Lecture 3A: Epithelial Border Mods
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Epithelia are allowed to perform specific functions due to
border modifications
Epithelial junctions can be classified according to their
function
most cell junctions are part of the
junctional complex
where is the junctional complex located?
on the lateral border of epithelial cells
Epithelial junctions are typically how big in size
20-90 nm
What is another name for tight junctions
zona occludens
tight junctions begin just beneath the
luminal surface
what do tight junctions do?
they seal neighboring cells
Tight junctions cause the outer membrane of neighboring cells to
fuse
the fuse between cells in the tight junction form a
circumferential belt
the circumferential belt of the tight junction seals the
intercellular space from the lumen
What are the 3 types of cytoskeletal linked junctions?
adherent
desmosomes
hemidesmosome
what is another name for adherent junctions
zona adherens
Adherent junctions form a continuous adhesion belt around each interacting epithelial cell near the apical surface just beneath the
tight junction
membranes of the adherent junction are fused as well - T or F
F - they are not fused but separated by a narrow space
plasma membranes found in the narrow space of adherent junction
cadherins
what is occurring in the narrow space of the adherent junction?
cadherins interact with one another
proteins are anchored by adjacent ________ _______ containing numerous _____ filaments
cytoplasmic condensations, actin
What forms the terminal bar
tight junction and adherent junction
Desmosomes are also called
macula adherens
How are desmosomes similar to adherent junction?
membrane apposition and protein interactions
how do desmosomes differ from adherent junctions?
they do not have to be located near the lateral luminal surface
desmosomes do not ______ the cell and occur more often as _____ _____
encircle, spot welds
Unlike adherent junctions, desmosomes also have extracellular filaments that space the _________ ______ and further -
extracellular space
anchor the membranes together
