Ancient Mediterranean Ancient Near East
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
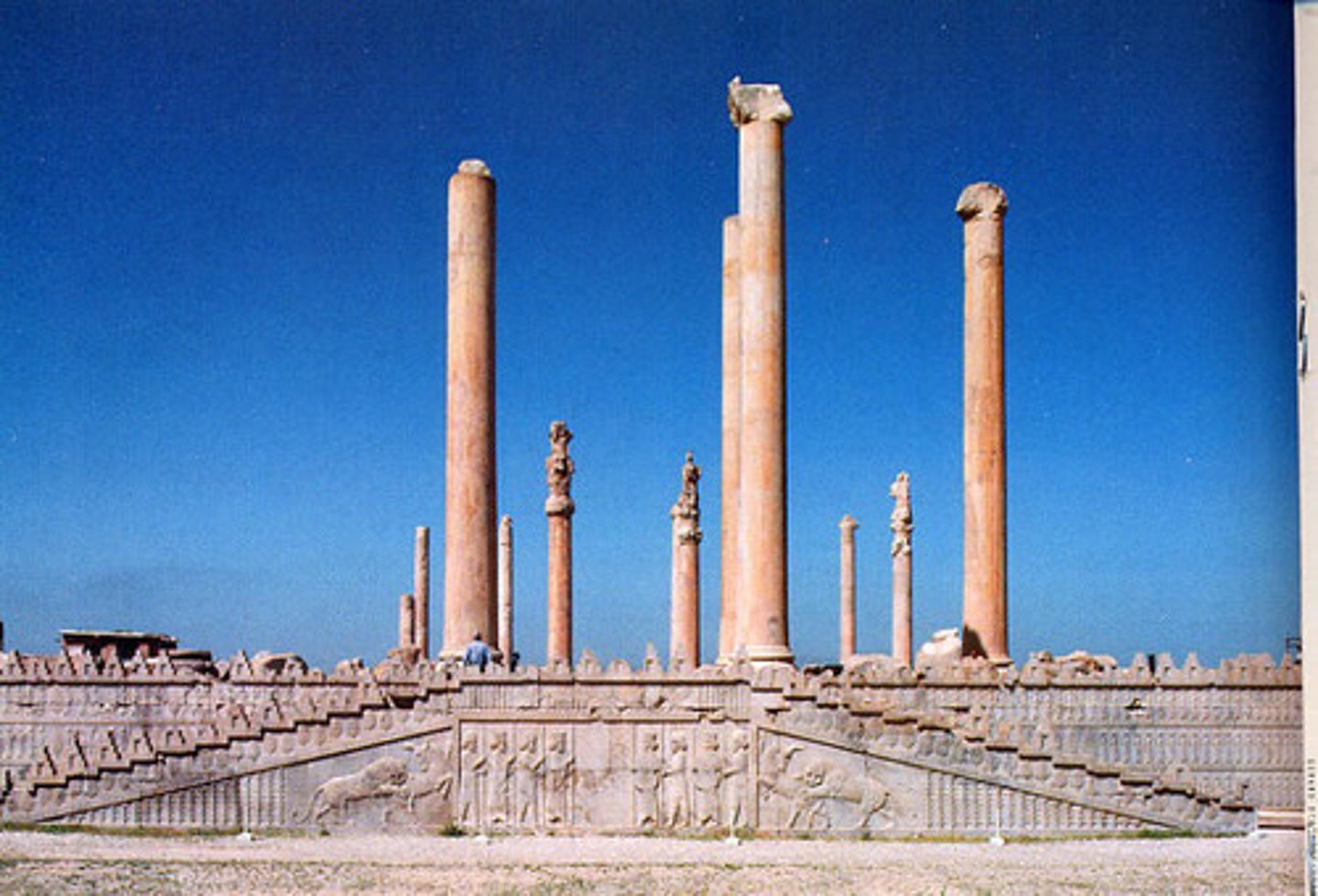
Apadana
the great audience hall in ancient Persian palaces

bent-axis plan
A plan that incorporates two or more angular changes of direction, characteristic of Sumerian architecture.
