AP Bio Flashcards
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
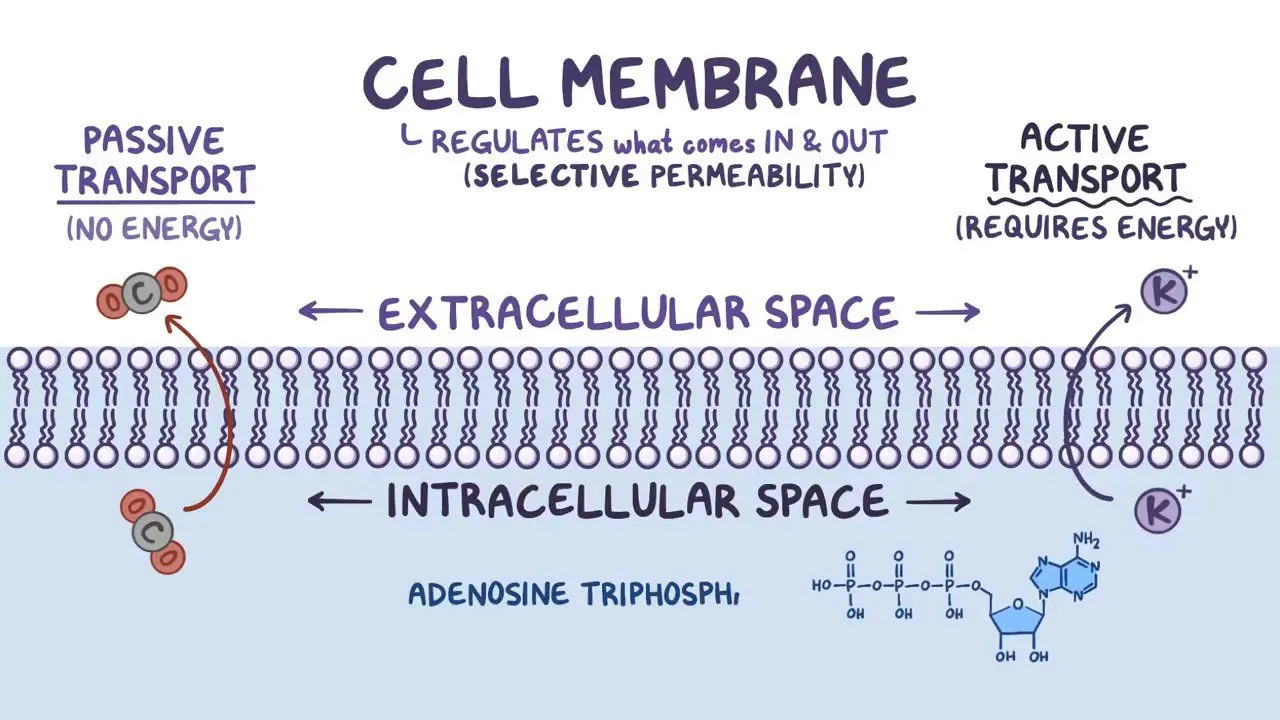
Active Transport
This is a process by which cells move materials across their membranes against a concentration gradient, from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. This process requires energy, typically in form ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
Unit 2
Analogous Structure
Analogous structures refer to body parts that have similar functions but different evolutionary origins. They are not derived from a common ancestor.
Unit 7

Cell Cycle
The cell cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication. It consists of stages such as interphase (growth), mitosis (nuclear division), and cytokinesis (cell division).
Unit 4
Darwin’s Finches
Darwin's finches are a group of bird species found on the Galapagos Islands that have evolved different beak shapes and sizes to exploit different food sources, demonstrating adaptive radiation.
Unit 7
Degrees of Freedom
Degrees of freedom refers to the number of independent variables that can vary in a statistical calculation or analysis. It represents the number of values in a calculation that are free to vary.
Unit 0
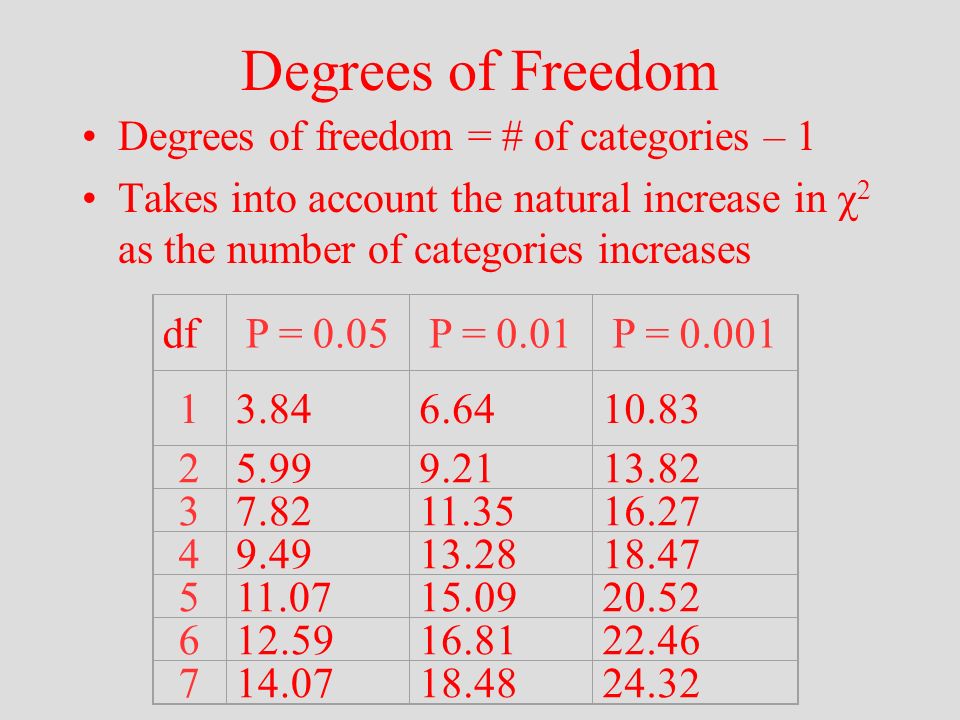
Electron Transport
The electron transport chain is a series of protein complexes and electron carrier molecules within the inner mitochondrial membrane that harvest energy from electrons to create ATP.
Unit 3
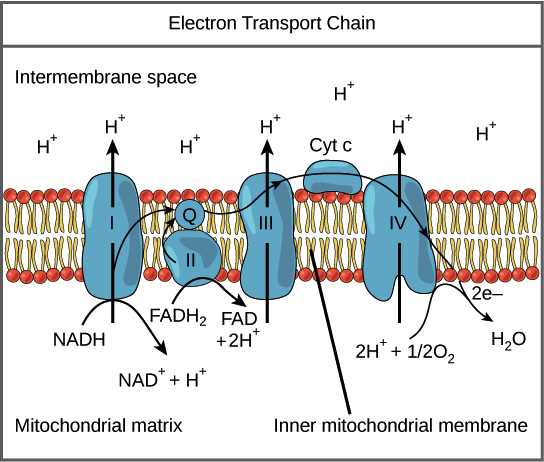
Endosymbiotic Theory
The endosymbiotic theory is the scientific explanation of how eukaryotic cells, which make up complex organisms like plants and animals, evolved. It proposes that certain organelles within eukaryotic cells, such as mitochondria and chloroplasts, were once free-living prokaryotic organisms that formed a symbiotic relationship with larger host cells.
