Botany 110 Purdue Final Exam
1/177
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
178 Terms
What is a molecule?
One or more elements held together by bonds
Levels of organization
Molecules, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, individual, population, community, ecosystem
Covalent bond
A chemical bond that involves sharing a pair of electrons
Ions
Atoms that lost or gained an electron
Ionic bond
When one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
Cation
Loses an electron, therefore, positively charged
Anion
Gains an electron, therefore, negatively charged
4 Macromolecules of life
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
3 types of membrane transportation
1. Simple diffusion
2. Facilitated diffusion
3. Active diffusion
Hydrogen bonding
Weakest bond but used in DNA to hold together nucleotides
Start codon
AUG (methionine); the codon that begins all RNA.
Stop codon
UAG, UAA, or UGA; the codon that ends all RNA.
Function of stems
1. Support
2. Transport
3. Produce food
4. Produce more stems
Nodes
The point where leaves or branches attatch
Buds
New stems or flowers form in the axil of leaves
Internodes
Length of stem between nodes
Modifications of the stem
Bulbs, corms, tubers
Function of leaves
1. Photosynthesis
2. Storage
3. Transpiration
Monocot
Single cotyledon; netted vein pattern
Dicot
Two cotyledons; parallel vein pattern
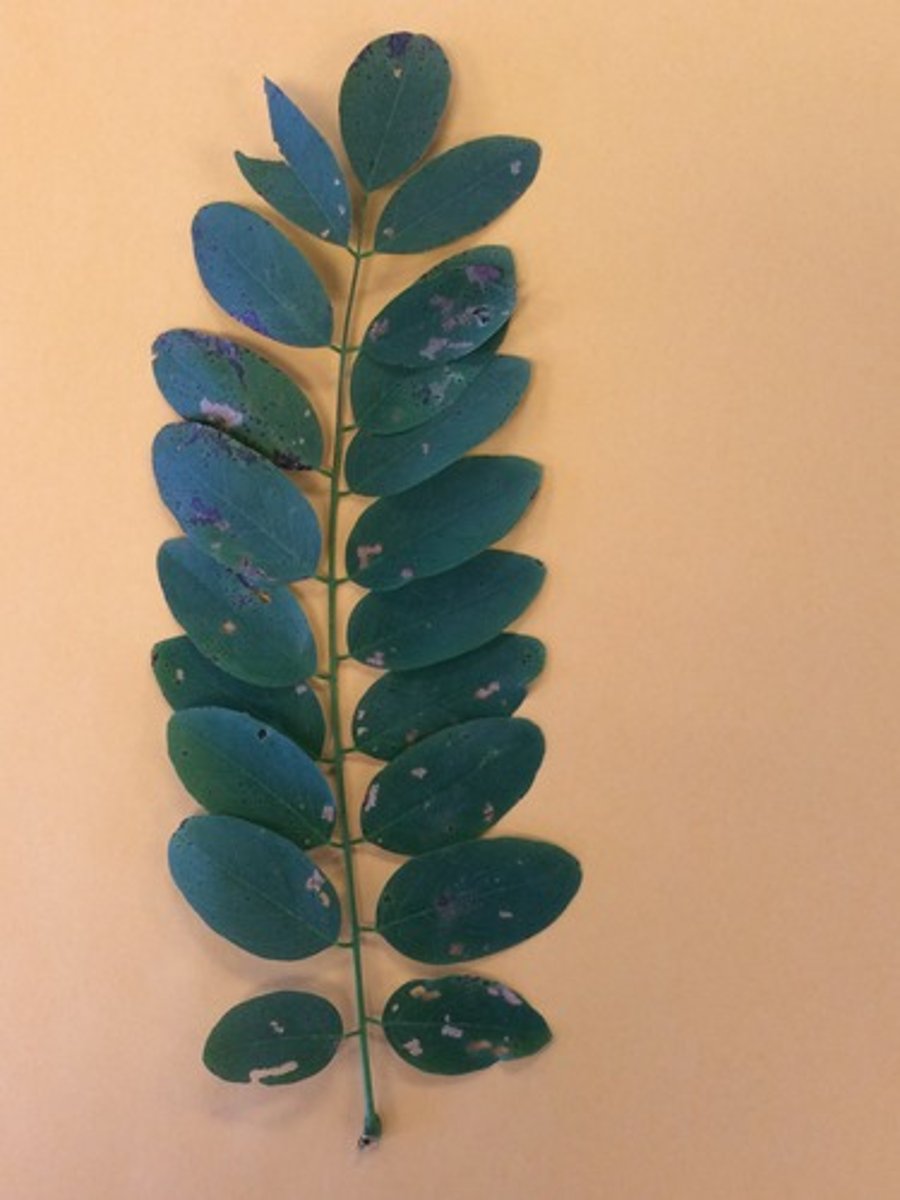
Compound leaf
Multiple leaves attached at a stem and then to the main stem

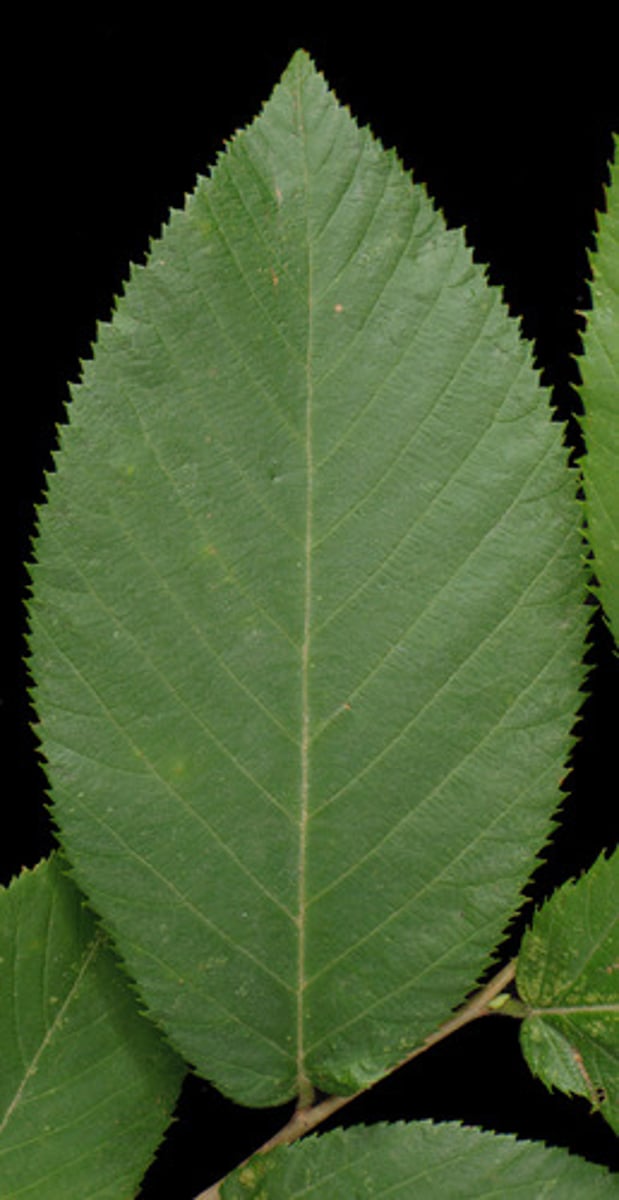
Simple leaf
Attatched directly to the stem

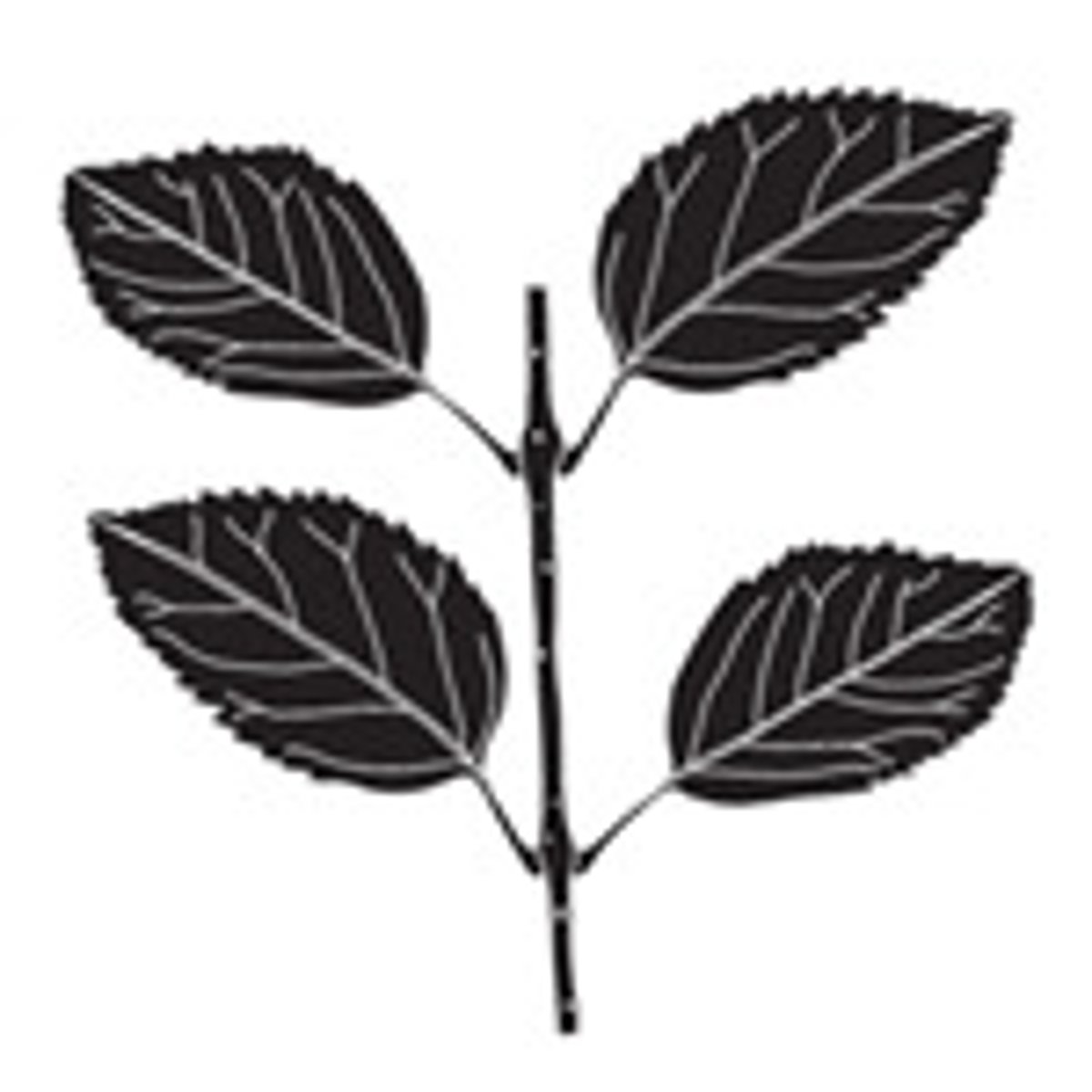
Alternate leaf arrangement
Opposite leaf arrangement

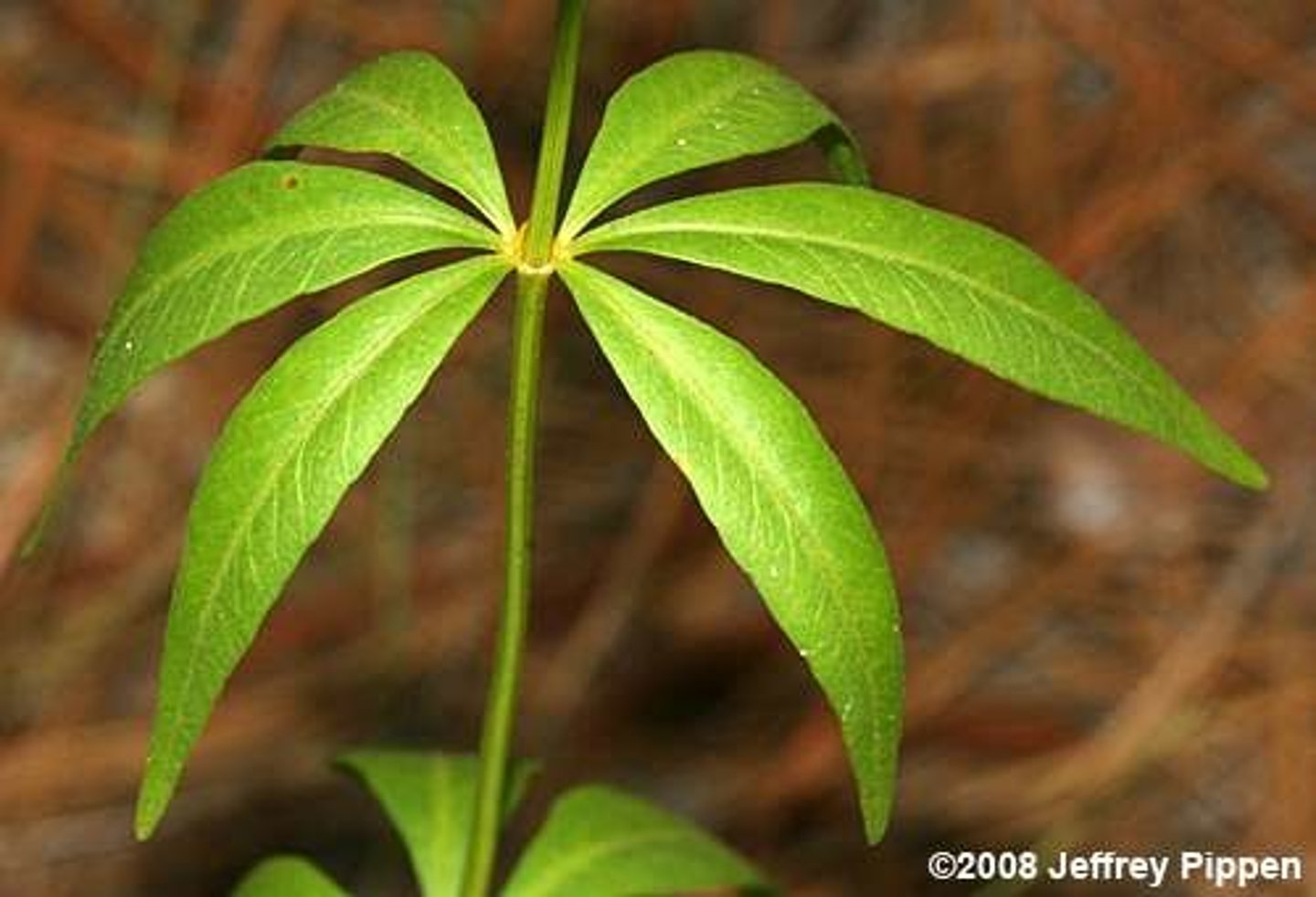
Whorl leaf arrangement

Function of roots
1. water and mineral uptake
2. anchorage
3. storage
4. produce lateral roots
Functions of the flower
1. reproduction
2. production of seeds
What is the pistil comprised of?
stigma, style, and ovary
What is the stamen comprised of?
anther and filament
Monoecious
has male and female reproductive parts
Dioecious
distinct male and female plants
Norman Borlaug
Father of the Green Revolution; created high yield wheat
Why is plant breeding important?
photo and thermos insensitivity, moisture and salt tolerance, elimination of toxic substances
Genetic markers
a DNA sequence associated with a given trait in one or more plant populations
Main tissue types
1. dermal
2. ground
3. vascular
What is dermal tissue (epidermis) in plants?
forms the outer layer of a root, shoot, or leaf that covers and protects the plant
What is ground tissue in plants?
Tissue between the dermal tissue and vascular tissue of a non-woody plant.
What are the functions of ground tissue?
Photosynthesis, storage, and support.
