Biochemistry - "The Murder That Never Was" Learning Objectives
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Transamination Reaction
amino group is transferred to a ketoacid to form a new amino acid
Alpha keto acids
have a ketone group adjacent to the carboxylic acid group
ex. oxaloacetate, alpha-Ketoglutarate
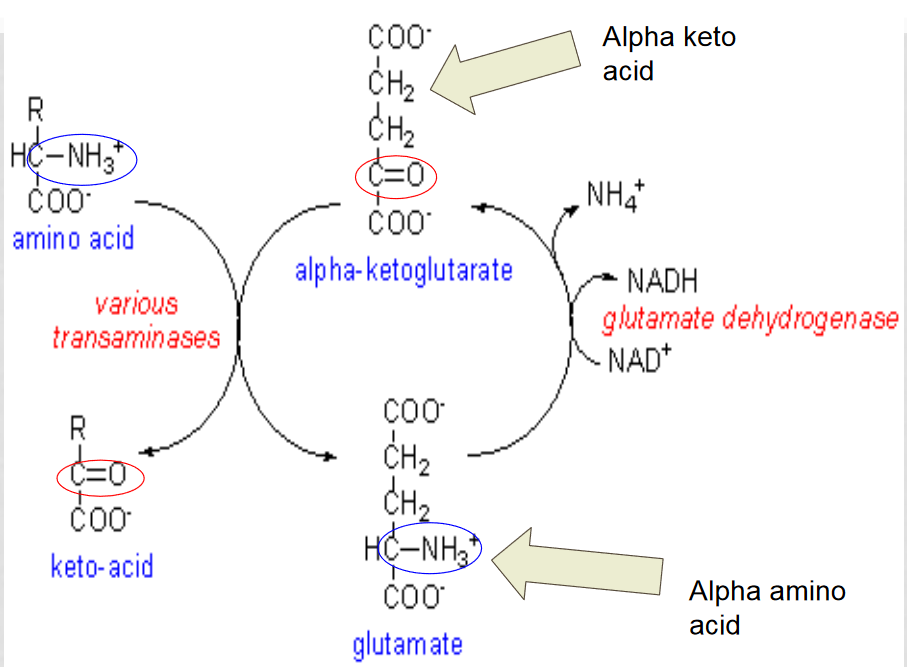
Oxidative deamination
the amino group from an amino acid is removed and attached to an alpha-ketoglutarate to create glutamate.
glutamate dehyrogenase converts the glutamate back into an alpha-ketoglutarase to be reused, releasing the ammonium ion
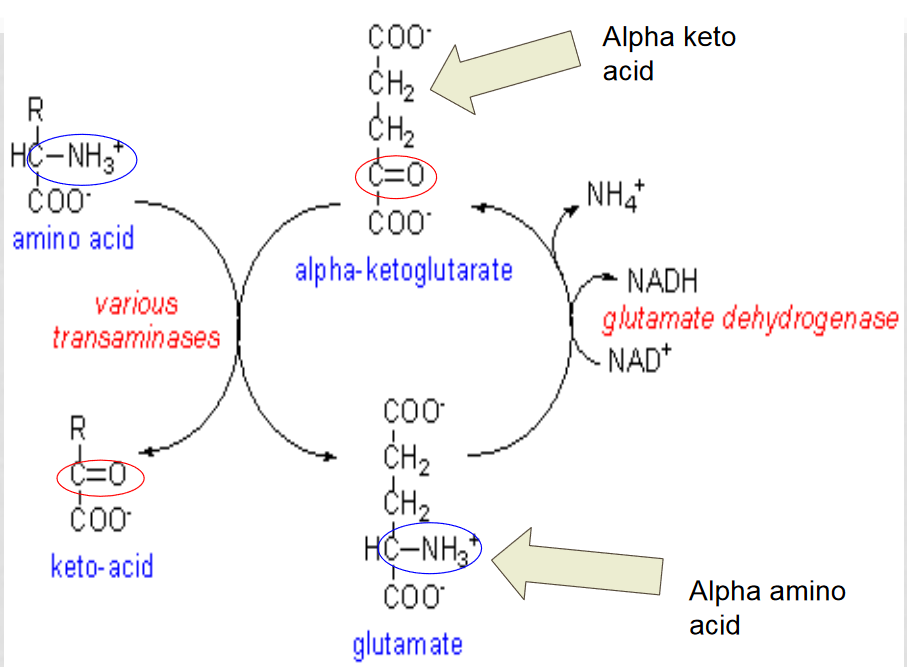
Which enzyme is involved in oxidative deamination?
