BIOL 243 - Theme 2D mutations
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Changes in sequences and spontaneous mutations/inheritance of DNA
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What are mutations?
Changes to nucleic acid sequence (DNA and RNA)
What is the word for mutations being inherited?
germline
What is the word for mutations being not inherited?
somatic
Mutation changes can be small (___) or large (____)
gene level or chromosomal
altered gene sequence can change _______ of the polypeptide resulting in…
can change the amino acid sequence, resulting in variation of phenotype
What can the effect on the phenotype be?
harmless/neutral, harmful/deleterous, beneficial/advantageous
What is primary force in evolution?
where nature selection favours beneficial mutations
what are germline mutations?
mutation originally occured in gametes and therefore becomes heritable
ex. sex-influenced trait - autosomal dominant trait that is dependent on sex (males express the trait in heterozygotes but females do not)
what are somatic mutations?
mutation occurs in a progenitor cell and all other daughter cells will express the mutation
cancer tumors are an example of somatic mutations
somatic cells are expressed as….
sectors (depends on time of mutation)
what are small-scale mutations?
changes to one of few base pairs
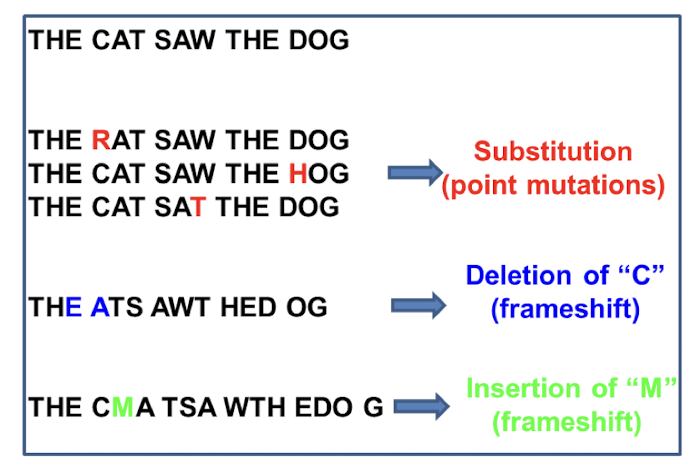
What is base substitution?
single nucleotide change as a result of point mutations
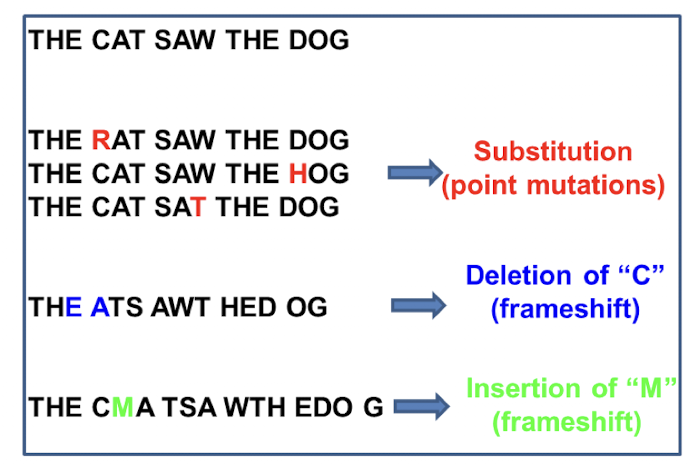
what is insertion?
one or more base pairs added in sequence during DNA replication usually resulting in frameshift mutation
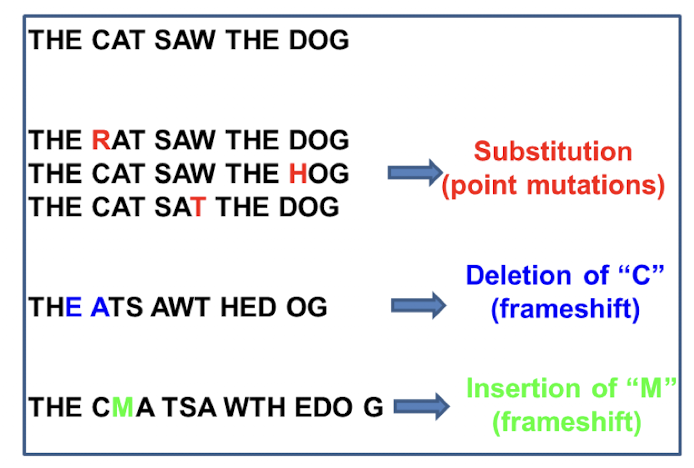
what is deletion?
