Chapter 20- Lymphatic System
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
132 Terms
Lymph, lymphatic vessels, lymphoid organs and lymphoid tissue (throughout the body)
What four structures comprise the lymphatic system?
Return fluid to the bloodstream, absorbs fat and fat soluble vitamins from the intestines, and defends the body against disease
What are the three main functions of the lymphatic system?
Lymph
A clear fluid that resembles plasma is known as _.
Water, electrolytes, waste products and proteins
Lymph is made up of what four components?
20
Approximately _ liters of lymph filter through from the interstitium each day.
True
True or False: Lymph is returned to the venous blood.
Edema
If the lymphatic system did not return fluid to the blood stream, _ would result.
Left
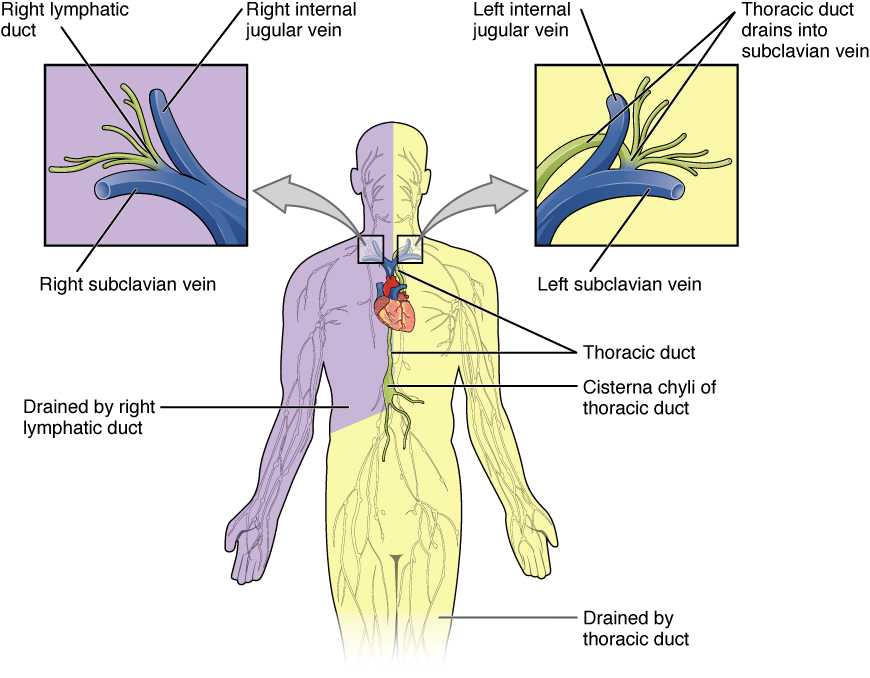
The thoracic duct is dumped into the (right/left) subclavian.
False (veins)
True or False: the distribution of lymphatic vessels is similar to that of the arteries.
Capillaries
Lymphatic _ contain pores and valves.
Subclavian vein / internal jugular vein
Lymphatic capillaries drain into larger vessels that eventually drain into the venous system at the junction of the ________and the _________on either side.
Left Thoracic Duct
The _ duct drains ¾ of the body's lymph.
Left
The majority of the body's lymph is drained from the _ side.
Right upper quadrant
The remaining lymph is drained from the of the body.
Contraction of skeletal muscles, changes in intrathoracic pressure, contraction/relaxation of the smooth muscle in the walls of lymphatic vessels.
What three mechanisms contribute to the movement of lymph through the body?
Valves
Multiple _ are present in the lymph vessels to prevent the backflow of lymph fluid.
True
Once lymph enters the right subclavian vein, it mixes with the venous blood. At that point, it is no longer called lymph — it becomes part of the blood plasma in the circulatory system.
True or False: once the fluid from the right side of the body is dumped into the right subclavian vein, it is no longer lymph fluid, it is blood.
True
True or False: swollen, tender lymph nodes mean that the lymph is active
Cancer
Swollen lymph nodes that present with no tenderness upon palpation may indicate what pathology is present?