aminotransferase, it removes the amino group from the amino acid and attaches it to alpha-ketoglutarate
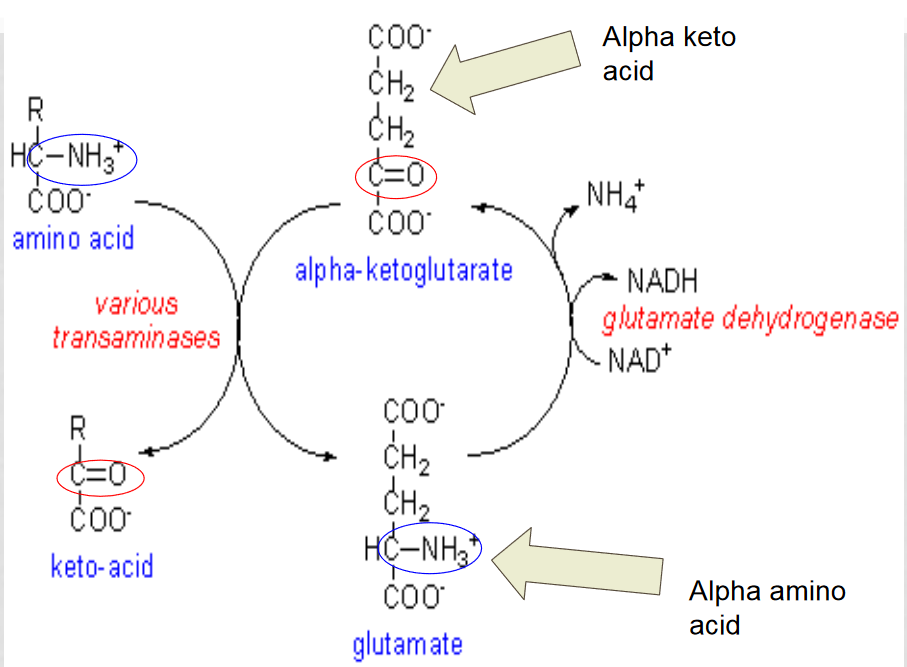
How is oxidative deamination regulated in response to a low energy charge?
low energy charge encourages oxidative deamination because it produces NADH, and it is allosterically inhibited by GTP and activated by ADP
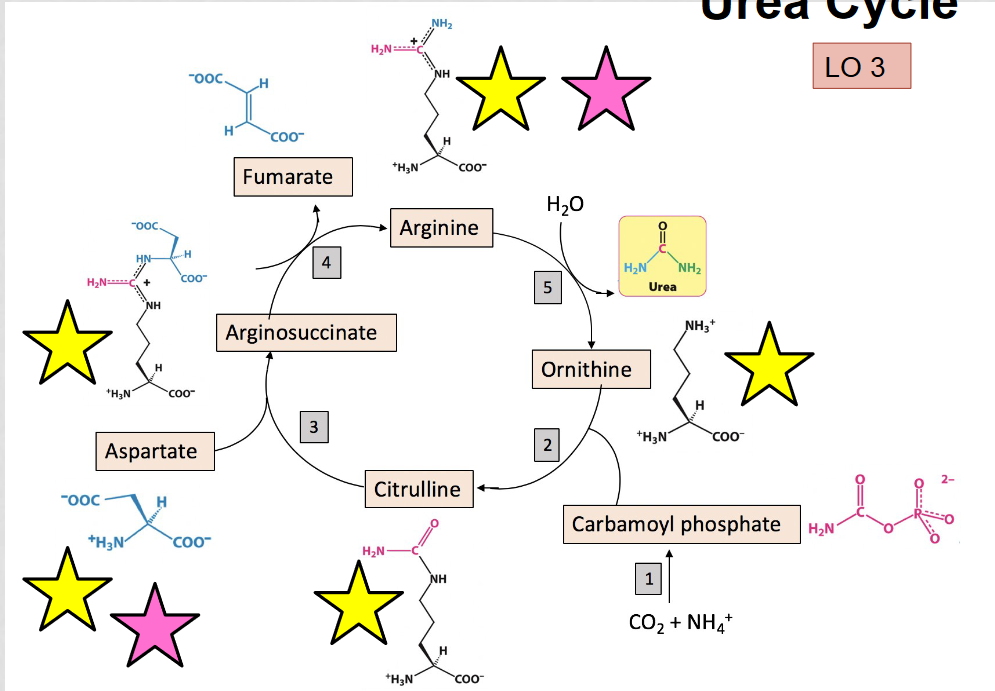
What is the purpose of the urea cycle?
