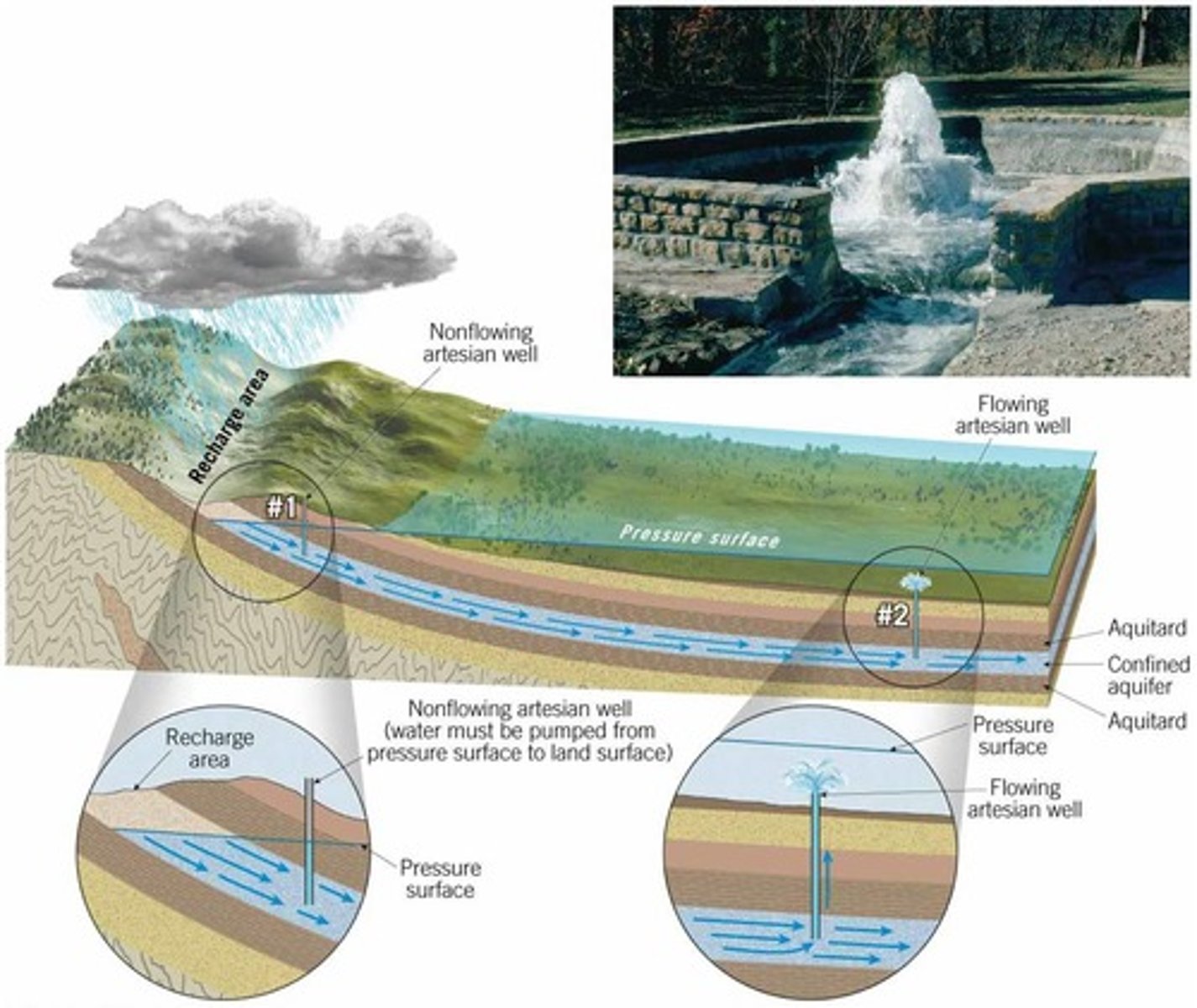
Aquifer
water quantity sufficient for springs and wells
Porosity
percentage of openings to total volume of rock
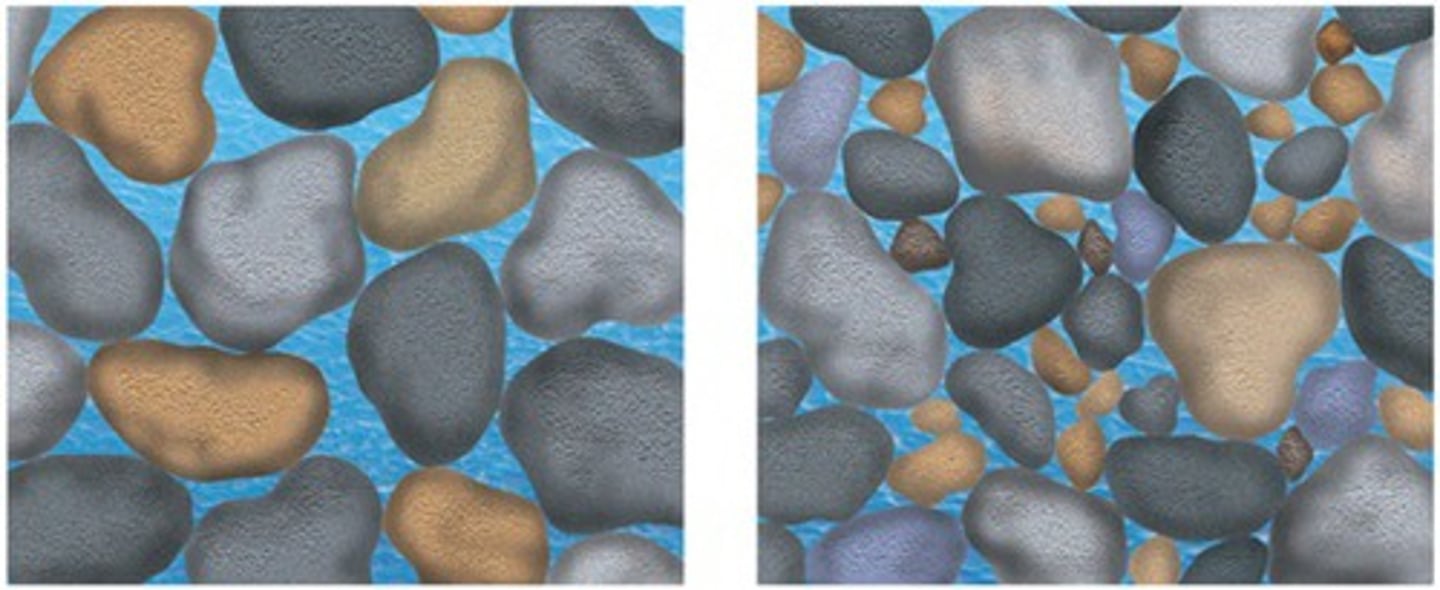
Permeability
