Biol 319 exam 4 Lee
1/254
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
255 Terms
Some of our "neuro" material we have been talking about from day one, so please do not overlook subjects such as:term-163
Neuron vs nerve, Nervous tissue as an excitable tissue, etc.
neuron
single nervous system cell
nerve
bundle of axons (neurons)
nervous tissue is excitable
-generate AP from RMP
-excitable=allow signals to transmit fast, immediate response to stimuli
3 major sections of the brain
hindbrain, midbrain, forebrain
forebrain
prosencephalon
A. -Diencephalon: thalamus, hypothalamus,
-epithalamus, pineal gland=melatonin
B. Telencephalon = cerebral hemispheres (cortex), basal nuclei and limbic system
Midbrain
Mesencephalon-Reticular Activating Centers (RAC)= Wakefulness (caffeine (adenosine receptor antagonist) hits receptors here)
hindbrain
rhombencephalon (brain stem - medulla and pons)
Medulla oblongata: Heart rate, breathing rate, blood pressure, blood flow, vomiting, swallowing
Pons: balance & posture (also cerebellum)
Cerebellum: coordination, intricate movements, spatial equilibrium
Reticular Activating Centers function
a network of neurons that regulate sleep-wake transition and arousal
Reticular Activating Centers location
-brainstem (above the spinal cord)
-midbrain
Reticular Activating Centers neurotransmitters
acetylcholine, serotonin, dopamine, histamine
Medulla Oblongata
controls HR,BP,RR,blood flow swallowing,and vomiting
Sulcus
depression=increase in surface area=greater number of neurons that can be packed into the cerebral cortex
fissure
deeper and more prominent than a sulcus
location of central sulcus
between frontal and parietal lobes
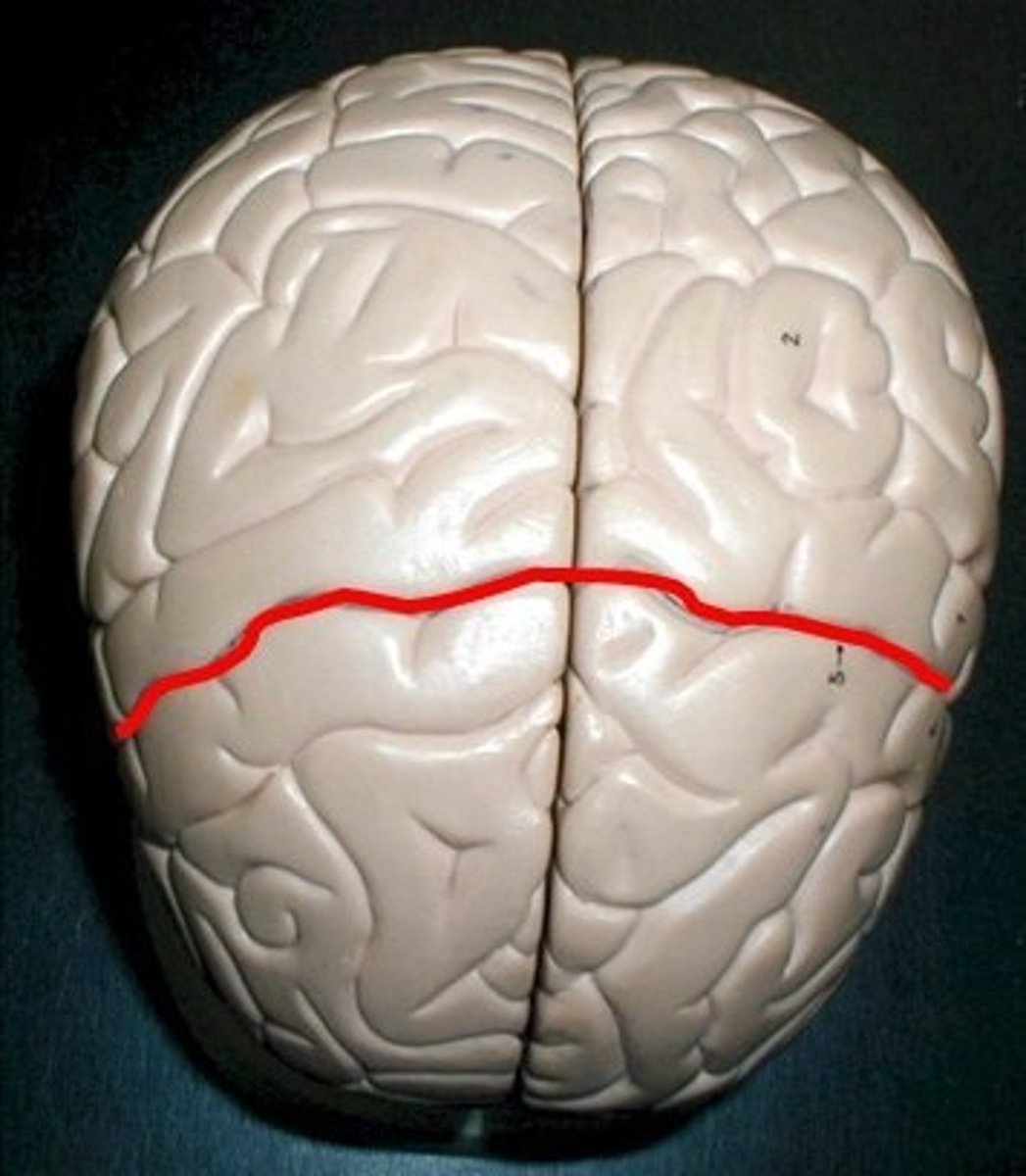
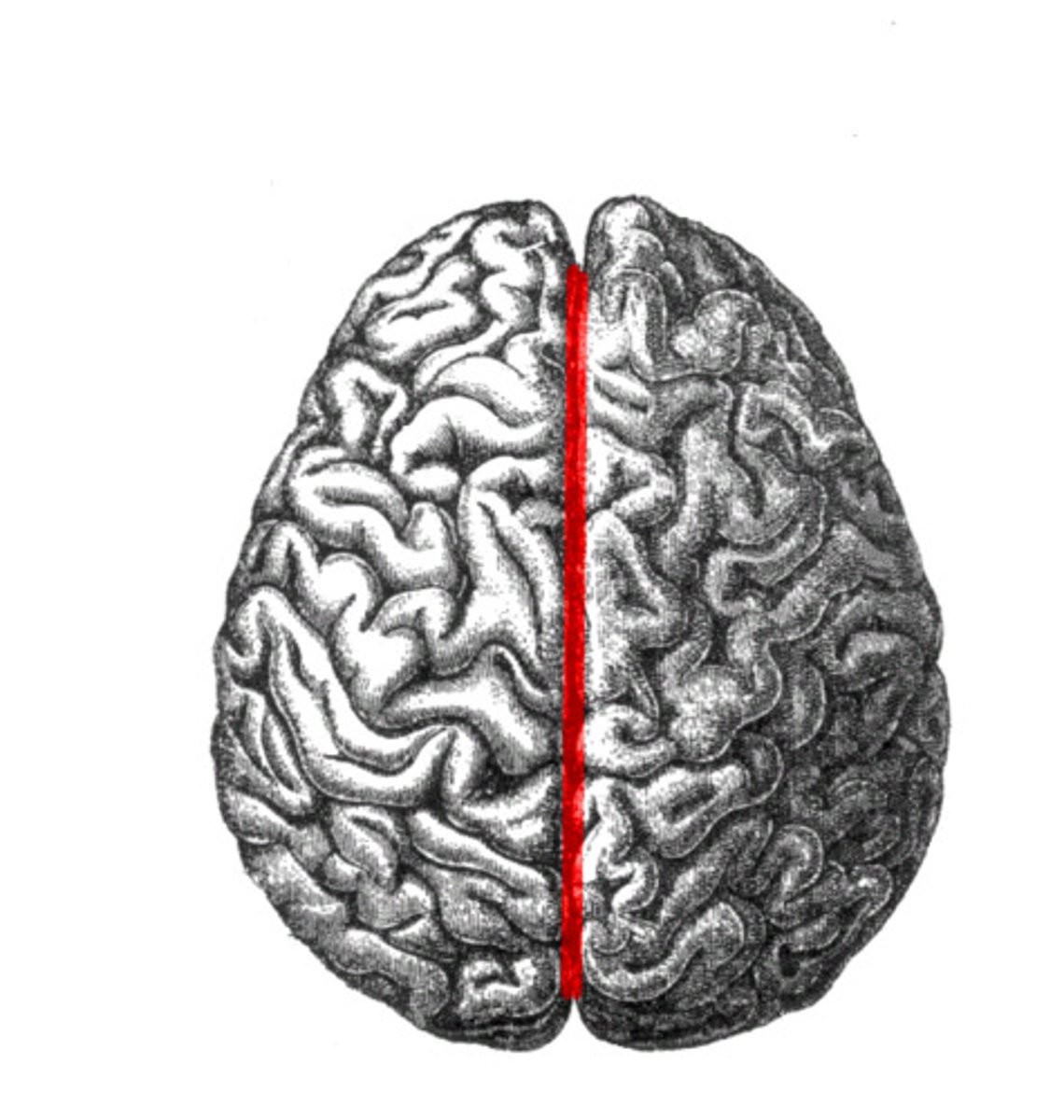
Location of longitudinal fissure
The space between the right and left hemisphere. It is located in the cerebral cortex. It divides the cerebral cortex.
