NTA bank
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/182
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
183 Terms
1
New cards
Which institution reiterates the importance of accurate lead placement and selection of the appropriate lead to monitor:
AHA
2
New cards
While prepping the patient for cardiac monitoring, as recommended by AHA 2017, why would you place the limb electrodes for hospitalized patient receiving continues electrocardiographic monitoring on anterior torso of the patient
reduce potential for artifacts
3
New cards
Any abnormal wave, spike or movement or movement on ECG tracing that is not generated by electrical activity of the heart is:
**Artifact**
4
New cards
The most common monitoring problems are related to:
**All of the above**
5
New cards
The most common high voltage artifact is considered:
muscle movements when the patient turning in the bed
6
New cards
Second most common high voltage artifact is as a result of:
Patient is having seizure
7
New cards
Third most common high voltage artifact are resulting from
**gastric pacemaker**
8
New cards
Gastric pacemaker is approved for use in:
**Adult and pediatric patient**
9
New cards
Indications for placement of gastric pacemakers in adult and pediatric patient is:
Refractory gastroparesis
10
New cards
Fourth most common high voltage artifacts is results of:
Tall T wave
11
New cards
High voltage artifact showing tall T wave. What are the most common reason for tall T wave?
**High serum potassium level and AMI**
12
New cards
Poor contact between skin and electrodes, which might be cause as a result of dried, expired electrodes can activate:
Low rate alarm
13
New cards
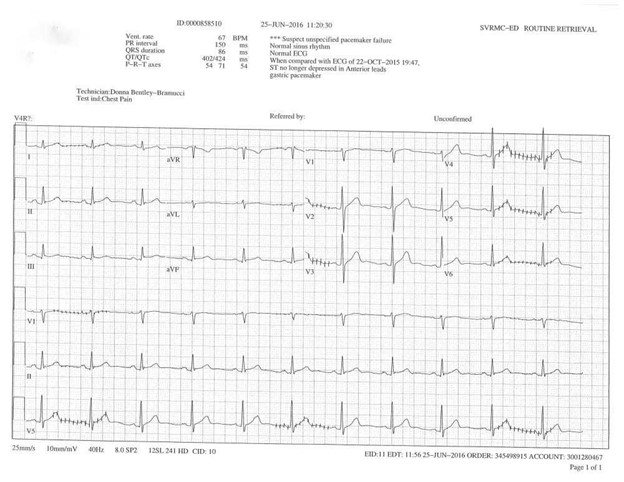
Please identify and name the artifact:
Gastric pacemaker in pediatric patient
14
New cards
Low rate alarm is on. QRS complex shows low amplitude. What would be your solution?:
Turn up
15
New cards
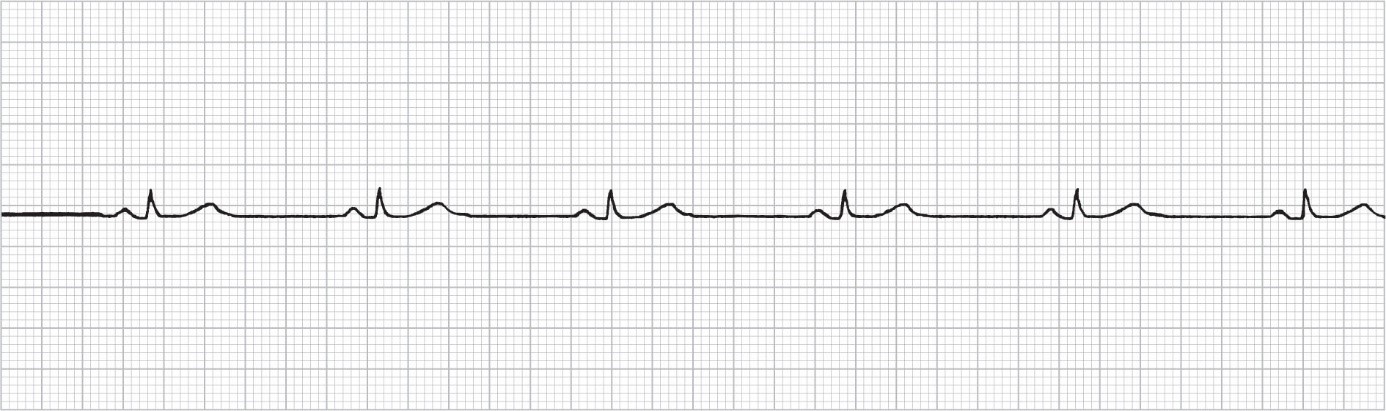
Use tracing below. Identify the artifact below
**Low rate alarm**
16
New cards
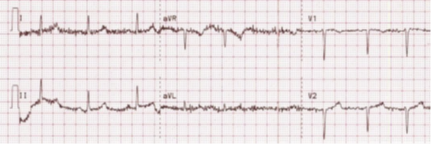
Use tracing below. Identify the artifact below:
Somatic tremor
17
New cards
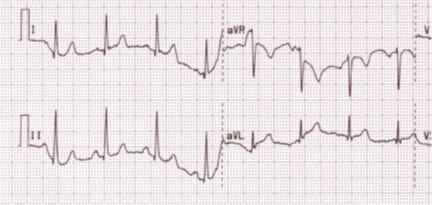
Use tracing below. Identify the artifact below:
Wondering baseline
18
New cards
Use tracing below. Identify the artifact below
A/C interference
19
New cards
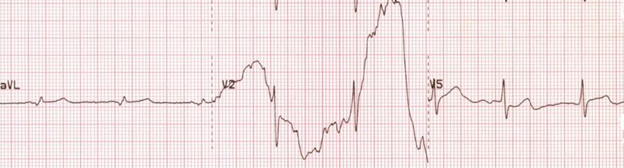
Use tracing below. Identify artifact below:
Broken recording
20
New cards
Partial paralysis of the stomach in diabetic patient is:
gastroparesis
21
New cards
Any deviation from the normal pattern of the heart rate or rhythm is:
**arrythmia**
22
New cards
During arrythmia heart beats:
all of the above (too fast, too slow, and irregularly)
23
New cards
Arrythmias can occur when:
**all of the above**
24
New cards
Arrhythmias may be completely:
Harmless of life-threatening
25
New cards
Guidelines published by the AHA on November 7, 2017, it is recommended that adult arrhythmia patients receiving continuous cardiac monitoring have:
V1
26
New cards
Guidelines published by the AHA on November 7, 2017, it is recommended the pediatric arrhythmia patients receiving continuous cardiac monitoring have the:
lead II selected.
27
New cards
Natural pacemaker of the heart located in the upper back wall of the right atrium is:
SA node
28
New cards
The apex of the heart lies.
touching the diaphragm, pointing toward the left lung
29
New cards
This structure is the part of the conduction system that makes the ventricles contract.
Purkinje fibers
30
New cards
The cardiac cycle consists of
**systole and diastole**
31
New cards
Intrinsic firing rate for AV node is:
40-60 bpm
32
New cards
Another name for increased heart rate is
tachycardia
33
New cards
A pulse rate below 60 beats per minute is known as
bradycardia
34
New cards
A congenital anomaly, known as dextrocardia exist in which
left ventricle, left atrium, aortic arch is located on the right side
35
New cards
The heart is
a hollow muscular organ situated in thoracic cavity.
36
New cards
Decreased blood flow to a body part or organ, caused by constriction or blockage of the supplying artery is:
**ischemia**
37
New cards
The heart is located in
mediastinum
38
New cards
you are performing ECG on 47-year-old patient. ECG machine indicates the patient’s heart rate, 56. Heart rate of 56 is considered as:
bradycardia
39
New cards
Purkinje fibers can initiate electrical impulse and act as pacemaker if higher level such as SA anode and AV node fail. What is intrinsic firing rate of Purkinje fibers is:
20-40 bpm
40
New cards
A thrombolytic medication:
**dissolves clots**
41
New cards
CDC estimates by the year 2030 the number of Americans with A-fib will exceed:
12 million
42
New cards
Most common arrythmia in general population is:
**A-fib**
43
New cards
A-fib is generating:
irregularly irregular rate
44
New cards
A-fib is especially common in the:
**all of the above**
45
New cards
A heart specialist would be called a:
**cardiologist**
46
New cards
Which of the following terms means *pounding, racing heartbeat*?
**palpitations**
47
New cards
Which term means *a yellow fatty deposit of lipids in an artery*?
**plaque**
48
New cards
Which abbreviation is an arrhythmia
**A fib**
49
New cards
Which abbreviation stands for high blood pressure?
HTN
50
New cards
The complete stopping of heart activity is called:
**cardiac arrest**
51
New cards
In which condition is the heart muscle too weak to pump efficiently?
congestive heart failure
52
New cards
Which of the following conditions is caused by an inflamed vein causing the formation of blood clots within the vein?
thrombophlebitis
53
New cards
Which of the following diagnostic procedures is a blood test?
cardiac enzymes
54
New cards
Which of the following diagnostic procedures measures cardiac fitness?
**stress test**
55
New cards
Which surgical procedure uses a blood vessel obtained from another part of the body?
**coronary artery bypass graft**
56
New cards
Which procedure uses a heart-lung machine?
extracorporeal circulation
57
New cards
Which therapeutic device is used to treat ventricular fibrillation?
**implantable cardioverter-defibrillator**
58
New cards
A thrombus is:
a stationary clot forming inside a blood vessel.
