gen module 8
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
antigen
Substance that stimulates production of an antibody
Seen as “foreign”
antibody
Made in response to the entry of a foreign protein Coded for by genes
Universal donor
O
Universal recipient
AB
What is RhoGAM? Who is it given to and under what conditions is it required?
Concentrated Rh+ antibodies injected into mothers 72 hours after she has RH+ babies
must be after every pregnancy (even abortions and miscarriages)
What does HLA stand for? Describe a situation when the alleles at the HLA loci are important medically.
Human leukocyte antigen
Specific alleles correlated with increased risk of food and pollen allergies
Greater Transplant Success if Match at HLA Loci
8.6e13 possible combinations possible
autograft
a graft of tissue from one point to another of the same individual's body.
isograft
genetically identical people (twins)
allograft
same species
xenograft
different species (pig to human)
haplotype
array of HLA alleles on a given chr #6
Organ trafficking
When someone sells an organ
Exploiting Poor
Forced Donation
Black Market Sales
Complications from Foreign Surgery
Transplant tourism
When someone goes to another country to receive an organ illegally (that is outside the laws of that country).
What is the purpose of T cells? Where are they formed?
Originate in bone marrow
fight pathogens directly
What is the purpose of B cells? Where are they formed?
Originate in bone marrow
Release antibodies
Bruton’s disease
X-linked
T cells, but no B cells so no antibodies
SCID
Missing T and B cells
1 type is missing adenosine deaminase enzyme
• Gene therapy for ADA-deficient SCID patients
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Autoimmune disease
Attacks linings of joints mainly in hands, wrists and shoulders
Tissue becomes inflamed and joint surfaces are destroyed
Usually an immuno-suppressant drug to reduce response to the disease
HLA-DR4 allele identified in about 60% of people with the disease, but about 20% who have this allele do not have the disease
HIV and AIDS
AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome)
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) Infection/Progression:
HIV infects T cells
When T cell called on to act in immune response, the viral genes are activated, making more virus particles that attack more T cells
T cell population decreases and patients become more susceptible to infections and some types of cancers and ultimately early death
What disorder did bubble boy have
SCID
Describe the characteristics that a cell must have to be classified as a stem cell.
Ability to continue to divide continuously (immortal) in culture
Produce more cells like itself
Ability to differentiate into specialized tissues in the body
What are some goals of stem cell research? What do scientists hope to be able to do some day?
Learn how heart disease, cancer, birth defects, etc develop and better treat or prevent these
Regenerate damaged tissues and organs
Recreate disease in cell line and test different drugs
Types of stem cells
Embryonic Stem Cells – have potential to differentiate into many/most (Pluripotent not Totipotent) tissue types
Adult Stem Cells – more limited as to types of tissues they can become (multipotent)
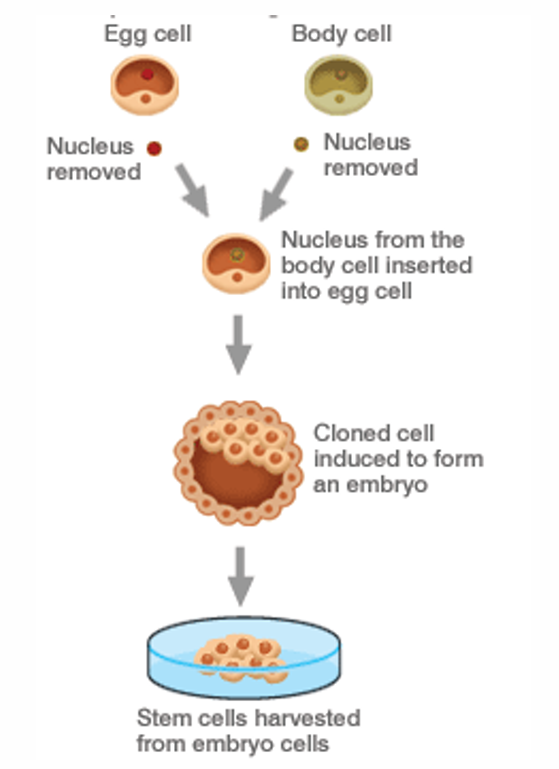
What is somatic cell nuclear transfer? Describe the procedure.