What are the three types of ground tissue?
Parenchyma, sclerenchyma, and collenchyma.
Types of dermal tissues
trichomes, guard cells, pavements cells
What is the vascular tissue in plants?
xylem and phloem
Cuticle
A waxy covering on the surface of stems and leaves that slows down evaporation
What are guard cells controlled by?
Changes in turgor pressure
Function of guard cells
open and close stomata and control transpiration
Parenchyma
comprise the bulk of the plant: the cortex of stems, roots, and leaves- photosynthesis occurs here- starch storage
Sclerenchyma
Thick walled cells, lignified, provide structure
Collenchyma
Wall thickening (cellulose), gritty texture
Xylem function
Transports water and dissolved minerals from the root up to all the other parts of the plant
-Xylem tubes are made up from dead cells
What is the primary function of phloem?
Transports food nutrients such as glucose from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
In which directions does phloem transport nutrients?
Moves in both directions.
What are the main components of phloem?
Composed of sieve elements.
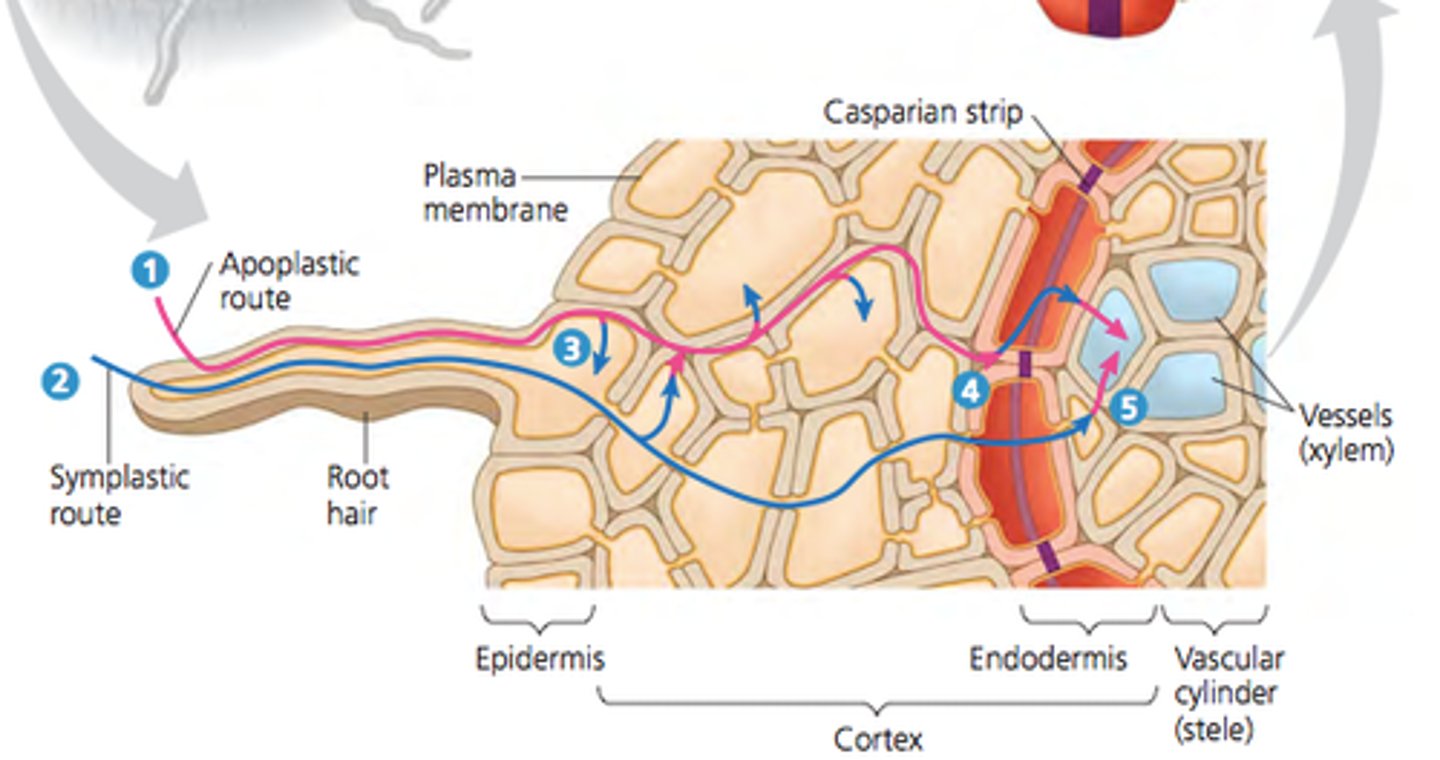
What are the two paths for water and minerals to enter the vascular system?
