Lecture #15 | Evolution, development and Macroevolution
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Allometry
Differential growth of parts or dimensions of an organism.
change in development that affect body plans
In crab claws: growth rate of one claw is much larger than other
Human growth: human babies have a large head that eventually becomes proportional
Heterochrony
Changes that occur in the timing of development
change in development that affect body plans
paedomorphosis
peramorphosis
Heterotopy
Changes in the spatial position of a future in an organism
change in development that affect body plans
can result in the expression of genes in novel part of a developing body
ex: roots on stems, bone on skin
Changes in modularity
Addition, subtraction, or differentiation of modules
distinct units of an organism that are under genetic
control
change in development that affect body plans
ex: teeth
Paedomorphosis
developmental shift leading to early maturity and a ‘child-form’ (juvenilized breeding adult)
example of heterochrony
biological process where an organism retains juvenile or larval characteristics into its adult stage
Peramorphosis
delayed maturity leads to exaggerated adult forms
example of heterochrony
ex: very large antlers showing that antlers grow until breeding maturity
changes in developmental rates that result in individuals reaching adulthood with traits that are larger or more extreme than those of their ancestors.
When does transcription occur?
Initiated when polymerase binds to the promoter after regulatory proteins like transcription factors bind to an enhancer
Cis-regulatory elements
modify the expression of a gene on the same stretch of DNA
Trans-regulatory elements
Modify the expression of distant genes
Hox genes
Genes responsible for the specific patterning of body structures during development
Master regulators that control the expression of other genes
ex: They define where each structure is placed in developing flies
History of Hox Genes
500 million years old ad exist in all animals
Members of a single gene family
evolved through duplication from a common ancestor
all have an amino acid site that binds DNA (Homeobox)
Occur in all animals by building an evolutionary tree of the family of Hox genes we can trace back the evolution of forms to the base of the metazoans
What happens if there are mutations in Hox genes?
Can change the body composition
ex: a mutation in a gene can transform a segment to be a duplicate of a previous segment like double wings in drosophila
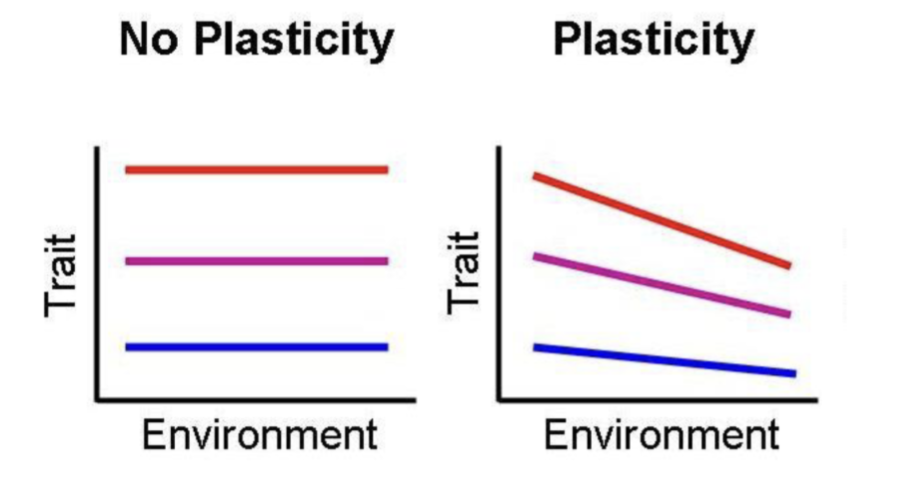
Phenotypic plasticity
When a single genotype can produce different phenotypes in repose to environmental stimuli