Lymph Nodes
Small bean shaped patches of lymphatic tissue which filter lymph as it flows through the vessels toward the circulatory system are called
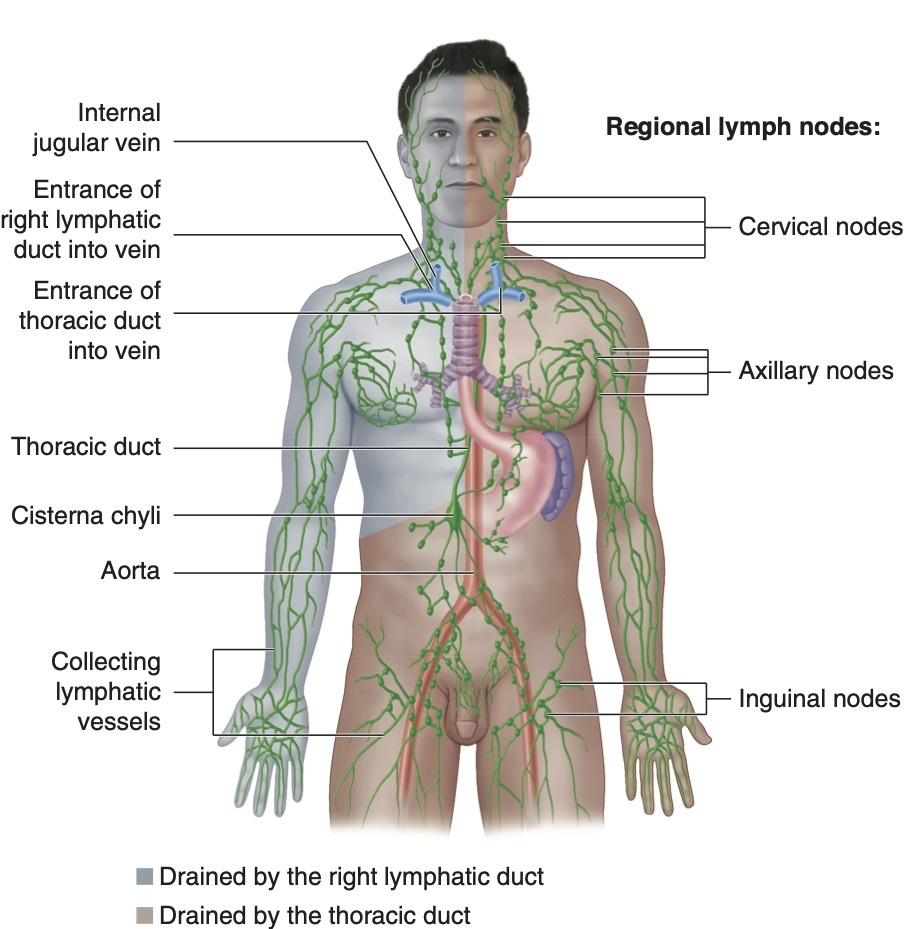
Cervical, axillary and inguinal
Lymph nodes appear in clusters in which three regions of the body?
nodules/sinuses
Lymph nodes consist of lymph and lymph _.
Afferent
_ vessels carry lymph toward the lymph node.
Efferent
_ vessels carry lymph away from the lymph node.
True
True or False: lymph nodes range in size from the head of a pin to a bean.
Lymphocytes
Lymph nodes are encapsulated with fibers inside that contain clusters of which act as a filter.
Macrophages
These cells inside a lymph node eat the bad stuff filtering through the lymph node.
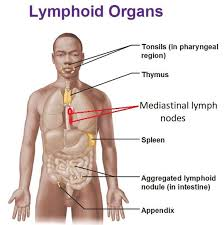
Thymus
The _ gland is located in the upper mediastinum.
Immune system
The thymus gland is involved in the development of the before birth and shortly after birth.
Thymosins (hormones)
The thymus secretes _ that promote the proliferation and maturation of T-cells in lymphoid tissue.
Thymus Gland
The is responsible for the development and maturation of the immune system.
Spleen
This is the largest of the lymphoid organs.
Blood
The function of the spleen is to filter and clean the _.
White and red pulp
Which two tissue types make up the spleen.
White pulp
Lymphoid tissue surrounding the blood vessels is called
Red Pulp
blood -filled venous sinuses that also contain lymphocytes and macrophages are called _.
Blood storage, destroys old RBCs, erythropoiesis before birth, lymphocyte production
Besides filtering and cleaning the blood, list four other functions for which the spleen is responsible.
Puberty
Lymphoid tissue reaches peak development at _.
False (decreases in size)
True or False: The lymphoid tissue gradually increases in size once you hit puberty.
True
True or False: The thymus gland involutes (shrinks) with age.
Connective
As you age, Thymus gland tissue is replaced with _ tissue.
Decreased
As you age thymosins decrease in production resulting in (increased/decreased) defense mechanisms with age.
White pulp
The lymphatic nodule of the spleen would be located in which tissue type?
True
True or False: by the end of the lymphatic cycle, lymph fluid has been cleaned several times.
True
True or False: Lymphatic capillaries have more and larger pores than regular capillaries.
True
True or False: lymphatics start blindly at the tissue space.
increasing pressure inside the lymphatic capillary
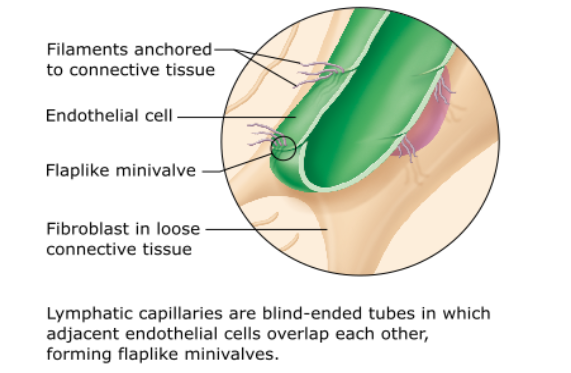
Minivalves will allow fluid in when external pressure exceeds internal pressure but will prevent fluid loss when the pressures are reversed.
Which of the following promotes closure of the minivalves associated with a lymphatic capillary?
increasing pressure inside the lymphatic capillary |
inflammation of tissues surrounding the lymphatic capillary |
anchoring of endothelial cells to adjacent structures by collagen fibers |
increasing pressure in the interstitial space |
They filter lymph.
Which of the following is a role of lymph nodes?
Lymph is excess tissue fluid formed from plasma that has leaked from capillaries
As blood circulates through the body, nutrients, wastes, and gases are exchanged between the blood and the interstitial fluid. The hydrostatic and colloid osmotic pressures operating at capillary beds force fluid (plasma) out of the blood at the arterial ends of the beds and cause most of it to be reabsorbed at the venous ends. The fluid that remains behind in the tissue spaces, as much as 3 L daily, becomes part of the interstitial fluid. The lymphatic vessels collect this excess interstitial fluid (now called lymph) and return it to the bloodstream.
