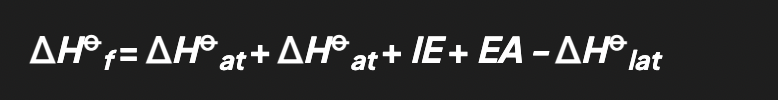Energy cycles in reactions
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
bond enthalpy
bond breaking is endothermic as it requires the input of energy
energy required to break a bond is called bond energy/enthalpy
bond formation releases energy, so is exothermic
amnt of energy released when bond is formed has same magnitude as energy taken in when bond is broken but with opposite sign
bond enthalpy is the enthalpy change for this process:
X-Y(g) → X(g) + Y(g)
enthalpy change from bond enthalpies
ΔHꝋ = enthalpies for bonds broken - enthalpies for bonds formed
overall enthalpy changes
if more energy released when new bonds formed than energy taken in to break bonds, it’s exothermic, products more stable than reactants
if more energy required to break bonds than energy released when new bonds are formed, it’s endothermic, products less stable than reactants
average bond energy
energy needed to break one mole of bonds in a gaseous molecule averaged over similar compounds
limitation:
bond energies are affected by the environment
so energy of a particular bond will vary in different compounds
an average measure isn’t very accurate
to calculate:
take bond enthalpy for the whole molecule and divide by number of bonds
hess’s law
enthalpy change for a reaction is independent of the pathway between the initial and final states
enthalpy change of formation
elements placed at the bottom of hess cycle
arrows pointing up

enthalpy change of combustion
combustion products always at bottom of hess cycle
arrows pointing down

born haber cycles
enables to calculate lattice enthalpy for ionic compounds
shows all the steps needed to turn atoms into gaseos ions, and then into ionic lattice
alternative route begins from enthalpy of formation
drawing born haber cycles
start with elements and their state symbols
turn these into gaseous atoms
this is a bond breaking process, so arrows drawn up
this is called enthalpy of atomisation
create gaseous ions
metal loses electrons, so this is first ionisation energy
arrow goes up because endothermic
non-metal gains electrons, so this is electron affinity
arrow goes down because exothermic
complete cycle
enthalpy of formation is added at the bottom of the diagram, above/below the elements
this can be exothermic or endothermic, so arrow will change direction depending on compound
lattice enthalpy is the change from ionic solid to gaseous ions, so arrow will point up
general born haber cycle equation