Unit 2
Genetic Drift
Genetic drift is a mechanism of evolution that causes random changes in the frequency of alleles (versions of a gene) in a population over time.
Unit 7

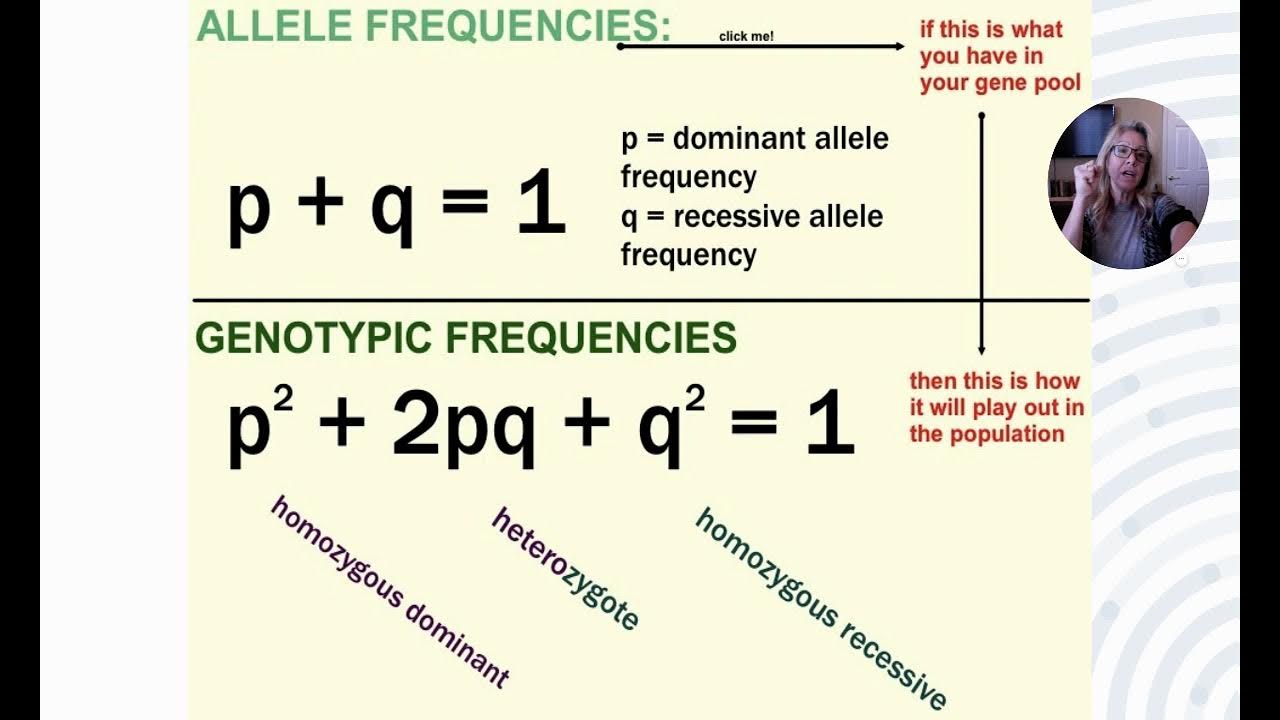
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
The Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium is a principle stating that the genetic variation in a population will remain constant from one generation to the next in the absence of disturbing factors.
Unit 7
Homologous Structures
Homologous structures are parts of different organisms that have similar structure but not necessarily the same function, indicating a common ancestry.
Unit 7
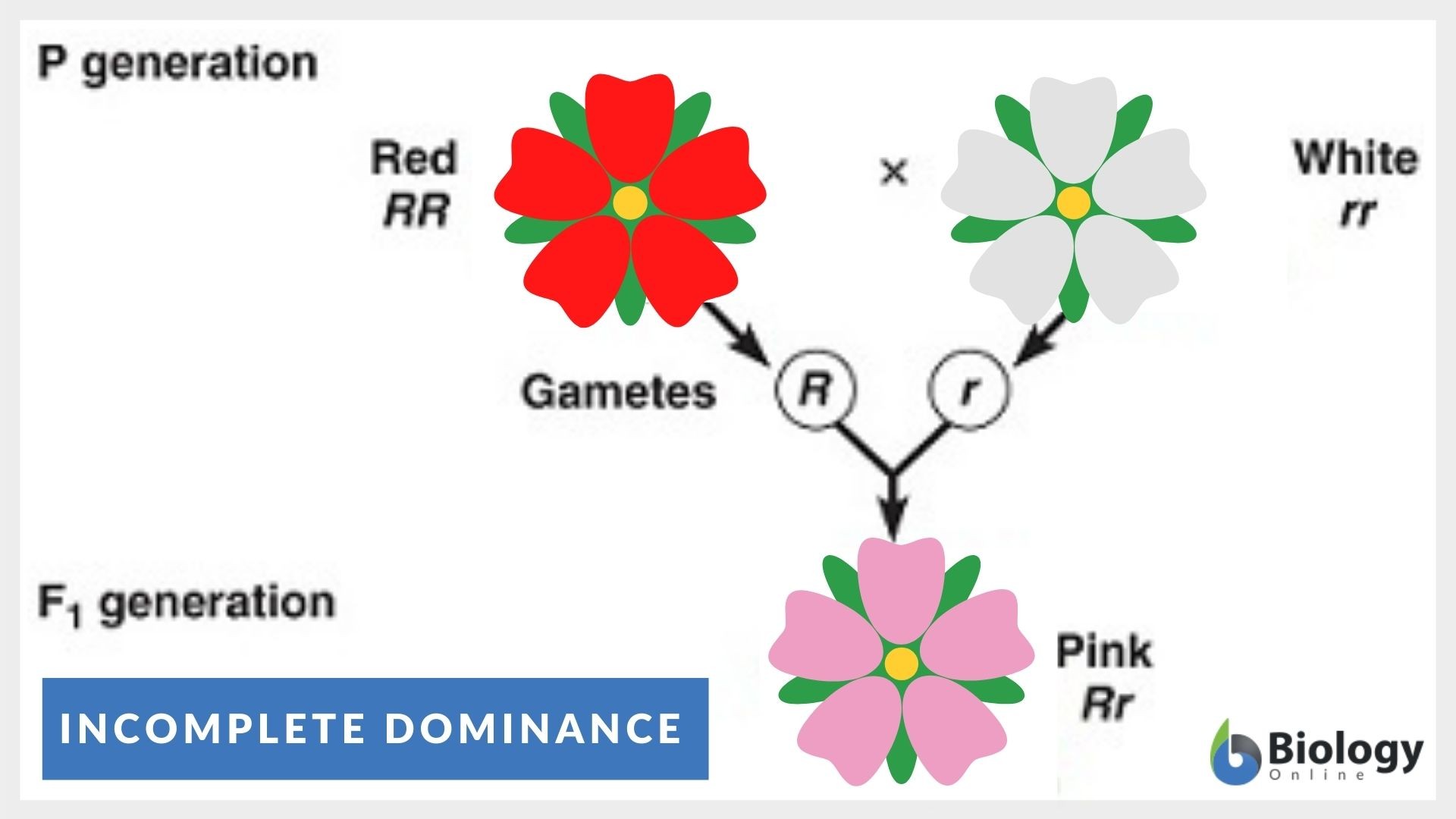
Incomplete Dominance
Incomplete dominance is a form of intermediate inheritance in which one allele for a specific trait is not completely expressed over its paired allele. This results in a third phenotype, where the expressed physical trait is a combination of the phenotypes of both alleles.