Brainstem
medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain
the brainstem connects
brain and spinal cord
Cerebellum
coordination, muscle tone, & spatial equilibrium
Female brain vs male brain
-female brain is better at multitasking
-increase in corpus callosum
-increase in synapse connections
substantia nigra (black substance)
Basal ganglia structure in mid brain
a modulator for the pyramidal tracts which is the main pathway for voluntary movement being sent to the spinal cord
substantia nigra produces
dopamine which helps fine-tune movement signals sent by pyramidal tracts
Parkinson's disease
dopamine-producing neurons are lost in the substantia nigra, which means pyramidal tracts can't send out signals properly, resulting in impaired motor control (tremors)
pyramidal tracts
-of the midbrain
-looks like pyramids
Limbic System: Amygdala
-also known as paleomammalian cortex (old)
-made up of the amygdala (plays a role in memory, decision making, and emotional responses), mammillary bodies, stria medullaris, ventral nuclei of gudden
-interacts with basal ganglia (see something scary)
-processes and regulates emotions, behaivors, motivation, forming memories, influence autonomic nervous system (includes HR and BP), playing a key role in fight or flight or sympathetic system
Why is it important that we have an emotional response and brain re-wiring when experiencing something scary?
it gets you ready to either face the threat or escape from it (fight or flight; sympathetic NS)
Lobes of the brain
frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, temporal lobe