ease with which fluids flow through an aquifer
Hydraulic conductivity
more precise term for flow through an aquifer
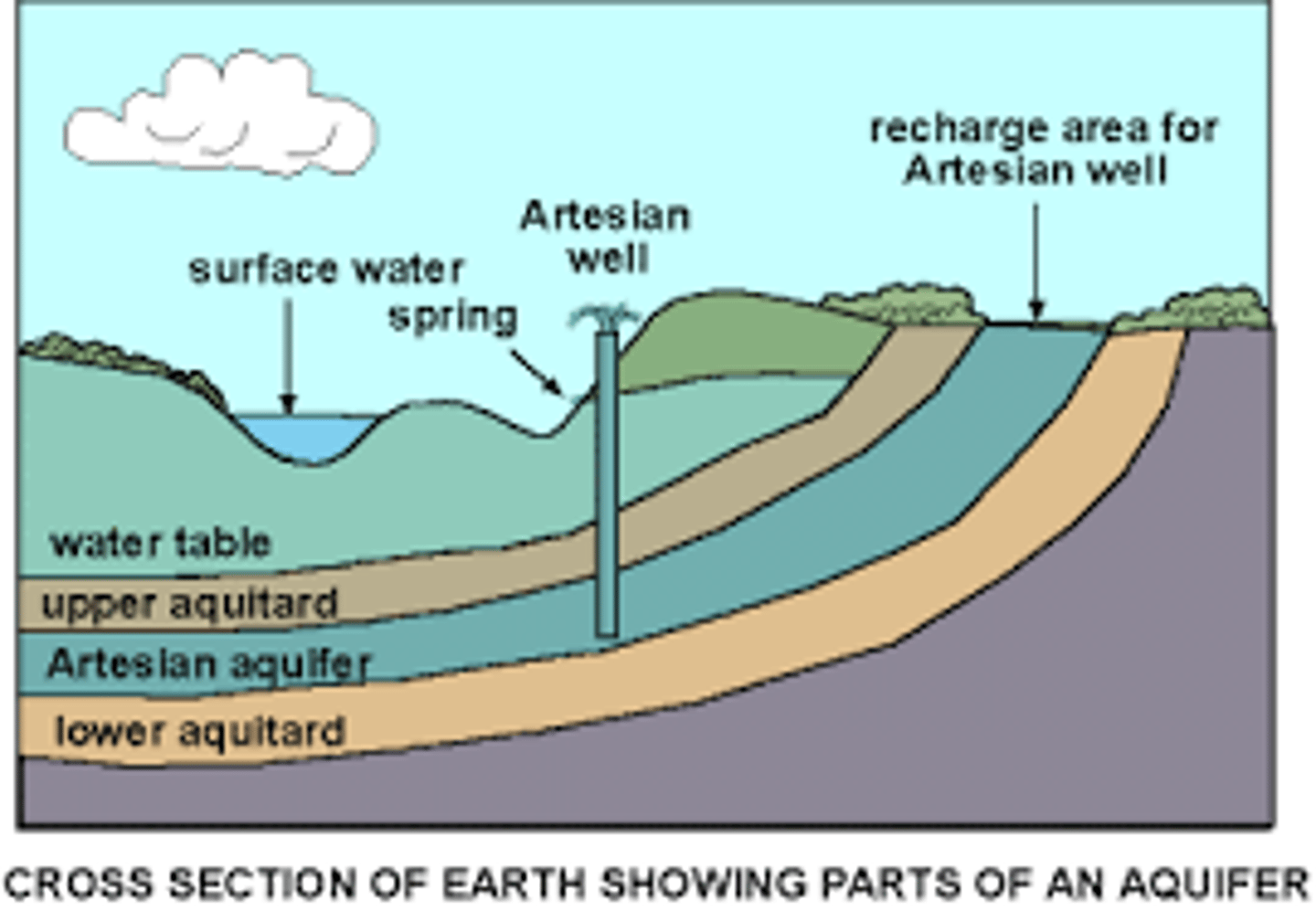
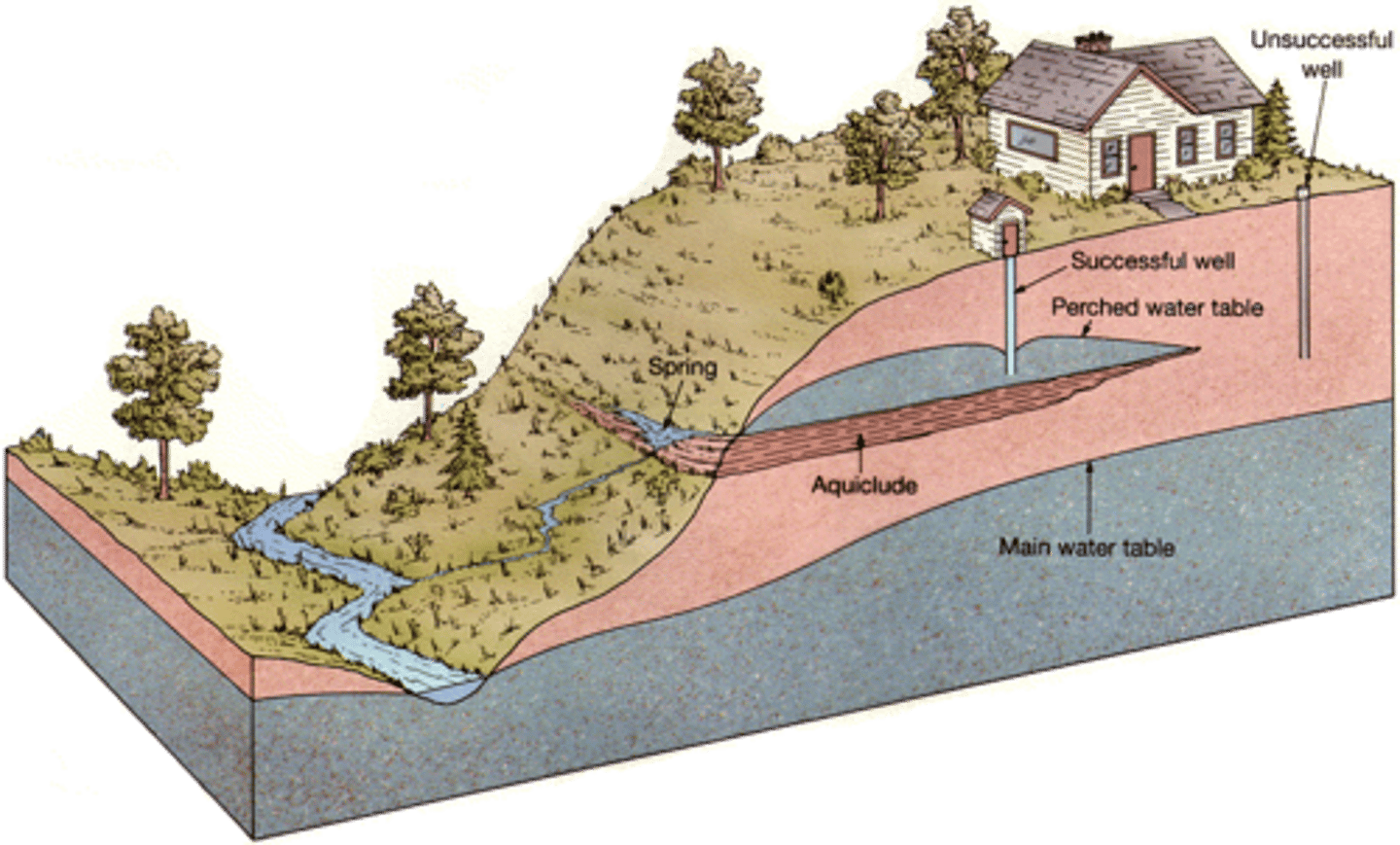
Perched water table
an isolated zone of saturation above the rest of the local water table
Capillary fringe
The area just above the water table, in the zone of aeration, where water moves upward from the water table by capillary action.