How do you Get Adult Stem Cells?
Umbilical cord at delivery
Bone Marrow of adult
Some adult cells (brain, liver, skeletal muscle, dermal tissues, others)
Amniotic fluid (surrounding fetus during pregnancy)
How do you get embryonic stem cells
From blastocyst of early embryo
Inner cell mass = ESCs
Implant DNA of somatic cell into an enucleated human egg
Pluripotent
stem cells can give rise to all cell types of the body (but not the placenta).
Multipotent
can only give rise to some types
Totipotent
stem cells can give rise to any of the 220 cell types as well as placenta
Name the researchers who received a Nobel Prize in 2012 for their work on stem cells and regeneration biology. Discuss the contributions each made to this field
John B Burdon
1962 - Discovered that a specialized cell possessed all the genetic information needed to develop all cells in a mature organism
Shinya Yamanaka
2006 - Determined that the insertion of 4 genes could reprogram differentiated cells and cause them to become pluripotent stem cells
Discuss some of the controversial/ethical issues regarding stem cell research.
Moral status of embryos and when life begins
Poor women could be exploited for eggs
Health risks from surgical removal and hormonal treatments used to extract oocytes
Discuss the historical and current state of federal regulations on stem cell research.
Federal funding is available for adult stem cell and iPS research
2001 Bush allowed federal funding for embryonic stem cell research on older but not new cell lines
2009 Obama- federal funding available on embryonic stem cell lines created after August 2001 and that NIH would be allowed to set regulations for ESC use
On July 7, 2009, NIH published guidelines for Human Stem Cell Research.
• Lines must be registered and approved for use
• Ok to use excess embryos from fertility clinics (with qualifications)
On September 21, 2009, NIH opened their website to accept requests for human embryonic stem cell line approvals for ESC lines.
December 2009: NIH approved first ESC line under new guidelines.
What genes involved in stem cells
Signal transduction genes are associated with the cell membrane. They receive signals from outside the cell and transmit these signals through receptor proteins and enzymatic reactions to cause changes inside the cell