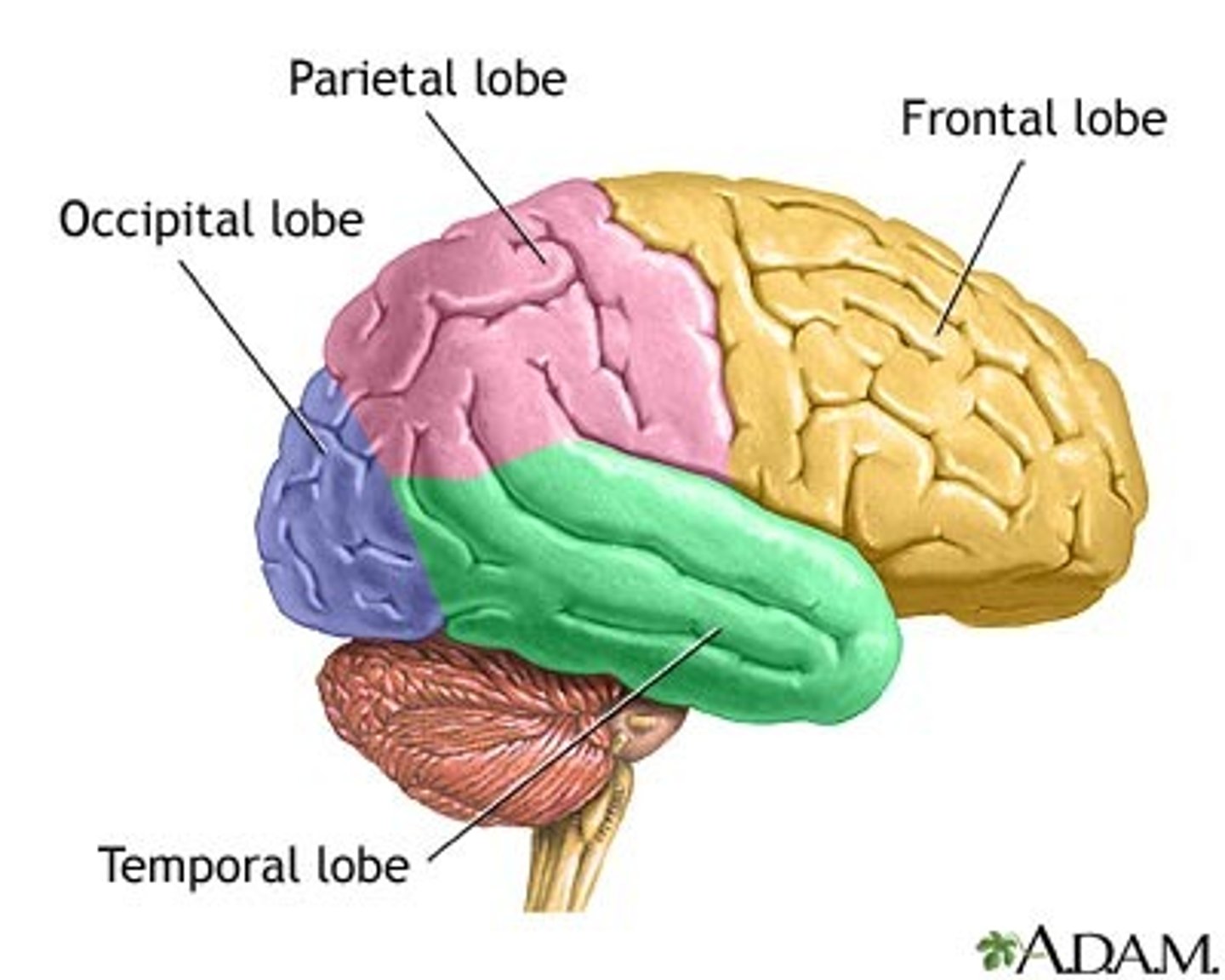
frontal lobe
voluntary movements, voluntary thought, cognition, thinking, engaging in reason/cause-effect, long-term memory, personality
parietal lobe
PMC (primary motor cortex - taste, temperature, touch, ) PSSC (Primary somatosensory cortex- pressure, vibration detection)
occipital lobe
vision
temporal lobe
short-term memory, emotions, speech, smell (olfaction), auditory stimuli
cerebellum
balance and posture (also pons works with this), muscle tone, coordination→spatial equilibrium
midbrain function
alert, awake, conscious
pons
balance and posture (also cerebellum works with this)
spinal cord
reflexes, walking, urination, sex organ function
Primary motor cortex
-anterior
-controls voluntary muscle movements
somatic sensory cortex
-posterior
-receives and provides sensory information from the body
the central sulcus divides
the primary motor complex and the somatic sensory complex
Hypothalamus
Part of the diencephalon in charge of body homeostasis, temperature regulation, endocrine functions, metabolism, circadian rhythms
6 functions of the medulla oblongata
BP,HR,RR,Blood flow, vomiting, swallowing
cerebrospinal fluid function
"cushion" the brain and provide nutrients
cerebrospinal fluid location
-in/around the brain and spinal cord
-within the ventricles of the brain
-subarachnoid space between the arachnoid matter and the pia matter
Meninges
-the dura matter, arachnoid matter, and the pia matter
-protect CNS
Meningitis.....bones......pressure......If they find WBCs in the CSF.....