to eliminate toxic ammonia produced by oxidative deamination, occurs in the liver
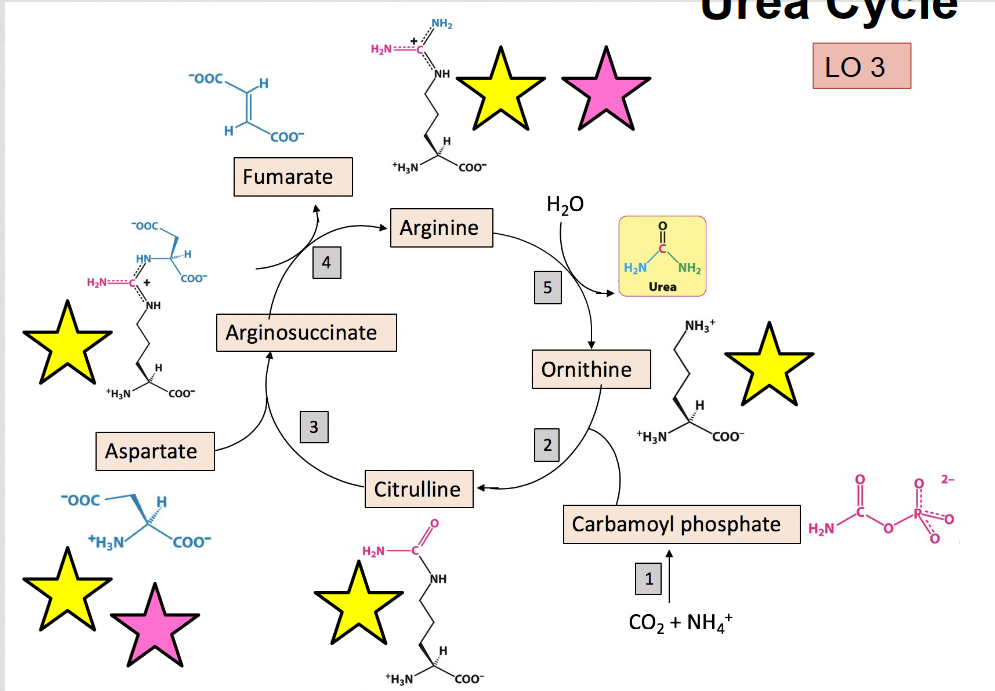
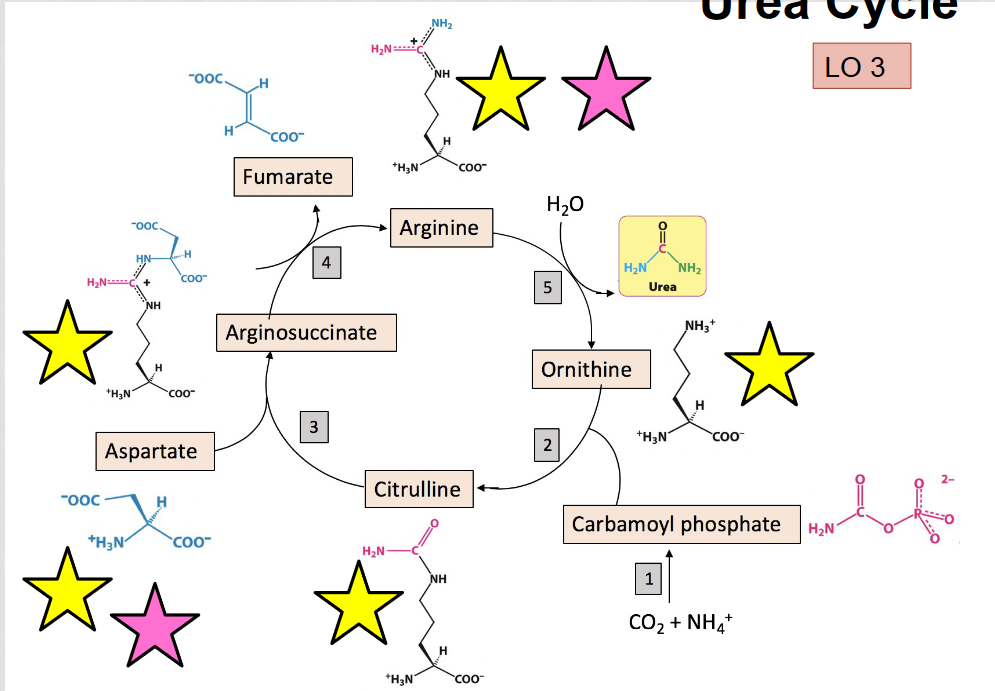
What are the alpha amino acids in the urea cycle?
