Protein Synthesis, Repression, & Mutations
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Transcription
DNA transcribed to make RNA 📝
Where does transcription occur in eukaryotes vs. prokaryotes?
Eukaryotes=Nucleus
Prokaryotes=Cytoplasm
What are the 3 steps of transcription?
Initiation 🟢
Elongation 🟡
Termination 🔴
What is the “promoter” region called and its sequence?
TATA Box (TATAAA)
What are the 4 steps of transcription initiation? 🟢
RNA Polymerase binds to TATA Box Promoter
helps unwind DNA H+ bonds
→ transcription bubble formed 🫧
RP reads DNA template in bubble
How is RNA synthesized during initiation?
thru complementary base pairing of nucleotides
use DNA template
(e.g., TATAAA → AUAUUU).
What do upstream/downstream mean in transcription?
which direction does RNA Polymerase move?
Upstream = left of promoter;
Downstream= right of promoter
down, it moves 5’→3’
What are the 4 steps of transcription elongation? 🟡
RNA Polymerase moves downstream
it adds nucleotides to the 3’ end
→ mRNA transcript elongated
previous DNA rewinds back to double helix 🧬
What are the 3 steps of transcription termination 🔴
RNA Polymerase reaches DNA terminator sequence
RNA polymerase & mRNA released
DNA fully re-winds to its helix 🧬
What happens specifically to mRNA in termination? 🔴
mRNA is released ◝(ᵔᗜᵔ)◜
so it travels nucleus → attaches to a ribosome

Translation
mRNA carries gene to be translated into amino acid chain to make protein💌
Where does translation occur?
ribosome in cytoplasm
3 functions occurring in ribosome in translation:
reads mRNA sequence codons 💌
pairs mRNA codons to tRNA codons