Which statement correctly describes the origin of lymph fluid?
Peyer’s patches is NOT true
B cells mature in one of the primary lymphoid organs such as bone marrow
Peyer’s patches are located in wall of distal portion of small intestine
destroy bacteria, preventing them from breaching intestinal wall
generate “memory” lymphocytes
Which of the following lymphoid organs is NOT matched with its function?
thymus: site of T cell maturation |
bone marrow: form lymphocytes |
Peyer's patches: site of B cell maturation |
spleen: remove old red blood cells |
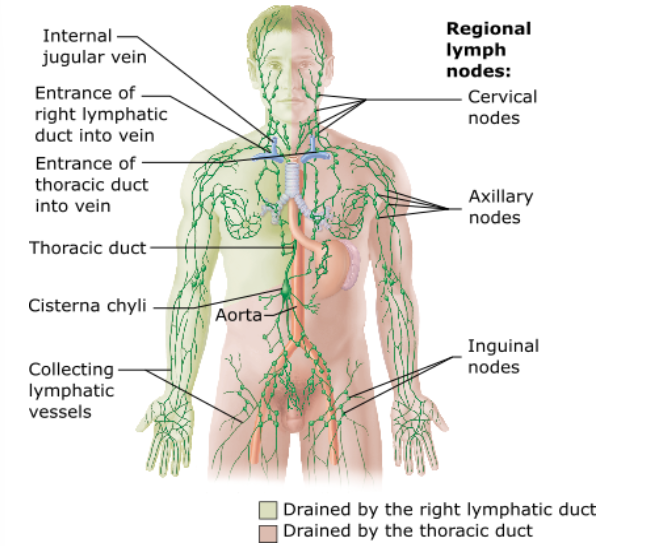
Cisterna chyli
passes lymph from the entire body below the diaphragm into the thoracic duct for return to the heart
What is the name of the enlarged sac to which the lumbar trunks and the intestinal trunk return lymph?
C) the spleen
the spleen harbors macrophages that ingest and recycle materials from erythrocytes that have aged or become damaged
Which lymphoid organ extracts aged and defective blood cells and platelets from the blood in addition to storing some of the breakdown products for later reuse?
plasma cells
activated B cells, called plasma cells, are responsible for producing antibodies
Which lymphoid cells produce antibodies?
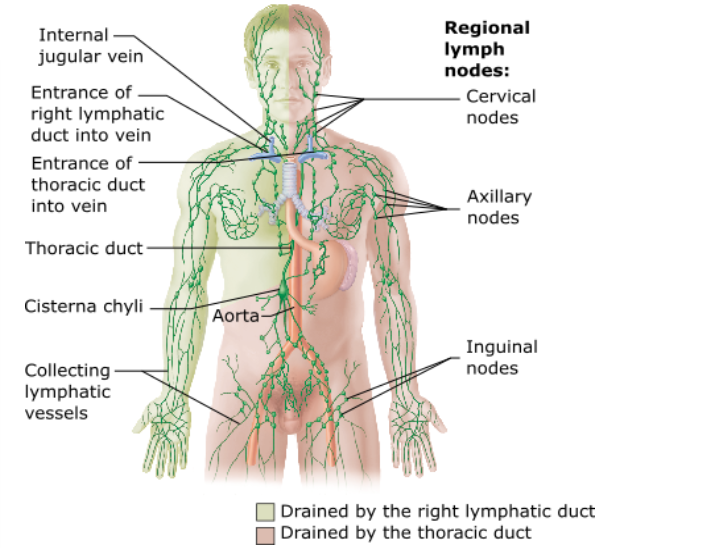
the right upper limb, the right side of the head, and the right thorax
^^^Enter the venous circulation via the right lymphatic duct
Lymph from what regions of the body is drained into the right lymphatic duct?
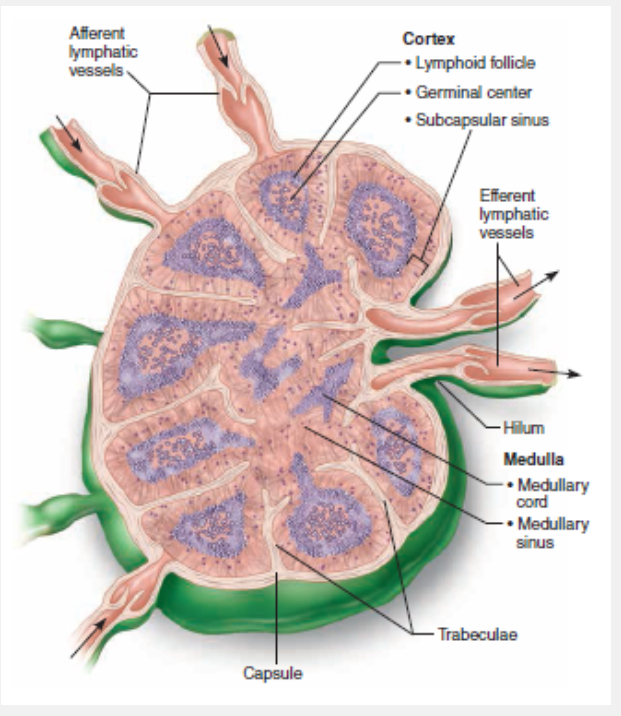
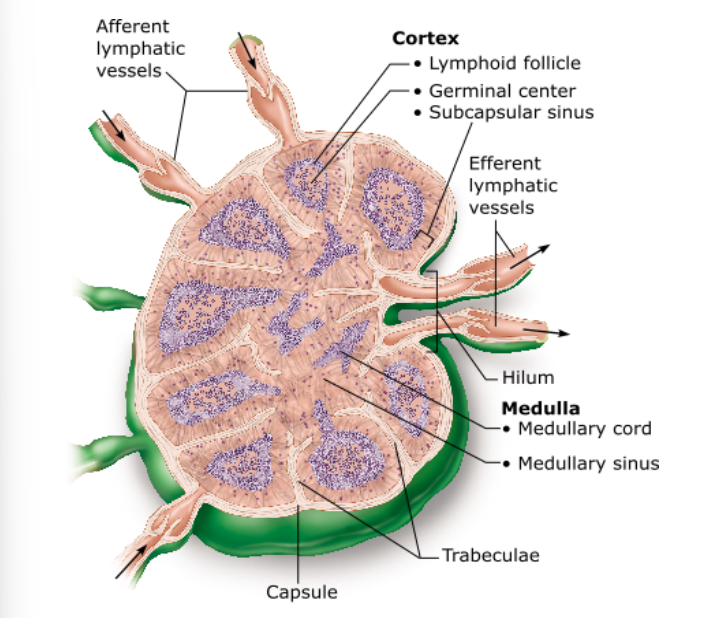
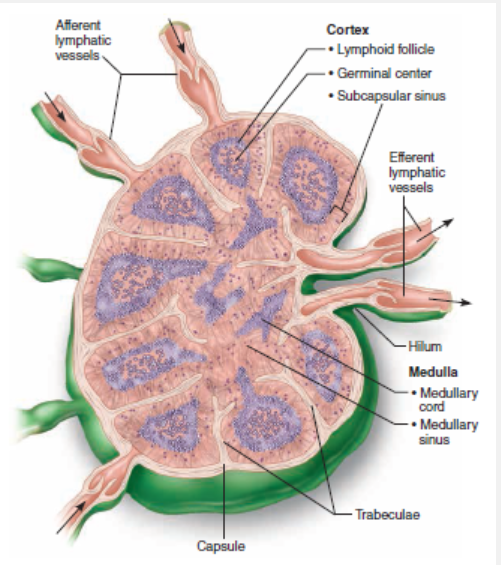
Cortex
The lymphoid follicles of the cortex contain germinal centers dominated by B cells, which produce antibodies against antigenic agents
What region of the lymph node contains follicles filled with dividing B cells?
Infection
After splenectomy, your patient has a markedly increased risk of overwhelming bacterial infection. You will help to minimize the risk by educating her and by insuring that she receives specific immunizations recommended for patients after splenectomy.
Your patient has had her spleen removed after it was ruptured in a motorcycle accident. Which of the following is your greatest concern for her future health status?