Which organization set the current regulations for ESC funding? What are some of the new regulations?
NIH
Nuclear Reprogramming Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPS)
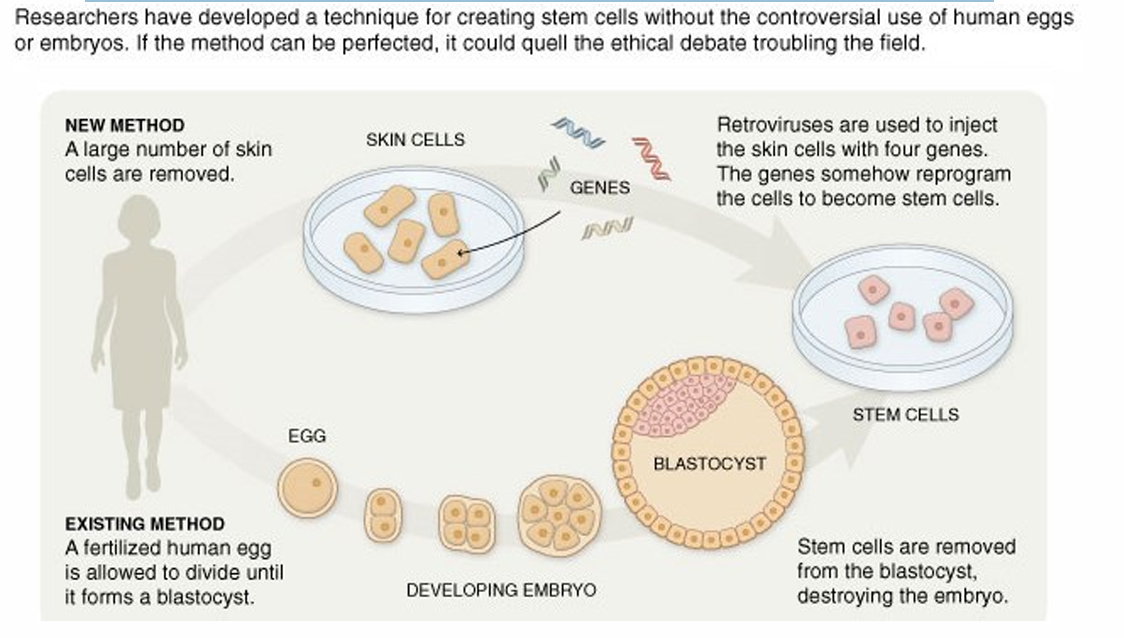
State regulations on stem cell research
Currently, it is restricted/banned in Arkansas, Indiana, Louisiana, Michigan, North Dakota, South Dakota
Carcinoma
Solid tumor from epithelial tissue
• Body surface coverings and derivatives
• E.g. skin, breast, respiratory, colon, urinary
• 85.3% of cancer
Sarcomas
Solid tumors from embryonic mesoderm tissue • E.g. bone, cartilage, muscle, fat • 1.9% of cancers
Lymphoma
Abnormally large number of lymphocytes (type of WBC) made by spleen and lymph nodes
• E.g. Hodgkin Disease
• 5.4% of cancers
Leukemia
Abnormally large number of leukocytes (WBCs) made by bone marrow
• Common in children. Can occur in adults
• 3.4% of cancers
Anaplasia
Structure/function of cell is undifferentiated
Hyperplasia
Uncontrolled cell division Immortal and Invasive
Metastasis
Ability to move to and establish tumors at other sites in body
G1/S checkpoint
monitors for proper cell size and undamaged DNA
G2/M
holds up cycle until replication and DNA repair are complete
M checkpoint
proper spindle formation and attachment
Malignant
cancer cells invade surrounding tissue
Metastatic
cancer cells spread and establish secondary tumors in other sites in the body
Cancer genetic causes
Single gene
Polygenic (more than 1 gene)
Chromosome aberration
Mutation(s) in somatic cell or in gamete producing cell
Viruses
How is cancer multi hit?
arises over time with multiple genetic changes.
sporadic and influenced by environment
How many of cancer causing mutations are errors in replication?
2/3
Proto-oncogenes
allow “good” cells to divide
dominant acting: only 1 copy mutated to cause cancer
Mutations of what genes cause cancer
tumor suppressor genes and proto onco genes
Loss of function mutation
Complete or partial absence of protein function Recessive-acting mutations
Gain of Function mutation
Cell produces protein that is not normally present
Either new gene product or gene product in new location or at an inappropriate time in development.
Dominant-acting mutations (usually).
Example: mutation in a gene that encodes a receptor for a growth factor might cause the mutated receptor to stimulate growth in the absence of the growth factor.
