FN
1/220
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
221 Terms
A neuroscientist is investigating how different neural circuits in the brain analyze sensory information, form perceptions of the external world, make decisions, and execute movements. At what level of analysis is this research conducted? Choose the correct option.
A) Molecular neuroscience level
B) Cellular neuroscience level
C) Systems neuroscience level
D) Cognitive neuroscience level
C) Systems neuroscience level
At which level of analysis do neuroscientists study the different types of neurons and their functions? Choose the correct option.
A) Cellular neuroscience
B) Cognitive neuroscience
C) Molecular neuroscience
D) Behavioral neuroscience
A) Cellular neuroscience
Galen suggested that the cerebrum, which was soft, should be the recipient of sensations. He was of the view that to form memories, sensations should be imprinted onto the brain. Thus, this must occur in the doughy cerebrum. Although the conclusion is right, the reason suggested by Galen is incorrect. True or false?
A) True
B) False
A) True
Scientists during the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries proposed the structure–function relationship between the white matter and gray matter in the brain. According to this relationship, gray matter contains the fibers that bring information to and from the white matter. True or false?
A) True
B) False
B) False
Neurons comprise two main structures: axons and dendrites. What is a major difference between the two? Choose the correct option.
A) Dendrites are of uniform diameter throughout, whereas axons taper to a point.
B) Dendrites receive incoming signals from other neurons, whereas axons carry the output of neurons.
C) A cell body gives rise to a single dendrite and multiple axons.
D) Dendrites travel long distances, whereas axons are always short.
B) Dendrites receive incoming signals from other neurons, whereas axons carry the output of neurons.
What is the function of a neurotransmitter receptor in the dendritic membrane? Choose the correct option.
A) Release synaptic vesicles
B) Detect neurotransmitters
C) Destroy extra neurotransmitter left in the synaptic cleft
D) Form gap junctions
B) Detect neurotransmitters
What is the region where the axon begins? Choose the correct option.
A) Soma
B) Axon hillock
C) Axon collateral
D) Axon terminal
B) Axon hillock
Which side of the cerebellum is concerned with movements of the right hand? Choose the correct option.
A) Right
B) Left
C) Frontal
D) Dorsal
A) Right
Which of the following regulates vital bodily functions such as breathing? Choose the correct option.
A) Cerebellum
B) Cerebrum
C) Brain stem
D) Meninges
C) Brain stem
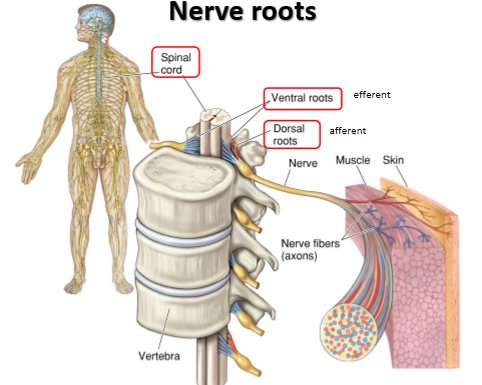
Axons of the nervous system are described as afferent and efferent according to the direction in which they carry information. Which of the following represents an efferent projection? Choose the correct option.
A) Sensory input to the spinal cord
B) Motor output from the spinal cord
C) Interneurons in the spinal cord
D) Sensory input to the spinal cord, motor output from the spinal cord, and interneurons in the spinal cord
B) Motor output from the spinal cord
At what point do the somatic sensory axons enter the spinal cord? Choose the correct option.
A) Dorsal roots
B) Ventral roots
C) Dorsal root ganglia
D) Ventral root ganglia
A) Dorsal roots
What plexus provides nerve connections to the abdomen, pelvis, and legs?
A) Cervical plexus
B) Brachial plexus
C) Lumbosacral plexus
C) Lumbosacral plexus
What lobe processes auditory info, learning, memory, and emotion?
A) Frontal lobe
B) Parietal lobe
C) Temporal lobe
D) Occipital lobe
C) Temporal lobe
Which membrane lies closest to the brain? Choose the correct option.