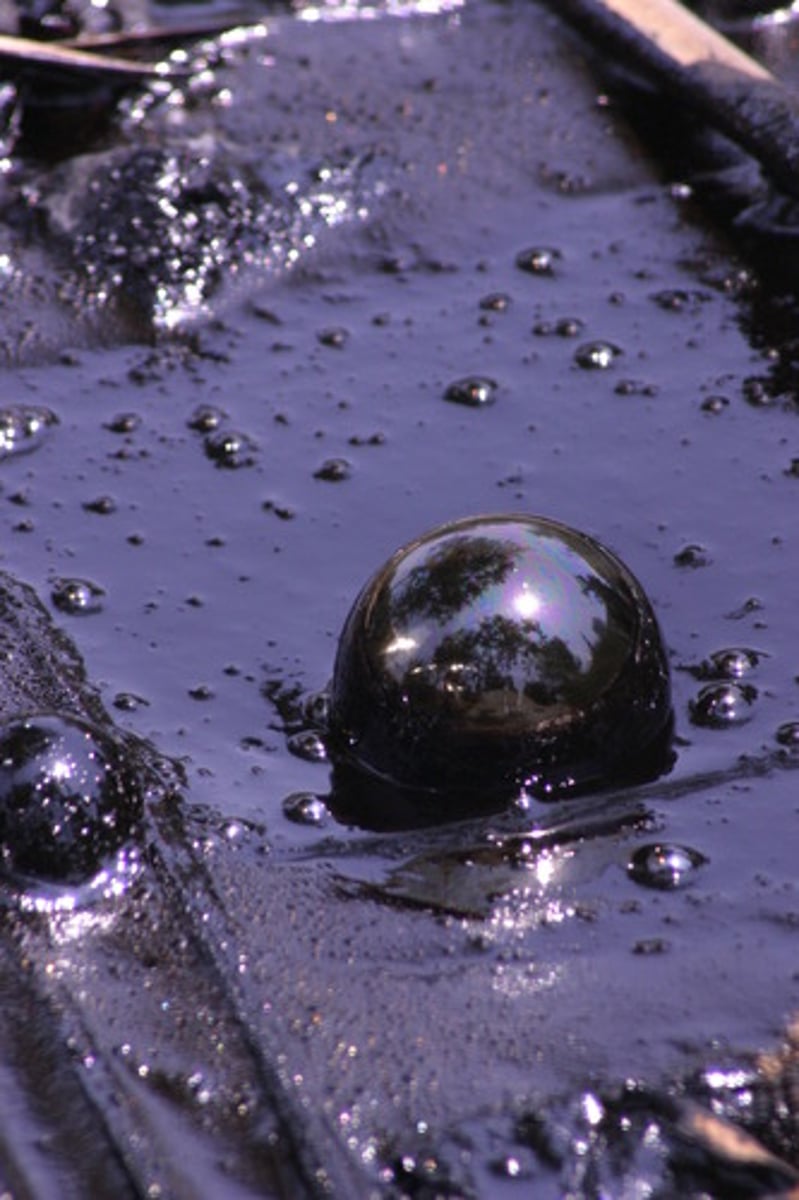
Bitumen
a black sticky substance obtained from oil, used for covering roads or roofs

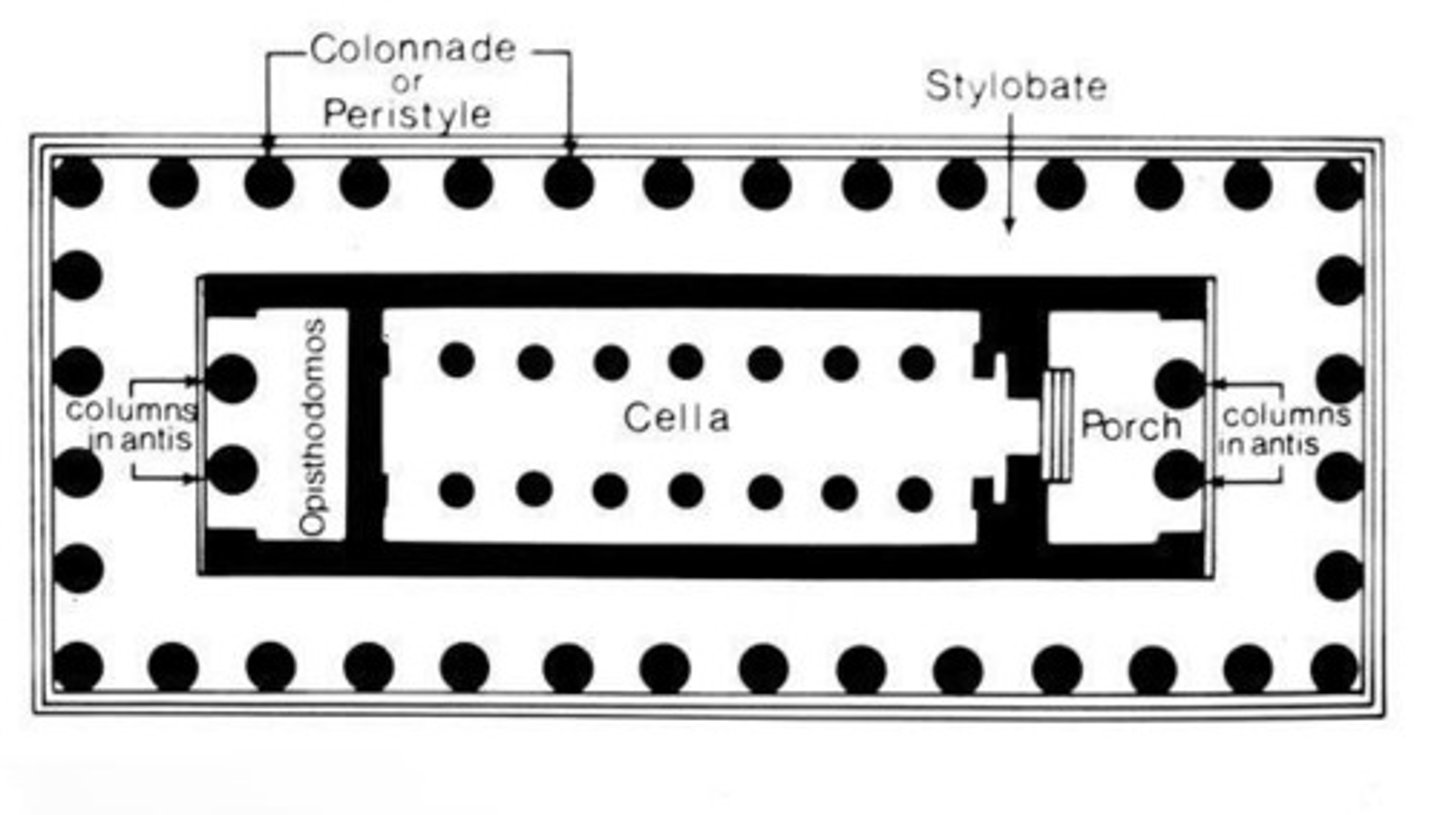
cella
The chamber at the center of an ancient temple; in a classical temple, the room in which the cult statue usually stood.