removal or aged and damaged red blood cells from the blood
Although the spleen is the main site of red removal from the blood of old and damaged red blood cells, macrophages in the bone marrow and liver are able to perform this function.
The spleen is a unique lymphoid organ that filters blood, rather than lymph. Following splenectomy in an adult, which of the following splenic functions would be performed by the bone marrow or liver?
Minivalves
minivalves are loosely overlapping endothelial cells that allow fluid into the vessels but that do not let fluid out
What is the unique structural modification in lymphatic capillaries that increases their permeability?

wall of the small intestine
Peyer’s patches are mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue located in the ________
The red streaks suggest lymphangitis, which occurs when the blood vessels that supply inflamed lymphatic vessels (vasa vasorum) become congested with blood. You are concerned that the patient's wound is infected by bacteria.
A patient's deep hand laceration was sutured at your clinic yesterday. When you make a follow-up call today, the patient reports "some red streaks on my forearm." Why are you concerned?
Chyle
Liquefied fat called _____ carried by lacteals from the small intestine to the bloodstream
(another word for lymph but for this specific one)
Red bone marrow
Where do B lymphocytes mature?
Yellow bone marrow |
Red bone marrow |
Thymus gland |
Spleen |
bone marrow and thymus
B cells mature in the bone marrow
T cells mature in the thymus
Which of the following are primary lymphoid organs?
areas where T and B cells mature
They become immunocompetent here and therefore able to do their role in fighting off antigens and bacteria
They are where T and B cells mature
They become immunocompetent here and therefore able to do their role in fighting off antigens and bacteria
What are primary lymphoid organs and what happens here?
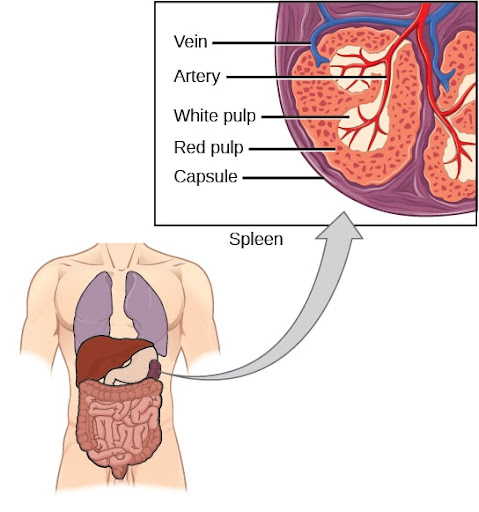
white pulp of the spleen
this is where lymphocytes are concentrated and the immune functions take place in the spleen
Which of the following areas in a secondary lymphoid organ allows intimate contact between blood and the lymphocytes?