A) Meninges
B) Dura mater
C) Arachnoid
D) Pia mater
D) Pia mater
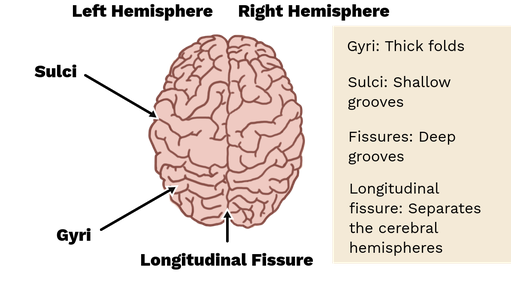
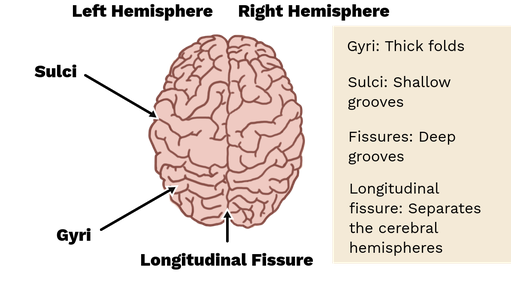
____ are deep grooves between gyri.
fissures
Where is CSF produced? Choose the correct option.
A) Choroid plexus in the cerebral ventricles
B) Subarachnoid space
C) Diencephalon
D) Arachnoid villi
A) Choroid plexus in the cerebral ventricles
Which major white matter system forms an axonal bridge linking the cerebral hemispheres? Choose the correct option.
A) Dorsal columns
B) Corpus callosum
C) Internal capsule
D) Posterior capsule
B) Corpus callosum
Which of the following is the most posterior cerebral lobe in the brain? Choose the correct option.
A) Occipital lobe
B) Temporal lobe
C) Parietal lobe
D) Frontal lobe
A) Occipital lobe
What lobe has the function of short-term memory, planning, and control of movement?
A) Frontal lobe
B) Parietal lobe
C) Temporal lobe
D) Occipital lobe
A) Frontal lobe
Who was the father of western medicine and believed the brain was the centre of sensation and intelligence?
A) Hippocrates
B) Aristotle
C) Galen
D) Andrea Vesalius
A) Hippocrates
Aristotle was a greek philosopher. Which of the following represents this view? Choose the correct option.
A) The heart as the center of intellect and the brain as the cooling system
B) Localization of brain function in the cerebrum and cerebellum
C) Mind–brain duality
D) Parceling the cerebrum into lobes
A) The heart as the center of intellect and the brain as the cooling system
Who was an anatomist that produced the dissection manual for medical students?
A) Hippocrates
B) Aristotle
C) Galen
D) Andrea Vesalius
D) Andrea Vesalius
____ identified the ____, which was considered the seat of the human “mind” and soul.
A) Rene Descartes; pineal gland
B) Andrea Vesalius; pineal gland
C) Rene Descartes; hypothalamus
D) Andrea Vesalius; hypothalamus
A) Rene Descartes; pineal gland
The function of the pineal gland is important in ____ by secretion of ____.
circadian rhythms ; melatonin
The gray matter is the axons of neurons.
A) True
B) False
B) False
The gray matter is the cell bodies of neurons… the white matter is the axons of neurons.
Sir Charles Bell and Francois Magendie found that nerves were attached to the spinal cord. They had two branches, ____, with a ____ flow of information.
ventral and dorsal ; bi-directional
____ are small grooves between gyri.
sulci
A glial cell produces a myelin sheath that is wrapped around the _________ of a neuronal cell:
A) Axon
B) Dendrite
C) Soma
D) Axon terminal
A) Axon
What plexus provides nerve connections to the neck and shoulders?
A) Cervical plexus
B) Brachial plexus
C) Lumbosacral plexus
A) Cervical plexus
If a neuronal cell is stimulated at the dendrites and the resultant action neuronal impulse travels down the axon, which part of the axon would be considered the "start" of the neuronal impulse?