Cuneiform writing
First writing, created around 3000 B.C., created by the Sumerians, written with reed stylus,
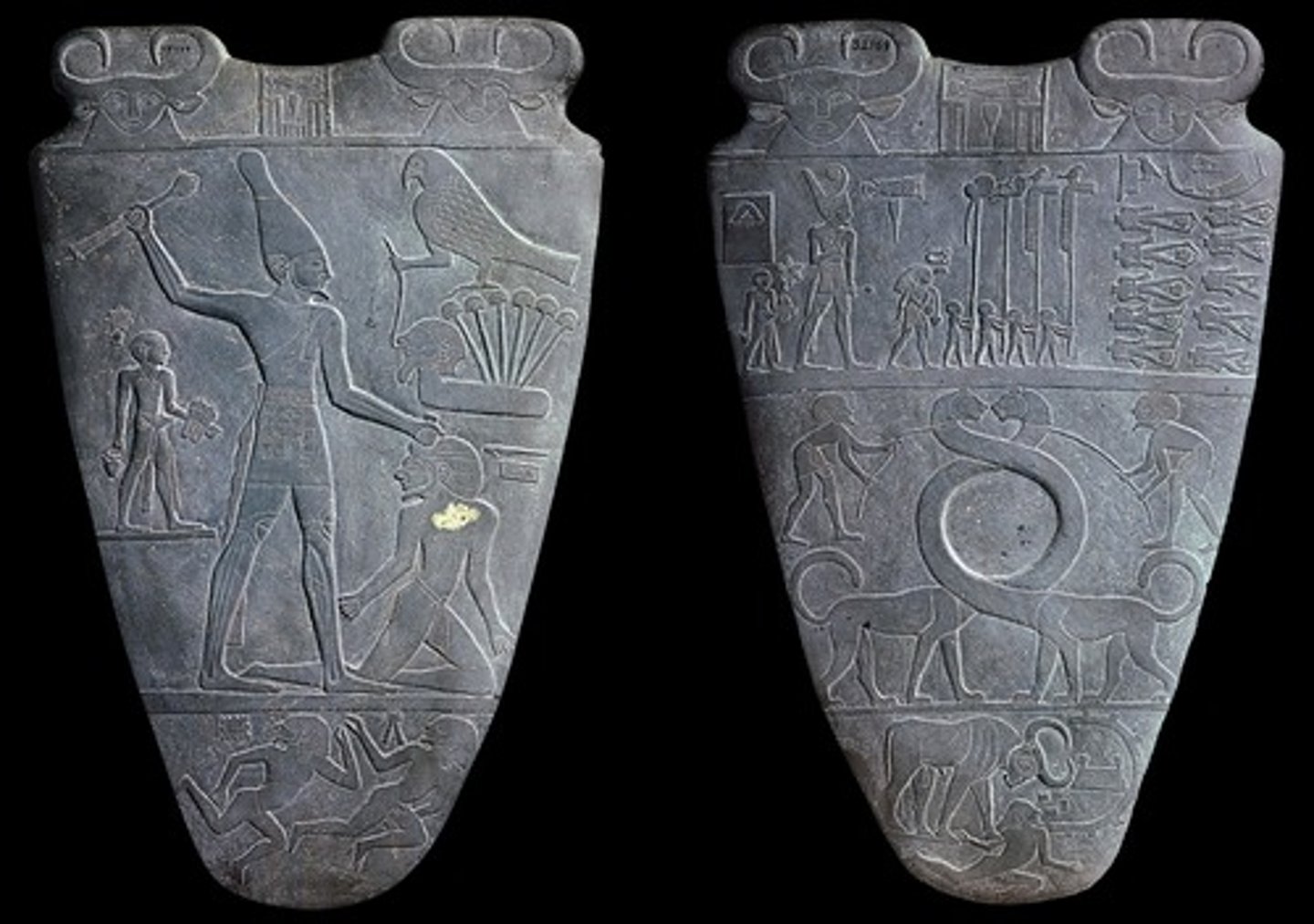
hierarchical scale
the use of size to denote the relative importance of subjects in an artwork

hypostyle hall