Unit 5
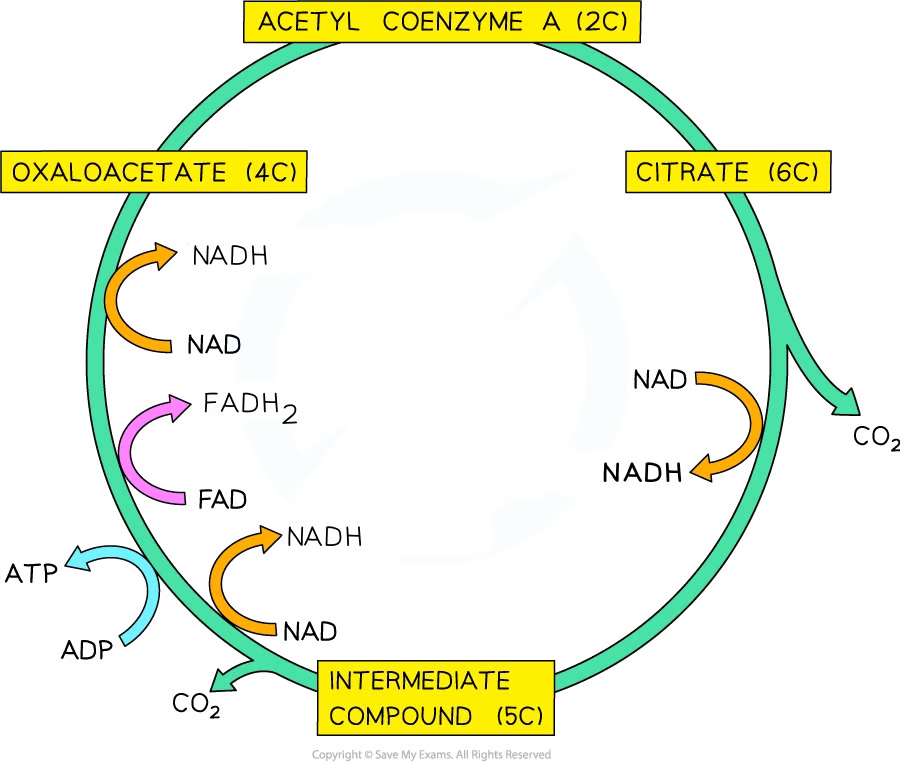
Krebs Cycle
The Krebs Cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle, is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into ATP.
Unit 3
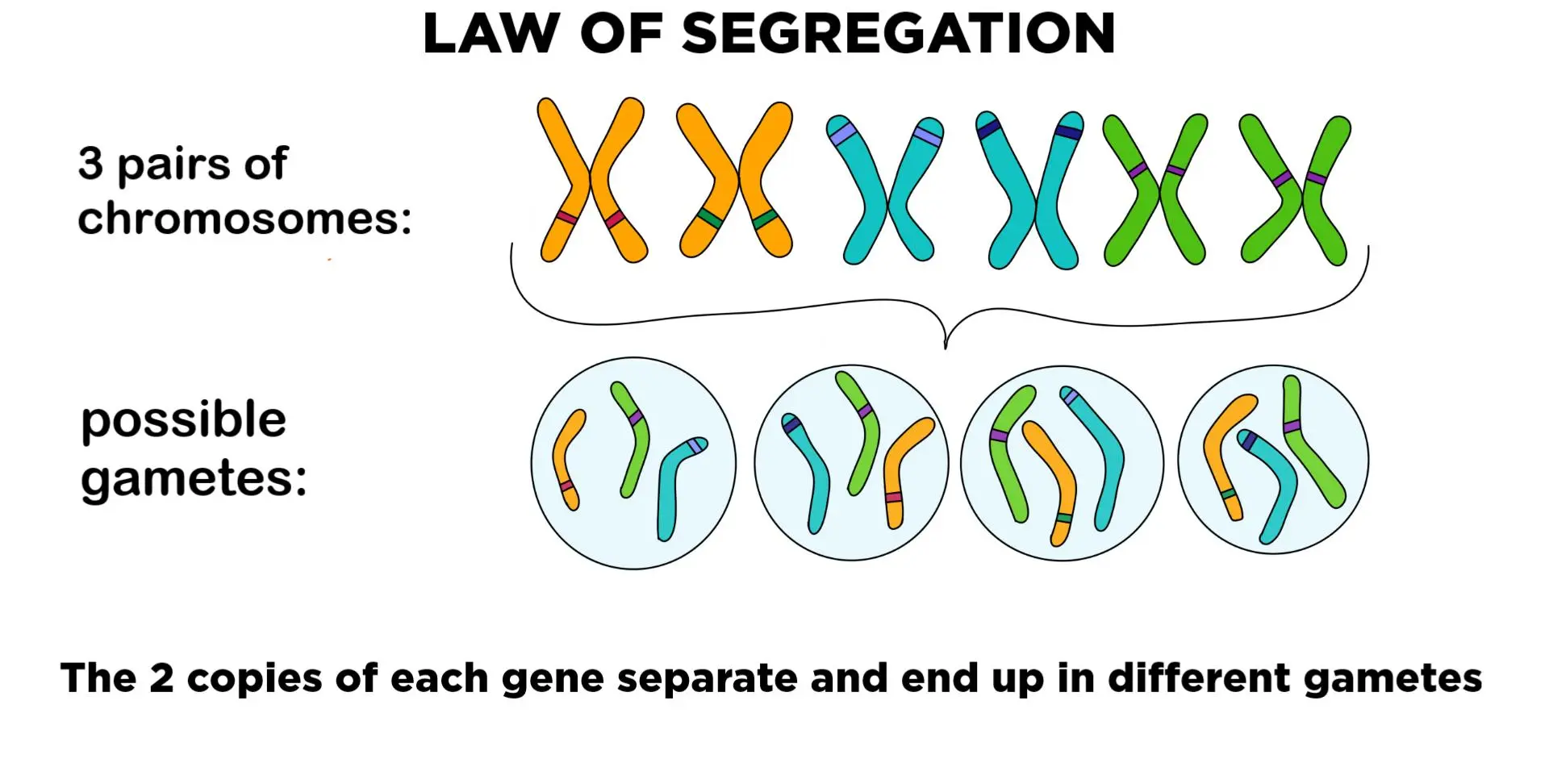
Law of Segregation
The Law of Segregation states that during the formation of sex cells (gametes), the pairs of hereditary traits (alleles) become separated, so that each sex cell carries only one kind of allele.