what are hemidesmosomes?
half a desmosome used to anchor cell to basal lamina
what is a gap junction?
broad area of closely opposed plasma membranes that are NOT fused.
The gap junction is spanned by assemblies of
hexagonal connexon proteins with central pore
the proteins and pore of the gap junction allows for a
low resistance channel of electrochemical communication between cells
what are the two types of apical border modifications
microvilli and cilia
Microvilli in comparison to cilia are
smaller but more numerous
microvilli have finger like projections about ____ microns long and usually have _____/cell
1-2 microns
3000/cell
Microvilli have an internal network of
actin filaments
microvilli act to
increase surface area in absorptive epithelia
Microvilli are referred to as ______ _______ in the gut, and ______ ______ in the renal tubules
striated border - gut
brush border - renal tubules
What are stereocilia
branched microvilli (uncommon)
where are stereocilia found
epididymis of male reproductive tract
Cilia are hair like projections about _____ microns long and have about ____/cell
5-10 microns
300/cell
cilia contain a core of
bundled microtubules
microtubules have _____ _____ that use ATP to cause the tubules to move ______ to one another
dynein motors
longitudinal
cilia occur in
parallel rows that beat together
Cilia rows beat together to move
fluid over the surface
cilia are most common in
respiratory and reproductive tracts
(from lecture) tight junctions and adherent junctions both
loop around the cell
(from lecture) epithelial cells do not have to have all types of junctions - T or F
T
(from lecture) Gap junctions have ___ channels of how many proteins
2 channels of 6 proteins
(from lecture) microvilli provide _____ and have _____ on the top/surface
structure, glycoproteins
(from lecture) the central microtubule of cilia has how many motors
9
(from lecture) what are the three types that make up the junction complex
tight, adherent, desmosome
gap is not part of it
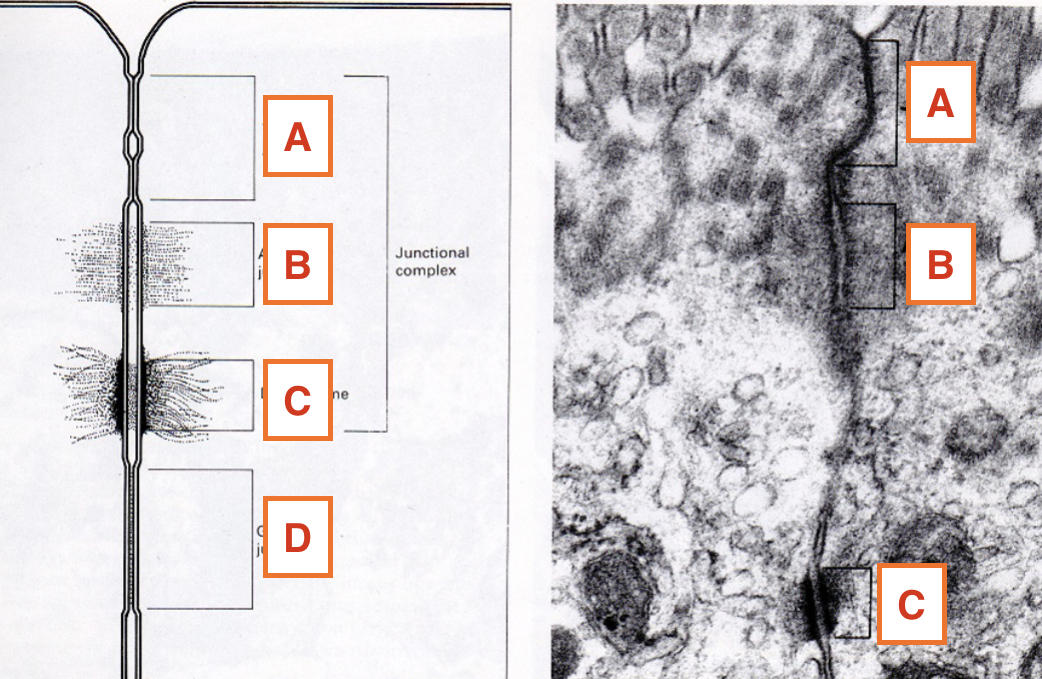
What is A?
tight junction
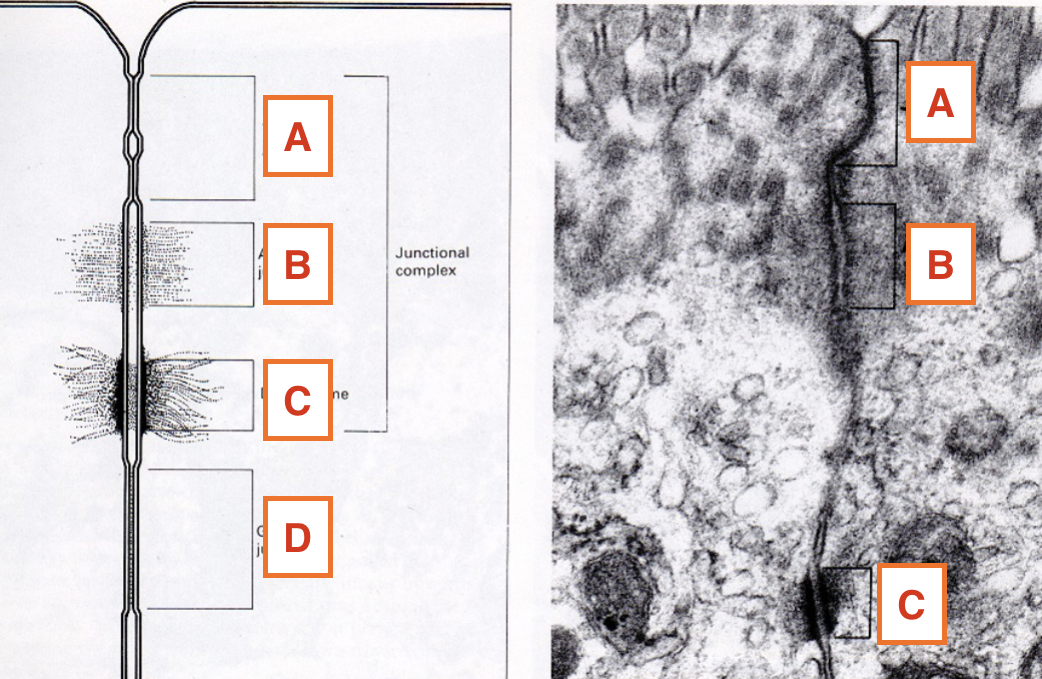
what is B?