If WBC's are in CSF then that could signify meningitis
meningitis
inflammation of the meninges of the brain and spinal cord
effects of meningitis
-purulent labrynthitis
-deteriorates the organ of Corti
-can cause ossification of the cochlea
-severe-to-profound sensorineural hearing loss
signs of meningitis
high fever, stiff neck, drowsiness, and intense headache; may progress to coma then death within hours of onset
caines
mepivacaine, ropivacaine, levobupivacaine, chloroprocaine
opioids
fentanyl, morphine, hydromorphone, oxycodone, sufentanil
*** Neuro-pharmacology in general!! ***
local pain blockers and systematic pain blockers
local pain blockers
-anaesthetics
-"caine" blocks VG Na+ so that there is no depolarization and no signal at the source of pain (signal never sent to brain)
systematic pain blockers
-opiates/narcotics
-lead to pleasure/reward pathways
-FLATPEG
-E= endorphins,endrogenous
**** "-caines"; narcotics/opiates; SSRIs vs SRIs
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRI)- legal, block serotonin from going back home (brain) causes us to feel happy (antidepressants) only blocked in brain and this a slow process
Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor (SRI) - not legal, Amphetamines - 3,4 MDMA also known as molly ooooo drugs,
Caines - Fast voltage gated Na+ channels, these will block the depolarization/ signal before it occurs and its localized
Opoids/Narcotics - Doesnt care as it will block all signals and hyperpolarize causing no processing of any pain signals. This is not localized and it is all over the body
SSRI
-take a long time to be effective (2-4 weeks)
-selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
-selective=only in brain
-elevates serotonin levels in brain
drug examples of SSRI
Zoloft (generic: sertraline), Prozac (fluoxetine), Lexapro (escitalopram)
SRI
-works very fast and short-term
-serotonin reuptake inhibitor
-illegal
-blocks all over body
-leads to feedback inhibition
-body stops production
-elevates dopamine levels in brain (plays into addiction centers in brain) because fast dopamine hit = brain happy -> brain wants easy happy feeling more)
examples of SRI
methamphetamine
both SSRi and SRi elevate
mood (dopamine and serotonin)
Proprioception...inner ear fluid....CN VIII....
-Vestibulocochlear Nerve (CN VIII)
- the semicircular canals of the ear have fluid that plays a role in balance in detection of acceleration/ deceleration
Cranial nerves
olfactory nerve I, optic nerve II,Oculomotor nerve III, Trochlear IV, Trigeminal Nerve 5,Abducens nerve VI, Facial Nerve VII, Vestibulocochlear nerve VIII,Glossopharyngeal nerve IX, Vagus nerve X, Accessory nerve XI, Hypoglossal nerve XII
Olfactory nerve I
-Larger in vertebrates with a better sense of smell
-Proprioception is a sensory function
-Smell and taste are linked and are both chemoreceptors
-Smell is linked to memory
-issues (lesions) - inability to smell
Optic Nerve II
-Vision
-Optic chiasm: part of the brain where optic nerves cross
-Vision centers are in the occipital lobe
-Issues = blindness on the affected side
Oculomotor nerve III
-Double vision and blurred vision and drooping eyelids (ptosis)
-Superior, inferior, medial rectus and inferior oblique = proprioceptive
-Parasympathetic to the sphincter of the pupil(constriction) and ciliary muscles (accomodation)
Trochlear Nerve IV
-Superior oblique, motor and proprioceptive
-Some of the smallest motor units are found within the muscle of the eye
-Lens mineralize= cataract
-Double vision
Trigeminal Nerve V
-Mastication = chewing (mainly V3)
V1 - Ophthalmic - sensory from nose to scalp
V2 - Maxillary - sensory from upper jaw to upper lip
-V3= mandibular branch = masseter, temporalis, medial and lateral pterygoids
-issues include Trigeminal neuralgia - intense pain along the course of branch of nerve; loss of tactile sensation in face or weakness or clenching jaw
Abducens Nerve VI
-Double vision
-Lateral rectus
Facial Nerve VII
-Facial expressions
-Facial palsy
-(facial palsy) -Loss of taste sensation on anterior 2/3 tongues = decreased salvation
Vestibulocochlear Nerve VII
-Semicircular canals of the ear have fluid that plays a role in balance and detection of acceleration/deceleration
-Cochlea play a role in hearing
-Lesions = loss of hearing (cochlear nerve), loss of balance and equilibrium; nausea, vertigo and vomiting (vestibular nerve)
Glossopharyngeal Nerve IX
-Parasympathetic increases salivary gland secretion
-Motor to pharyngeal muscle
-Proprioceptive to pharyngeal
-Issues - difficulty swallowing loss of tase sensation posterior 1/3 of tongue; decreased salvation
Vagus Nerve X
-"To wander"
-Vagus nerve goes all over the body; Only nerve to extend beyond head and neck to visceral organs in thorax and abdomen
-Parasympathetic to SA node of the heart= HR down
-Remember, the SA node will fire twice per second without "vagal tone"
-Difficulty swallowing and/or hoarseness; uvula deviates away from side of the dysfunction
Accessory Nerve XI
-Most posterior
-Sternocleidomastoid
-Trapezius
-Issues are difficulty elevating the scapula or rotating neck
hypoglossal nerve XII
-"Under tongue"
-Intrinsic tongue muscles are entirely within the tongue
-Extrinsic tongue muscle attach the tongue to other structures
**Cranial nerves associated with vision ***
optic nerve II
**Cranial nerves associated with double vision ***
Oculomotor Nerve lll, Trochlear nerve lV, Abducens nerve Vl
Motor units are BACK on CN IV! Why the need for such small motor units associated with the eye??