Hassall’s corpuscles of the thymus |
red pulp of the spleen |
germinal centers of the lymph nodes |
white pulp of the spleen |
deep in the cortex
The T cells encounter antigens presented by dendritic cell sin the deeper part of the cortex. The cortex is the outer area of the lymph node
Where in the lymph node do the T cells first encounter antigens presented by dendritic cells?
medullary cords in the medulla |
germinal centers of the cortex |
deep in the cortex |
lymphoid follicles of the outer cortex |
Peyer’s patches are located in the small intestine and they guard against bacteria from the large intestine
Collections of lymphoid tissues, called MALT, are strategically placed throughout the respiratory, digestive, and genitourinary systems. Which one of these is located at the end of the small intestine?
The appendix is the offshoot of first part of large intestine
Contains a large number of lymphoid follicles
Same function as peyer’s patches
destroy bacteria, preventing them from breaching intestinal wall
generate “memory” lymphocytes
Empties contents into cecum (makes sense for location bc it is attached to cecum)
Where is the appendix located and what is it’s function in relation to the lymphatic system?
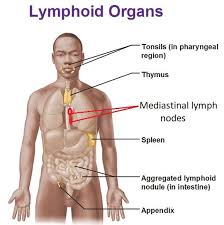
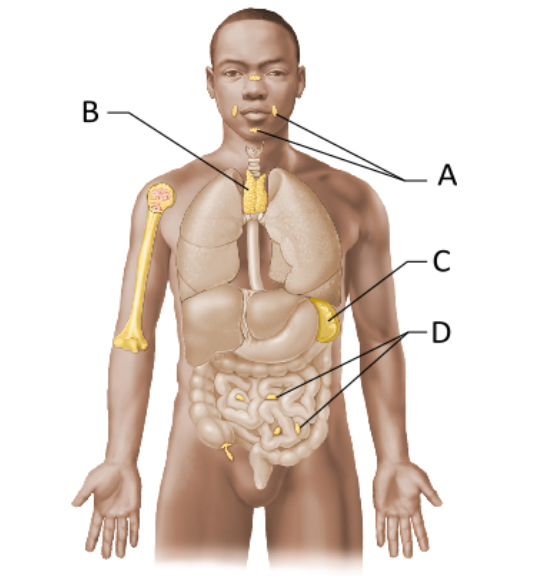
Label lymphoid organs
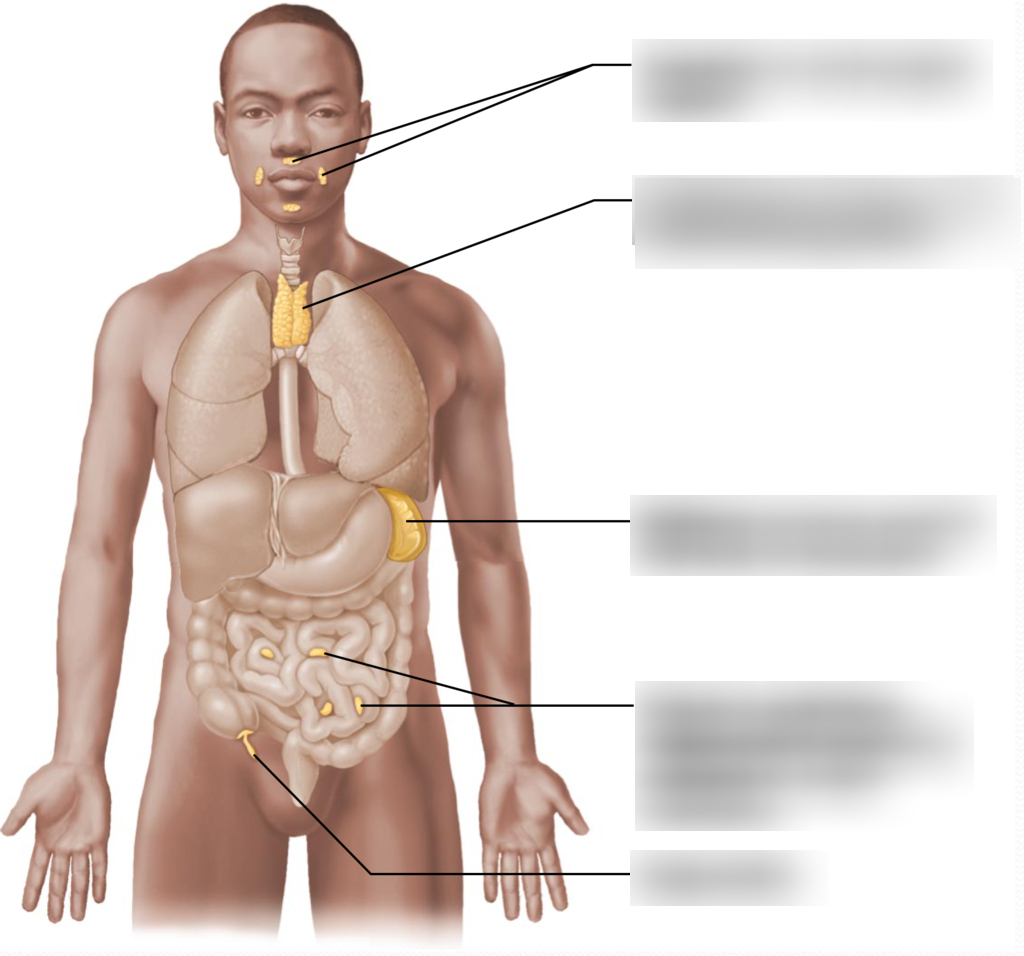
thymus
The relative size of the thymus as well as its function decreases with age. Thymic atrophy may be one reason the elderly are more susceptible to infection.