A) None are correct
B) Axon Proper
C) Axon Terminal
D) Axon Hillock
D) Axon Hillock
What lobe processes visual info?
A) Frontal lobe
B) Parietal lobe
C) Temporal lobe
D) Occipital lobe
D) Occipital lobe
The region of the axon that contains mitochondria and synaptic vesicles (but not cytoskeletal proteins) is the:
A) Axon Proper
B) Axon Hillock
C) None are correct
D) Axon Terminal
D) Axon Terminal
Marie-Jean-Pierre Flourens identified the functions of which of the following?
A) Cerebrum
B) Cerebellum
C) Brain stem (Medulla oblongata)
D) All of the above
D) All of the above
What is the mode of communication in the nervous system? ____ energy; generated at the ____ level (AP).
bioelectric energy; generated at the cellular level (AP)
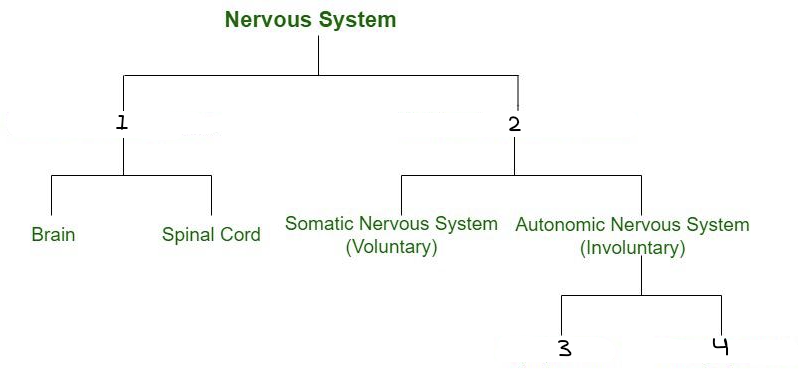
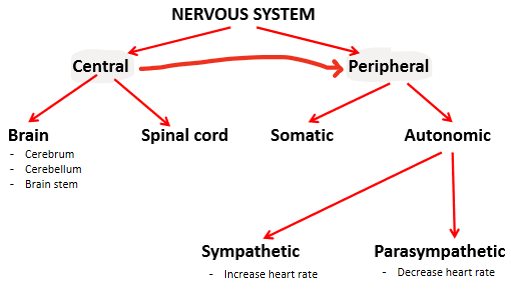
The brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, brain stem) and spinal cord are part of which system?
A) Central Nervous System
B) Peripheral Nervous System
C) Somatic Nervous System
D) Autonomic Nervous System
A) Central Nervous System
Which of the following is part of the peripheral nervous system?
A) The medulla oblongata.
B) The cerebellum.
C) The sympathetic nervous system.
D) The spinal cord.
C) The sympathetic nervous system.
Which of the following are correctly matched?
i. Sympathetic; fight or flight
ii. Sympathetic; rest and digest
iii. Parasympathetic; fight or flight
iv. Parasympathetic; rest and digest
A) ii and iii
B) i and iv
C) i only
d) none of the above
B) i and iv
Fill in the blank. (sympathetic, CNS, PNS, parasympathetic)
____ are “bumps” along the surface of the brain.
gyri
Which of the following is a function of the frontal cortex?
A) Providing perception to activation of skin receptors.
B) All of the options are frontal cortex functions.
C) Processing optic neuron stimuli.
D) Short-term memory.
D) Short-term memory.
What lobe has the function of somatic sensation (processing spatial info and integrating sensory info)?
A) Frontal lobe
B) Parietal lobe
C) Temporal lobe
D) Occipital lobe
B) Parietal lobe
The ____ separates the pre-central and post-central gyri.
central sulcus
Fill in the blank. (ventral roots, spinal cord, dorsal roots)
What is the term for the network of nerves exiting the spinal cord at two different directions?
A) Nerve system
B) Nervous system
C) Nerve network
D) Nerve plexus
D) Nerve plexus
What plexus provides nerve connections to the arms and upper arms?