-Smaller motor units create finer motion
-Smallest motor units are used in eye muscles (small movements and help with focusing sight)
sympathetic
-Regulates arousal and energy generation
-Fight or flight
-Stronger: hormone from adrenal medulla
-Thoraco-lumbar nervous system
parsympathetic
-antagonistic effects on target organs and promotes calming and a return to "rest and digest" functions
-default system
-Cranio-sacral nervous system
CN V - branches
-Ophthalmic (V1)
-Maxillary branch (V2)
-Mandibular branch (V3)
.....teeth.....dentist......"-caines"....This question is writing itself!!!
-Canines=local anesthesia
-Blocks voltage-gated sodium channels
-No depolarization
Both parasympathetic and sympathetic
PNS
-have pre and post-ganglionic
-Acetylcholine=pre and post NT
CNS
-Acetylcholine= ONLY post ganglionic
CN X.....parasympathetic.....heart rate.....NT (?)......NOT a nicotinic ACH
receptor....which means the same binding molecule can have different effects of different tissue...? And one's answer must be more than "a different receptor"!
-all over the body
-parasympathetic to SA (sinoatrial) node of the heart = HR down
-remember the SA node will fire twice per second without "vagal tone"
CN XI....muscles....medical condition
-sternocleidomastoid and trapezius
-difficulty elevating the scapula or rotating the neck
Graded Potential
-barrage of EPSPs
-determine if an AP is generated
-Na+, Cl-, K+
-summation
Action Potential
-transmit signals over long distances
-Na+, K+
-no summation
Leak Channel
-ion channel that is always open, allowing ions and substances to pass through
-aka passive channels or non-gated channels
Carrier
-membrane protein that moves molecules across a cell membrane
Pump
-generate a membrane potential by creating an electrochemical gradient across the membrane (against the concentration gradient)
LIGAND GATED RECEPTOR/CHANNEL
-protein embedded in a cell membrane that acts as a gate, allowing specific ions to pass through only when a signaling molecule (called a ligand) binds to it
-opening the channel by triggering a conformational change in the receptor protein
VG CHANNEL
-transmembrane protein that opens and closes in response to changes in a cell's electrical potential
sympathetic fibers
pre-ganglionic: short
post-ganglionic: long
sympathetic NTs
Acetylcholine is pre
sympathetic location of origination within spinal cord
thoracic and lumbar
why is sympathetic stronger?
due to release of Ach on adrenal medulla, which releases norepinephrine
Parasympathetic fibers
pre-ganglionic: long
post-ganglionic: short
Parasympathetic NTs
Acetylcholine is pre and post
Parasympathetic location of origination within spinal cord
sacrum and coccyx
Myelination....APCV
-Myelinated sheaths are faster sheaths
-Length doesn't matter (hence the myelination=saltatory conduction)
-BUT diameter does matter
-fastest ever recorded is 250mph
release of NT
Step 1: An AP arrives at the axon terminal
Step 2: voltage gated Ca2+ channels open and Ca2+ diffuses into axon terminal
Step 3: the calcium ions stimulate vesicles to release their NT via exocytosis
Step 4: The NT crosses the cleft via diffusion
Step 5: The NT binds to its receptors on the postsynaptic cell and causes chemical gated channels to open, iniating graded potential
Step 6: NT activities cease when:
a. neurotransmitter reuptake back into axon occurs
b. the NT diffuses away from its receptor
c. enzymes degrade or break up NT
Fate of NT
Can be enzymatically degraded
Ex) acetylcholinesterase: can be inhibited by SARIN nerve gas, ach levels for WAY up = intense skeletal muscle contraction
Part or all of the NT can be taken up by reuptake proteins on the presynaptic side
Ex) FE- SSRI- selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, serotonin levels go up in the brain slowly and only in the brain
Sometimes NTs escape from the synapse and are usually scavenged by astrocytes
summation
-graded potentials between resting and threshold