Immune System: Anatomy, Non-Specific Immunity, And Humoral Immunity (Cram)
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
What are the five primary lymphoid organs in the body?
Remember: Tasty BLT Sandwiches
Thymus
Bone marrow
Lymph nodes
Tonsils
Spleen
What are the four functions of the lymphatic system?
Remember: Down To F*ck Rednecks (a favourite Fairview pastime)
Drains excess fluid
Transports fat
Filters lymph (for antigens)
Removes waste (like pus)
True or false: Like the circulatory system, the lymphatic system relies on pressure to move lymph in one direction from lymph capillaries, to larger thoracic ducts, and finally large vessels like the vena cava
False. The lymphatic system has NO pressure. It relies on valves and muscle movement to move lymph
Lymph is 95% water, what is the other 5% comprised of, and what is its largest cellular componant?
The other 5% is comprised of plasma proteins, with the largest cellular componant being lymphocytes
Fluid released from the capillaries into the spaces between tissue cells
Interstitial fluid
Strutures located throughout the body where ALL lymph fluid gets filtered
Lymph nodes
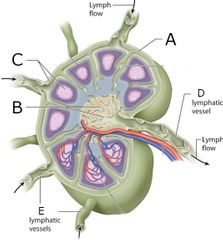
Name the structures labelled A,B,C,D,and E
A = Capsule
B = Medulla
C = Cortex
D = Efferent
E = Afferent
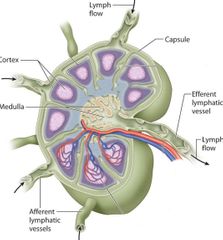
In most animals, the cortex is found around the outside of the lymph node, and the medulla is on the inside. In which species is the opposite true?
Pigs
Which structure in the lymph node contains lymphocytes?
Cortex
Which structure in the lymph node contains macrophages?
Medulla
Which organ is located near the stomach/rumen and has both lymphatic and hematological functions?
Spleen
What part of the spleen contains blood and red blood cells?
Red pulp
What part of the spleen is where lymphocytes live and clone themselves?
White pulp
Which organ is located in the neck near the trachea?
Thymus
What type of lymphocyte is processed and distributed in the thymus?
T–lymphocytes
True or false: Like lymph nodes, the tonsils have a capsule, cortex, and medulla. They are located in the back of the throat
False. Tonsils DO NOT have a capsule. These nodules of lymphoid tissue contain mature lymphocytes and are located ALL OVER the body in moist epithelial surfaces
What is GALT an acronym for?
Gut–associated lymphoid tissue
What is MALT an acronym for?
Mucosa–associated lymphoid tissue
The area of all red and white blood cell production
Bone marrow
White blood cells that phagocytize invader, foreign material, and dead or damaged cells. They are released from the bone marrow into the blood as needed, and enter tissues when attracted there by inflammatory chemicals
Neutrophils
White blood cells that enter tissue from blood where they inhibit local allergic reactions (their granules contain antihistamines), and phagocytize foreign materials, especially parasites
Eosinophils
White blood cells that are not normally found in tissues, only in blood, but there appears to be a relationship to mast cells which are normally found only in tissues and not in blood. Function is not well known, but their granules contain histamine which enhances inflammatory reaction, and heparin which inhibits blood coagulation
Basophils
White blood cells that become macrophages once they leave the blood and enter the tissues. These are largely phagocytic cells which clean up cellular debris and ingest foreign substances. They also are involved in the immune response against microbes
Monocytes
White blood cells that are involved in various types of immune responses. There are several different types
Lymphocytes
Anything the body recognizes as foreign, and different from itself
Antigen
What kind of immunity is this: It involves tissues, cells, and processes that protect the body from anything it recognizes as foreign. This type of immunity is NOT specific, not directed at any particular antigen but against anything and everything that may cause harm
Non–specific immunity
Another term for non–specific immunity
Innate immunity
What kind of immunity is this: It involves recognition of antigens which are NOT self and then producing responses which are specific against the antigens
Specific immunity
Another term for specific immunity
Acquired/adaptive immunity
What type of non–specific immune response is this: An animal is not capable of contracting certain diseases because of physiological and anatomical differences between species
Non–susceptibility
What type of non–specific immune response is this: The body has certain barriers such as skin, mucous membranes, stomach acid, ciliated upper respiratory tract, flushing action of urinary tract /eyes which help prevent foreign materials and invaders from entering
Physical and chemical barriers
What type of non–specific immune response is this: This is a tissue reaction to any damage or injury of body cells, regardless of the cause. The release of chemicals from injured or dead cells causes five key signs
Inflammation
What type of non–specific immune response is this: Some WBC are involved in ingestion & digestion of any foreign particles (eg. neutrophils, macrophages) regardless of what the foreign agents are
Phagocytosis
What type of non–specific immune response is this: A group of normally inactive enzymes in the plasma which can be activated to rupture cell membranes of foreign cells
Complement
What type of non–specific immune response is this: A chemical produced by cells which is released upon the death of the cell and which inhibits replication and spread of viruses
Interferon
True or false: If the body has encountered an antigen before, and it enters the body a second time at a later date, the immune response will occur more quickly because of a memory of the antigen
True
What are the two main types of specific immunity responses?
