Direct Restorative Dentistry 1 Midterm
1/164
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
165 Terms
hydrocolloids
impression material - are mixed with water to form a gel
hydrated materials examples
alginate, agar, gypsum - (mixed with water to make a set structure)
colloid
a substance of large and small particles equally mixed (particles dont settle)
examples of colloids
gels, sols, emulsions
Alginate
irreversible, hydrocolloid impression material - poured immediately
Gelation
transforming a hydrocolloid from a sol to a gel
Sol
the mixture of substances forming a flowing mixture that can thicken up into a gel
Gel
hydrocolloid for impressions that is slightly elastic
Phases of gel formation
sol phase
chemical rxn
transition to gel
gel formation
Thixotropic
substance that isn’t fluid but is spreadable
when water is squeezed out of a gel mould as it dries
Syneresis
imbibition
when one fluid replaces/displaces another in a hydrocolloid (ex saliva replaces water)
Agar
hydrocolloid that sets at 37-50ºC - reversible at high temp - immediate poor required before it cools
Gypsum
Stone that is poured into a hydrocolloid mould forming a cast - expands in air
Cast vs Model
Cast is pt replica, model is perfect anatomy for learning
Hygroscopic setting expansion
when a substance expands due to exposure to moisture or water
Gypsum type 1
plaster or paris (fragile) - for endentulous pt’s - calcium sulfate B-hemihydrated
water/powder ratio 0.75
gypsum type 2
mounting stone to articulate for dentures or for study models - calcium sulfate B-hemihydrate
water/powder ratio 0.5
Gypsum type 3
Dental stone for models or base for cast - calcium sulfate alpha-hemihydrate
water/powder ratio 0.3
gypsum type 4
die stone for detailed cast - microstone - calcium sulfate alpha-hemihydrated
water/powder ratio 0.24
gypsum type 5
die stone - jade stone - calcuim sulfate alpha-hemihydrated modified
water/powder ratio 0.18
Instrument Nomenclature by G.V Black
order - purpose of instrument
suborder - matter of use
class - form of blade
angle - number of angles
driving power - electric or not
contrangle
shank with two or more angles
3 digit numbering on instruments
width-length-angle
4 digit instrument numbering
width - angle of primary edge to long axis - length - angle of blade to long axis
Use for diamond bur
wear through enamel
use for bladed bur
made of tungsten carbide for removing caries in dentin
more blades on a bur = ________ roughness
less
bigger abrasive particles on a bur = ___________ resulted surface roughness
decreased
CAD CAM stands for
Computer Aid Design
Computer Aid Machining
outline form
form of the prep
cavosurface margin
junction between the prep surface and the outside of the tooth
resistance form
the form of the prep that helps the filling resist failure
retention form
convergence or divergence of prep to retain the prep
convenience form
the form of the prep being a good size that makes it easily accessible
dental liners
when prep is close ot pulp it is put down to protect it
dental bases. applied when
if carrie is too deep, place base to get surface back to ideal restoration
cavosurface angle
angle of prep following pulp horns and cusp shape
debridement
process of cleaning/disinfecting the cavity prep
G.V. Black Classifications are for what?
cavity classifications based on location
Class 1 carries
on one surface
class 2 carries
prep covers two surfaces ot the tooth (molar/premolar)
class 3 carries
in between teeth (anterior incisers)
class 4 carries
on an angle of tooth (anterior incisors)
class 5 carries
prep at neck of tooth by gingiva
class 6 prep
cavity at cusp tip (of molar/premolar)
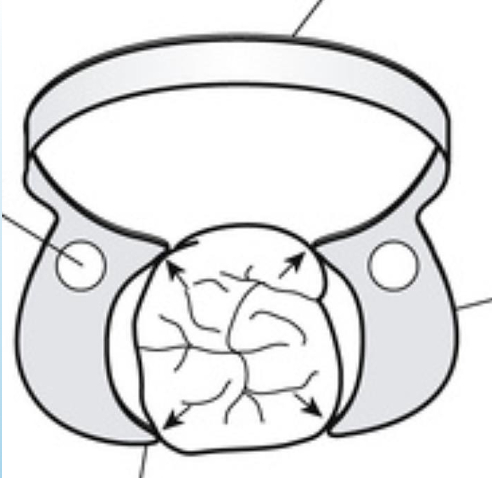
Name with lines
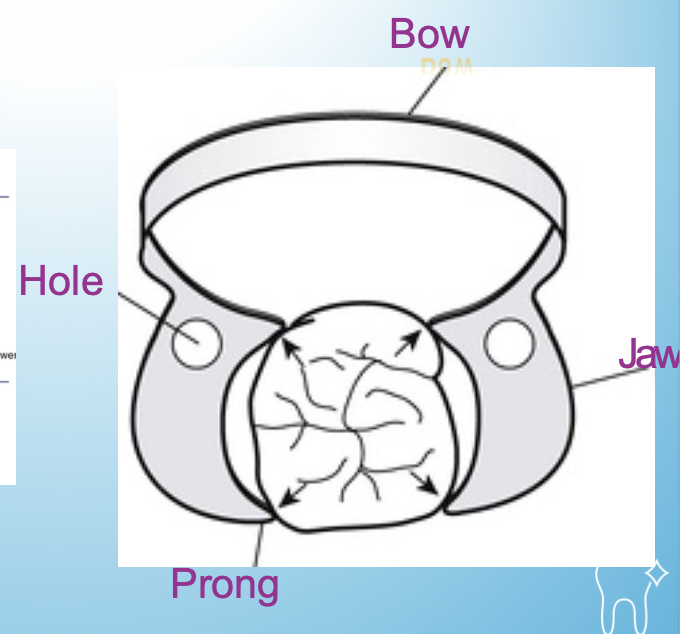
septa
rubber dam material that goes between teeth
light cure dental dam
barrier that is squeezed on gingival like to create a dry field
indirect restoration
done by lab and dentist
tensile stress
the stress of pulling/stretching the material
shear stress
grinding stress, sliding force
flexural stress
bending/tension/compression force (bridge or prosthetic)
strain
deformation (elongate or shorten) due to applied force
fatigue of structure
progressive damage due to repeat stress
Surface Energy
Extra energy at a solid’s surface makes it want to bond with other substances.
