Taxonomy
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
Taxonomy
classifying characteristics of organisms
Carolus Linneaus
swedish botanist made physical characteristic taxonomy in 1700s
How have we improved since Carolus Linneaus taxonomy system
Use genetic and biochemical information to classify organism
Taxonomy hierarchal system
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
Taxa
The different groups of classification, sing. Taxon
Species
Species that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring
three types of taxonomical evidence and why
See how closely related they are, Anatomical evidence, physiological evidence, DNA evidence
Anatomical evidence
Do structures look the same
Physiological evidence
Do proteins, enzymes, molecules in cell work the same
DNA evidence
How genetically related are the genes and proteins they make, ie how similar is DNA location
three domains
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya, bac and arc are names of kingdoms as well
Eukarya 4 kingdoms
Protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia
What are domains based on
Prokaryotes vs eukaryotes
Prokaryote domains and why
Bacteria and archaea because they lack a nucleus and membrane bound organelles, and are smaller
traits of eukarya
Nuclear membrane, have golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum unlike prokaryote
Other names for bacteria
Monera or Eubacteria
Why are viruses not living organisms and unclassified
Has nucleic acids but only reproduce in host, no cells, cannot make proteins by themself, cannot use energy, without host simply group of chemicals
Aristotle
Developed first method of classification based on habitat
Genus
Consist group of related species
Binomial Nonmenclature
System gives organisms two names
Three species concept to classify in taxonomy
Biological species concept, morphological species concept, phylogenetic species concept
Biological species concept
breed and produce fertile offspring, only works for living sexually reproducing organisms
Morphological species concept
Compare physical descriptions + measurements, used for plants or sexually reproducing organisms
Phylogenetic species concept
Looks for evolutionary relationships between organisms. USUALLY based on DNA studies or fossil evidence
Dichotomous keys
Ask yes/no questions to classify new organism, ask based on known characteristics of organism
Other way dichotomous keys can be shown
Branching tree diagram, start with multicelluar? tissues? Radial symmetry? Bilateral symmetry?
Who developed binomial naming
Carolus Linneaus
How to name binomial nonmenclature
Genus then species, itacilized or underlind, Genus is capitalized, species lowercase,
Why use bionomial nonmenclature
Universal language standard bc different in every language
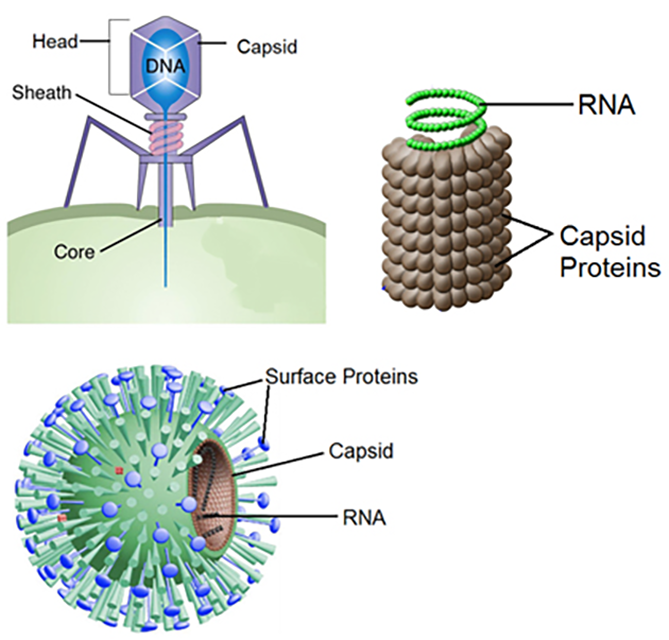
Physical structure of virus
nucleic acid core: capsid/protein coat, genetic material RNA/DNA but not both,
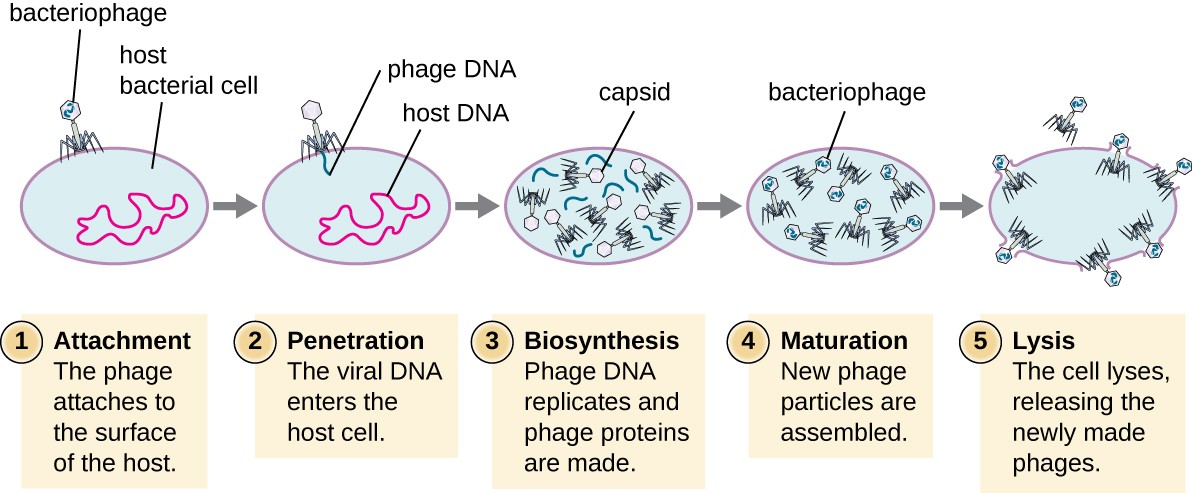
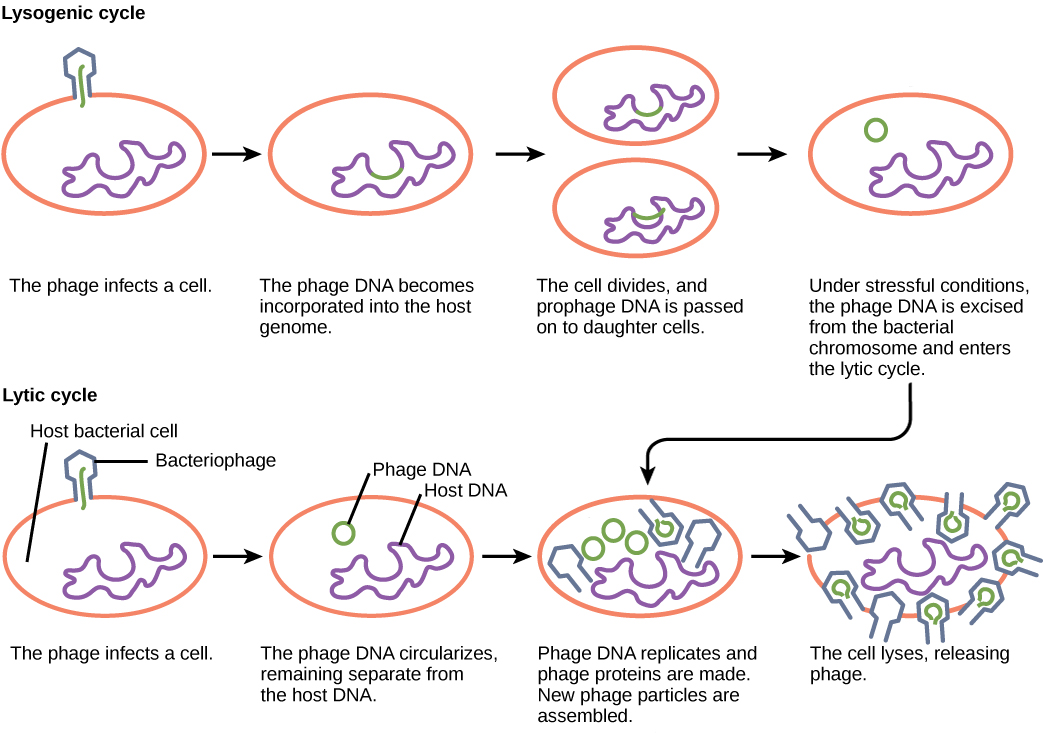
lytic cycle
attach to host, ingrain dna in cell, replicate take over, assembly of new viruses then release
can viruses be helpful