links amino acids to build polypeptide chain
What holds amino acid chains together? ⛓
Peptide bonds
Define a codon and give an example
mRNA triplet bases that code for 1 amino acid
DNA’s TAC → mRNA’s AUG
How many mRNA bases code for 1 amino acid
3 bases = 1 codon = 1 amino acid.
What is the start codon
amino acid it codes for?
AUG signals start of translation
Methionine.
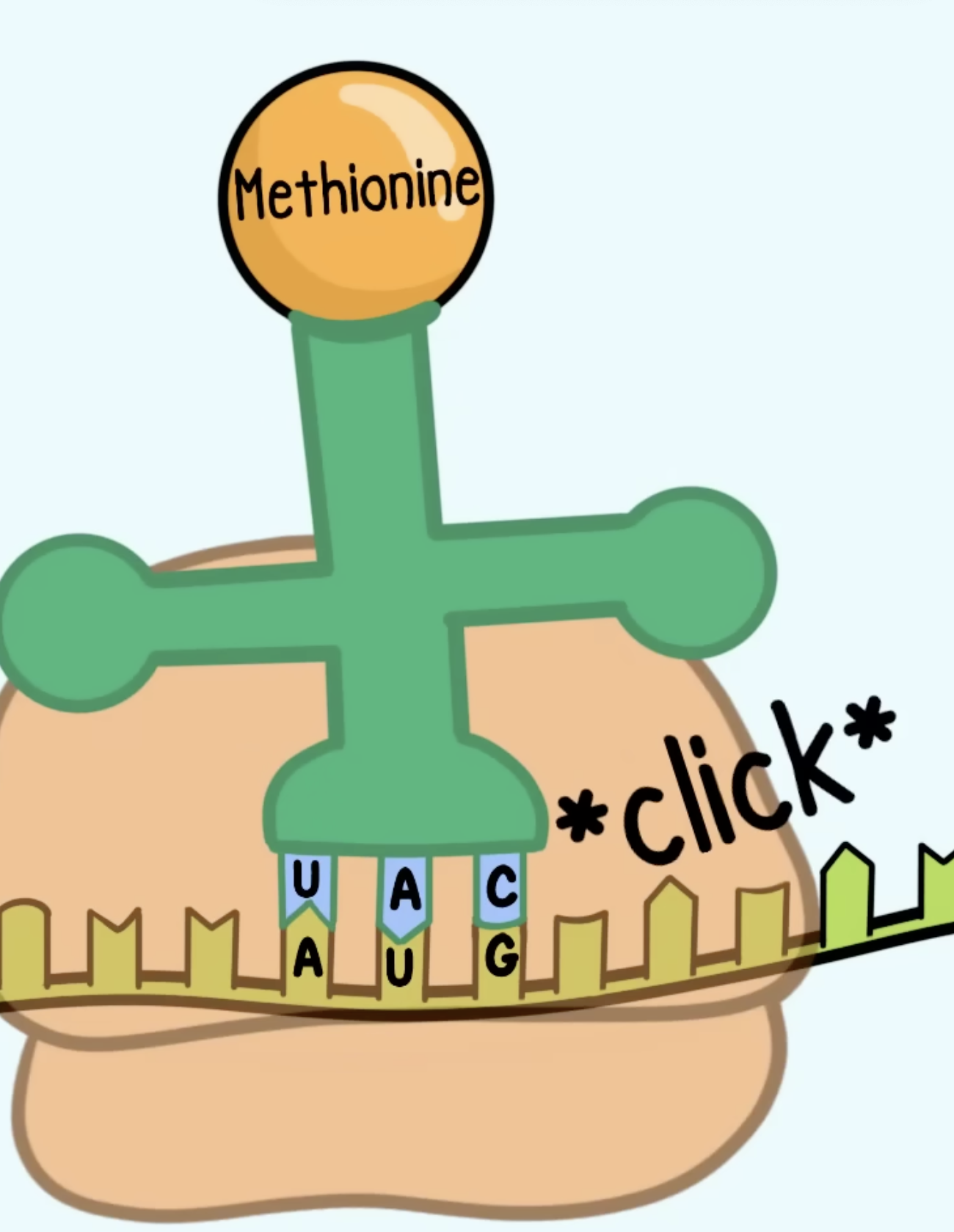
Function of stop codons & what are the 3
signal end of translation:
UAA
UAG
UGA
How many total codons exist in the genetic code?
64 triplet codons.
Why is the genetic code described as “redundant”/“degenerate”?
bc multiple codons can code for same amino acid.
How many ‘sense’ codons
& what do they code for
61 sense codons
amino acids
How many ‘nonsense’ codons are there
what do they code for
3 nonsense codons
stop signals
how tRNA and mRNA work tchugetha in translation
tRNA carries amino acids from cytoplasm→ ribosome 🚛
mRNA directs message for these amino acids

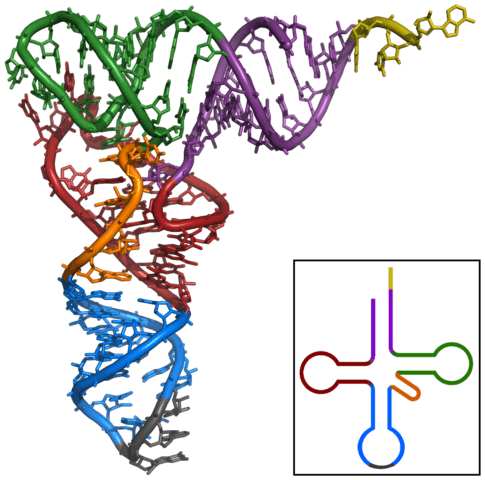
tRNA
how long
shape
~80 nucleotides
H+ bonds twist into 3D L-shape (🍀)
Ribosome A site function
Holds tRNA carrying next amino acid to be added to chain
Ribosome P Site function
Holds tRNA carrying growing polypeptide chain ⛓
Ribosome E site function
where tRNA exits ribosome
What are constitutive genes?
housekeeping genes always on expressed at fixed rate 🏡💡
Two regulated genes only expressed when needed
inducible & repressible genes
Catabolite Repression function
What does it prevent?
prefers+metabolizes glucose🍰 for energy efficiency
expression of other genes to not waste energy
What is an operon & where mostly found?
