Earth Materials Exam Three
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
what is refractory index
velocity of light through a crystal
what is Snell’s Law
n1(sin1) = n2(sin2)
what is relief
how much one mineral “stands out,” to another
which displays higher relief in thin section, quartz or garnet
garnet
is pleochroism in cross polarized light or plane polarized light
plane polarized light
what color is biotite in thin section
dark brown to light brown
wave interference is key to understanding what
interference colors
how do isotropic minerals appear in cross polarized light
black
how do anisotropic minerals appear in polarized light
interference colors are displayed
do you observe interference colors in plane polarized light or cross polarized light
cross polarized light
what is it called when light emits in a mineral and refracts into two rays to different amounts in different directions
double refraction
what are the 3 eras of mineral evolution
planetary accretion, crust and mantle reworking, biologically mediated mineralogy
what are the 3 main mechanisms that have driven mineral diversity
1) separation and concentration of elements from original relatively uniform distribution in the presolar nebula
2) increase in range of combinations of intensive variables such as temperature, pressure, and activities of H2O, CO2, and O2
3) far-from equilibrium conditions that produce thermodynamically metastable minerals
what happens in stage 1
primary chondrite minerals
Ni-Fe metals, sulfides, phosphides, silicates, oxides
what happens in stage 2
olivine crystals in an iron-nickel matrix
alteration of primary chondrite minerals
what are some components of crust and mantle re-working
metamorphism, planetary “water pump,” mountain building, mid-ocean ridges, subduction zones, deep crust
what are the oldest minerals? from where? how old?
zirons, Jack Hills, Australia, 3.3 billion years
oxygen isotopes suggest the zircons came from what
granite
what is Bowen’s reaction series
description of how the minerals crystallizing from a magma change as temperature decreasesand how this affects the composition of igneous rocks.
what is adiabatic decompression
depressurization without exchange of heat with the surroundings
what happens in melt segregation
unmelted minerals get compacted and expel the melt upward
what is the 4 step process to form granites and pegmatites
1) melt mantle
2) make a basalt
3) make a granite
4) make pregmatite
“black smokers” are chimneys formed from deposits of
iron sulfide
“white smokers” are chimneys formed from deposits of
barium, calcium, and silicon
the era of biologically-mediated mineralogy was prompted by this event and created this
great oxidation event
banded iron formation
what is the red and gray colors in BIFs
red is oxidized hematite, gray is reduced magnetite
what happened during era 3
intermediate ocean, snowball earth, and phanerozoic era of biomineralization
what are 3 examples of man-made minerals in the anthropogenic era