a large interior room characterized by many closely spaced columns that support its roof
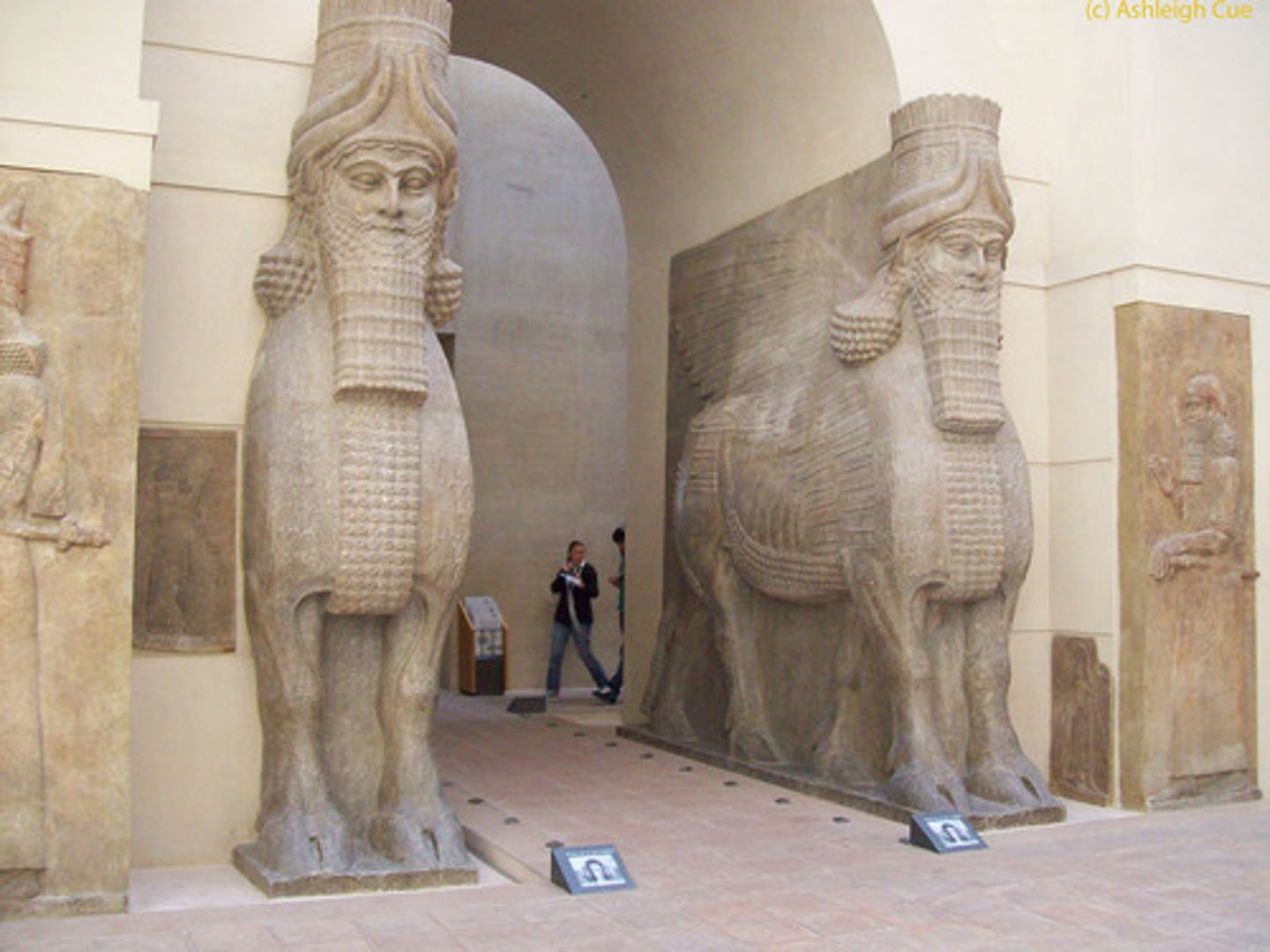
Lamassu
Assyrian guardian in the form of a man-headed winged bull

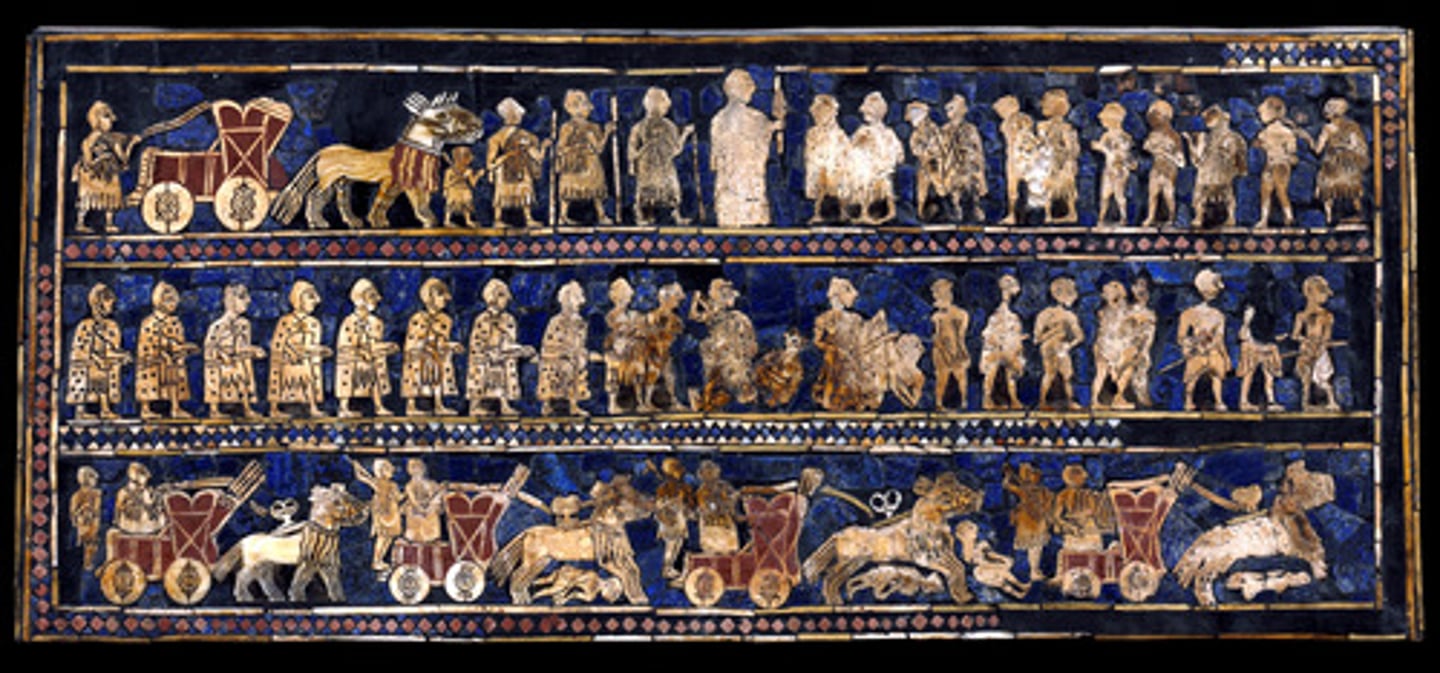
lapis lazuli
a semiprecious blue stone

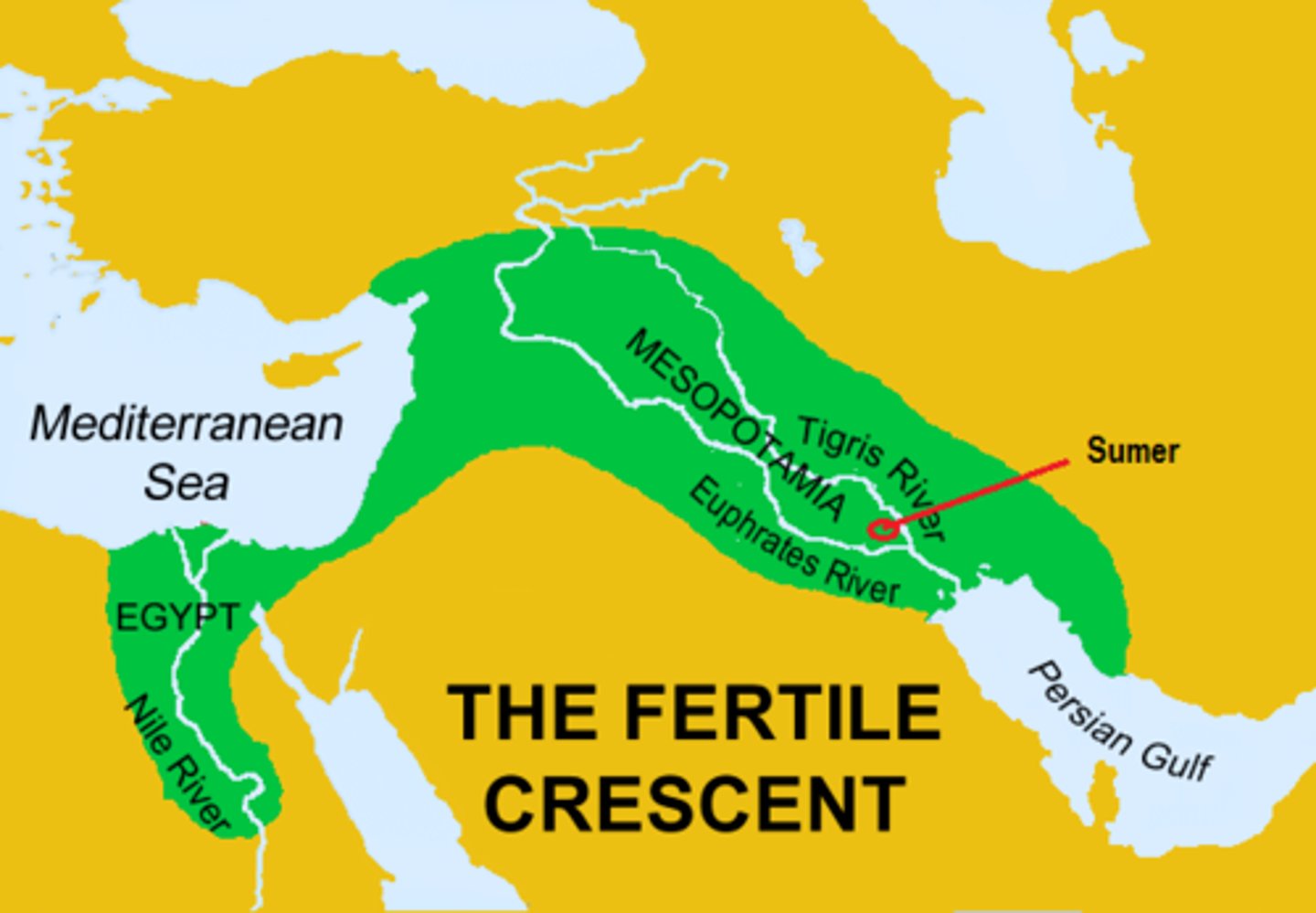
Mesopotamia
A region between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers that developed the first urban societies. In the Bronze Age this area included Sumer and the Akkadian, Babylonian and Assyrian empires, In the Iron Age, it was ruled by the Neo-Assyrian and Neo-Babylonian empires.