- Humoral immune response
- Cell–mediated immune response
Which type of specific immune reponse involves T–lymphcytes?
Cell–mediated immune response
Which type of specific immune response involves B–lymphcytes?
Humoral immune response
In humoral immunity, when B–lymphocytes are activated, what do they become? And what is the function of this new type of cell?
B–lymphcytes become plasma cells, which produce antibodies
Another term for antibodies
Immunoglobulins
True or false: In order to defend against different foreign antigens, each B–lymphocyte will produce many different types of antibodies. One for every antigen they encounter
False. Antibodies are specific for an antigen, and each B–lymphocyte can make a lot of antibodies. But they can only produce one type of antibody, which is specific for one type of antigen
Fill in the blank: When activated, some B–lymphocytes become _______ cells, which remain in the body for years
memory
When B–lymphocytes are activated, they become plasma cells. These cells divide many times. This results in many cells that can make antibodies to the antigen. What are the three outcomes when these antibodies combine with the antigens?
- Antigens are transformed into harmless substance
- Antigens are stuck together into clumps to be more easily phagocytized by macrophages
- Antibodies adhere to the antigens, and activate complement or natural killer cells which destroy the forgein cell
What are the five types of antibodies?
Remember: MADE Good (the granola bars)
IgM
IgA
IgD
IgE
IgG
Which type of antibody is associated with allergic responses?
Remember: E for eosinophils
IgE
Which type of antibody is produced on second or continuous exposure to an antigen. The production of this antibody is also relatively slow. It can cross the placenta into the fetus
IgG
Which type of antibody has a function that is unknown, though has similar actions to IgE
IgD
Rememer: D for don't know bro
Which type of antibody are produced on the first exposure to an antigen, and the production of these is relatively slow
IgM
Which type of antibody can leave the plasma and enter tissues and are often found on mucosal surfaces (eg. in the lungs and intestinal tract) to catch antigens entering the body through those routes
Remember: A for airways
IgA
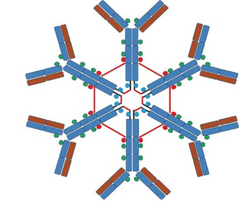
Which immunoglobulin is this?
IgM
The initial response of B–lymphocytes, it is moderately slow, taking days to weeks
Primary response
Any response after the initial response, the antigen is encountered again and memory cells speed up and intensify the response
Secondary response
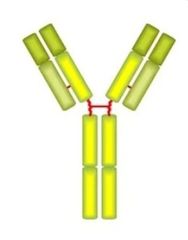
Which immunoglobulin is this?
IgE
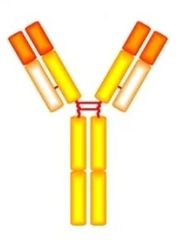
Which immunoglobulin is this?
IgG
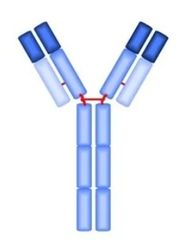
Which immunoglobulin is this?
IgE
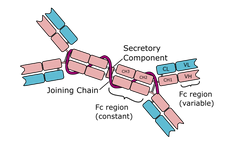
Which immunoglobulin is this?
IgA