A) Cervical plexus
B) Brachial plexus
C) Lumbosacral plexus
B) Brachial plexus
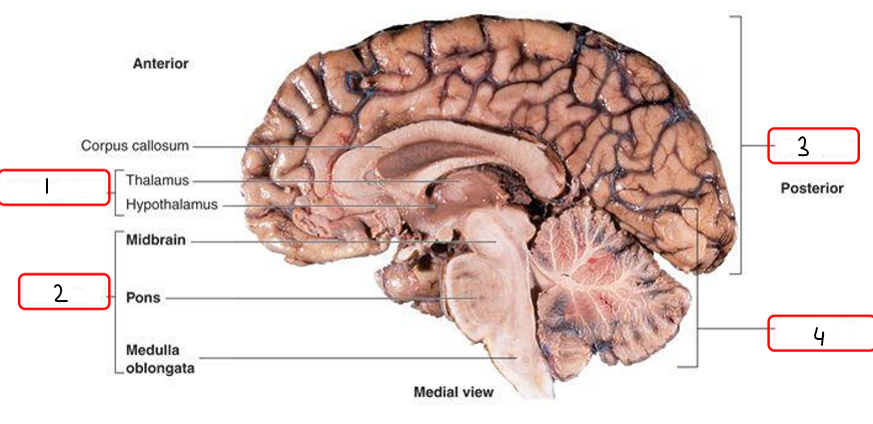
Fill in the blank. (cerebrum, cerebellum, diencephalon, brainstem)
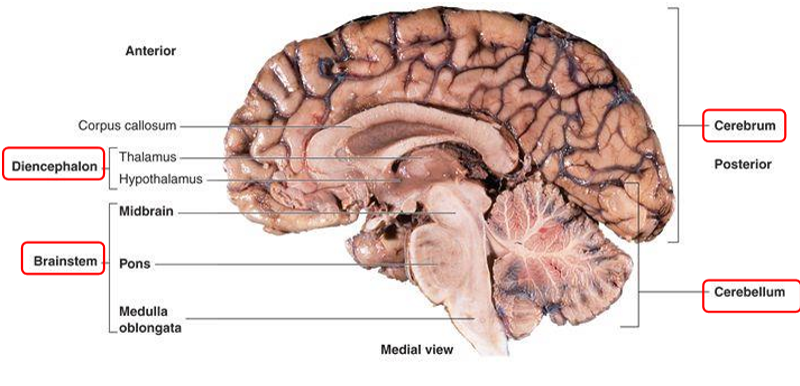
Which structure of the CNS relays information between the brain and body?
A) Cerebellum
B) Spinal cord
C) Medulla Oblongata
D) Pons
B) Spinal cord
The spinal cord handles functions without the brain such as ____.
reflexes
Which structure of the CNS is responsible for learning of motor skills, and fast responsive movements?
A) Cerebellum
B) Spinal cord
C) Midbrain
D) Cerebrum
A) Cerebellum
The ____ contains several major tracts (peduncles).
cerebellum
Which structure(s) makes up the brainstem?
A) Midbrain
B) Medulla oblongata
C) Pons
D) All of the above
D) All of the above
The ____ is responsible for digestion, breathing, and heart rate.
medulla oblongata
Which structure from the brain stem regulates the function of the medulla oblongata (e.g breathing)?
A) Midbrain
B) Medulla oblongata
C) Pons
D) All of the above
C) Pons
The pons conveys information about ____ from cerebrum to cerebellum.
movement
The ____ regulates eye movement, visual and auditory reflexes.
midbrain
The ____ maintains homeostasis by regulation autonomic, endocrine, visual functions.
hypothalamus
The ____ processes sensory information to the cerebral cortex (eg. proprioception).
thalamus
The wrinkled surface layer of the cerebrum is called the ____.