Aquiclude
A body of rock that will absorb water slowly, but will not transmit it fast enough to supply a well.
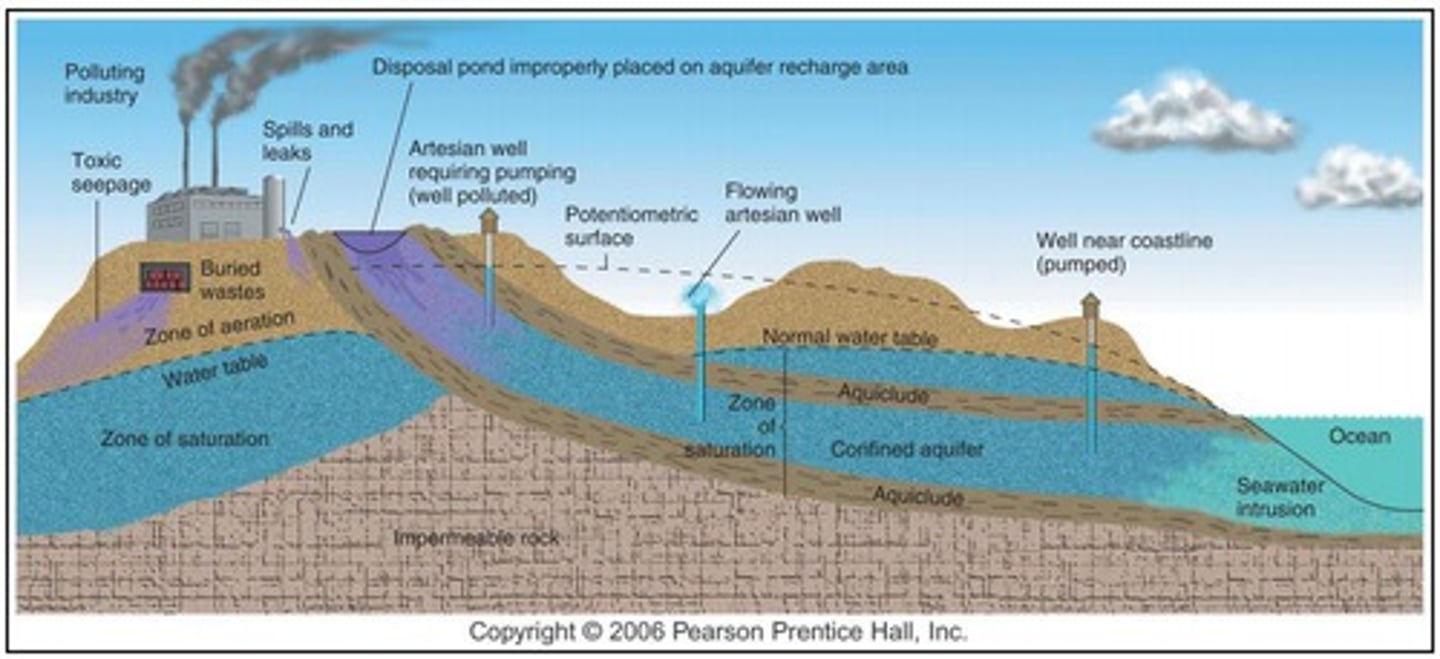
"Confined" aquifer
A groundwater storage area trapped between two impermeable layers of rock.