Attack disease bacteria, bacteriophages can destroy bacteria but not human cells, insert ‘good genes’ into genetic diseases, introduce desired traits in plants and animals
Lysogenic cycle
insert genome into host reproduce genome for long time until activation trigger to lytic cycle
meaning of archaea
early or primitive
Thought for origins of archaea
evolved from first living organism on Earth
How is archaea different from bacteria
originally classified as bacteria, biochemical and genetic info reveal that different ash, cell walls NOT made of peptidogly like bacteria, and theyre found everywhere, live in extreme environments unlike bacteria
characteristics of archaea
prokaryotes, have nucleid region lack organelles, do not require oxygen, anaerobic, no photosynthesis but from organic molecules or sun
Anaerobic
No oxygen
3 types of archaea
Methanogens, halophiles, thermoacidophiles,
Methanogens
anti oxygen in marshes, sewage plants, intestines of plant eating like cows, grow on co2 or hydrogen gas, produce methane as waste product
halophiles
salty environments, ex dead sea
Thermoacidophiles
heat + acid, pH 1 or 2 habitats, hot sulfur springs, volcanoes, deep sea vents, mine drainage lakes
use of methanogens
digest sewage and oil spills, methane used as alternative energy source
Thermus aquaticus
Heat resistant enzyme used make copies of small samples of DNA
heterotroph
living organism who eat other living organisms for energy
µm
millionth of a meter
how is archaea classified
based on metabolism
How is bacteria classified
their shape and colony groupings, their cell wall structure, sources of food or metabolism
Bacterial shapes
Cocci, bacillus, spirrillium
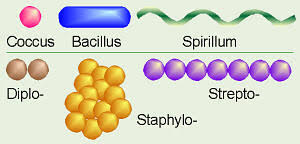
cocci
sphere shaped bacteria
bacillus
rod shapes bacteria
spirrillium
spiral shaped bacteria
colony shapes in bacteria
diplo, staphylo, strepto
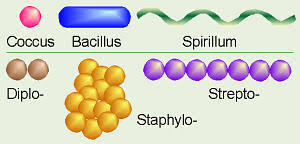
diplo
Cells arranged in pairs
Staphylo
Arranged in grape looking clusters
strepto
cells arranged in chain
gram negative
thin layer of cell wall protein, make pink stain bacteria
gram positive
Thick cell wall protein stain purple bacteria
four groups organizing how organisms consume food sources
photoautotrophs, photoheterotrophs, chemoautotrophs, chemoheterotrophs
photoautotrophs
use light energy for photosynthesis get carbon from CO2
Photoheterotrophs
consume other organisms to get carbon and light energy
Chemoautotrophs
Get energy by breaking bonds in innorganic molecules like ammonia and hydrogen sulphide
Chemoheterotrophs
get both their carbon and energy from eating organic molecules like sugar made of carbon and hydrogen (C + H)
cillia
tiny hairs on surface of cell beat and move the cell
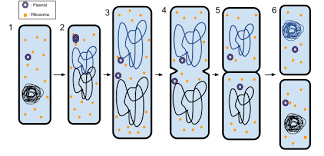
binary fission
bacteria reproduction asexual copy genetic info from DNA loop then splits into two daughter cells
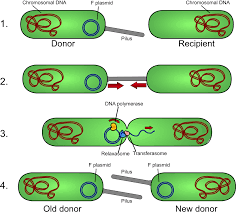
conjugation
bacteria share DNA sexually transfer plasmid DNA loop to another
endospores
dormant cell no life, resistant to environmental stresses like high temperatures, irradiation, strong acids, disinfectants
beneficial bacteria
decomposers, digestion, clean toxins seep into soil and water
how many species of protista
200 000
characteristics of protists