cerebral cortex
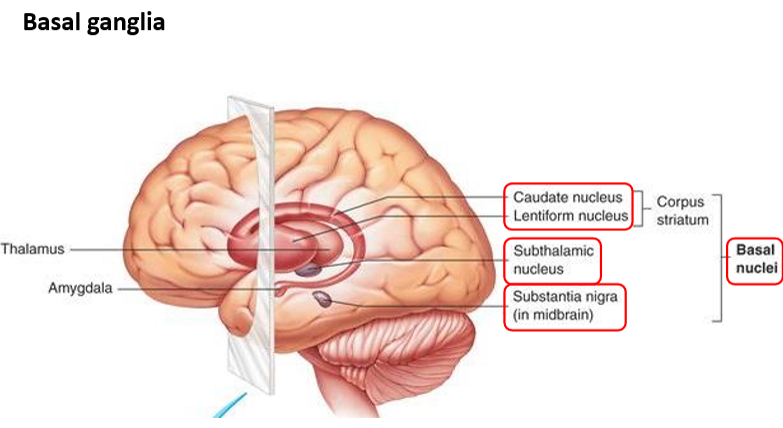
Which deep structure regulates motor performance (e.g. Parkinson’s disease)?
A) Hippocampus
B) Amygdaloid nuclei
C) Basal ganglia
D) All the above
C) Basal ganglia
Which deep structure is important in memory storage?
A) Hippocampus
B) Amygdaloid nuclei
C) Basal ganglia
D) All the above
A) Hippocampus
— if you saw a hippo on campus you would remember
Which deep structure is important in coordinating autonomic and endocrine responses of emotional states?
A) Hippocampus
B) Amygdaloid nuclei
C) Basal ganglia
D) All the above
B) Amygdaloid nuclei
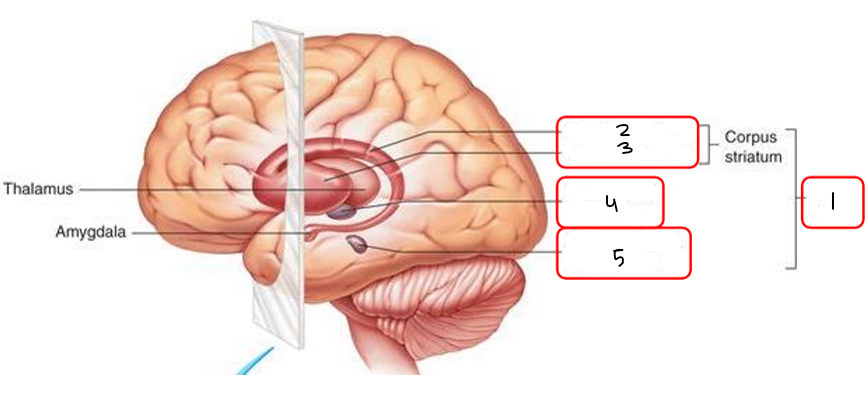
Fill in the blanks. (lentiform nucleus, basal nuclei, subthalamic nucleus, caudate nucleus, substantia nigra)
Which type of neuron in the brain functions to link some parts of the brain to other parts of the brain?
A) α - motor neurons
B) γ - motor neurons
C) Cutaneous sensory neurons
D) Pyramidal neurons
D) Pyramidal neurons
Which neurons are skin surface level?
A) α - motor neurons
B) γ - motor neurons
C) Cutaneous sensory neurons
D) Pyramidal neurons
C) Cutaneous sensory neurons
Which neurons function to activate motors?
A) α - motor neurons
B) γ - motor neurons
C) A and B
D) Pyramidal neurons
E) B and D
C) A and B
What part of the neuron is the metabolic centre of the neuron?
A) Cell Body (soma)
B) Dendrites
C) Axon
D) Axon Terminal
A) Cell Body
What part of the neuron receives incoming signals from other neurons?
A) Cell Body (soma)
B) Dendrites
C) Axon
D) Axon Terminal
B) Dendrites
What part of the neuron conveys information to other neurons and cells?