one or more base pairs skipped during DNA replication usually resulting in frameshift mutations
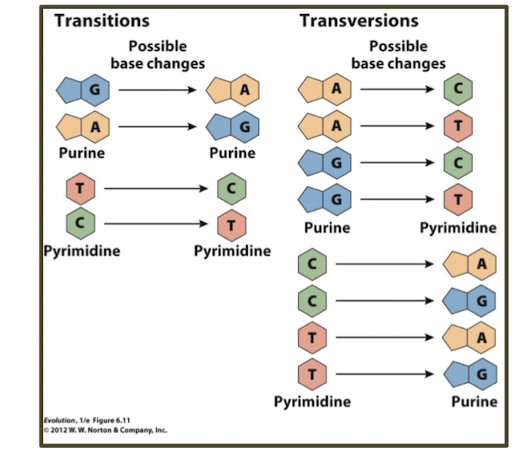
what are transitions?
purine to purine or pyrimidine to pyrimidine changes
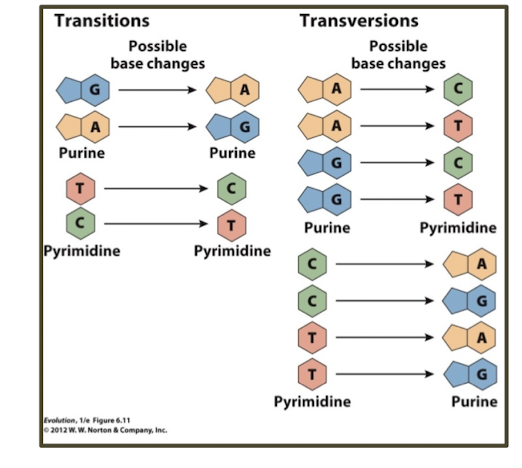
what are transversions?
purine to pyrimidine or pyrimidine to purine chages
point mutations affect what?
amino acid sequence of polypeptides
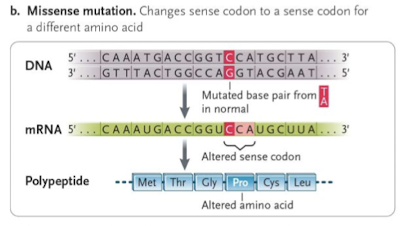
what is missense mutation? (non synonymous)
codon change causes change in an amino acid
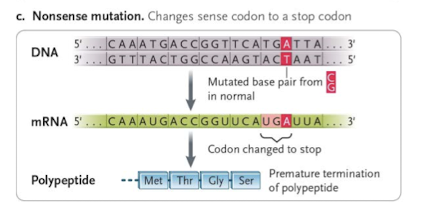
what is nonsense mutation (premature stop)
sense codon change into a stop codon (truncated polypeptide)
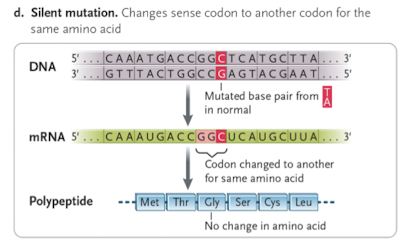
what is silent mutation (synonymous)?
codon change does not change the amino acid due to degeneracy of the genetic code
what is frameshift mutation?
