exam 3 pt 4 (long-term climate change -> intertidal zone)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
how do we predict what will happen to organisms as our climate changes?
we refer to the past
biome
major ecological associations that occupy broad geographic regions of land or water
→ varying combinations of biotic + abiotic factors determine the nature of biomes
aquatic biomes account for the _______ part of the biosphere in area (~75% of earth’s surface)
→ they contain fresh water or salt water
largest
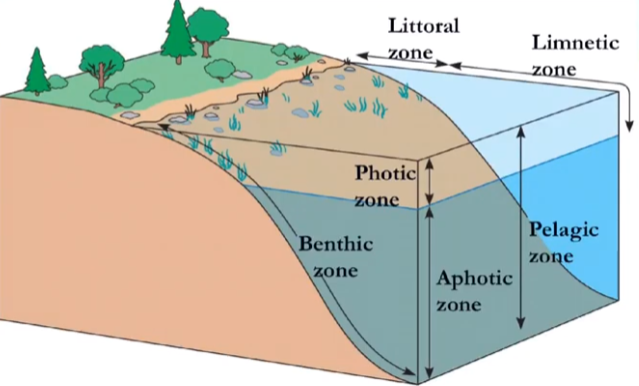
what are these stratified regions called?
zonation
what defines zonation in aquatic biomes?
light penetration + temperature + depth
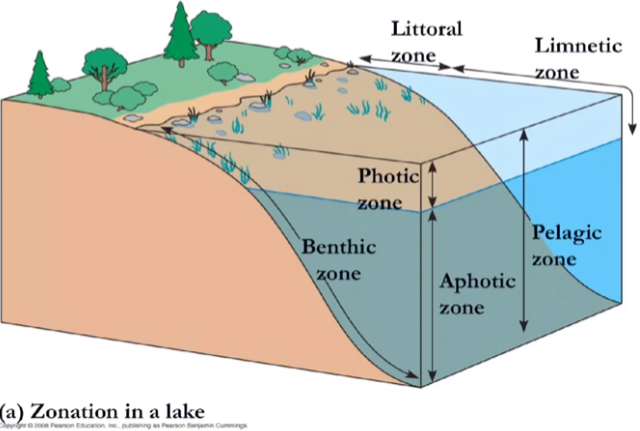
what are the zonations you should know in a lake?
A) littoral
→ the shoreline; where the water is shallow enough that plants can root and still do photosynthesis
B) limnetic
→ no plants can root here; much deeper, open water
C) photic
→ enough light penetration for organisms to do photosynthesis
D) aphotic
→ not enough light for photosynthesis
E) benthic
→ anywhere on the bottom
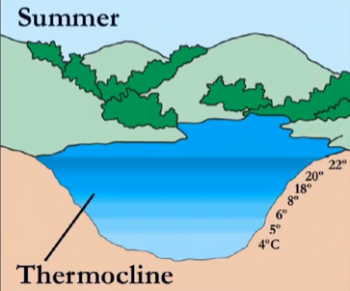
thermocline
(in most oceans + lakes) a temperature boundary separates the warm, upper layer from the cold, deeper water
turnover
semiannual mixing of upper/lower water
→ mixes oxygenated water from surface with nutrient-rich water from depths
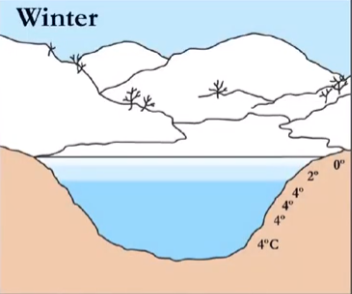
in winter, why does 0 go at the top?
why does 4 go on the bottom?
0 is when water freezes → it STAYS 0 on due surface because ice floats due to being less dense
4 is when water has it’s highest density
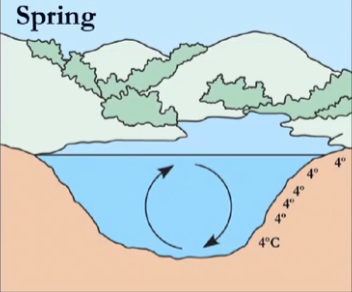
why is it 4 all throughout in spring?
surface warms up to 4, making it’s density highest. high density will attempt to sink down, causing a cyclic motion which creates turnover #1
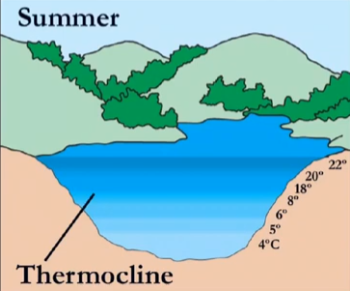
in summer, why is 22 at the top?
why is 4 at the bottom?
the surface warms more and begins to stratify. warm water goes to the top because it is less dense
4 stays at the bottom because it’s at its highest density
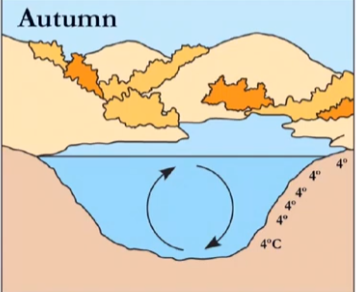
why is it 4 all throughout in fall?
surface cools down to 4, making it’s density highest. high density will attempt to sink down, causing a cyclic motion which creates turnover #2
oligothropic lake
nutrient-poor, clear water, low plant + algae growth
eutrophic lake
nutrient-rich, lots of algae + plant growth
→ has dead zones where the water is without oxygen (USUALLY due to excess nutrient runoff from agriculture and dumping !!)
rivers/streams
flowing water, high oxygen levels, organisms adapted to currents, nutrients move downstream
wetlands
land saturated with water, high biodiversity, act as natural water filters, reduce flooding/erosion
estuaries
where freshwater + saltwater mix, brackish (mixed) water, diverse ecosystems, salinity changes with tides
pelagic zone
open water AWAY from shore + bottom, includes surface→deep waters, photic upper zone supports photosynthetic organisms, home to free-swimming organisms like fish and whales
coral reefs
built by coral animals, found in warm + shallow + clear oceans, high biodiversity, sensitive to temperature/pollution, depend on algae for its maintenance
benthic zone
bottom of aquatic biomes, nutrients accumulate here, includes sediment + organisms living on or in it, organisms include worms + clams + crabs
intertidal zone
area between high and low tide (beach), alternates between wet and dry, organisms adapted to waves, high stress on organisms but high diversity