Unit 5
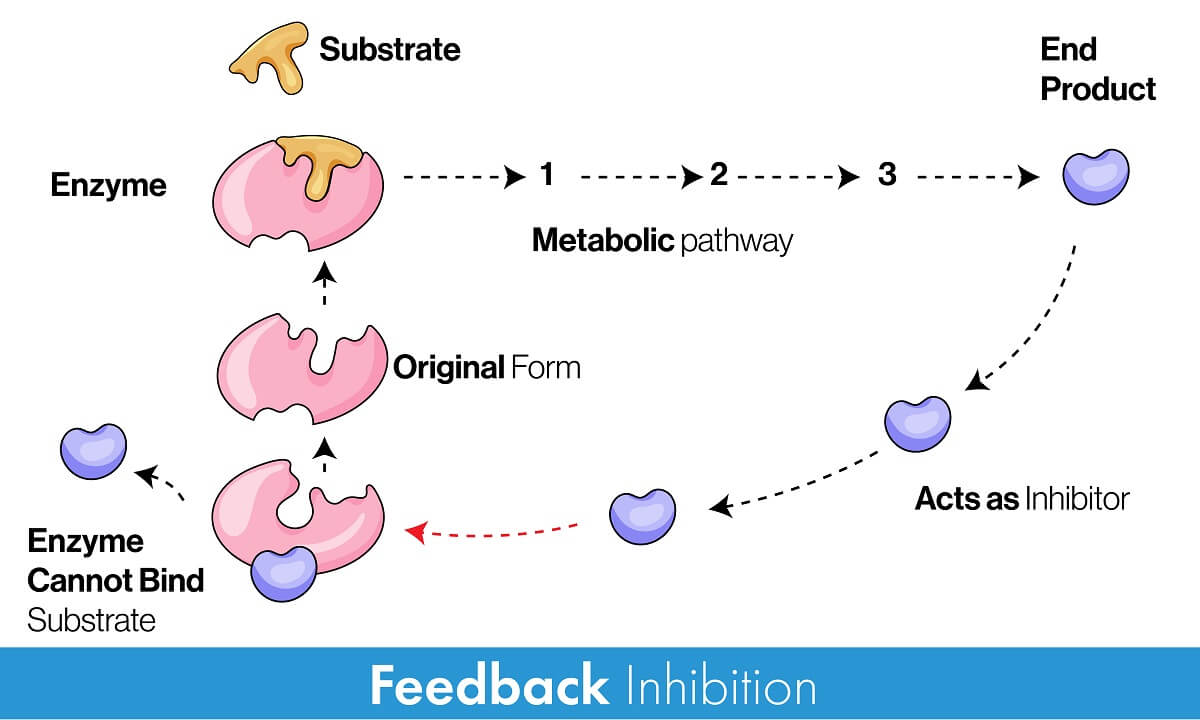
Negative Feedback Loops
A negative feedback loop is a process in which the body senses a change and activates mechanisms to reverse that change.
Unit 4
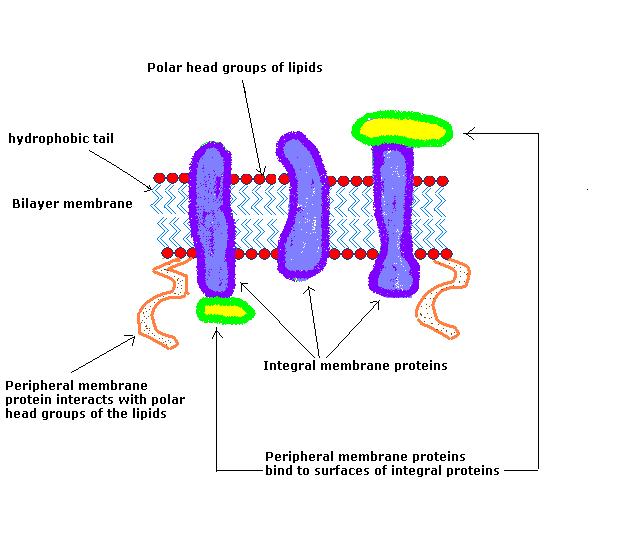
Phospholipid Bilayer
The phospholipid bilayer is a two-layered arrangement of phosphate and lipid molecules that form a cell membrane, the hydrophobic lipid ends facing inward and the hydrophilic phosphate ends face outward.
Unit 2
Positive Feedback Loops
A positive feedback loop amplifies or increases changes; this tends to move a system away from its equilibrium state and make it more unstable.
Unit 4
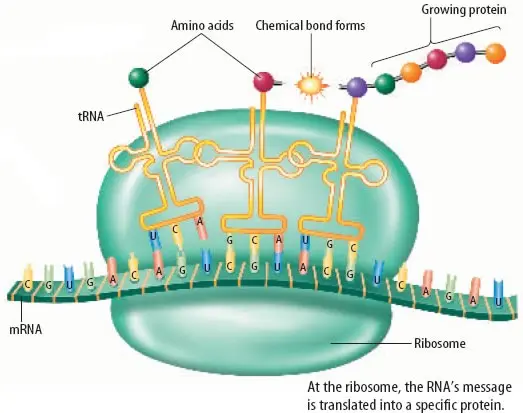
Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis is the process by which cells build proteins. This involves two main stages - transcription (where DNA is converted into RNA) and translation (where RNA is used to produce proteins).
Unit 6
Second Law of Thermodynamics
This law states that the total entropy, or disorder, in an isolated system can only increase over time. It also implies that energy transfers or transformations are never 100% efficient.
Unit 3
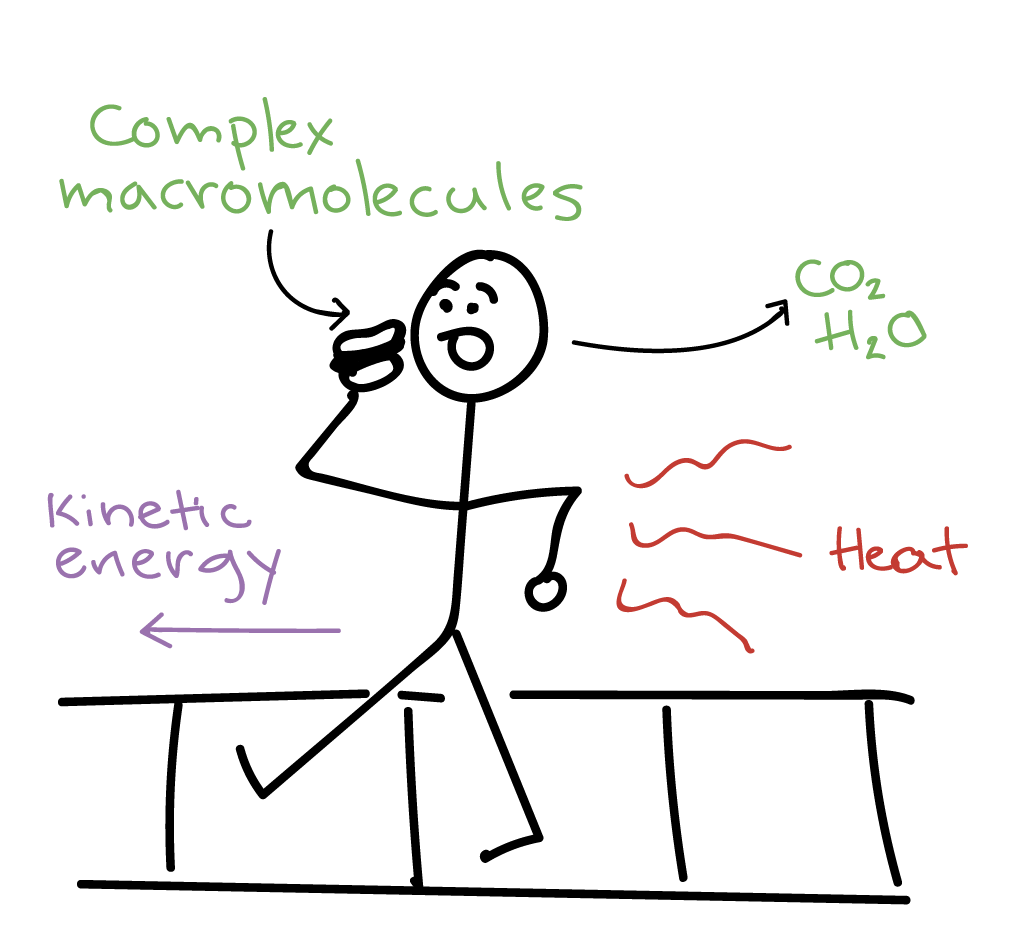
Protein Structure
The tertiary structure of a protein is its three-dimensional shape, formed by further folding and bending of the secondary structures into a complex shape due to interactions between side chains of amino acids.