mud brick
a brick made from baked mud

registers/friezes
one of a series of superimposed bands or friezes in a pictorial narrative, or the particular levels on which motifs are placed

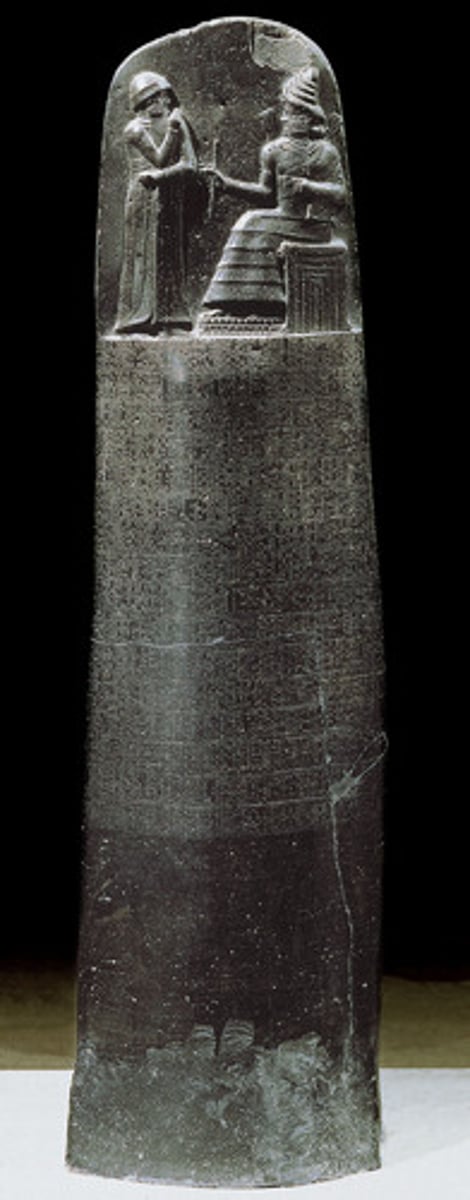