aspartate, arginosuccinate, arginine, citrulline, and ornithine, they can be identified by the presence of the amino group (NH3)
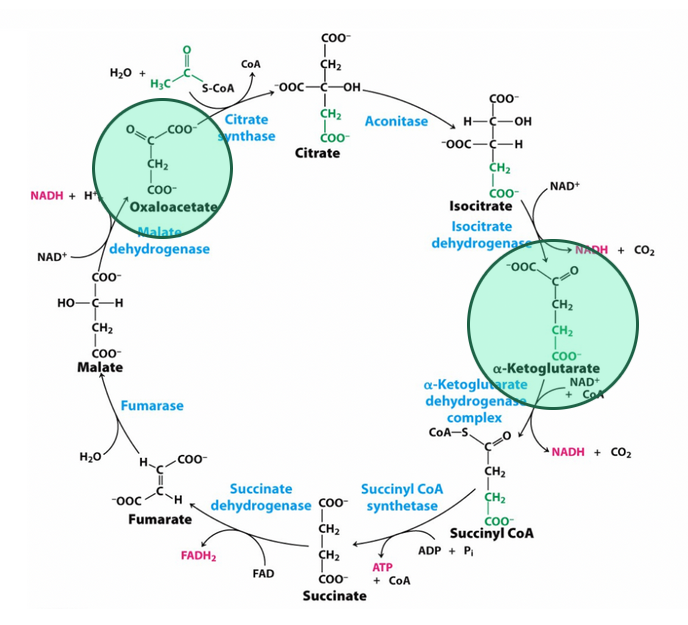
What are the 7 molecules produced from the carbon skeletons of amino acids after deamination?