Unit 1
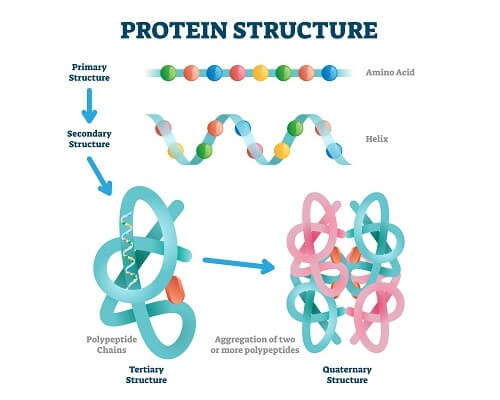
Trophic Cascade
Trophic cascades are ecological phenomena triggered by changes in top predators' population size that cause ripple effects down through lower levels of the food chain.
Unit 8

Chi-square
a statistical test used to compare observed results with expected results
Unit 9
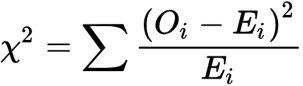
kingdom
major taxonomic rank used to group organisms based on shared characteristics, serving as one of the highest levels of classification below domain and above phylum
Unit 7
Biotic factors
the living components (organisms) that shape up the environment.

Abiotic factors
non-living parts of an environment that can affect living organisms and functioning ecosystems.

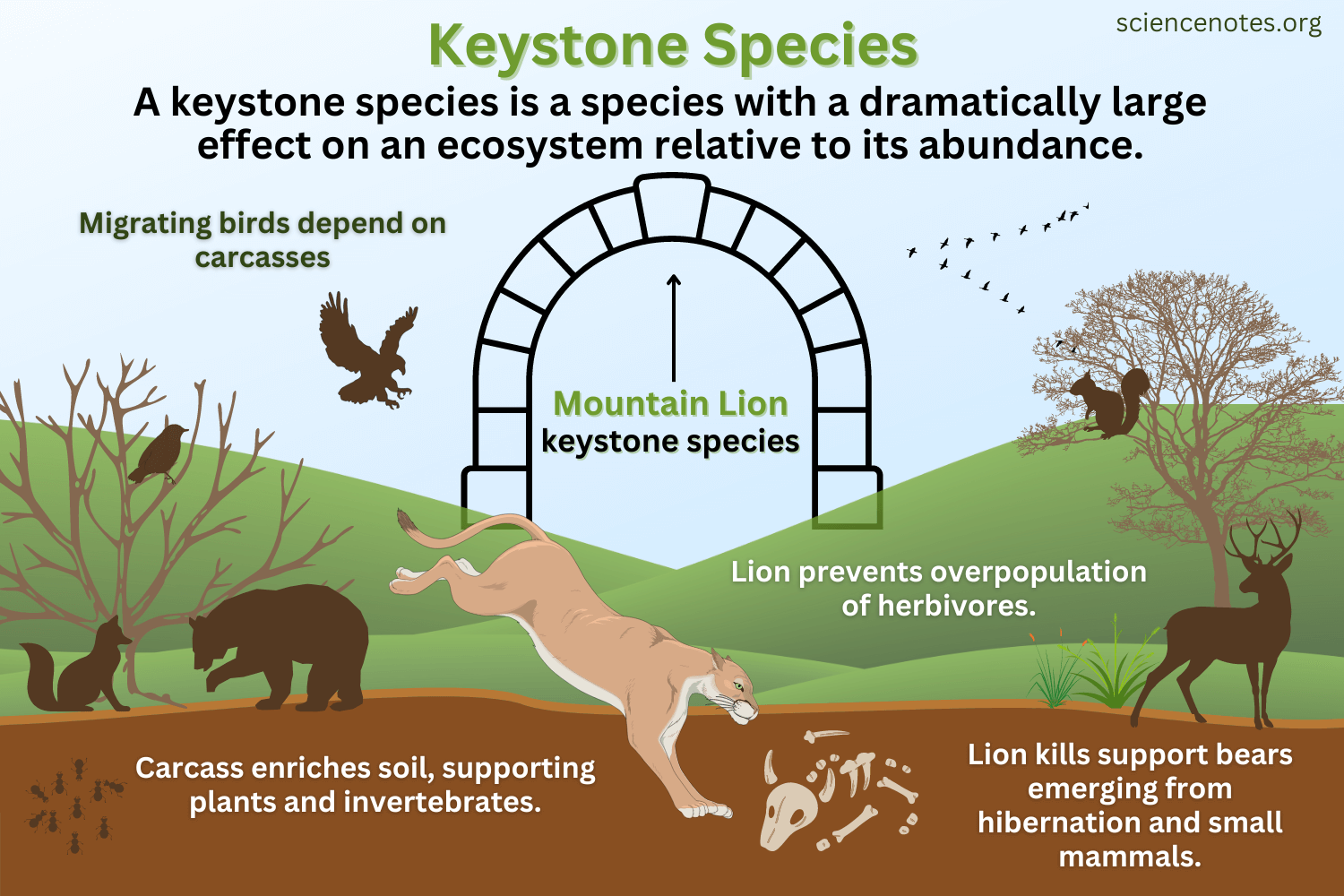
Keystone Species
a plant or animal that plays a unique and crucial role in the way an ecosystem functions
10% Rule
when energy is passed in an ecosystem from one trophic level to the next, only ten percent of the energy will be passed on.
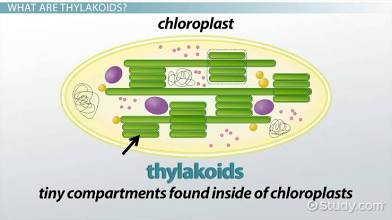
Thylakoids
They contain chlorophyll and play a crucial role in capturing light energy and converting it into chemical energy during photosynthesis.