Streams and springs are influenced by...
groundwater
Losing stream
- above local water table
- can create a recharge mound
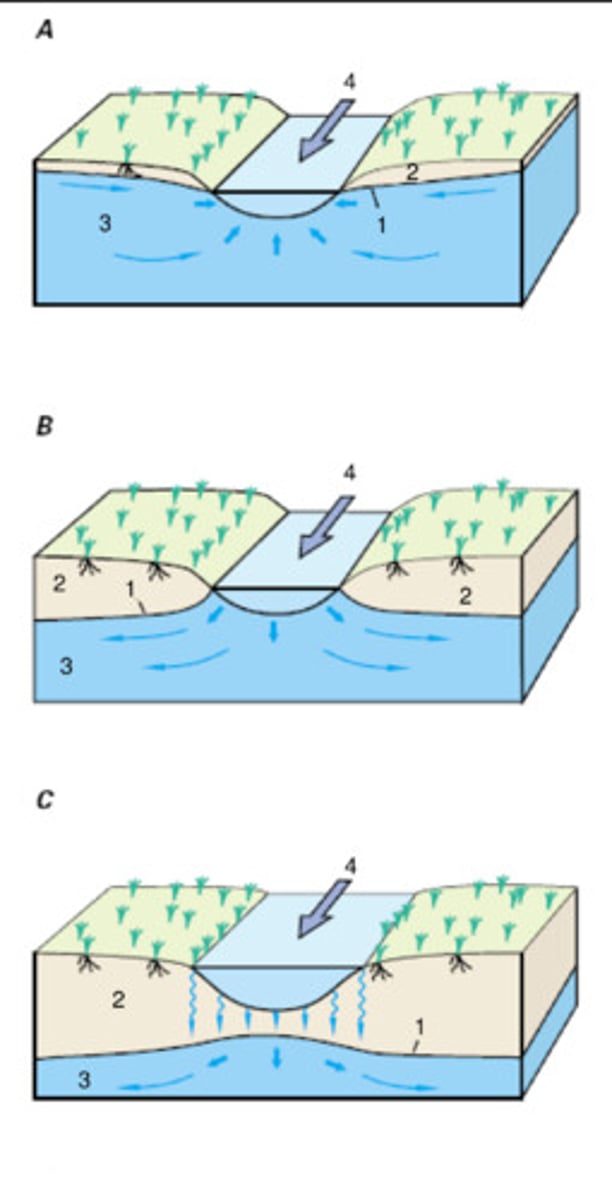
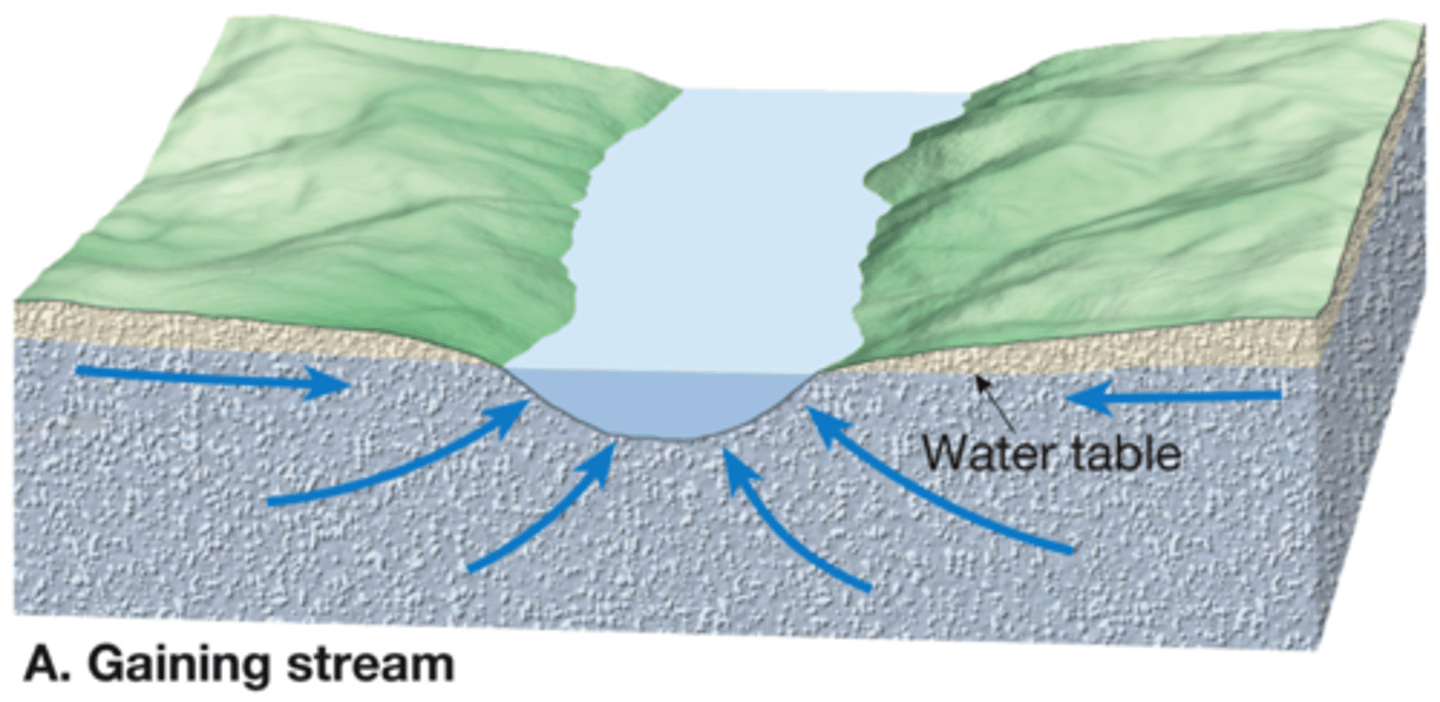
Gaining stream
Intersects water table and is fed in part by groundwater
Cone of depression
lowering of the water table around a pumping well
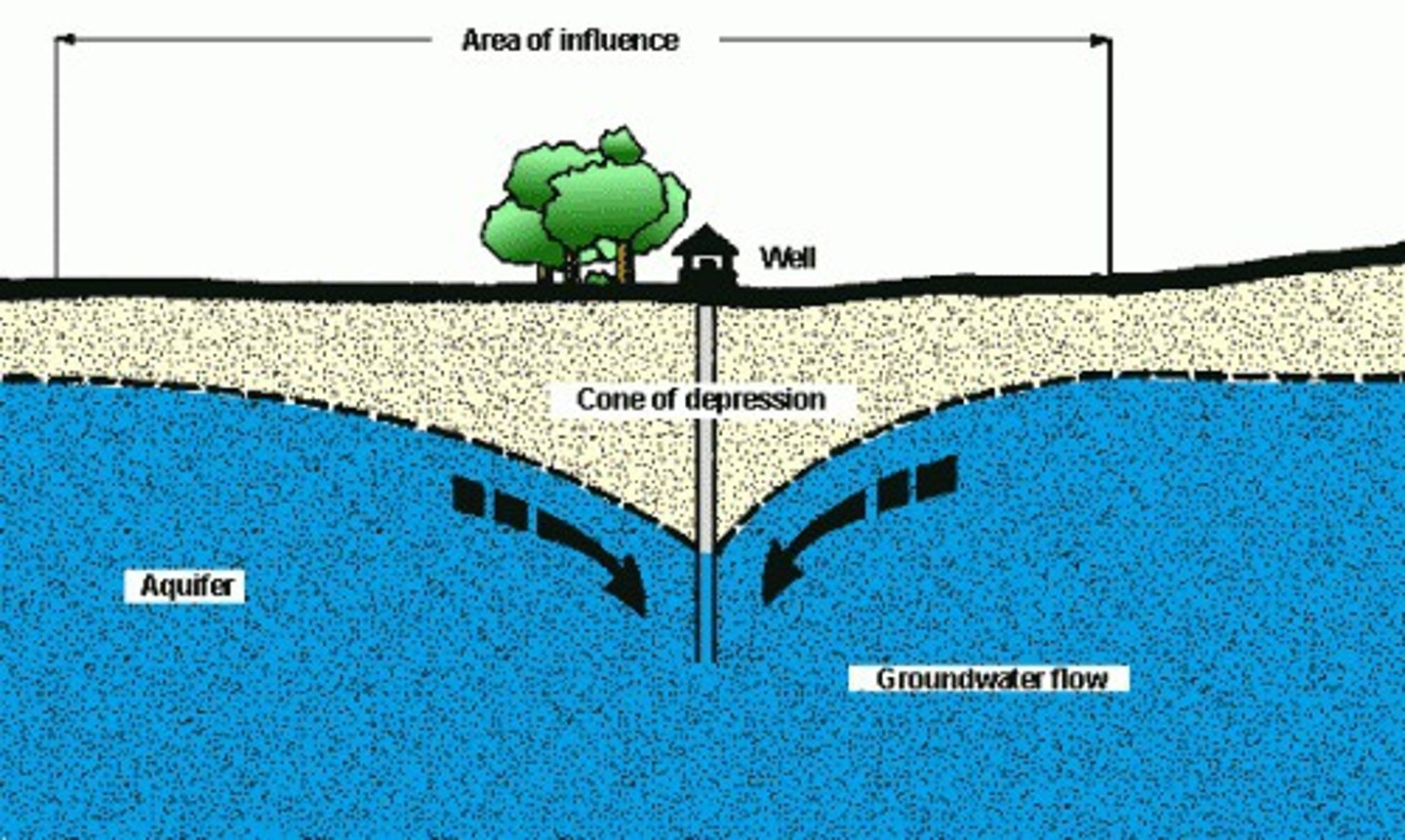
Mining groundwater
can cause shallow wells to go dry
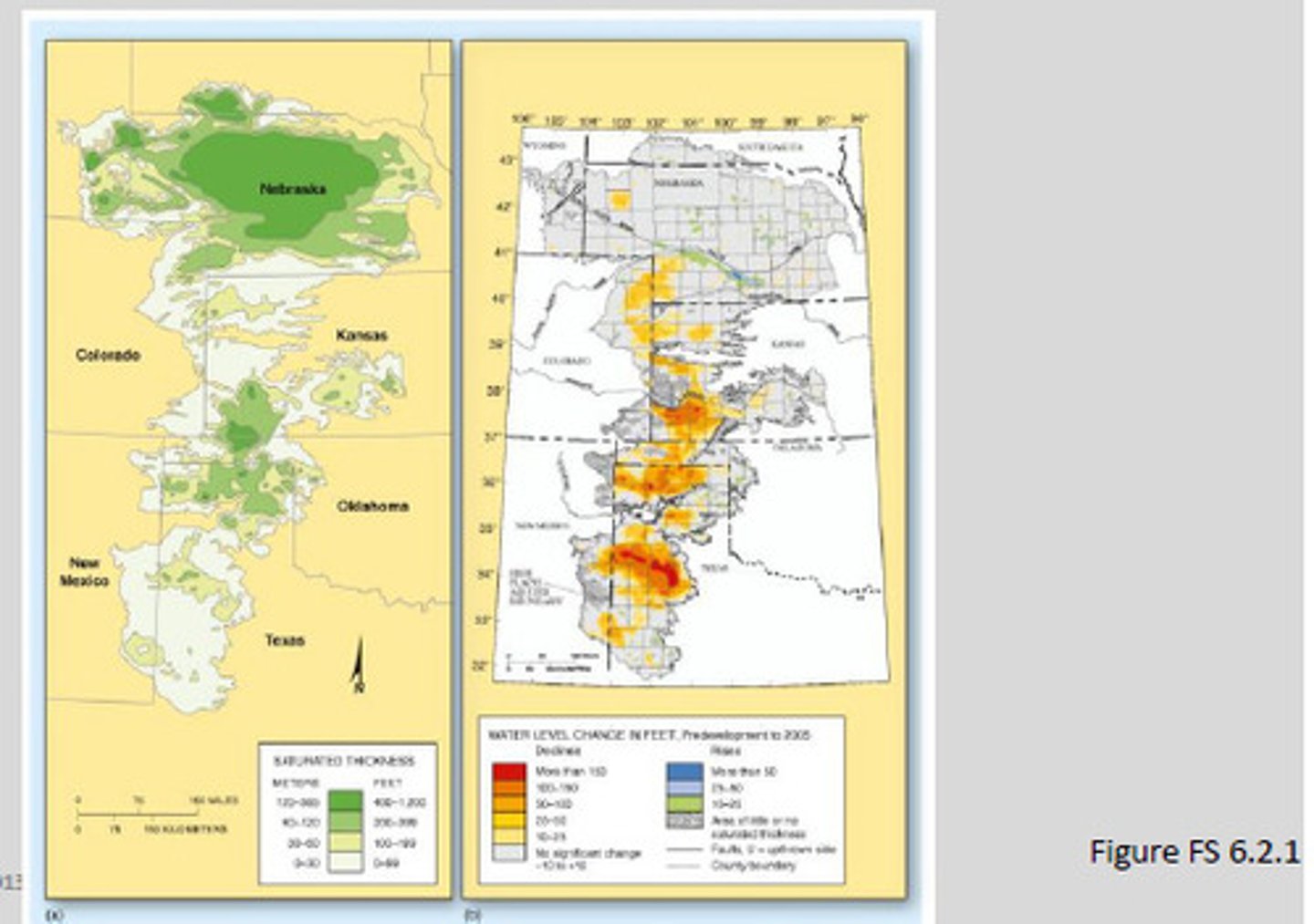
High Plains aquifer
- Ogallala Sandstone
- Large overdrafts
- Government subsidies favor water-loving corn