A) Cell Body (soma)
B) Dendrites
C) Axon
D) Nucleus
C) Axon
The nucleus is important for neuron structure because
A) It starts the process of making new proteins.
B) It is the origin of the bioelectrical signal needed for communication.
C) It is the primary site for ATP production.
D) It restricts what can or cannot enter the cell.
A) It starts the process of making new proteins.
The reason why neurons don’t expand is because they have ____.
limited capacity
Which type of glial cells function with astrocytes to protect neurons?
A) Astrocytes
B) Microglia
C) Oligodendrocytes
D) Schwann cells
B) Microglia
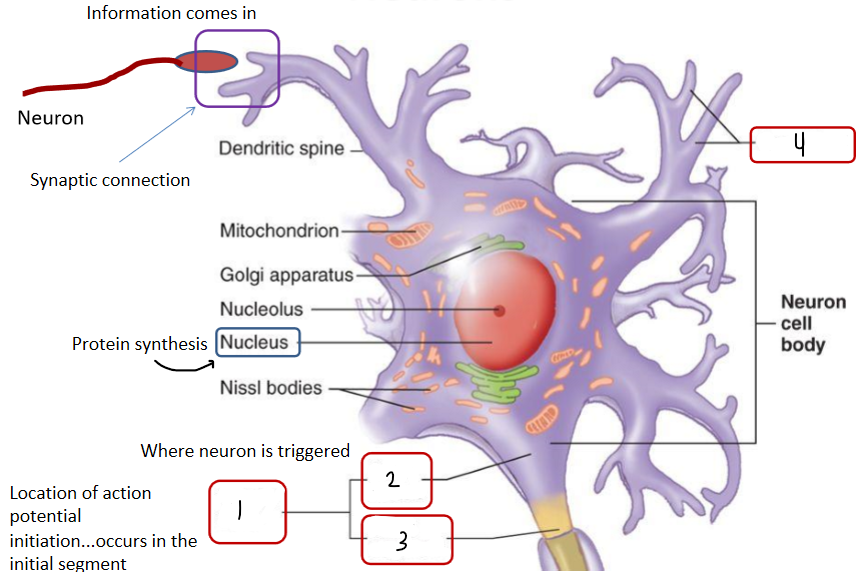
Fill in the blank. (dendrites, axon hillock, trigger zone, initial segment)
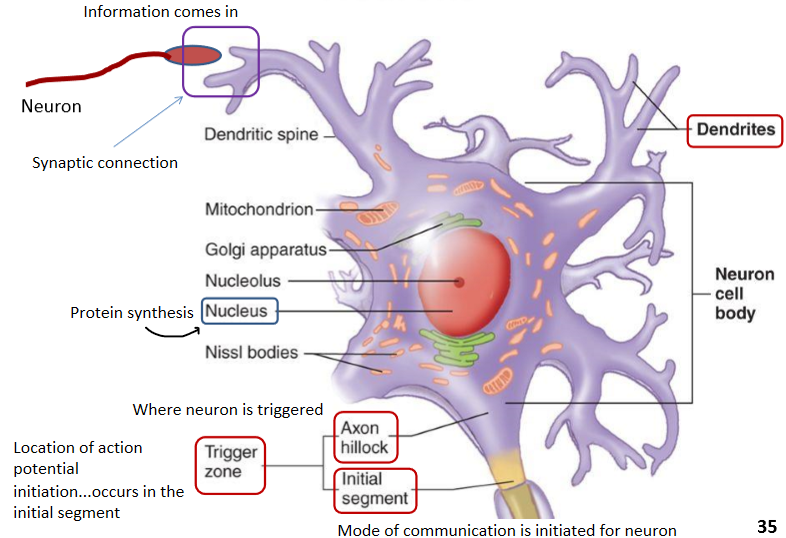
Where in the neuron does the action potential initiation occur?
A) Axon terminal
B) Initial segment
C) Axon hillock
D) Dendrites
B) Initial segment
The exposed region of the axon called the ____ and the electrical insulation covering called the ____ increase the speed of action potentials.
nodes of ranvier ; myelin sheath
The neuron with the fastest speed is
A) Multipolar neuron
B) Bipolar neuron
C) Pseudo-unipolar neuron
D) None of the above
A) Multipolar neuron
Which neuron is a motor neuron?
