6. Transplant
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Autograft
Allograft
Isograft
Xenograft
MHC ___________ encode for __________ such as ________
genes; proteins; HLA
MHC I encodes for _________________________________
antigen presentation in all nucleated cells
MHC I span the membrane of almost every ____________
nucleated cell
Class I mainly presents _______________ antigens to CD8 T cells
Endogenous (Ag that appears within the cell i.e. infected by organism)
Class I proteins include: __________________________
HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C
MHC II encodes for ____________ ____________ _________
Antigen Presenting Cells
MHC II is primarily found on ______ ______ ______
Antigen Presenting Cells ( Dendritic, monocytes, macrophages, B cells)
Class II mainly presents _______________ antigens to CD4 T cells
Exogenous (Ag present extracellularly i.e. ingested the organism)
Class II proteins include: ___________________
HLA-DR, HLA-DQ, HLA-DP
MHC III encodes for ____________, ______________, and ____________
complement, cytokines, other genes
HLA system is the strongest immunologic _____________ for successful allogenic organ transplants
barrier
HLA antigens exhibit a high degree of __________ ________________
allelic polymorphism
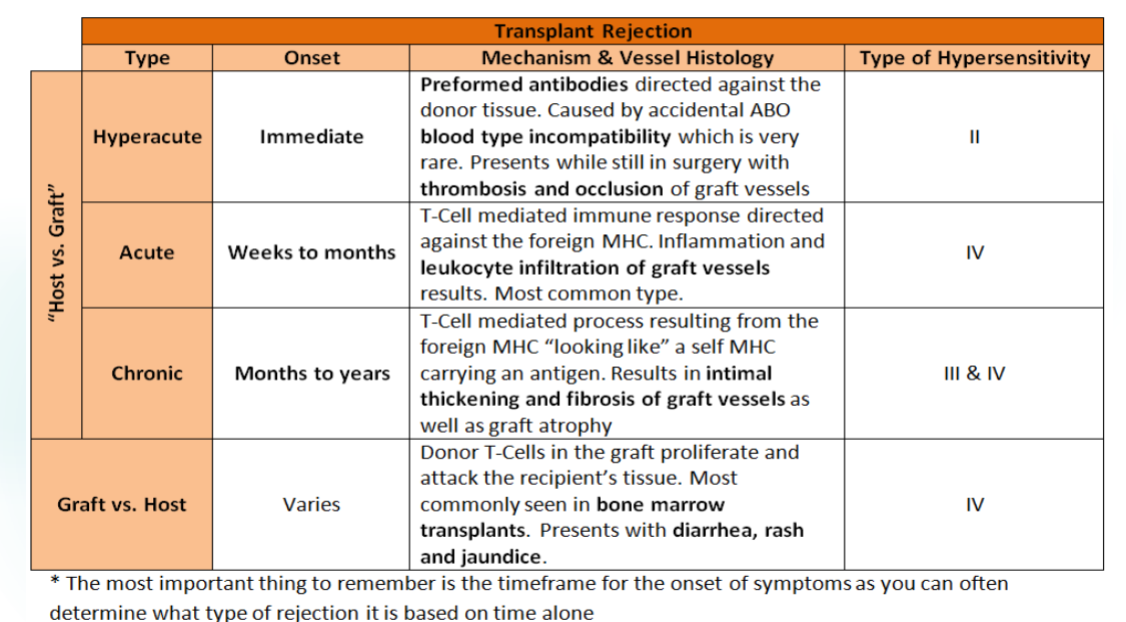
Hyperacute Rejections is an_____________ and _____________ mediated response
immediate and antibody
In Hyperacute Rejection recipient has _________________ antibodies reactive with donor tissue
pre-exisiting
Hyperacute Rejection leads to_______________ activation
complement
In Hyperacute Rejection, Thrombosis and occlusion of ______________ vessels
Can be prevented by:
graft
Prevented by:
ABO matching
Cross-matching donor and recipient
Acute Rejection is________ mediated immune response against foreign MHC
T cell
Acute Rejection can take __________ to _____________
weeks to months
In Acute Rejection, Inflammation and _____________ _______________ of graft vessels results
leukocyte infiltration
Acute Rejection is the_____________ common type
most
Chronic Rejection can take __________ to _____________
months to years
Chronic Rejection is the_________ cause of long-term failure of transplantation
major
Chronic Rejection is________ mediated immune response against foreign MHC
T cell
Chronic Rejection results in ______________ and ____________ of graft vessels leading to organ_____
thickening and fibrosis; ischemia (atrophy)
The most common GVHD is from __________ ____________ transplants
bone marrow
In GVHD ____________ T cells proliferate and attack _____________ tissue
Donor; Recipient
In GVHD, patients present with ______________, ___________, and _______________
diarrhea, rash, juandice
Types of Rejection summary chart
What 4 things will a transplant recipient be tested for?
ABO
HLA
CMV
Test for anti-HLA antibodies to eliminate unacceptable donors
DNA Inhibitors or Anti-proliferatives; How do these work?

What are the 2 common DNA Inhibitors or Anti-proliferatives named?
1.Methotrexate
2.Mycophenolic Acid (MPA)
T cell inhibitors help prevent ______________ rejection
allograft
Calcineurin inhibitors

mTOR inhibitors

Corticosteroids inhibit inflammation in what ways?