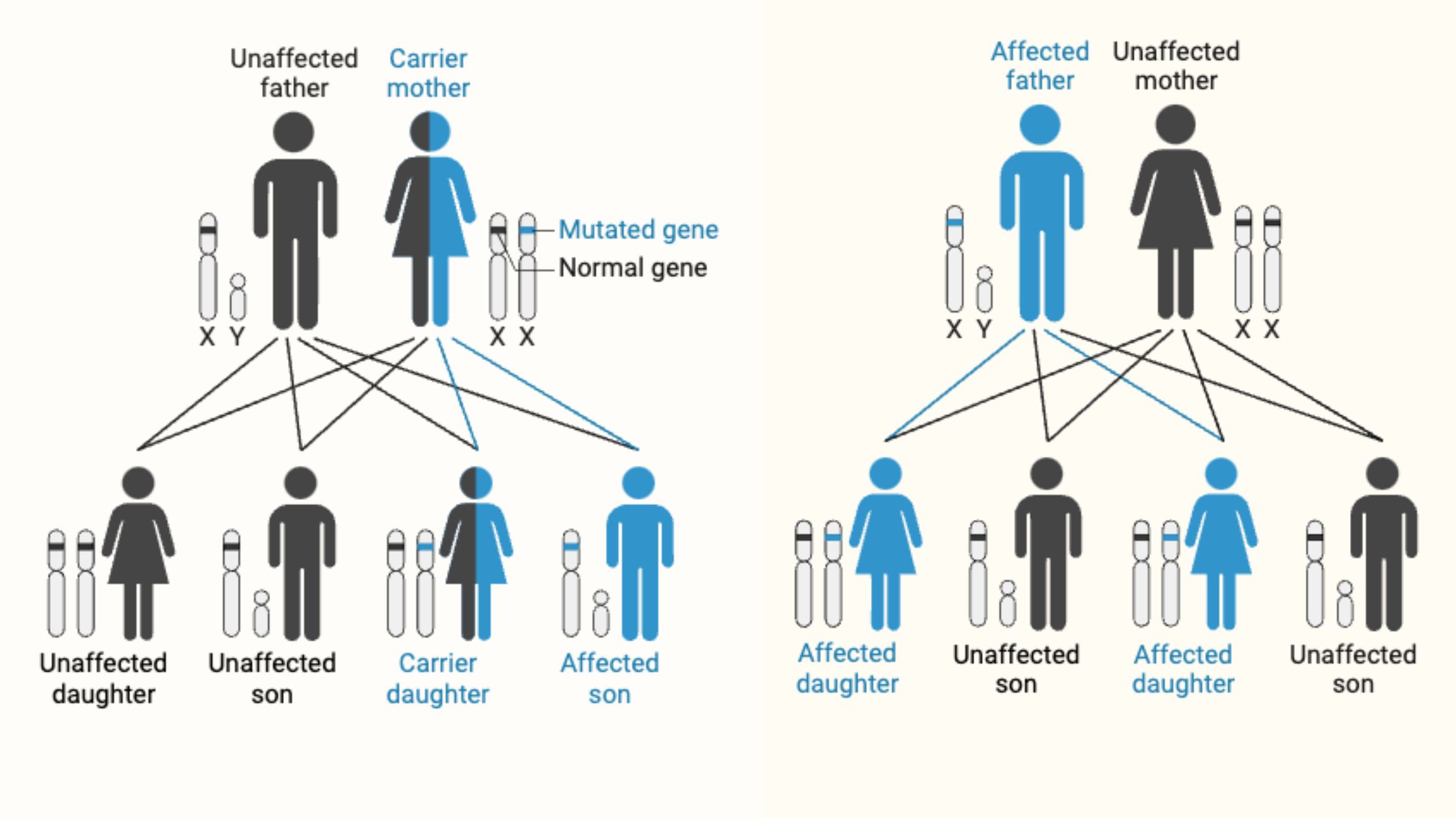
Sex Linked Gene
These are genes that are located on the sex chromosomes (X and Y in humans). Their expression can result in traits that differ between sexes.
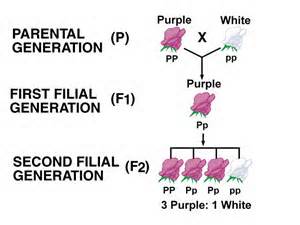
F2 Generation
The F2 generation is the second filial generation in a genetic cross, which results from the self-fertilization or mating of individuals from the F1 generation. This generation is crucial in understanding inheritance patterns, as it reveals the segregation and recombination of alleles that define traits in offspring. Analyzing the F2 generation helps illustrate Mendel's principles of dominance and recessiveness, as well as the ratios of different phenotypes and genotypes that arise from genetic crosses.
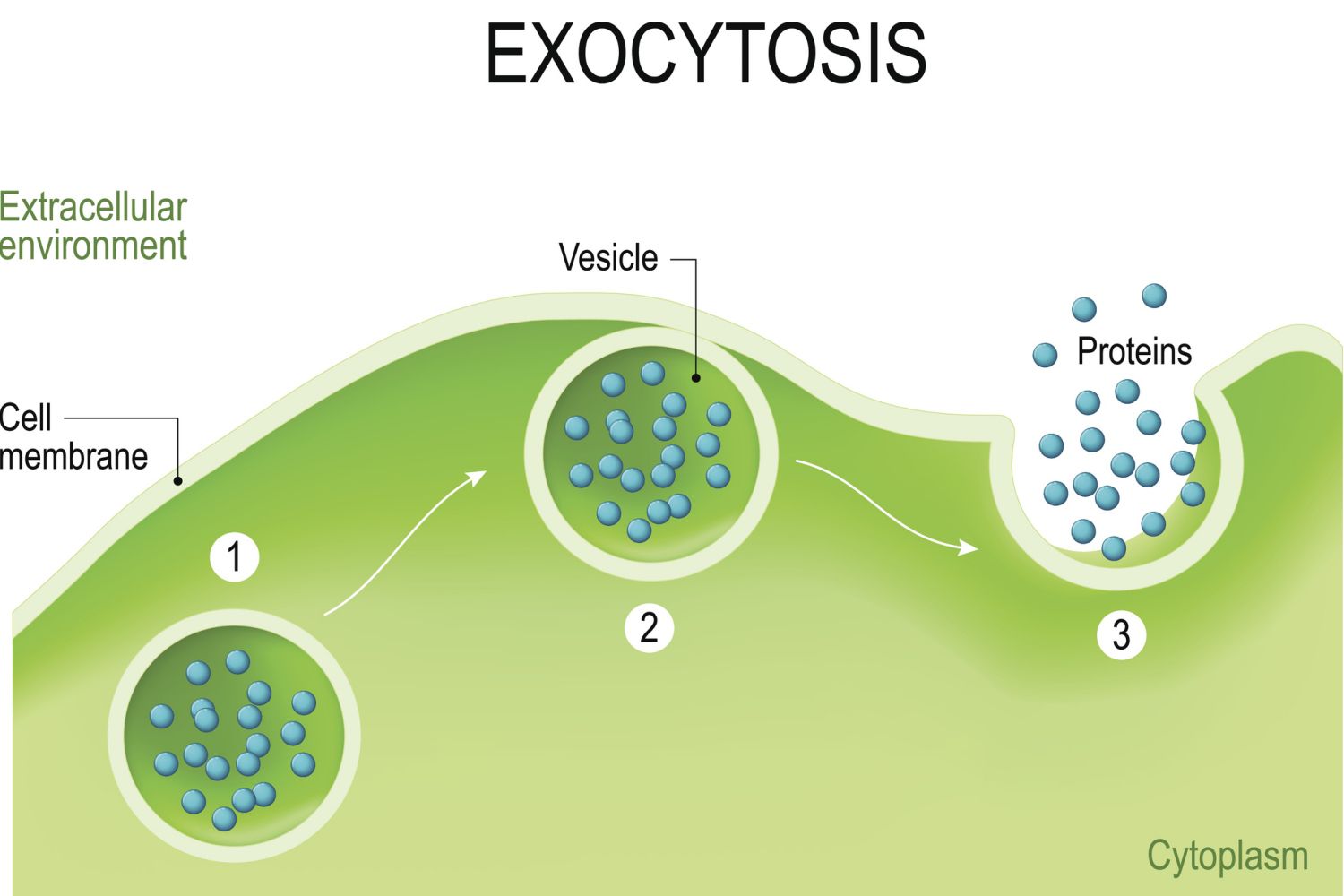
Exocytosis
a vesicle (a small, membrane-bound compartment) containing the molecules to be released fuses with the cell membrane, and the contents of the vesicle are expelled
selectively permeable
some substances are able to pass through the membrane, while other substances are not able to pass through
Lysosome
a membrane-bound cell organelle that contains digestive enzymes. They break down excess or worn-out cell parts. They may be used to destroy invading viruses and bacteria.