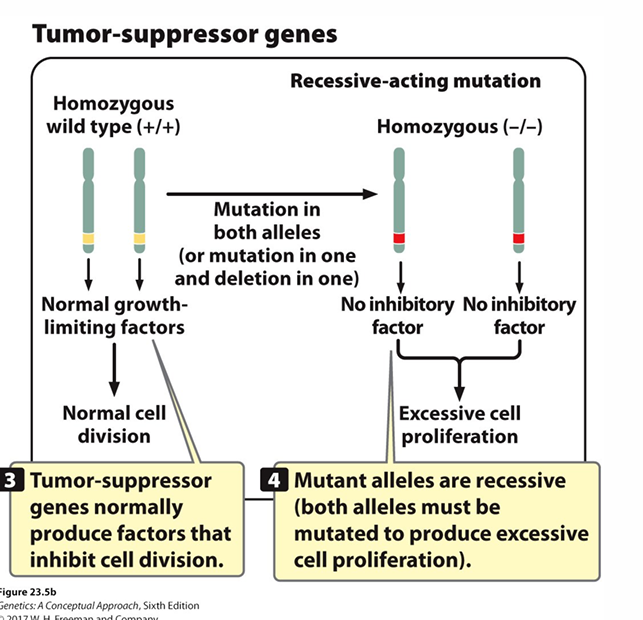
Tumor suppressor genes
recessive action: both need to be mutated for cancer
examples: APC, BRCA1, CDKN2A, NF1, p53, RB
Retinoblastoma – RB Gene
40% of cases are inherited (1 mutant allele in zygote)
Normal protein responsible for regulation at G1/S checkpoint
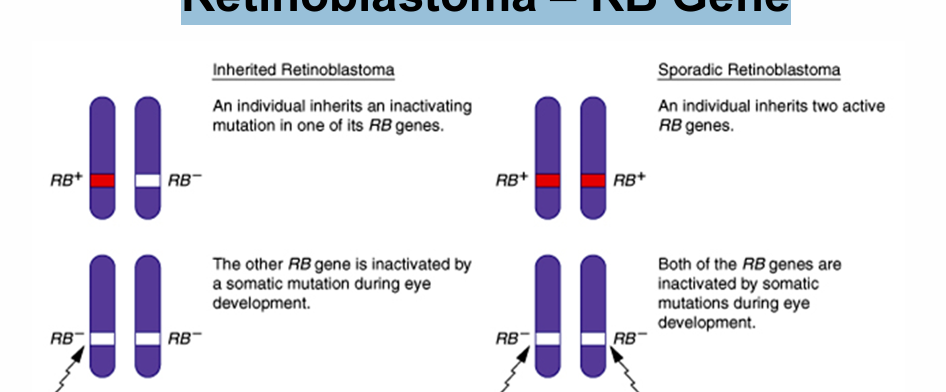
Knudson’s Two Hit Hypothesis
both copies have to be defective in same cell to allow tumor to develop
BRCA1and BRCA2 normal action
repair double strand breaks
BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 cancers
5-10% of all breast cancers
20-25% of hereditary breast cancers
Strong family history of breast or ovarian cancer may indicate a mutation in one of these genes.
Men with these mutations Have an increased risk of breast cancer and prostate cancer.
Can genetic test
p53
Chromosome 17
G1/S checkpoint
Colon, lung, breast, brain cancers
found in altered form in 50% of human tumors
The fork in the road: if DNA is damaged, p53 delays cell division until damage is repaired or programs cell to die
Haploinsufficiency
Individuals can still be affected even if they have one normal allele.