acid mine drainage, toxic spills, radioactive waste
what are the 3 major divisions of Earth’s structure
crust, mantle core
the mantle is mainly this mineral which is composed of 4 minerals
peridotite
olivine, clinopyroxene, orthopyroxene, and aluminum mineral
what are the aluminum minerals from low to high depth
plagioclase, spinel, garnet, Si to VI coordinated SiO6
what does the An-Fo binary look like
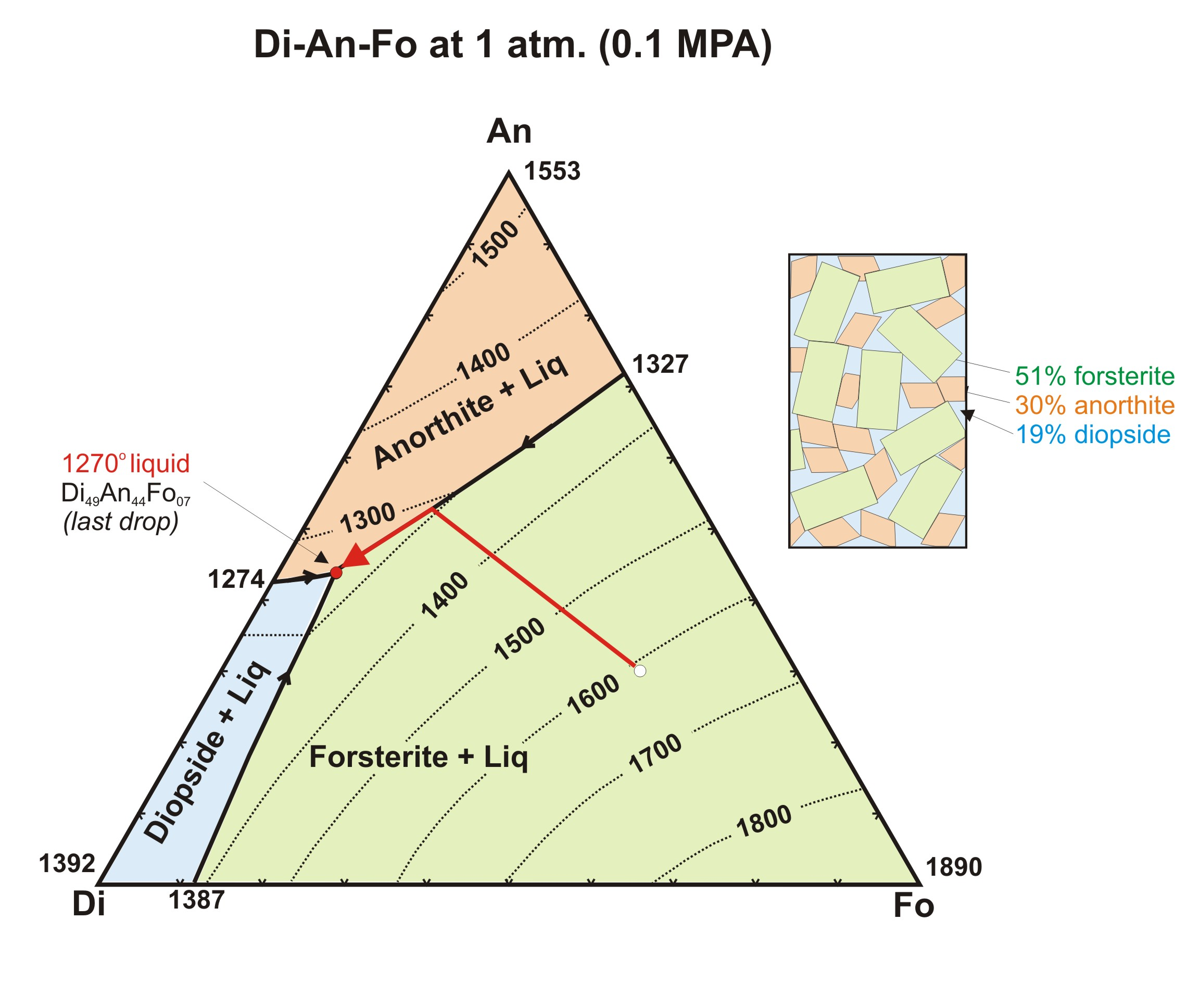
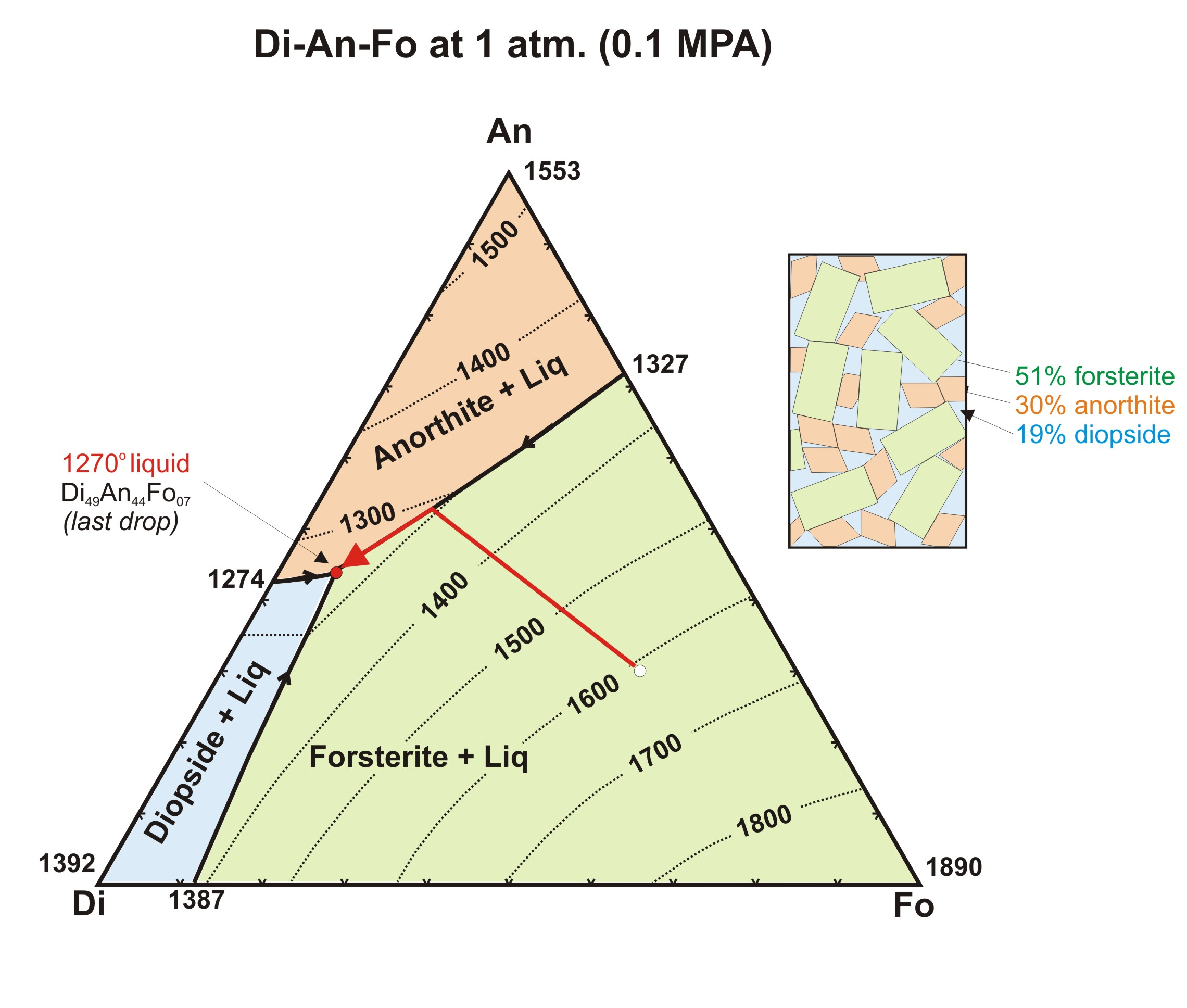
what is the composition of the first magma to form from the melting of the mantle
point “M” (basalt), eutectic point
naming of mafic (basalt-like) rocks are assigned based on these 2
1) relative amounts of different minerals (coarse grained)
2) chemical composition (fine grained)
what are the relative amounts of minerals present in plutonic rocks
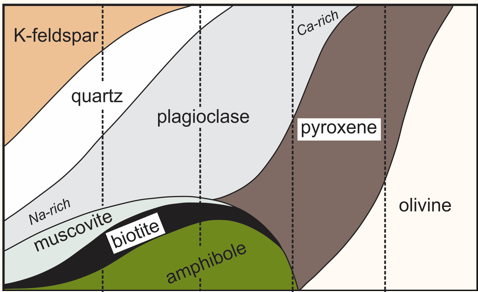
what are the light and dark minerals in intermediate igneous rocks
light: plagioclase and/or quartz
dark: amphibole and/or biotite
which is more felsic, granodiorite or diorite
granodiorite
what are the 2 ways fractional crystallization can happen
physical separation of crystals from magma
chemical zoning of crystals
igneous processes result in a differentiated crust. lighter minerals on top, heavier below. name 2 light and 2 heavy minerals
light: granite and pegmatite
heavy: gabbro, peridotite
lithium is found in what mineral
illite, which was altered from clay minerals by hydrothermal fluids