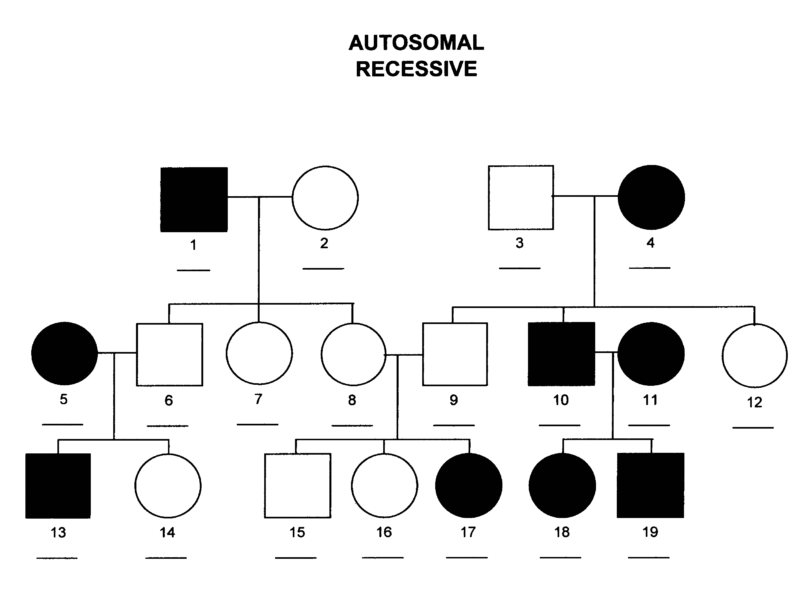
Autosomal Recessive Disorders
Require two copies of the affected allele (one from each parent)
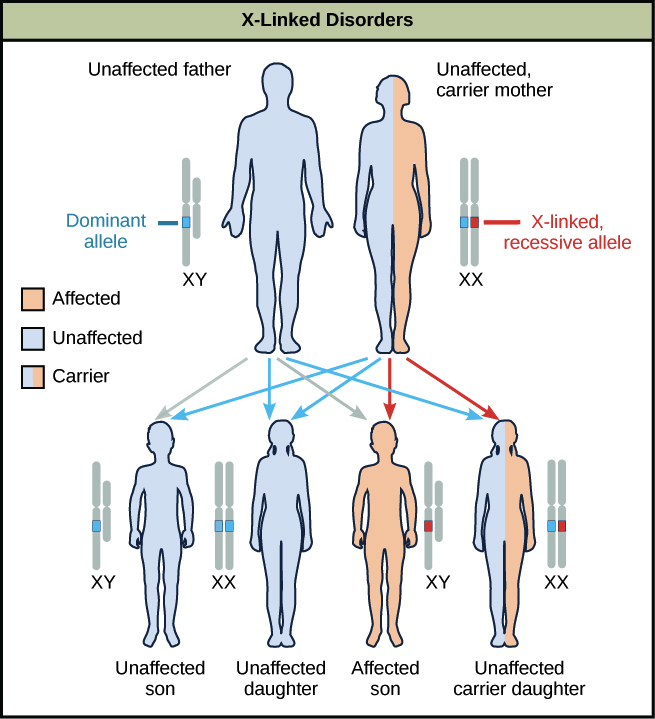
X-Linked Disorders
Caused by mutations in genes on the X chromosome
More commonly expressed in males (who have only one X chromosome)
Gene Repression
the switching off of individual genes whose products are needed to maintain the function of the cell such as the production of vital enzymes or cofactors
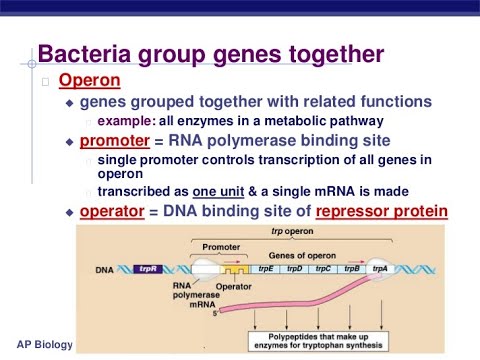
Operon
genetic regulatory units in bacteria and their viruses that group genes for functionally related proteins and control their coordinated synthesis
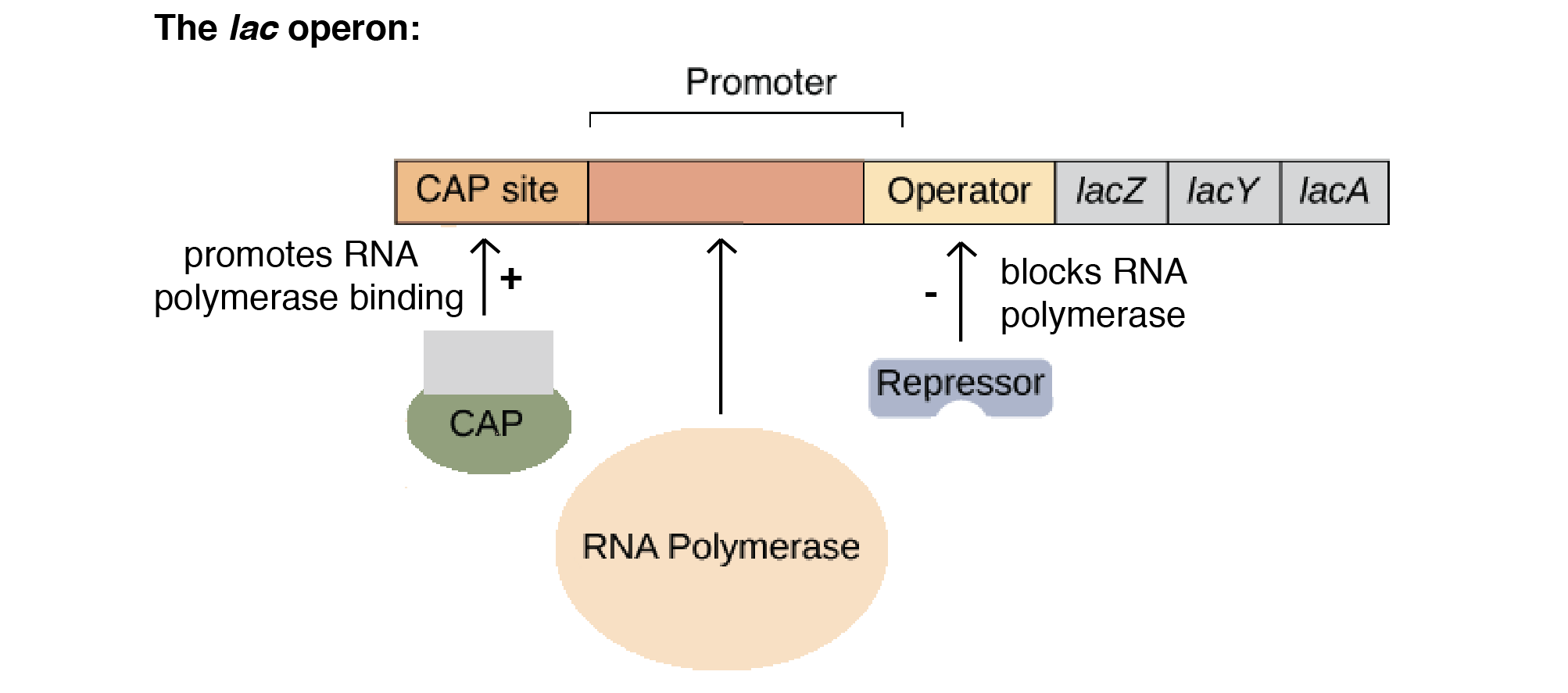
Strands
runs 5' to 3' towards the fork and is made continuously. The other, the lagging strand, runs 5' to 3' away from the fork and is made in small pieces called Okazaki fragments.