Symplastic route and the apoplastic route
Symplastic route
through the cytosol
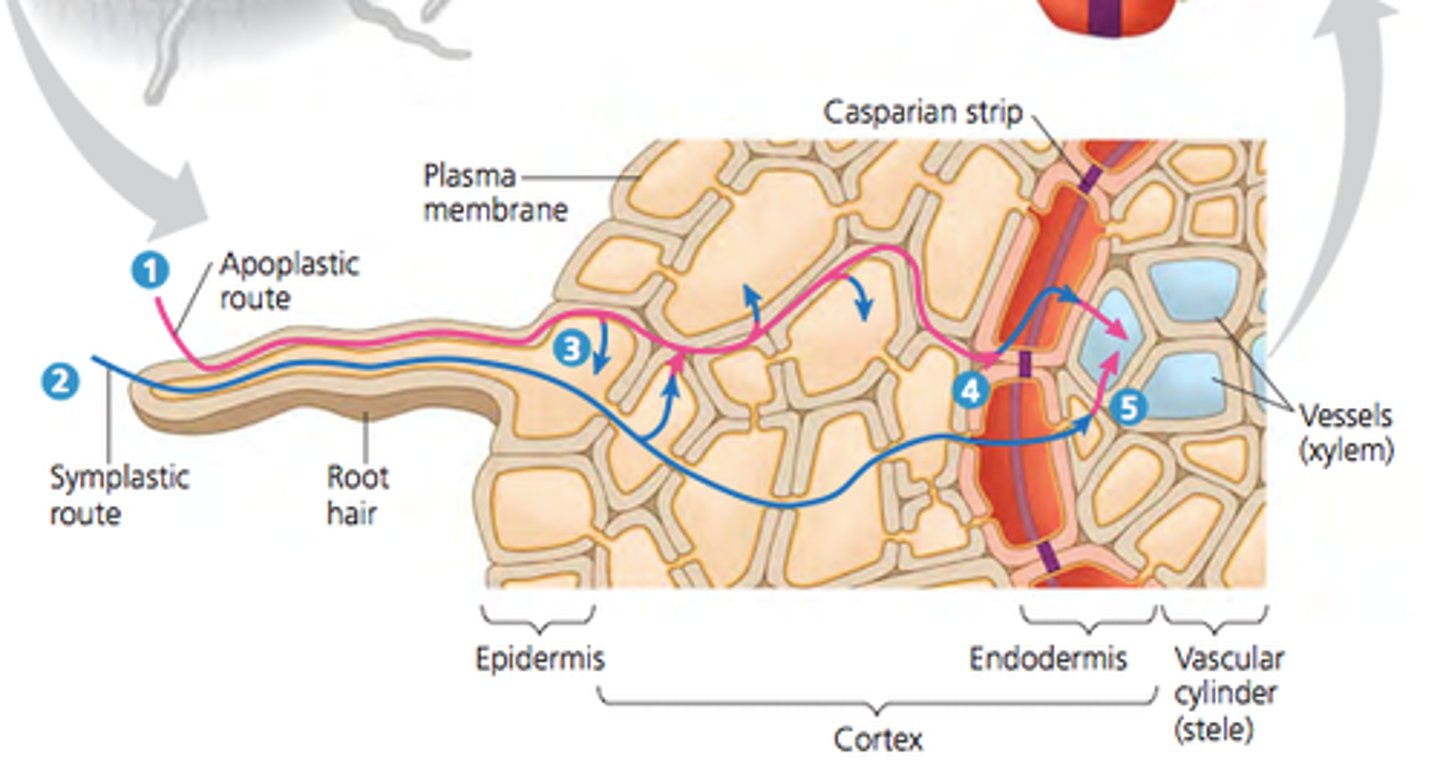
Apoplastic route
through the cell walls and extracellular spaces
Source cells
cells in plant tissue where sugars are made
Sink cells
cells in plant tissue where sugars are to be used or stored
Function of the vascular cambium
adds layers of vascular tissue called secondary xylem (wood) and secondary phloem
Function of the lateral meristem
expands vascular and epidermal tissue
Tap root
Fibrous root
Where does cellular respiration take place?