- By 2020, 1/4 of water will have been mined
The shrinking Aral Sea
- Once fourth-largest lake in the world
- Soviet Union diverted rivers for irrigation (evaporation exceeds inflow)
- Blowing dust from dry lake-bed causes air pollution
Pollution
introduction of harmful materials or conditions to environment

Contamination
rendering something unusable due to pollution

Toxic
materials that are harmful to humans and other organisms

Carcinogen
cancer-causing agent

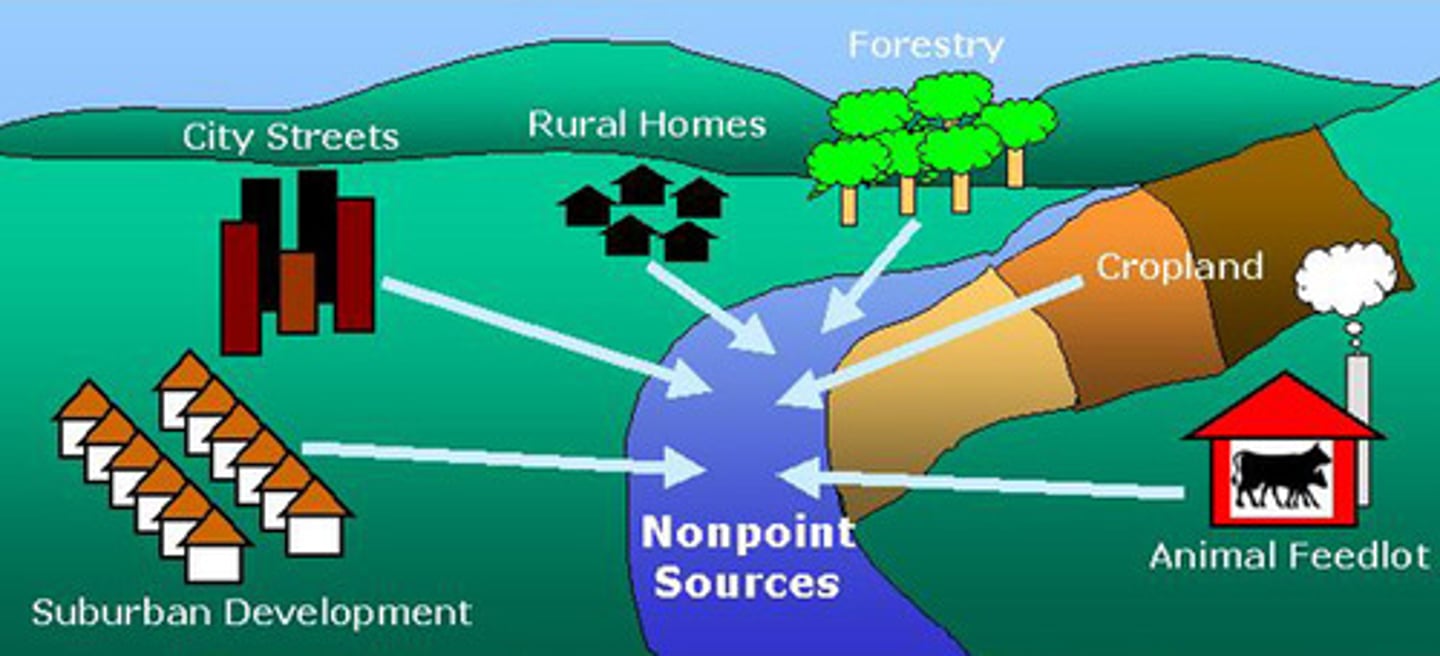
Point Source
a specific locality at which pollutants enter the environment

Non-point Source