how it functions
A cluster of genes mostly in prokaryotes
regulatory protein binds near promoter to switch gene on/off 🎛
2 Functions of regulatory promoter gene?
turn promoter & operators on/off,
→ controlling gene expression
Lac Operon🍼
default state
turns operon on/off if _
using _
OFF (lactose absent)
tuns ON if lac present
using Lac Operon Inducer, Allolactose
5 steps of how LAC operon is induced
Allolactose binds to the ACTIVE repressor protein
repressor changes shape → INACTIVE
INACTIVE repressor can’t bind to !OPERATOR
RNA polymerase now free to bind to operator
Transcribes lacA, lacY, lacZ,
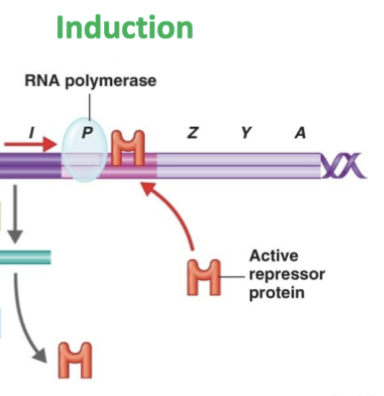
lacZ, lacY, lacA
enzymes that break down lactose
Tryptophan Operon 🦃
default state
turns operon on/off if _
using _
ON (tryp absent)
turns OFF if tryp is in excess
using a corepressor
5 steps of how Tryp operon is repressed
Tryptophan binds to INACTIVE repressor protein,
changes its shape→ ACTIVE
ACTIVE repressor binds to !OPERATOR
RNA Polymerase now blocked,
cant transcribe genes E-D-C-B-A anymore
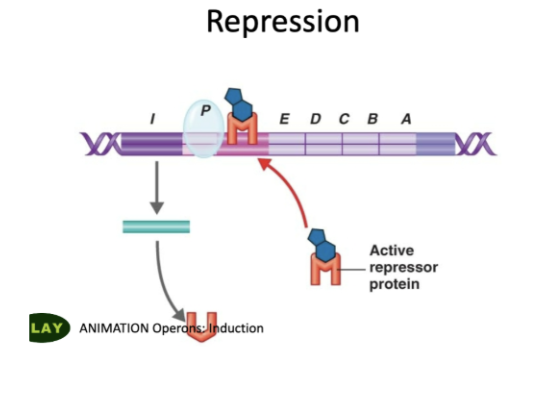
Function of genes E-D-C-B-A
synthesize/make tryptophan
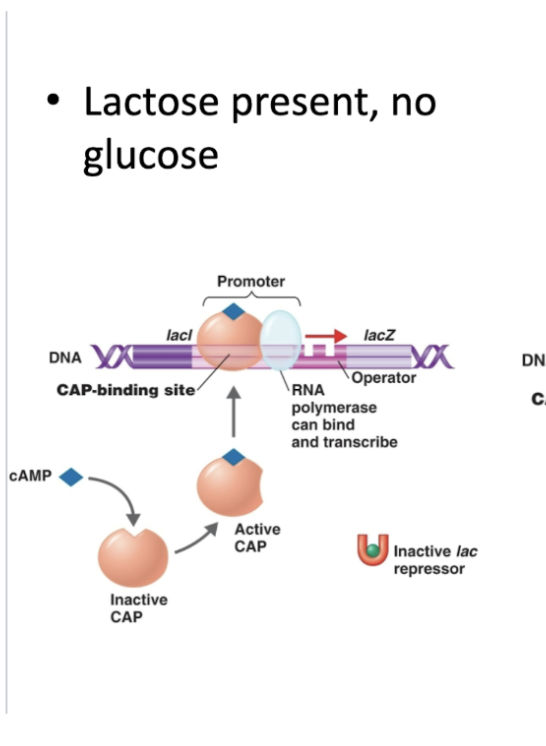
In Catabolite Repression, what 5 steps occur if:
glucose is absent but lactose is present?
cAMP levels rise ↑
cAmp binds to CAP→ cAmp-CAP complex
complex binds near !PROMOTER
RNA polymerase binds so
Lac operon turns on for lactose metabolism.
In Catabolite Repression, what 5 steps occur if:
glucose is present?
cAMP levels drop ↓
prevents cAMP–CAP complex
complex cant bind near !PROMOTER!
RNA polymerase cant bind
→ Lac operon stays off.
Change in genetic material (*neutral, beneficial or harmful*)
Mutation
Agent that causes mutation
2 examples
Mutagens🐢
chemicals
radiation 🧪☢
What are the two main types of mutations & what they change
Frameshift Mutation: inserts or deletes 1/+ nucleotide
Point/Base Pair/Substitution Mutation: changes 1 base pair
What happens in frameshift mutation
1+ nucleotide inserted/deleted
→ shifts whole sequence after

What are the 3 types of point mutations & describe
Silent – No change (ex: UUU → UUC, phe → phe)
Missense – Changes to a diff amino acid (ex: UUU → UUA, phe → leu)
Nonsense – changes to a stop codon (ex: UAC → UAG, phe → stop)
2-aminopurine:
replaces _
pairs w _
Replaces adenine
cytosine instead of thymine (ex: AT now AC)
5-bromouracil
is a _
mistaken for __ by __
pairs with _
anticancer drug
thymine by enzymes
cytosine instead of adenine (ex AT now AC)
ionizing radiation:
2 examples
cause __
X-rays & gamma rays
ions to damage nucleotides & DNA’s sugar-phosphate backbone