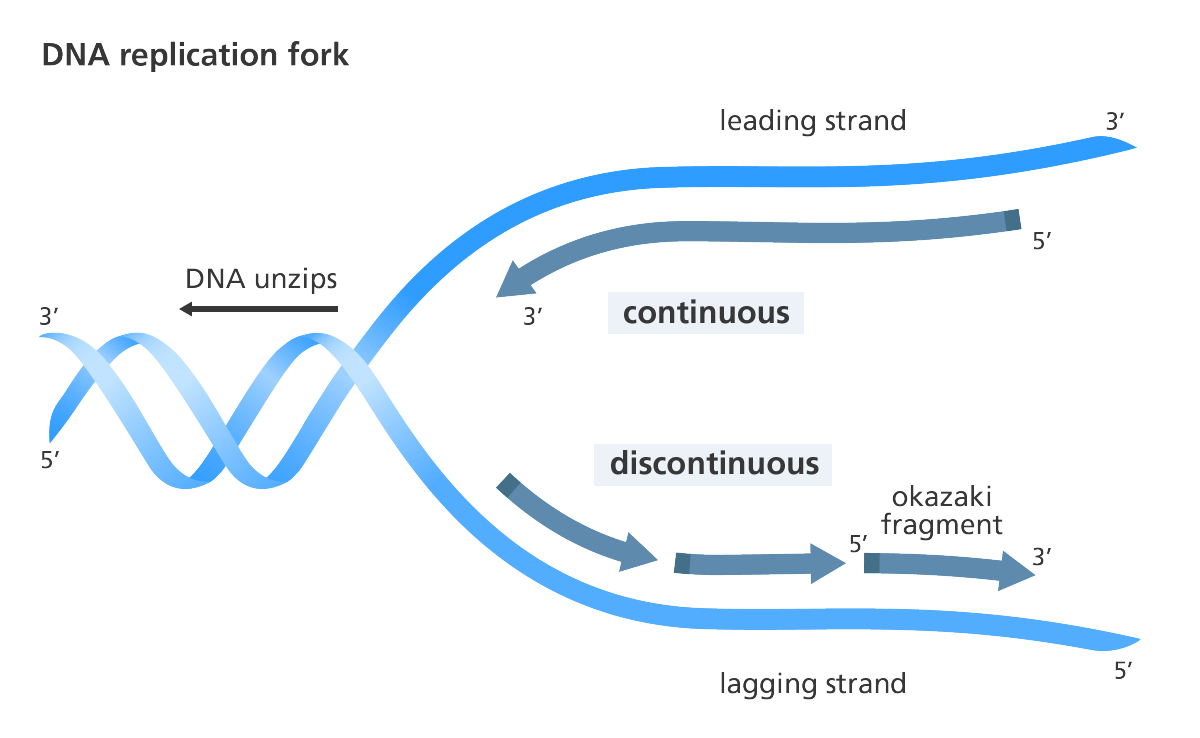
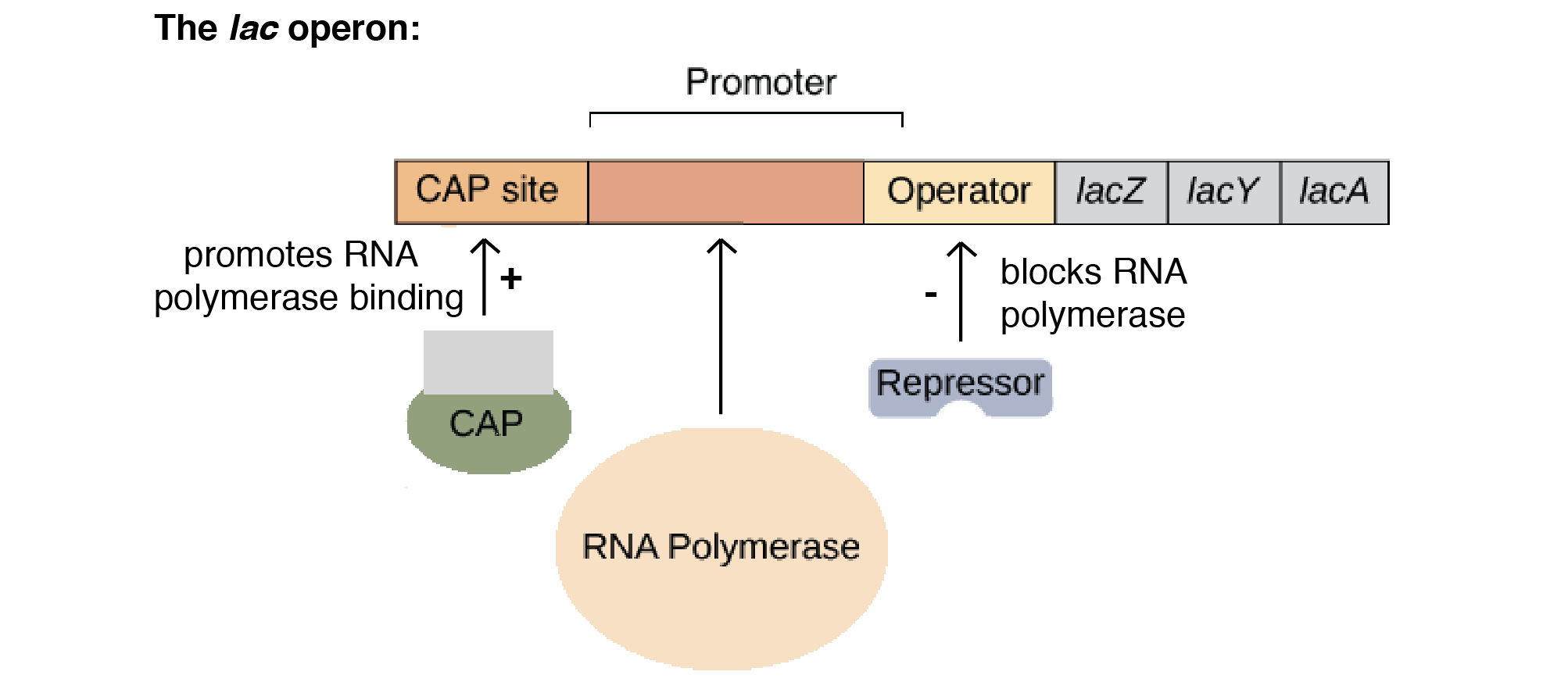
Lac operon
a group of bacterial genes that code for enzymes that break down lactose into glucose and galactose for energy.
Morphogenesis
biological process that causes an organism to develop its shape, involving the organization of cells and tissues into structured forms. T
Accessory pigment
light-absorbing compounds, found in photosynthetic organisms, that work in conjunction with chlorophyll a