insertion or deletion of a small number of base pairs that alter the reading frame
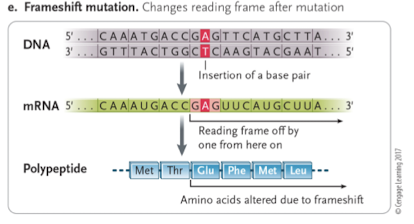
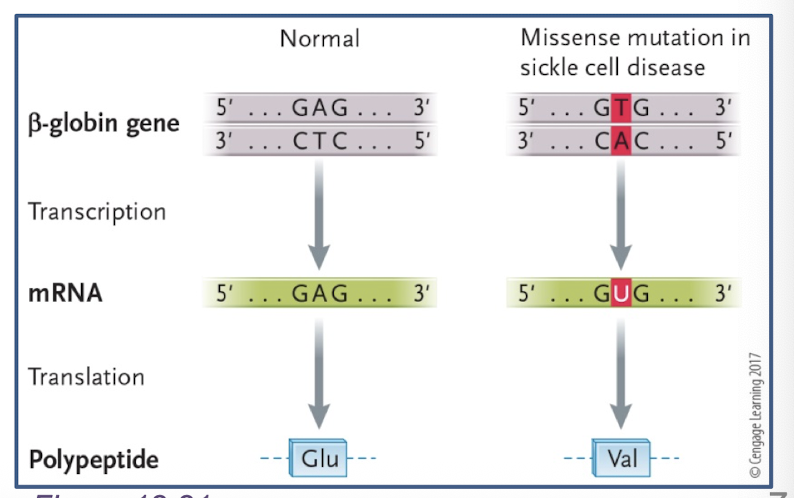
sickle cell anemia is a missense mutation effect?
single missense mutation in entire genome and a resulting amino acid change can have drastic effect on phenotype
missense mutation in the beta hemoglobin gene causes 6th amino acid change from glutamic acid to valine
red blood cells: deficiency in oxygen exchange, clog arteries, circulatory problems, higher risk of heart attack and stroke
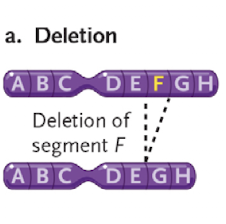
large scale chromosomal mutations - what is deletion?
loss of genes
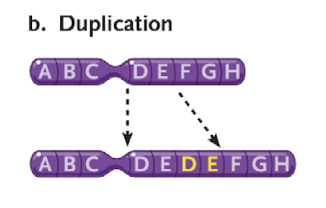
what is duplication/amplification?
increasing dosage of genes
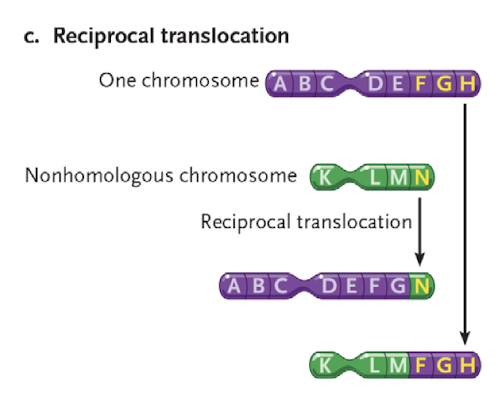
what is translocation
interchange of genetic parts from nonhomologous chromosomes
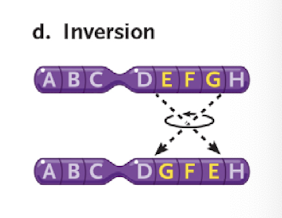
what is inversion
reversing orientation of a segment of the chromosome
what are spontaneous mutations
naturally occuring mainly caused by replication errors (1 mutation/1010 bp of DNA replicated) and spontaneous lesions
what do spontaneous lesions include?
depurination and deamination of bases
what are induced mutations?
natural (environments) or artificial agent or mutagen that causes mutations at a rate much higher than spontaneous mutagens
what do mutagens do?
induce mutations by replacing a base, alter a base so it mispairs with another base or damage a base where it can no longer pair with any base
what are base analogs
mimic bases and incorporates into DNA (can cause mispairing during DNA replication)
e.g. 5-bromouracil;thymine analog that can pair with A or G
chemicals alter…
base strucutre to cause mispairing
what are alleles
one of different forms of gene (sequence variation) which cause different phenotypes
what are wild-type alleles
normal form of the gene found in nature or the standard laboratory strain of a model organism
what are loss of function alleles
mutations that reduce/eliminate gene function/expression
what are gain of function alleles
mutations that enhance gene function/expression

learning objectives
slay