Health beliefs and behaviours
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Health belief model - HBM
Components of HBM

Percieved susceptibility
believes they are at high risk = more likely to take preventative action
Percieved severity
The more severe the perceived consequences, the more motivated the person will be to avoid or manage the health threat.
Perceieved benefits
individual’s belief in the effectiveness of the advised health behavior to reduce the risk or severity of the health problem.
Percieved barriers
individual’s perception of the costs or obstacles that may prevent them from taking the recommended health action. These can include things like fear, inconvenience, financial cost, or lack of time
Cues to action
triggers that prompt individuals to take action.
Internal = symptoms
External = seeing an advert for smoking cessation, advice from a doctor
Self efficacy
People are more likely to engage in a health behavior if they feel confident they can successfully do it.
belief in one’s ability to successfully perform the recommended health behavior
Social Cognitive theory
highlights the ways in which individuals acquire and maintain new behaviors based on thei own experience and obervation of actions and results of others.
The following affect health behaviour and decisions:
Self efficacy
Behvioural capability
Outcome expectations
Self regulation
Reinforcements and punishments
behavioural capability
If a person does not have the necessary knowledge or skills, they will be less likely to engage in the desired behavior
Outcome expectations
If individuals believe that the outcome will be positive and more immediate , they are more likely to engage in the behavior.
Self regulation
controlling one’s own behavior through self-monitoring, goal-setting, self-reward, and self-punishmen
Reinforcements and punishments
Positive reinforcement (rewards) encourages the repetition of a behavior, while negative reinforcement (avoiding an unpleasant outcome) can also encourage behavior change.
Punishment, on the other hand, can discourage behaviors.
integrative model of behavioural prediction
Follows social cognitive theory
Identifies a set of variables that can account for health related behaviour
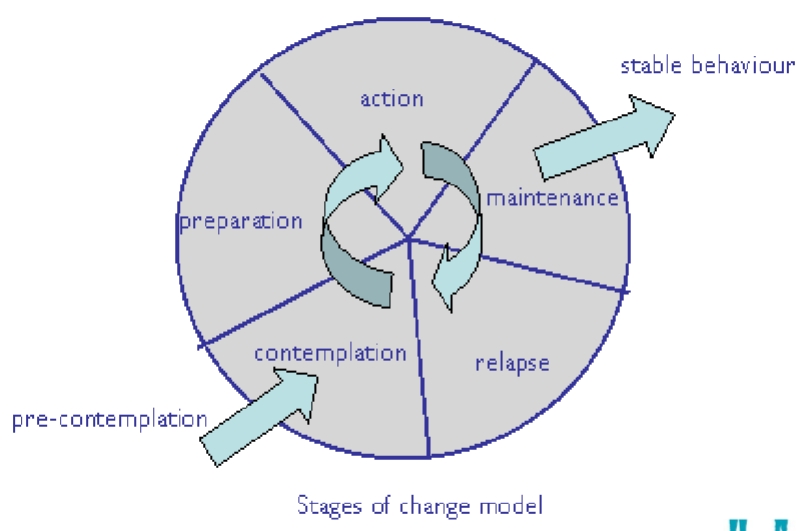
Stage models of health behaviour

Stages of change model components

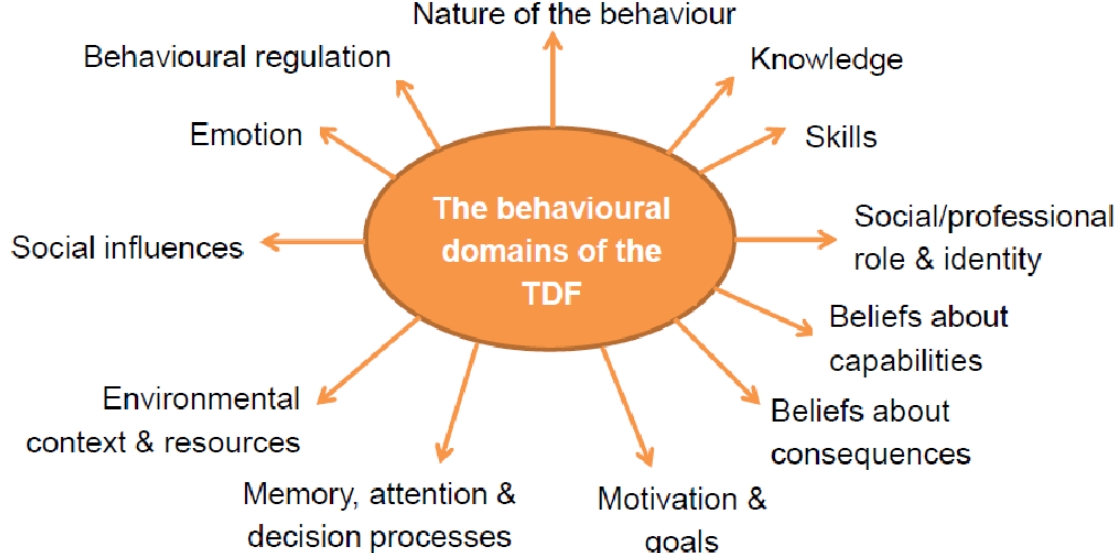
Theoreticl domains framework

Examples of changing health behaviour in phamacies
Smoking cessation
Weight loss
New medicines service
Medicine adherance