shows how an environment can affect the developmental expression of genotypes
May or may not be adaptive
Reaction norms
The set of phenotypes that a genotype is capable of expressing under different environmental conditions
tells how flexible a trait is dependent on the environment
Adaptive phenotypic plasticity
is the ability of an organism to adjust its physical characteristics (phenotype) in response to environmental changes, improving its ability to survive and reproduce in a specific local environment
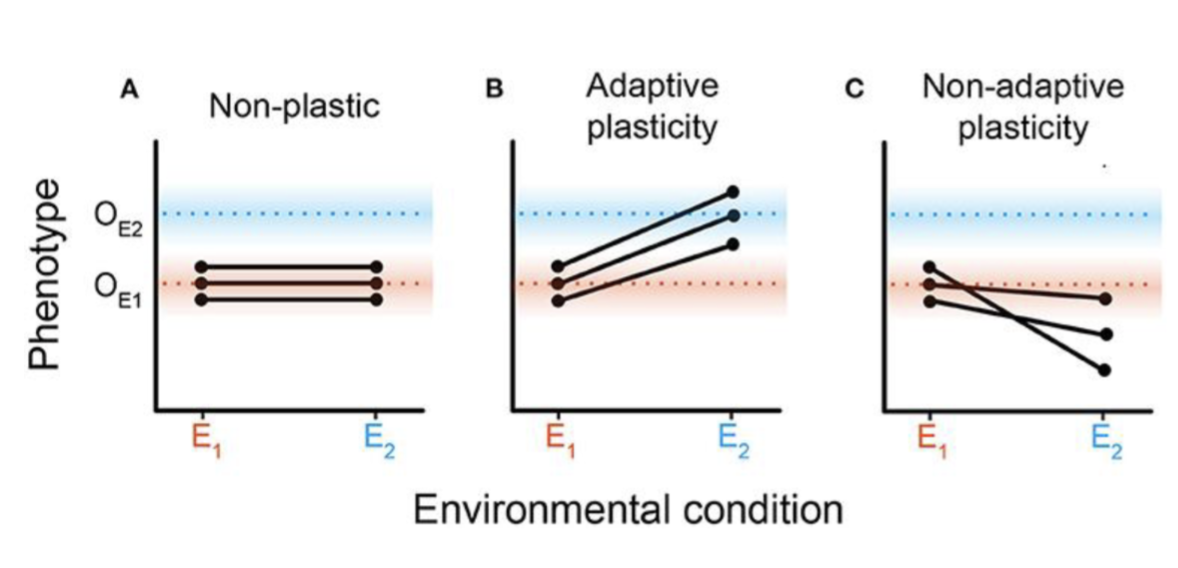
ex: larvae hatching in different seasons look different from each other, and reflect the flowers blooming during that season
Microevolution
Mutations (new variation) followed by allele frequency change (drift, gene flow, natural selection)
processes that lead to changes within populations of species
Macroevolution
Evolution above the species level or patterns of the origin, diversification, and extinction of higher taxa
What patterns have been observed through studying macroevolution?
Evolution is gradual
New characters evolve as modifications of ancestral ones
Stasis is common
Complex characters evolve via intermediate steps
Most trends are passive
Evolution is no teleological
Example of gradualism
Horses have evolved increased biomass over millions of years
Example of modification of ancestral characters to new characters?
Giants pandas and moles both have a 6th finger that independently evolved via the extension of the sesamoid bone
Stasis
Lack of phenotypic change
common over time
How can stasis be explained over great spans of time?
Stabilizing selection for the same optimized character over great spans of time
could be common with habitat tracking
How do complex characters evolve?
Via intermediate steps
we can observe many potential intermediate steps for eyes by looking at their features across a diversity of invertebrates
There is no trend toward increased complexity
Active/Driven trends
Caused when changes in a lineage in one direction are more likely to occur than in another direction
Passive trends
Caused when a lineage is just as likely to evolve in one direction versus another, but there are morphological/evolutionary barriers that exist in one direction
most evolutionary trends are passive
passive trends can cause the illusion of progress where non exists
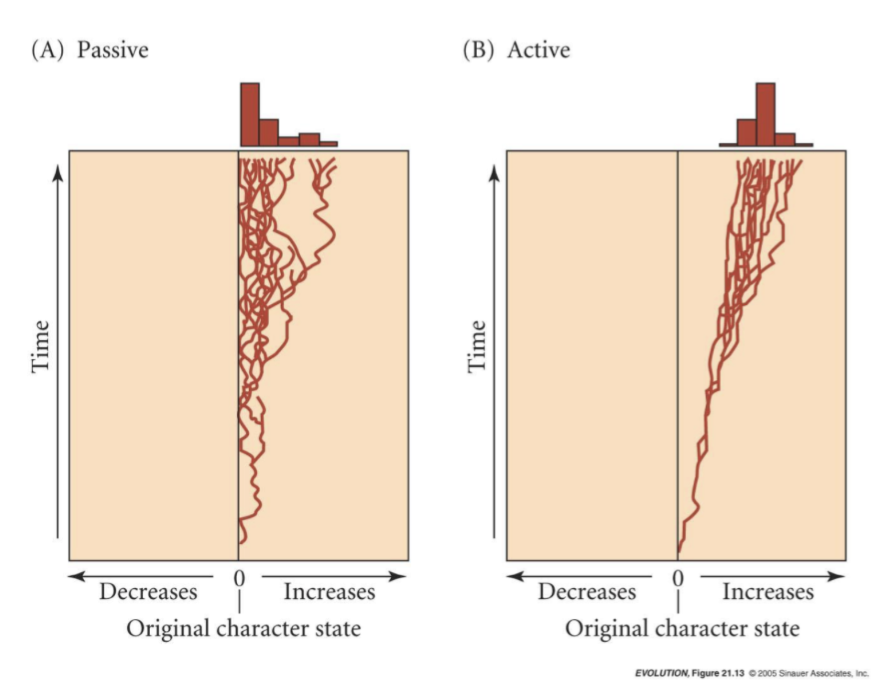
Cope’s rule
predicts that mammal lineages tend to increase in body size over time.
This is mostly a passive trend. Most mammals were near their minimum size when they emerged as a lineage
What does it mean that evolution is not teleological?
Means there is no plan or purpose
natural selection can only favor or disfavor traits based on the current environment