Acetyl CoA, aceacetyl CoA, pyruvate, alpha-ketoglutarate, succinyl CoA, fumarate, and oxaloacetate
Ketogenic amino acid
amino acids that can be degraded to acetyl CoA or aceacetyl CoA
Glucogenic amino acids
amino acids that are degraded to pyruvate, alpha-ketoglutarate, succinyl CoA, fumarate, or oxaloacetate
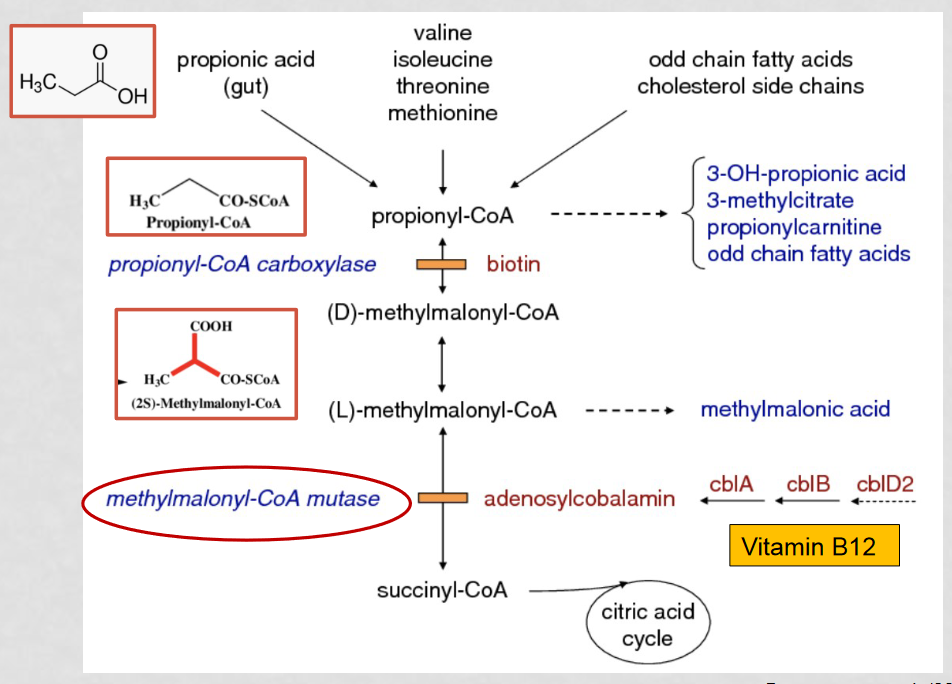
How does MMA affect lipid and amino acid metabolism?