There is a decrease in our ability to fight infection as we age. Which lymphoid organ may have a role in this decline?
small, heart-like pumps
There is no direct pumping action in the lymphatic system. Movement of fluid depends on factors such as skeletal muscle contraction, pressure changes in the thorax during breathing, and contraction of lymphatic vessels
Which of the following mechanisms is NOT used to propel lymph through lymphatic vessels?
small, heart-like pumps |
contraction of the lymphatic vessels |
pressure changes in the thorax during breathing |
skeletal muscle contraction |

venous circulation
from the terminal lymphatic ducts, lymph rejoins venous circulation via the subclavian veins
Once collected, lymph is ultimately transported into ___
How are lymphatic capillaries different from blood capillaries?
Lymphatic capillaries have endothelial flap valves, but blood capillaries do not.
The endothelial cells forming the walls of lymphatic capillaries are not tightly joined. Instead, the edges of adjacent cells overlap each other loosely, forming easily opened, flaplike minivalves (figure below).
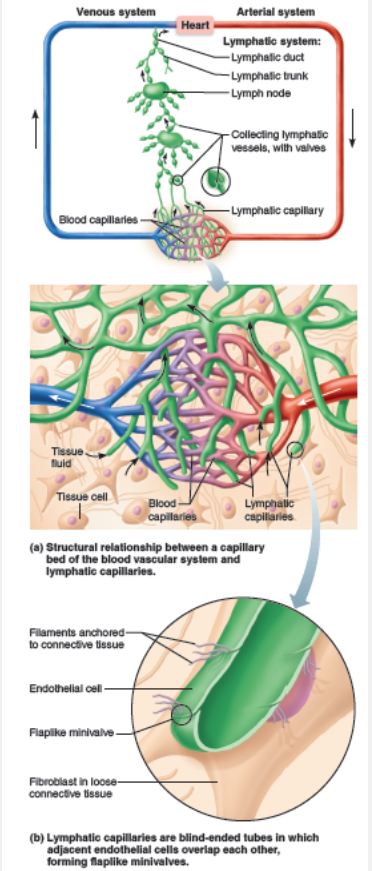
Which of the following features is not common to both lymphatic vessels and veins?