bloom syndrome
bloom syndrome
defective DNA helicase enzyme that is important in repairing double stranded breaks of DNA
mutated gene causes cancer even in heterozygotes
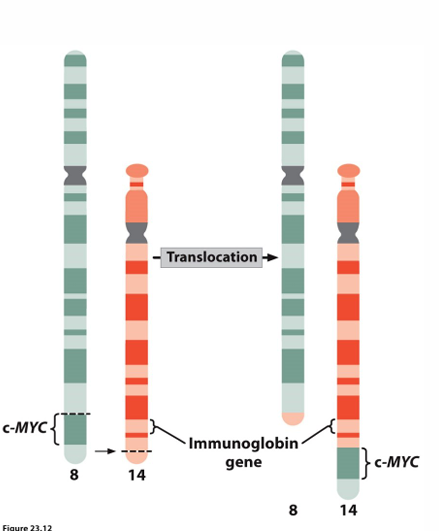
burkitts lymphoma
Abnormal function of B cells
Reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 8 and 14 places c-myc (oncogene) next to enhancer
enhancer leads to abnormally high function of c-myc gene
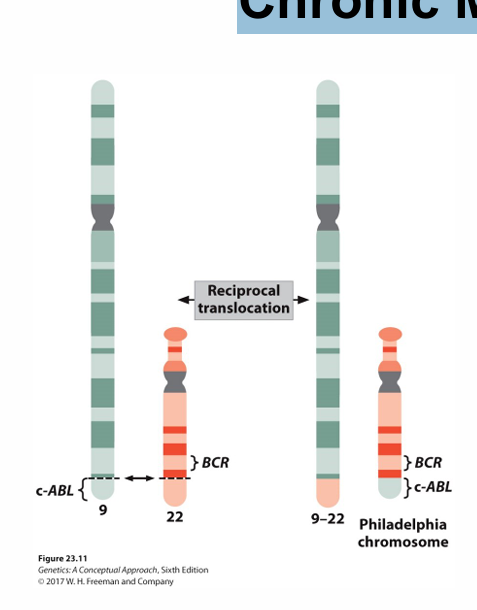
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
Fatal, uncontrolled replication of myeloid stem cells
90% of patients have the Philadelphia chromosome
Reciprocal translocation involving chromosomes 9 and 22 places 2 oncogenes near each other
ABL oncogene
Epstein-Barr Virus
linked to Burkitt's lymphoma
Infects B cells of the immune system
• Hepatitis B Virus
liver cancer
Human Papilloma Virus
cervical cancer
Pancreatic cancer
4th leading cause of cancer death even though only about 37,000 new cases occur each year.
Palladin gene
causes pancreatic cancer
codes for a cytoskeleton protein that is important in maintaining cell shape.
Cells that metastasize generally have poor cytoskeleton structure causing them to detach from the tumor mass easily
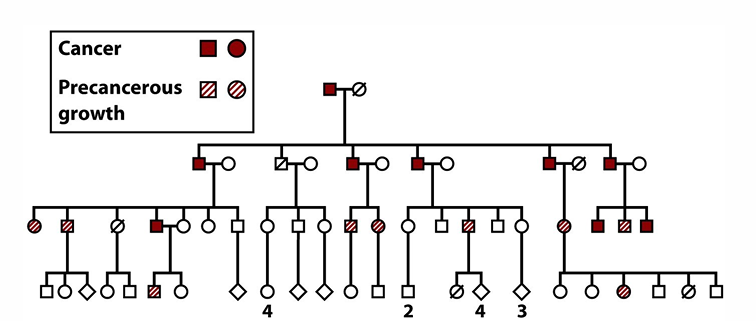
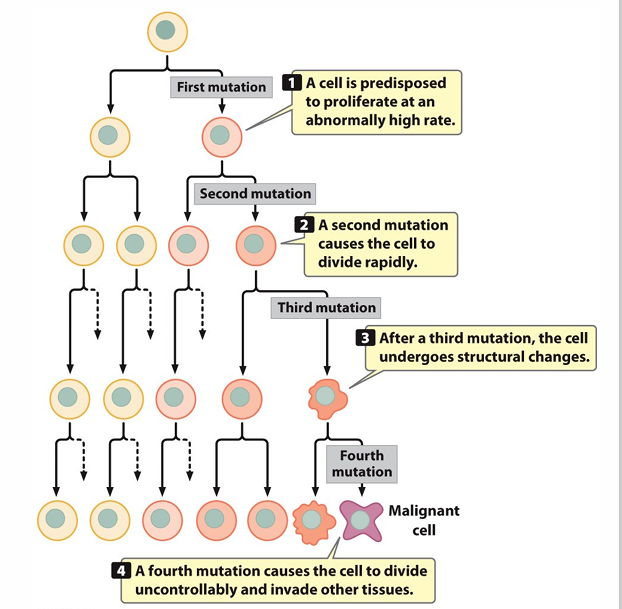
Clonal Evolution
Over time, tumor cells acquire more mutations that allow them to be progressively more aggressive in proliferation.