Surface tension
Cohesive force at a liquid’s surface resists spreading.
Wetting
How well a liquid can spread determined by the contract angle
<90 = good wetting - also, surface energy > surface tension
TheraCal
Light-cure resin - liner or pulp capping
Mineral Trioxide Aggregate
Material for pulp capping that releases calcium
Biodentine
Dentin substitute that helps regenerate dentin
Glass Ionomer Cement
self-adhesive, releases fluoride, lower strength
Compomers
polyacid resin, fluoride release, low stress areas
Giomer
with pre-reacted class ionomer, sustained fluoride release
Dental Sealants
Applied to pit and fissure to prevent carries
non-carious cervical lesions
Loss of hard dental tissue near CEJ (groove)
Abfraction
Tooth structure loss from flexural forces causing denting on front of tooth
Abrasion
Mechanical wear of tooth structure from external objects
Erosion
Chemical loss of tooth structure from acids not involving bacteria
Etiology
the study of the cause of a disease
White spots in enamel
start of carries, can be remineralized
Desensitizer (Gluma)
seals dentin close to pulp (like a liner)
Amalgamation
the process of mixing the liquid mercury with the powder metal alloys
Amalgam thermal expansion
higher than human enamel which can cause fractures if heated too muc (material expands but enamel doesn’t)
How to protect the pulp from the thermal conductivity of amalgam?
Cements or liners
Types of powder configurations with amalgam
lathe-cut
spherical
admixed
Lathe-Cut amalgam configuration
irregularly shaped amalgam that resists condensation of material but requires more mercury - stronger because of resistance to condenastion
Spherical Amalgam configuration
regular spherical shaped amalgam with reduced surface area - requires less mercury for reaction
it is harder to condense because of the spherical shape, meaning the filling is weaker
Admixed amalgam configuration
both spherical and lathe-cut (cylindar) amalgam particles - middle of the two types, resistant to condensation and requires middle amount of mercury
Tritration
mixing of mercury and alloy to make amalgam (microstructures)
Gamma phase of amalgam formation
Unreacted silver and tin phase - present before and after tritration
gamma 1 phase of amalgam formation
silver and mercury together (like a glue) - strongest phase - matrix phase
gamma 2 phase of amalgam formation
phase that we don’t really want - tin and mercury together - we want to minimize by condensing and removing mercury - weakest and least stable
Copper as an alloy in amalgam
Strengthens silver-tin alloy (brittle and difficult to blend) and reduces corrosion and gamma 2 phase
zinc and an alloy in amalgam
more brittle instead of deforming - can lead to delayed expansion if contaminated with water or saliva (fractures)
preparing an amalgam restoration
2mm deep into dentin
creep of amalgam
strain of deformation produced by stress over time when the patient uses the tooth with the amalgam filling (slow but permenant)
Examples of inelastic materials
plaster of paris, impression compound
plaster of paris is used for what
for edentulous patients
synersis
loses water as it dries.
imbibition
The process where certain impression materials, particularly hydrocolloids like alginate, absorb water from saliva and outside things and swell
mounting stone
what is gypsum type 1 used for
dental stone used for models
gypsum 3
the time from start mixing until setting rxn of impression material stops
Setting time
the time from start of gelation until the material becomes solid
working time
what are the three numbers on a handpiece
width of blade to 1/10 mm - length of blade in mm - angle of blade to long axis
what are the four numbers on a handpiece
width of blade to 1/10 mm - length of blade in mm - angle of blade to long axis - the second angle of the blade
bevel
the angle that one surface/line makes w/ another when not at right angles
flutes
ridges in carbide bur
G.V. Black Principals of cavity design
outline form
prep depth - 1.5 to 2 mm
prep width - ¼ to 1/3 intercuspal dimensions
line angles
mesial and distal walls diverge
buccal and lingual walls
convergecavosurface margin