all eukaryotes, most aerobic single-celled, live in moist environment
Three major protista phyla
Animal-like ie protozoa, plant-like ie algae/protophyta, fungus like ie moulds
animal like (protozoan) characteristics,
heterotrophs, unicellular
how are animal like protists (protozoan) classified
how they move and where they live
classification of animal like protists (protozoa)
flagellates, pseudopods, cilates, sporozoans (most parasites)
flagellates
zooflagellates, motorboats, freshwater or marine habitats, self sufficient, flagella, some cause disease like Giarda/amblia cause upset stomach prominent in Ontario lakes
pseudopods
sarcodines, free living blobs, no cell wall, move using pseudopods/plasma extensions, engulf food by phagocytosis, reproduce by binary fission
Phagocytosis
flowing around food particles to eat
ciliate
hairy ones ie paremecium, freash water, marine habitats, cillia, reproduce usually binary fission, but also conjugation
sporazoans
parasites, non-motile, must have host, one type cause malaria,
non-motile
Do not move on their own
malaria
reproduce in liver binary fission, liver get full and burst out travel in blood until mosquito bites again
characteristics of plant like protists
protophyta, autotrophic/photosynthetic, uni,multicellular or live in colonies
four main groups of plant like protists
algae, euglena, diatoms, dinoflagellates
algae
Uni or multicellular, photosynthetic have chlorophyll, red, green or brown, no roots, stems or leaves
euglena
aquatic, animal like move, photosynthetic in light, heterotrophic in dark, asexual binary fission
diatoms
Silica glass like shells, photosynthetic pigments called carotenoids give golden color, crushed diatoms ie can kill ants
dinoflagellates
spin around using flagella, flagella look like rowing a boat, red tides dangerous form toxins kill animals and people
fungus like protists characteristics
moulds, heterotrophic, feed on dead animals and animals, cool damp habitats, dont need water but moisture, cell walls, reproduce with spores,
two groups of fungus like protists/moulds
slime moulds, water moulds
what are fungi evolutionarily closer to
animals than to pants
fungi characteristics
chitin (stuff fingernails) cell wall, eukaryotes, most multicellular but yeast are unicellular, heterotrophs, no brain, large fungal networks, decomposer called saprophyte
How do fungi eat
extracellular digestion, releasing digestive enzyme into surroundings to absorb nutrients into cell, must live or near food
two main parts of fungi structure
Hyphae, and mycelium
Hyphae
fine filament network make bodt, frow in different direction get different names, eat this part top
Mycelium
branching network of hyphae that grow together undergound, largest organism bottom
how do fungi reproduce
one cycle sexual other asexual
Two types of asexual fungi reproduction
Spores, fragmentation
Spores
can w/ mitosis, windblown reproductive cells grow iin suitable environment
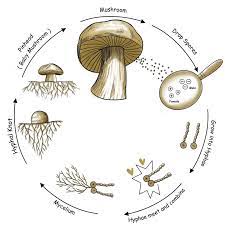
Fragmentation
piece of hyphae break off grow into mycelia bc maybe environmental stressor tear apart grow somewhere else
why would fungi sexually reproduce
hot or dry environment sex make genetically diverse spores