A) Multipolar neuron
B) Bipolar neuron
C) Pseudo-unipolar neuron
D) None of the above
A) Multipolar neuron
Which neuron is found in the retina and olfactory epithelium?
A) Multipolar neuron
B) Bipolar neuron
C) Pseudo-unipolar neuron
D) None of the above
B) Bipolar neuron
Which neuron is a somatosensory neuron?
A) Multipolar neuron
B) Bipolar neuron
C) Pseudo-unipolar neuron
D) None of the above
C) Pseudo-unipolar neuron
Which of the following is considered to be one of the functional categories for neurons?
A) Interneurons
B) Sensory neurons
C) Motor neurons
D) All of the options are functional categories
D) All of the options are functional categories
____ neurons carry information from body peripheral into the nervous system. They are considered ____.
sensory ; afferent
____ neurons transmit signals from the brain and sensory systems (CNS) to muscles. They are considered ____.
motor ; efferent
Relay (projection) interneurons convey signals over large distances and have long axons.
A) True
B) False
A) True
Local interneurons make connections with nearby neurons and have long axons.
A) True
B) False
B) False
Local interneurons make connections with nearby neurons and have short axons.
What cell ensures appropriate fluid balance?
A) Astrocyte
B) Microglial cells
C) Ependymal cells
D) Oligodendrocytes
C) Ependymal cells
Glial cells are not considered neurons.
A) True
B) False
A) True
— they are neuron supporting cells
How are glial cells different from neurons?
A) Glial cells are about half as numerous as neurons
B) Glial cells occupy far less space in the human brain than neurons
C) Glial cells are not electrically excitable
D) Glial cells are able to produce force that aids in human movement
C) Glial cells are not electrically excitable
Which type of glial cells are derived from hematopoietic stem cells?
A) Astrocytes
B) Microglia
C) Oligodendrocytes
D) Schwann cells
B) Microglia
Which type of glial cells signal for myelination?
A) Astrocytes
B) Microglia
C) Oligodendrocytes
D) Schwann cells
C) Oligodendrocytes
What area of study focuses on human movement generated at behavioural level of analysis?
A) Motor control
B) Motor Behaviour
C) Motor development
D) Motor memory
B) Motor Behaviour
What area of study focuses on understanding neural, physiological, and behavioural aspects of movement?
A) Motor control
B) Motor behaviour
C) Motor development
D) Motor memory
A) Motor control
What area of study is concerned about changes in motor behaviour due to growth?
A) Motor control
B) Motor behaviour
C) Motor development
D) Motor memory
C) Motor development
What area of study is for the memory of movement or motor information?
A) Motor control
B) Motor behaviour
C) Motor development
D) Motor memory
D) Motor memory
What area of study has two aspects of neural- and muscle structure- based?
A) Motor control
B) Motor behaviour
C) Motor development
D) Motor memory
D) Motor memory
____ is the conscious awareness of body position and movement.
proprioception
The elementary attribute proportional to the type and number of neurons discharged is:
A) Duration
B) Location
C) Modality
D) Intensity
D) Intensity
Sense of balance, head position and equilibrium are characteristic of:
A) Electromagnetic waves
B) Mechanical air vibrations
C) Internal and external chemicals
D) Mechanical deformations
B) Mechanical air vibrations
The function of ____ is to create an internal representation of the external world or internal state of body.
sensory processing
____ begins with an internal representation; image of the desire outcome.
motor processing
The term psychophysics focuses on the physical characteristics of a stimulus and the attributes of its’ perception.
A) True
B) False
A) True
The basic stimuli that generate reflexes, reactions, and conscious decisions is:
A) Electromagnetic waves
B) Mechanical air vibrations
C) Internal and external chemicals
D) Mechanical deformations
A) Electromagnetic waves