Stele
A carved stone slab used to mark graves or to commemorate historical events.

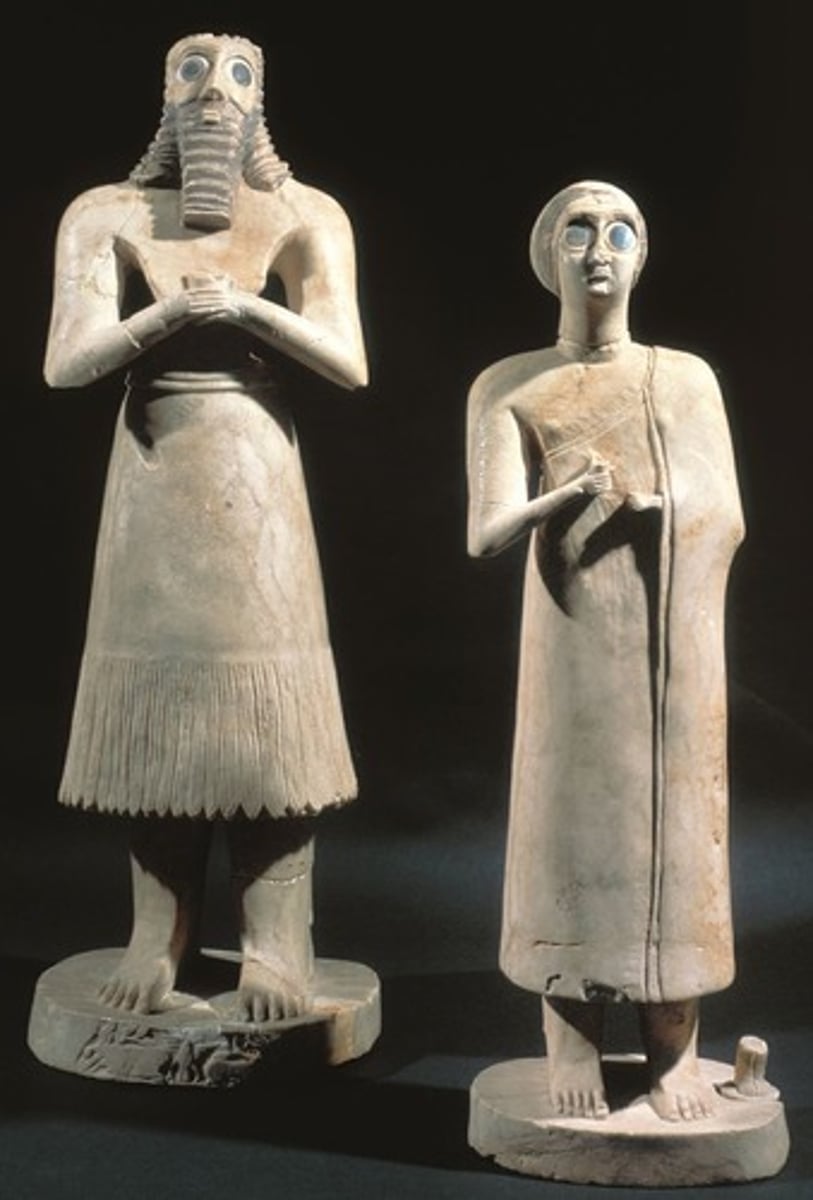
Votive Statues
small devotional statues that Sumerians left in the ziggurat to appease their gods