emission from diffuse or broad area-based sources
Measurements for concentrations
micrograms/cc, milligrams/cc, ppm, ppb, etc.
Physical hazards
• Earthquakes
• Tsunamis
• Storms
• Floods
• UV radiation
• Volcanoes
Chemical hazards
Metals (Mercury, Chromium, Lead, Arsenic)
Herbicides/Insecticides (Dioxin, others)
Fertilizers
Petroleum
products/solvents
Endocrine disruptors
( DDT, PBCs, BPA?)
Ozone

Lead
impairs neurological function
Arsenic
Arsenic occurs in groundwater-
Variable spatially
Natural sources?
Concentrated in some regions?
Why?
Hormonally Active Agents (HAAs)
transmit information in addition to that provided by natural hormones to control DNA formation in cells.
Amphibians are particularly vulnerable to DDT and other pesticides
Tropospheric Ozone
a powerful oxidant
Leads to respiratory problems (asthma, etc.), and
disrupts plant cells as well!
Asbestos
Fibrous mineral (Chrysotile) used for insulation
- carcinogenic when inhaled

Electromagnetic Fields
Concerns regarding radio-frequency radiation and health.
Effective dosage
ED-50 Does something (beneficial) for 50% of people
Toxic dosage
TD-50 Is toxic for 50% or people
Threshold Dose: Level below which there is no effect (could be 0)