Transport of chyle
Tumors that block the lymphatics or lymphatics are removed during cancer surgery may result in what condition?
Lymphedema
Match the lymphatic structure with the correct characteristic: right lymphatic duct
Drains right side of the head, upper limb, and neck region
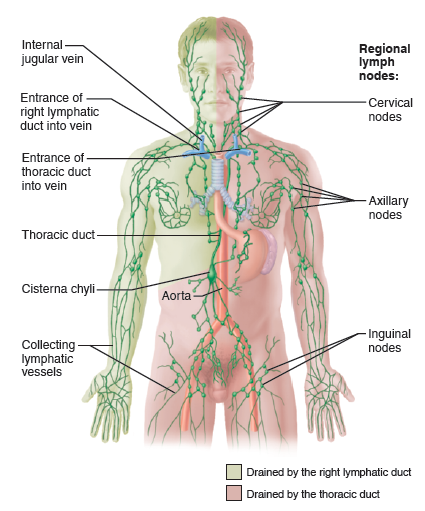
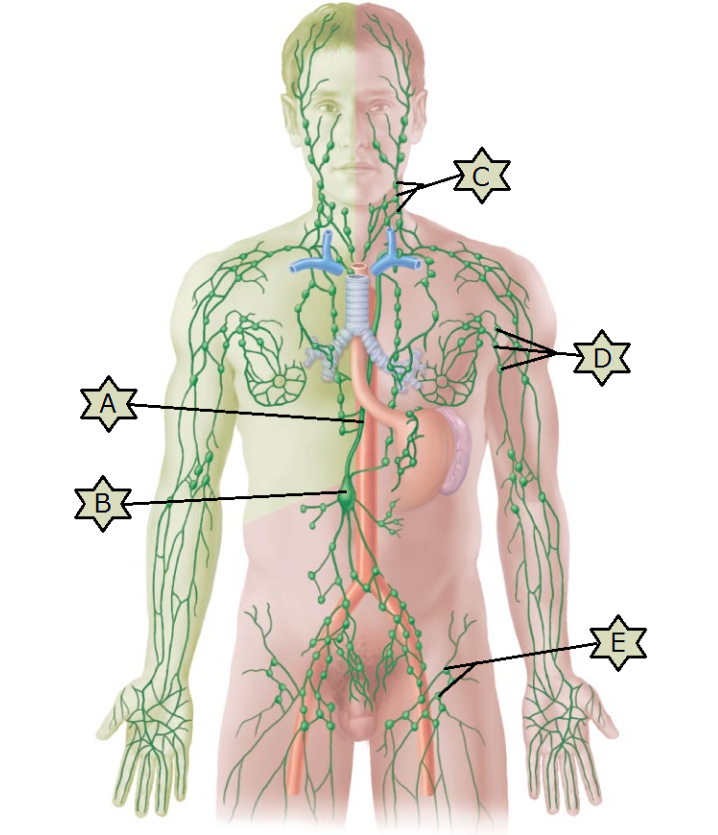
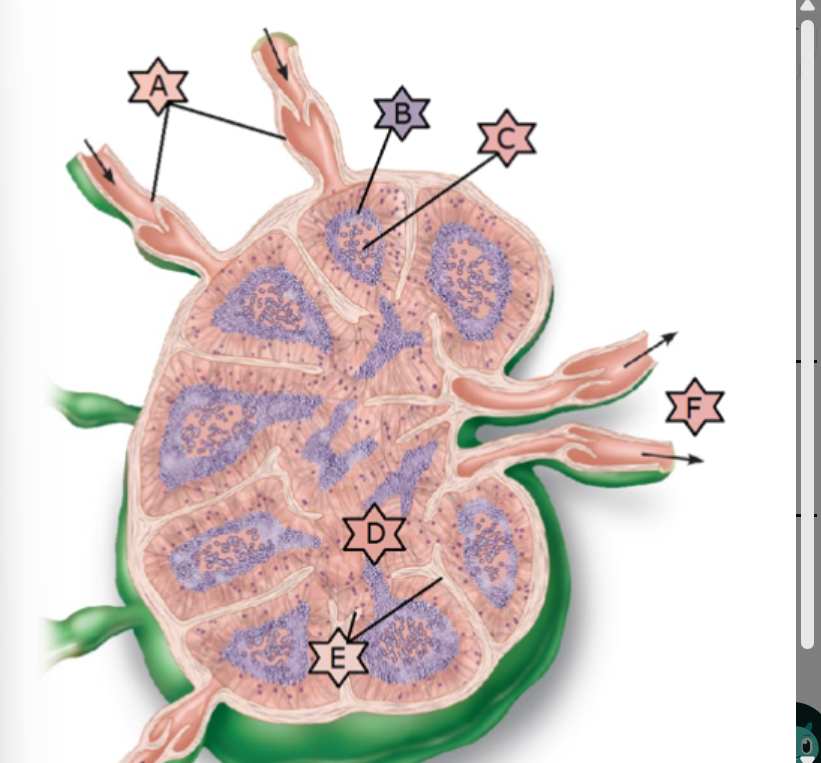
What is “A”?
Thoracic duct
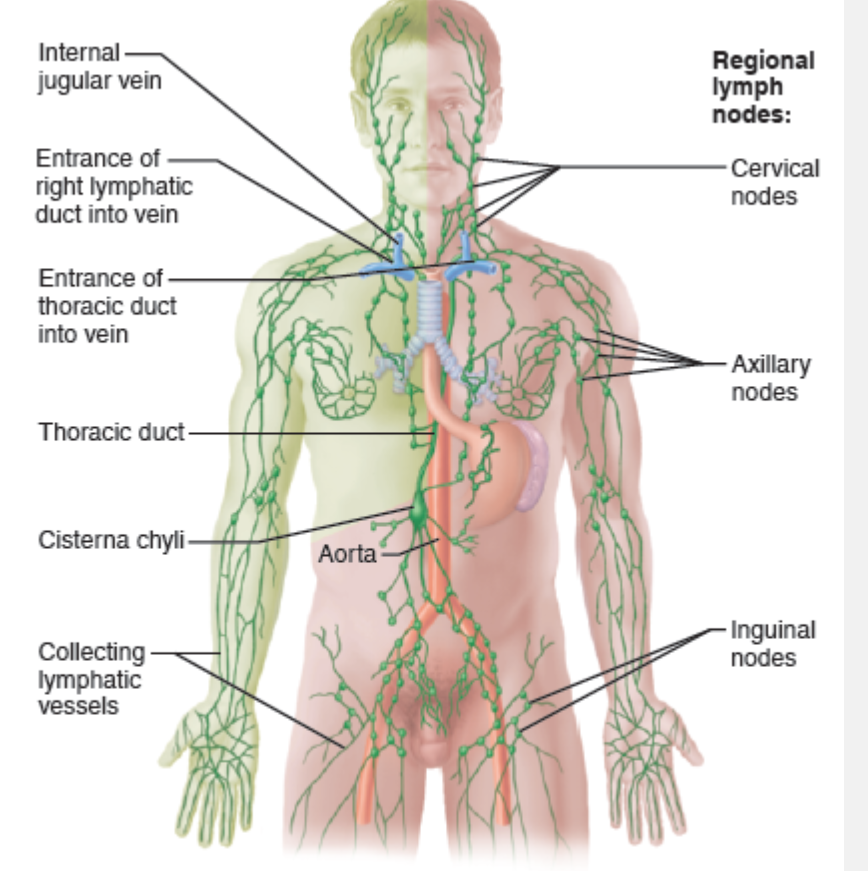
What is the function of the lymphatic collecting vessels?
Collect lymph fluid draining from lymphatic capillaries
Description of lymphoid tissue
A type of loose connective tissue called reticular connective tissue; dominates all lymphoid organs except the thymus
Which sequence best describes the flow of lymph through the lymphatic system?
Capillaries → vessels → trunks → ducts
What part of the lymphatic system is most closely associated with capillary beds?
lymphatic capillaries
Match the following with the appropriate description: Collecting lymphatic vessels.
Same three tunics as veins (intima, media, and externa) ; the second-smallest lymph vessels
Like veins, collecting lymphatic vessels are structured for low-pressure flow and have valves to prevent backflow.