mitochondria and cytoplasm
Cellular respiration equation
C6H12O6+6O2---> 6CO2+6H2O+36ATP+heat
Where does glycolysis occur?
The cytoplasm
What occurs during glycolysis
glucose is converted to pyruvate
What is the second step of respiration?
The production of acetyl CoA
The production of acetyl-CoA
pyruvate moves into the mitochondria is converted into one molecule of CO2 and one molecule of 2-carbon acetyl which attaches to coenzyme A in order to make acetyl CoA
What is the third step of respiration?
The Krebs Cycle
The Krebs Cycle
pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of energy-extracting reactions
Electron transport chain
A sequence of electron carrier molecules (membrane proteins) that shuttle electrons during the redox reactions that release energy used to make ATP.
Chemiosmosis
A process for synthesizing ATP using the energy of an electrochemical gradient and the ATP synthase enzyme
Fermentation
an anaerobic process that allows glycolysis to continue
Where does photosynthesis occur?
chloroplasts (plant cells)
Photosynthesis equation
6CO2 + 6H2O ------> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Light-dependent reactions
reactions of photosynthesis that use energy from light to produce ATP and NADPH
does photosystem 1 or photosystem 2 happen first?
Photosystem 2 occurs first
Light-independent reactions
set of reactions in photosynthesis that do not require light; energy from ATP and NADPH is used to build high-energy compounds such as sugar; also called the Calvin cycle
Visible light wavelength
Short wave length- higher energy
Where do light independent reactions take place?
stroma of the chloroplast
Where do light dependent reactions take place?
thylakoid membrane
C3 Photosynthesis
The most common form of photosynthesis
C4 Photosynthesis
process that first converts CO2 into a 4-carbon molecule in the mesophyll cells, converts that product to malate and then shuttles it to the bundle sheath cells, where the malate releases CO2 and rubisco picks it up as if all were normal
CAM photosynthesis
Desert plants store CO2 at night as malic acid in the vacuole to use during the day. Allows them to keep leaves closed during day and reduce water loss.
3 Parts of a nucleotide
1. Phosphate group
2. 5 carbon sugar
3. Nitrogenous base
Pyrimidines
single ring bases- cytosine and thymine
Purines
double ring bases- adenine and guanine
Chargraff's rule
# of adenines = # thymines; # of guanines = # of cytosines
Complimentary base pairing principle
A+T= 2 hydrogen bonds
C+G= 3 hydrogen bonds
Double helix structure
2 polynucleotide strands wrapped around each other
Leading strand
the new complementary DNA strand synthesized continuously along the template strand toward the replication fork in the mandatory 5' to 3' direction
Lagging strand
The strand in replication that is copied 3' to 5' as Okazaki fragments and then joined up.
RNA primer
short segment of RNA used to initiate synthesis of a new strand of DNA during replication
DNA polymerase
Enzyme involved in DNA replication that joins nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule on the 3' end
DNA helicase
unwinds DNA
DNA ligase
seals areas between bases
DNA primase and topoisomerase
begins DNA replication
What does "prime" mean?
the position of the carbons in the sugar ring
What is attached to the 3' carbon?
hydroxyl group (-OH)
What is attached to the 5' carbon?
phosphate group (PO4-)
What way can the daughter DNA strand only grow?
5'->3'
What base does uracil replace in RNA?
Thymine