MMA causes MUT enzyme deficiency which prevents the complete metabolism of lipids and amino acids into succinyl CoA, which passes through the citric acid cycle, generating energy. This causes the build up of intermediates instead.
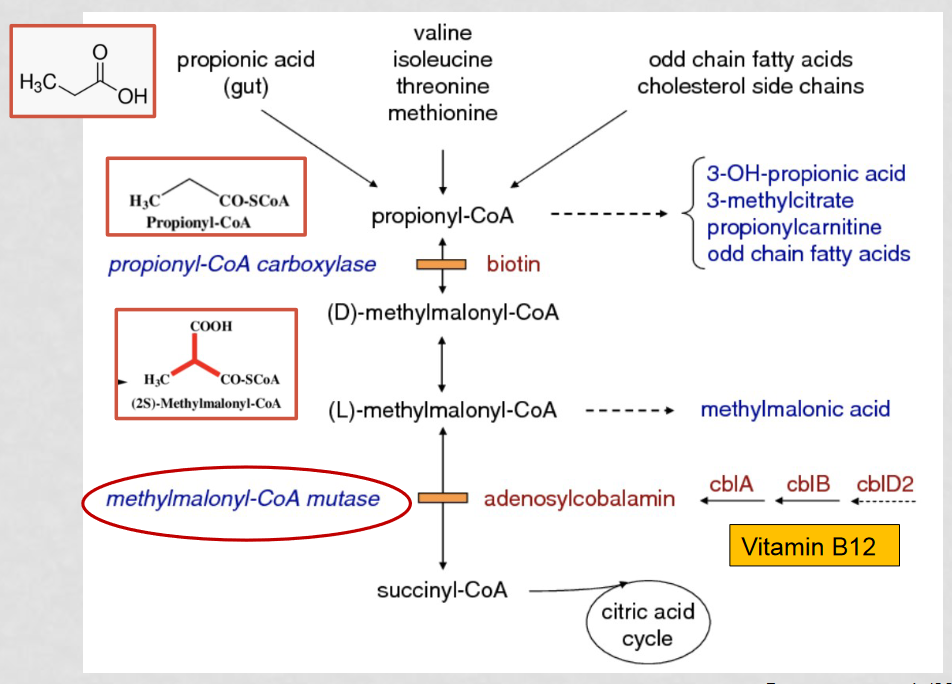
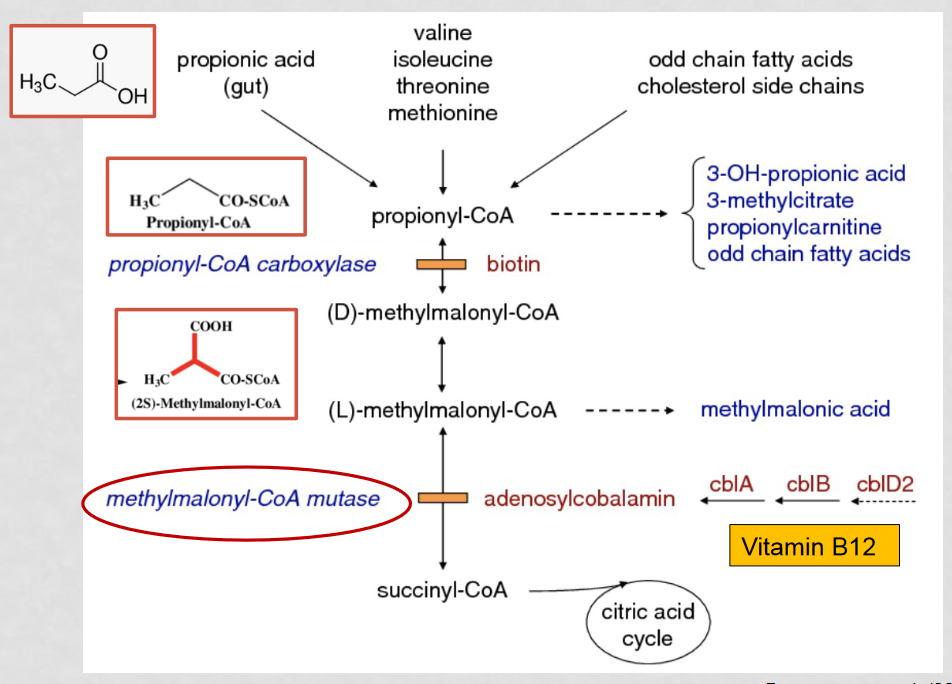
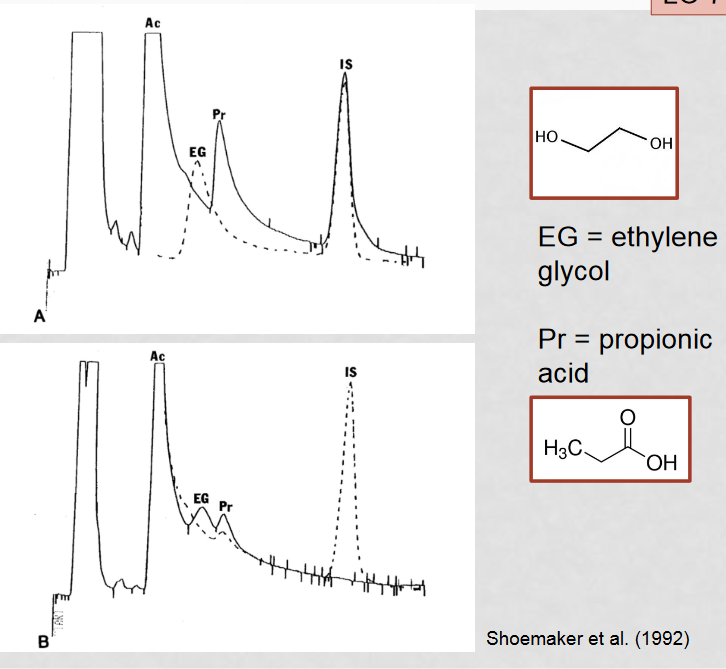
How can MMA be mistaken for ethylene glycol poisoning?