Defective Nucleotide Excision Repair for pyrimidine dimers
Xeroderma pigmentosum
High risk of skin cancer since many pyrimidine dimers do not get repaired
Defective Mismatch Repair
Colorectal, endometrial, stomach cancers
Defective Double Strand Break Repair
BRCA1 BRCA2
Role of Telomere Length in Cancer
Normally, telomerase works in germline cells, but not in somatic cells: allows somatic cells to die, be replaced, etc.
Tumor cells often have telomerase expression, which is thought to contribute to the “immortality” of cancer cells.
Chromosome Segregation
Cancer cells often have abnormal karyotypes
Vascularization
Angiogenesis (growth of new blood vessels) is important to tumor progression
Growth factors and other proteins involved in angiogenesis are often overexpressed in tumor cell
Angiogenesis inhibitors may be inactivated or underexpressed
Metastasis is the cause of death in 90% of human cancer cases
International Cancer Genome Consortium
To obtain a comprehensive description of genomic, transcriptomic and epigenomic changes in 50 different tumor types and/or subtypes which are of clinical and societal importance across the globe
Cancer genome atlas
a collaboration between the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), has generated comprehensive, multi-dimensional maps of the key genomic changes in 33 types of cancers
Tests/screenings for Cancer
Regular breast exams
Mammograms
Colonoscopies
PSA Test (prostate cancer)
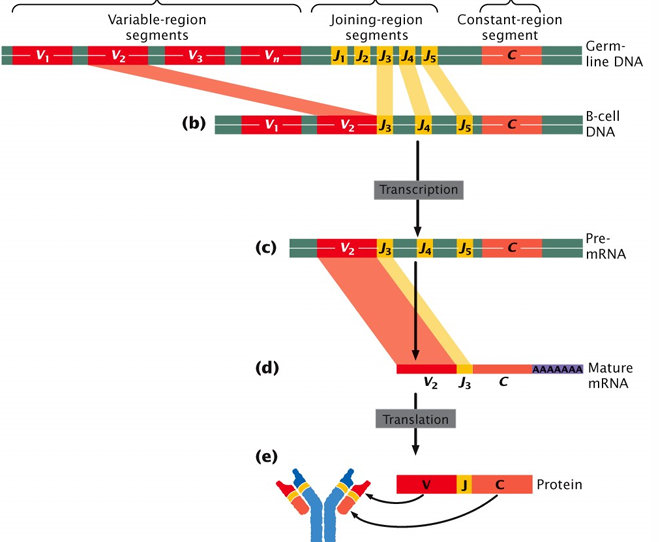
Somatic Recombination in B Cells
Germ line DNA (chr. 22) Processed to mature B cell DNA
Different cells that put the same regions together in processing do it slightly differently: Junctional Diversity
Pre-mRNA is processed causing additional segments to be removed
High frequency of Somatic Mutations (~2%) in the variable region of the DNA is also common
Allergies
The tendency to develop an allergy seems to be inherited (twin studies
Specific alleles of the HLA-DQ and HLA-DR genes are correlated with an increased risk of developing food and pollen allergies
HLA
death rate of people waiting for organs
20 per day in US
Types of Organs and Tissues Transplanted
Cornea Transplants
Kidney Transplant
Liver Transplants
Heart Transplants
Heart-Lung Transplants
Bone transplants
Diamond Blackfan Anemia
RBC not produced properly due to bad protein in ribosomes
Anemia, higher frequency of some cancers, higher frequency of congenital disorders like cleft palate and abnormal limb development
National Organ Transplant Act – 1984
Organ Procurement and Transplant Network established to promote fairness in allocating organs
Factors considered include
• Medical urgency
• Blood type, tissue and size match
• Time on wait list
• Proximity to organ
Compensation for Organ Donation
Financial compensation for live kidney donors
Compensation by placing a living relative at a higher priority for organs if a dead primary relative donates
Compensate family of deceased person for allowing the deceased organs to be used for transplant