Adherent junction
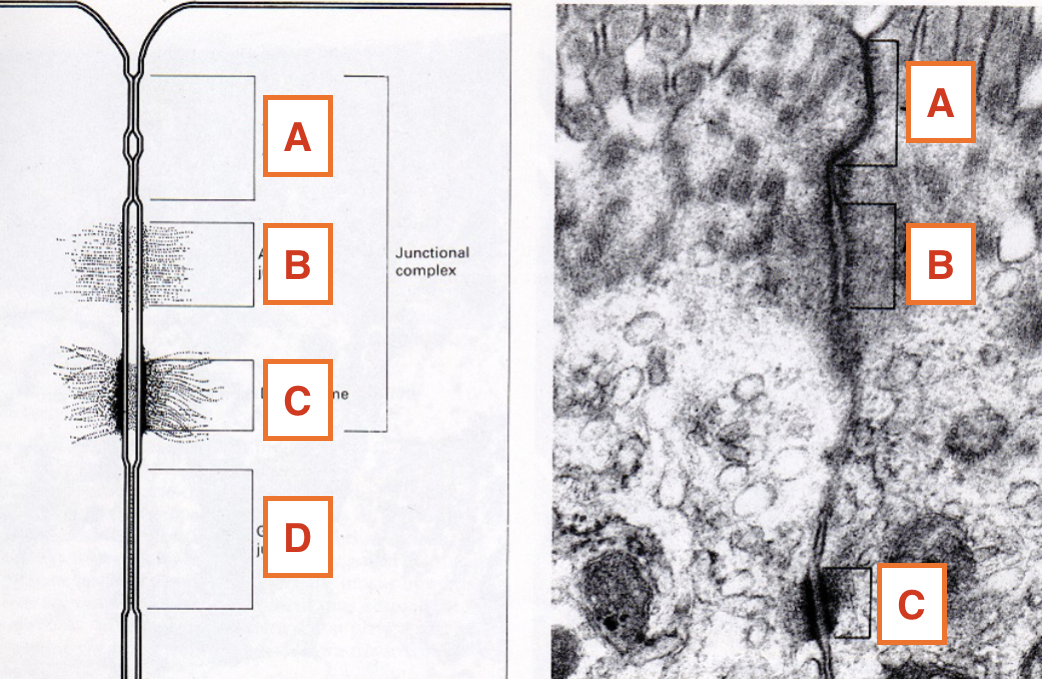
What is C?
desmosome
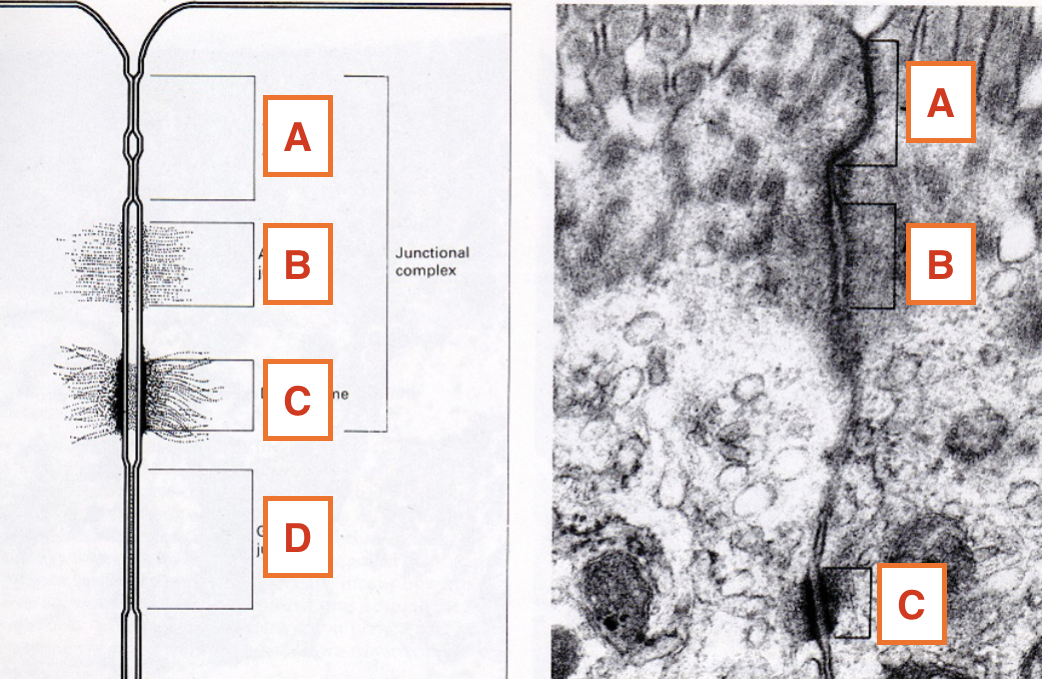
What is D?
Gap junction