A build up of intermediates results in a high concentration of propionyl-CoA, which converts to 3-OH-propinoic acid to alleviate the high concentration. 3-OH-propinoic acid appears close to ethylene glycol through gas chromatography, causing them to appear as one big peak which can be mistaken for ethylene glycol
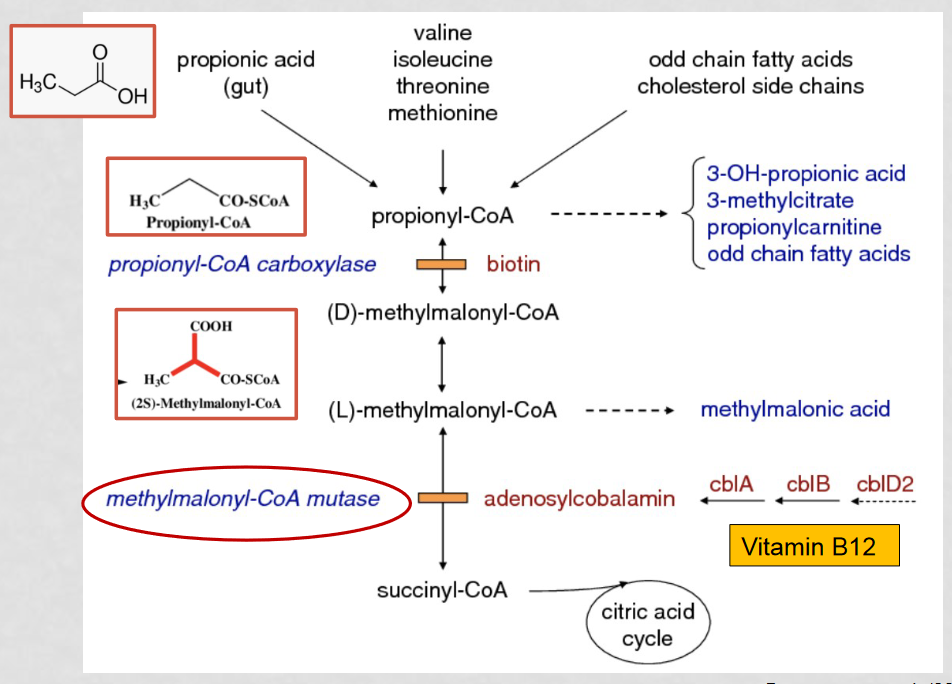
How can misidentification of MMA for ethylene glycol be avoided?
a combined gas chromatography - mass spectrometry approach, as well as preforming a spiked gas chromatography as a comparison to the normal gas chromatography
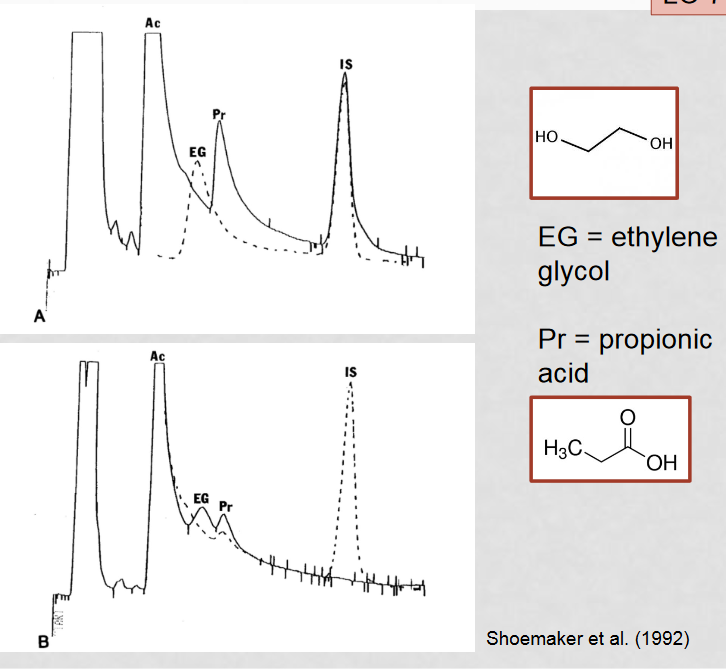
How is gas chromatography used to analyze blood samples?
Gas chromatography separates samples into their individual components to determine the makeup of the overall sample.
What is the purpose of spiking a gas chromatography sample?
Spiking a sample helps differentiate peaks by increasing the concentration of a known component by a known amount, providing a comparison to the standard screening.