Match the following structure with its function: lymphatic capillaries
smallest lymphatic vessels that collect tissue fluid
Lymphatic ducts
Largest vessels; carry lymph fluid to subclavian veins
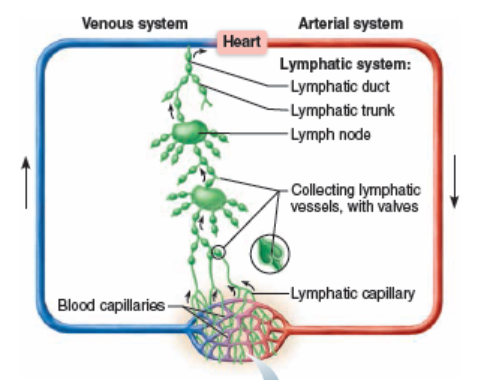
Lymphatic capillary
Smallest lymphatic vessel that collects excess tissue fluid
Lymphatic collecting vessels
Collect lymph fluid draining from lymphatic capillaries
Which of the following vessels transport fluid back into the blood that leaks from the vascular system?
lymphatics
Select the lymphoid organ that cleanses the lymph
Lymph nodes
Which of the following best describes the arrangement of lymphatic vessels?
A one-way system of vessels beginning with blind-ended lymphatic capillaries
NOT a function: delivery of nutrients to tissues
Which of the following is NOT a function of lymphatic vessels?
Delivery of nutrients to tissues
Transportation of absorbed fat from the intestines to the blood
The return of tissue fluid to the bloodstream
The return of leaked proteins to the blood
It maintains blood volume, and hence pressure
Which statement below describes the lymphatic system’s role in relation to the cardiovascular system?
B lymphocytes
Which of the following is not a characteristic of lymph nodes?
Bean-shaped structures that filters lymph as it goes toward circulatory system
Match the following structure with its function: Lymph nodes.
They have fewer efferent vessels than afferent vessels in order to slow down the flow of lymph, allowing the immune system more time to filter and inspect it
Which statement is true about lymph nodes?
Match the following term to its description: Dendritic cell.
Swollen lymph nodes
The bubonic plaque was named for what condition?

A- afferent lymphatic vessels
B-Lymphoid follicle
C- germinal center
D- medullary sinus
E- trabeculae
F- efferent lymphatic vessels
Identify all
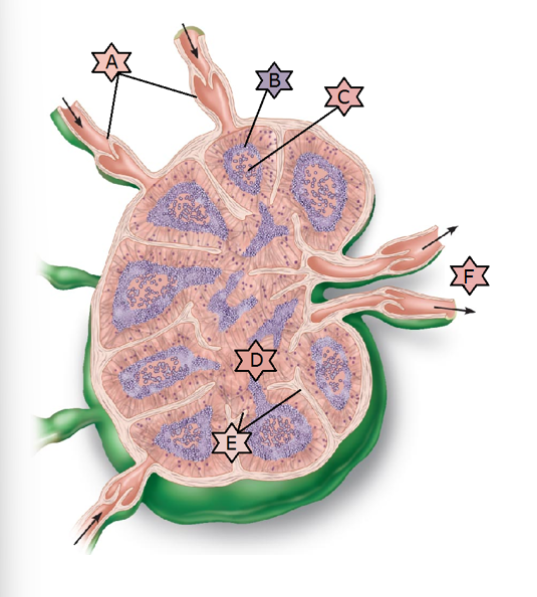
Afferent vessel, subcapsular sinus, medullary sinuses, efferent vessel
Which of the following lists the correct order of lymph flow through the lymph node?
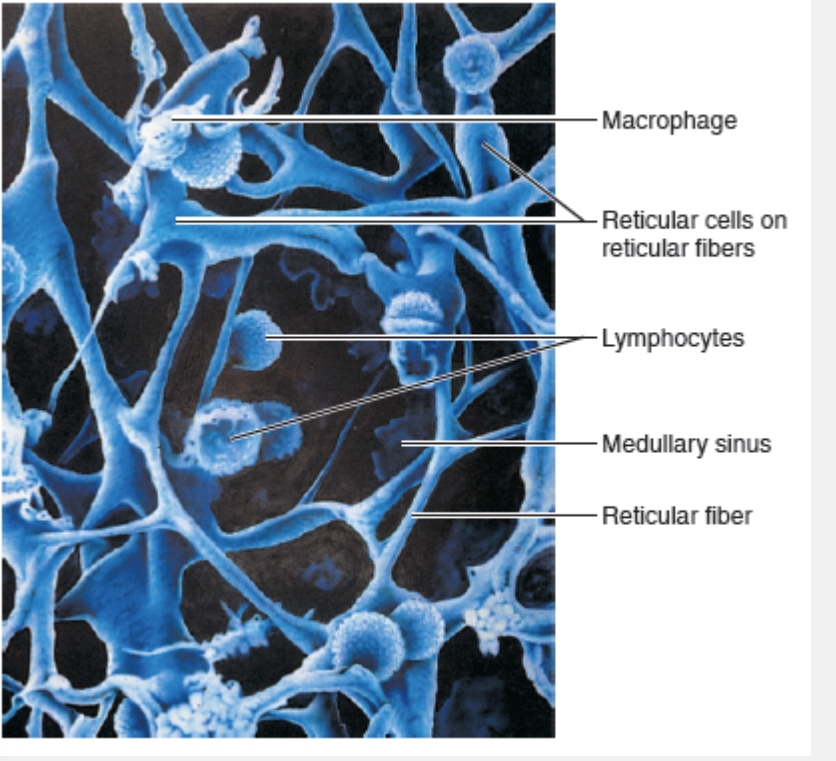
Fibroblast-like cell that produces the reticular fiber stroma, which is the network that supports the other cell types in lymphoid organs and tissues
net-like support that build a mesh framework where immune cells can live and work
especially in lymphoid organs such as spleen, lymph nodes, and bone marrow
Match the following term to its description: reticular cell
The indented region on the concave side of the node leading into the efferent vessels
Match the following term to its description: hilum