59
New cards
A catheter is a flexible tube inserted into the body or blood vessels:
**True**
60
New cards
In the United States
1 in every 4 deaths is caused by Heart disease
61
New cards
The leading cause of death in United States is
**Heart Disease**
62
New cards
In United States, 1 person dies from heart disease every:
36 seconds
63
New cards
About _____ Americans die from heart disease each year
655,000
64
New cards
Atrial flutter is more likely to occur in people who have some form of heart disease or medical condition. Which of the following types of heart disease or conditions is/are most likely to cause atrial flutter?
**all of the above**
65
New cards
When atrial flutter occurs in people with a normal, healthy heart, it is called
lone atrial flutter
66
New cards
You are scheduled to monitor a patient on the Cardiothoracic floor. The patient recently had open heart surgery. Which of the following atrial arrhythmia would you anticipate in the first 24 hours
**atrial flutter**
67
New cards
The incidence of atrial flutter during a postoperative period following open heart surgery is:
**20-30%**
68
New cards
Which of the following waves is thought to represent the repolarization of the Purkinje fiber
U wave
69
New cards
A biphasic wave is
**a type of waveform across the isoelectric line with part of the wave being above the isoelectric line and part of the wave under the isoelectric line**
70
New cards
Which of the following waves occasionally presents in an ECG as a result of hypokalemia:
U wave
71
New cards
Which of the following is calculated by using the horizontal axis on an NSR ECG strip:
heart rate
72
New cards
Occasionally, deflection seen following T wave is the:
U wave
73
New cards
If present, the Q wave is a
negative wave
74
New cards
A wave form plus the segment represents a(n):
interval
75
New cards
The complex that indicates ventricular depolarization is the:
QRS complex
76
New cards
A complex represents:
several waveforms
77
New cards
The waves produced by myocardial depolarization and repolarization are recorded on EKG paper and like any wave , have _______ as a chief characteristic(s):
all of the above
78
New cards
Normal sinus rhythm has:
60-100 beats per minute
79
New cards
TP interval represents:
atria and ventricle are in diastole
80
New cards
Premature atrial contraction (PAC) is commonly referred to as
all of the above (atrial premature complexes (APC), atrial premature beat (AEB), atrial extrasystole, and premature supraventricular complexes)
81
New cards
Premature atrial contraction when isolated are usually:
benign condition
82
New cards
Premature atrial contraction (PACs) can present:
all of the above (occasionally, in a regular pattern, in a sequence and disappear)
83
New cards
Focus (plural, foci) stands for
cardiac cell or group of cells that can produce ectopic beat
84
New cards
Risk factors for premature atrial complexes are classified as identifiable or idiopathic.
Identifiable risk factors are:
Identifiable risk factors are:
**all of the above (**structural, chemical, and chronic conditions such as chronic heart failure)
85
New cards
The presence of premature atrial contraction, PACs, will make inherent regular rhythm into
**into an irregular rhythm.**
86
New cards
The P waves associated with PAC have different morphology, maybe:
all of the above (flattened, notched, equiphasic or biphasic, and unusual shape or negative wave)
87
New cards
The characteristic pattern of premature atrial contraction, PAC is
the contraction that occurs “too soon”
88
New cards
When PACs is present, you must determine
underlying rhythm and type of premature atrial contractions, PACs
89
New cards
You are performing ECG on John Smith, the 57-year-old patient. ECG machine indicates premature atrial contraction, PACs with normal sinus regular. How would you document the event?
**normal sinus rhythm with premature atrial contraction**
90
New cards
Trigeminy
**refers to a pattern in which every third complex is premature**
91
New cards
Bigeminy
refers to a pattern in which every second complex is premature
92
New cards
Which of the following atrial rhythm is left untreated can cause blood clots?
atrial fibrillation
93
New cards
Occasional premature atrial contractions, PACs:
has no clinical significance
94
New cards
Frequent premature atrial contractions, PACs, have been associated with:
all of the above (atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and ischemic syndrome)
95
New cards
Contrary to popular belief, ___________is not considered as risk factor in incidence of PACs
**caffeine**
96
New cards
A waveform that has an uneven positive (upward) and negative (downward) deflection on the ECG tracing is
**biphasic**
97
New cards
When both positive and negative deflection is approximately equal, biphasic wave is considered
**equiphasic**
98
New cards
Natural pacemaker of the heart located in the upper back wall of the right atrium is
SA node
99
New cards
Structural abnormalities associated with premature atrial contractions is/are?
all the above (septal defect, coronary artery disease, left ventricular hypertrophy, and **valvular heart disease)**
100
New cards
The common features of arrhythmia include P waves that are absent, inverted, buried in the QRS, or retrograde:
**Junctional rhythm**