Economic Indicators and Policy Study Guide
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is GDP?
Gross Domestic Product. The sum of the market value of all FINAL goods and services in a country.
What is GDP Per Capita?
Each person’s economic output. Real GDP divided by the country’s population. (Can measure the average income and standard of living.)
__ makes up the biggest part of GDP.
Consumption
What is the GDP Formula?
(Label them and describe what counts.)
C + I + G + NX
C = consumption = the value of all final goods count, intermediate goods do not count.
I = business investment = capital goods and unsold goods count, stocks do not count.
G = government spending = any level of government spending counts, social security does not count.
NX = net exports minus imports = the value of everything you sell to another country minus the value of everything you buy from other countries.
What is unemployment and who counts in it?
The number of jobless people who was actively looking for work (4 weeks), are in the labor force, able to work, and unemployed through no fault of their own.
Unemployment Rate Formula:
Unemployed / Labor Force x 100
(LF = employed + unemployed)
Labor Force:
The number of employed people plus unemployed people. Must be over the age of 16, able to work, and actively looking for work (4 weeks).
Underemployment:
When an employed person’s human capital (skills, education) exceeds the requirements for the job.
Types of Unemployment:
(Give definition)
Fractional unemployment: newly entering the work force or you left your job to find another one.
Structural unemployment: your job was removed from the economy. (Mainly technology wise but other factors exist).
Seasonal unemployment: when your job is tied to a specific season.
Cyclical unemployment: when you lose your job because of a recession.
Inflation:
An increase in the price of goods and services in an economy over a specific period of time.
What are the 2 main causes of inflation?
Cost-push Inflation and Demand-pull Inflation
Cost-push Inflation:
supply goes down, demand stays the same
Demand-pull inflation:
demand increases, supply stays the same
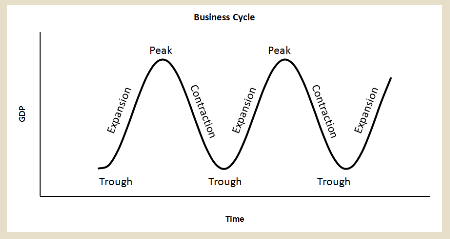
Business Cycle:
The growth and decline of an economy as economic activity increases and decreases periodically.
Recession:
Economic decline usually lasting at least 6 months.
(A depression lasts at least 2 years)
Monetary Policy:
(Who uses it and what is their strategy to fix a recession?)
Federal Reserve / Central Banks use it.
They change interest rates and change money supply.
Fiscal Policy:
(Who uses it and what is their strategy to fix a recession?)
The government uses it.
They cut / lower taxes and increase government spending and making policies to increase consumer demand.
Name and explain the 4 phases of the business cycle.
Expansion: a period of growth / expansion in economic activity
Peak: the highest point of economic expansion before the economy enters a period of decline
Contraction: a period where economic activity is in decline
Trough: the lowest point of economic contraction before the economy enters a period of growth
Study business cycle graph