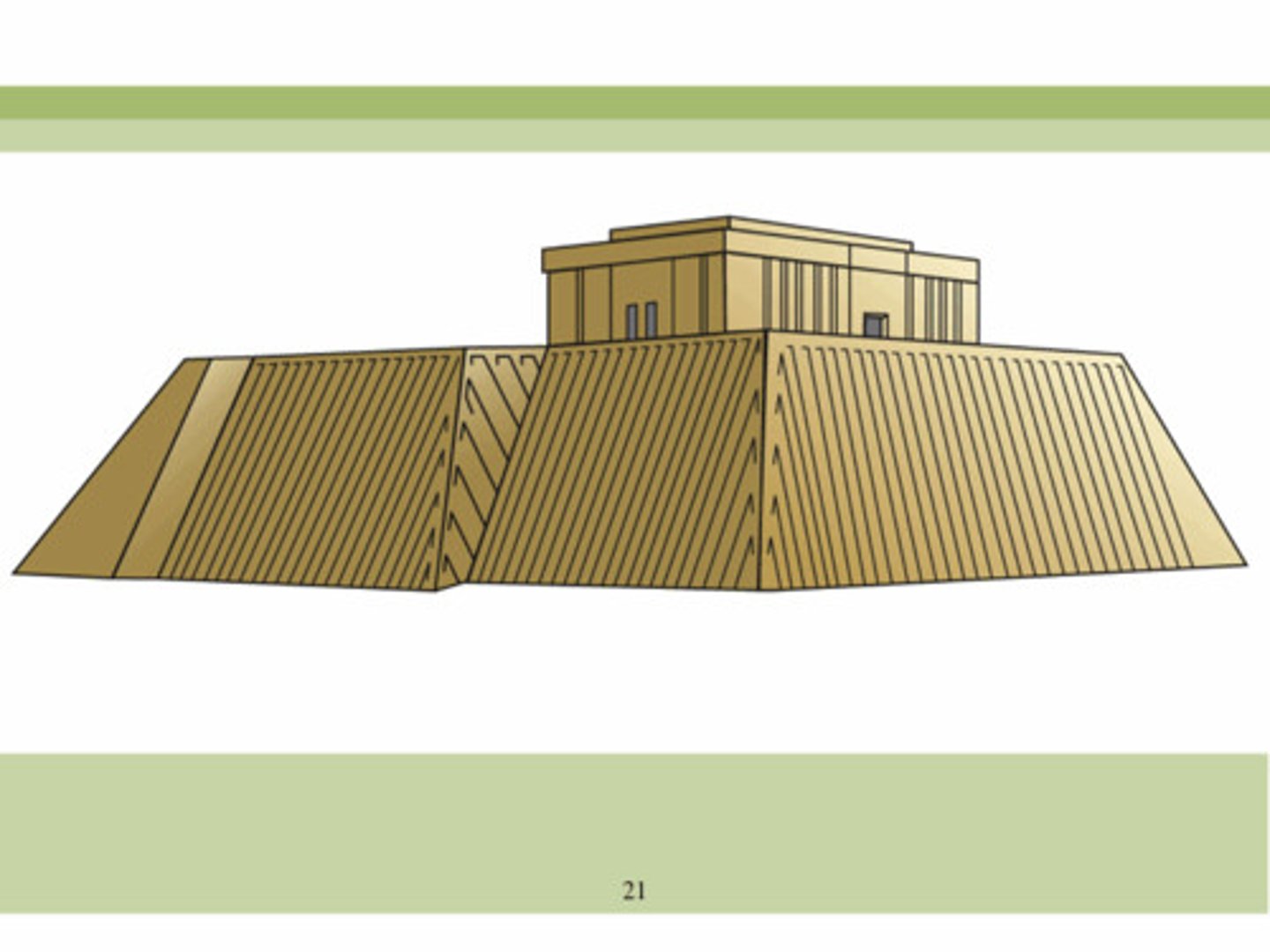
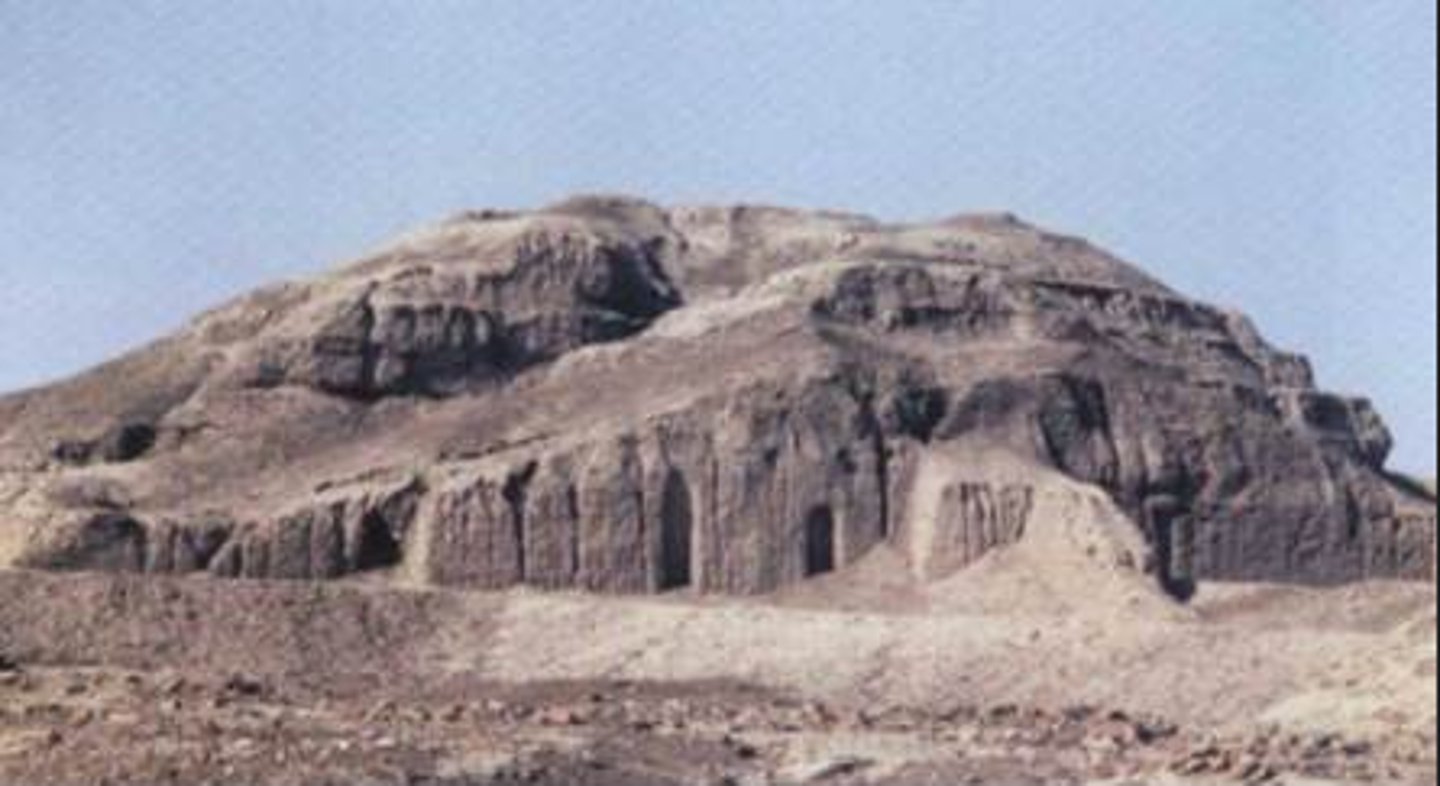
Ziggurat
A rectangular tiered temple or terraced mound erected by the ancient Assyrians and Babylonians
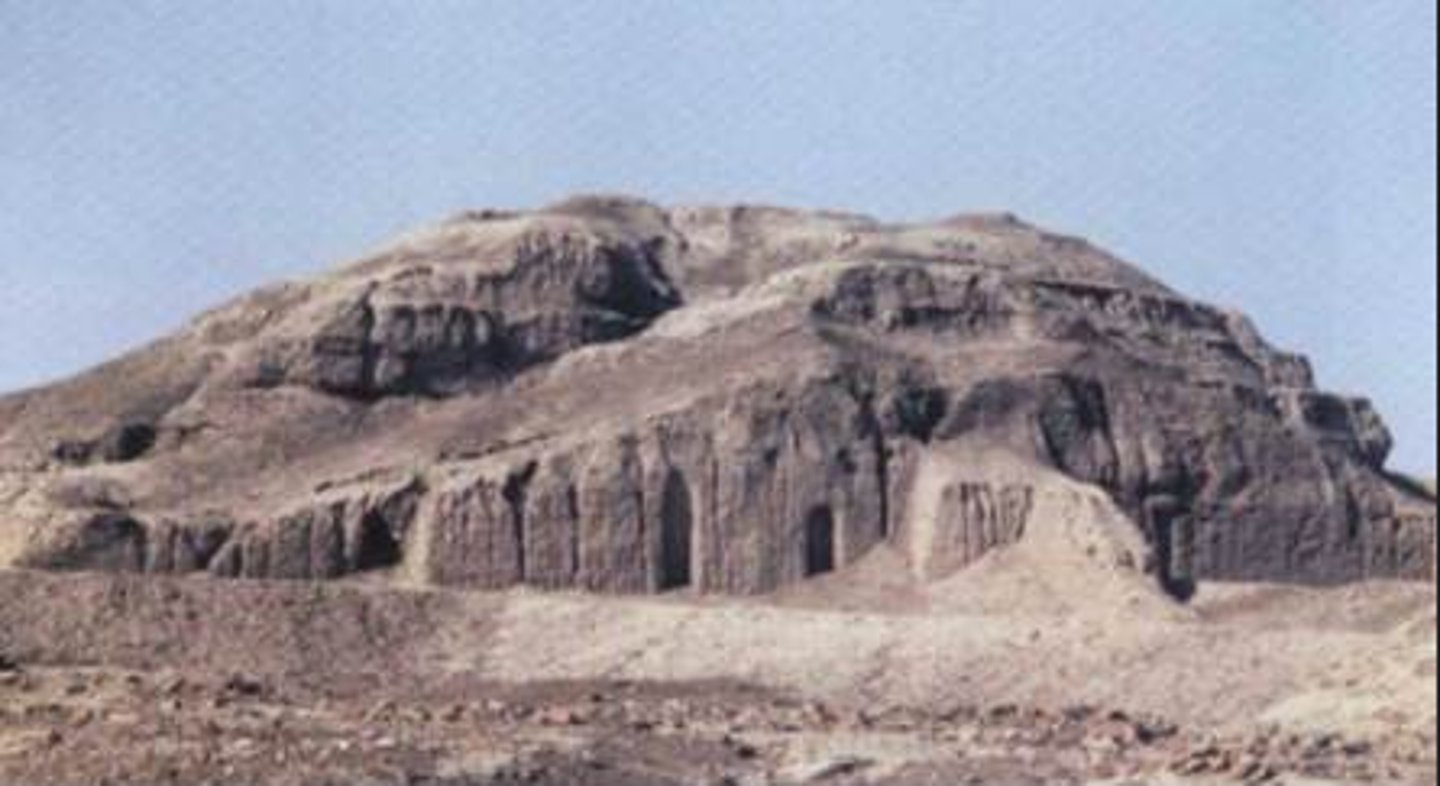

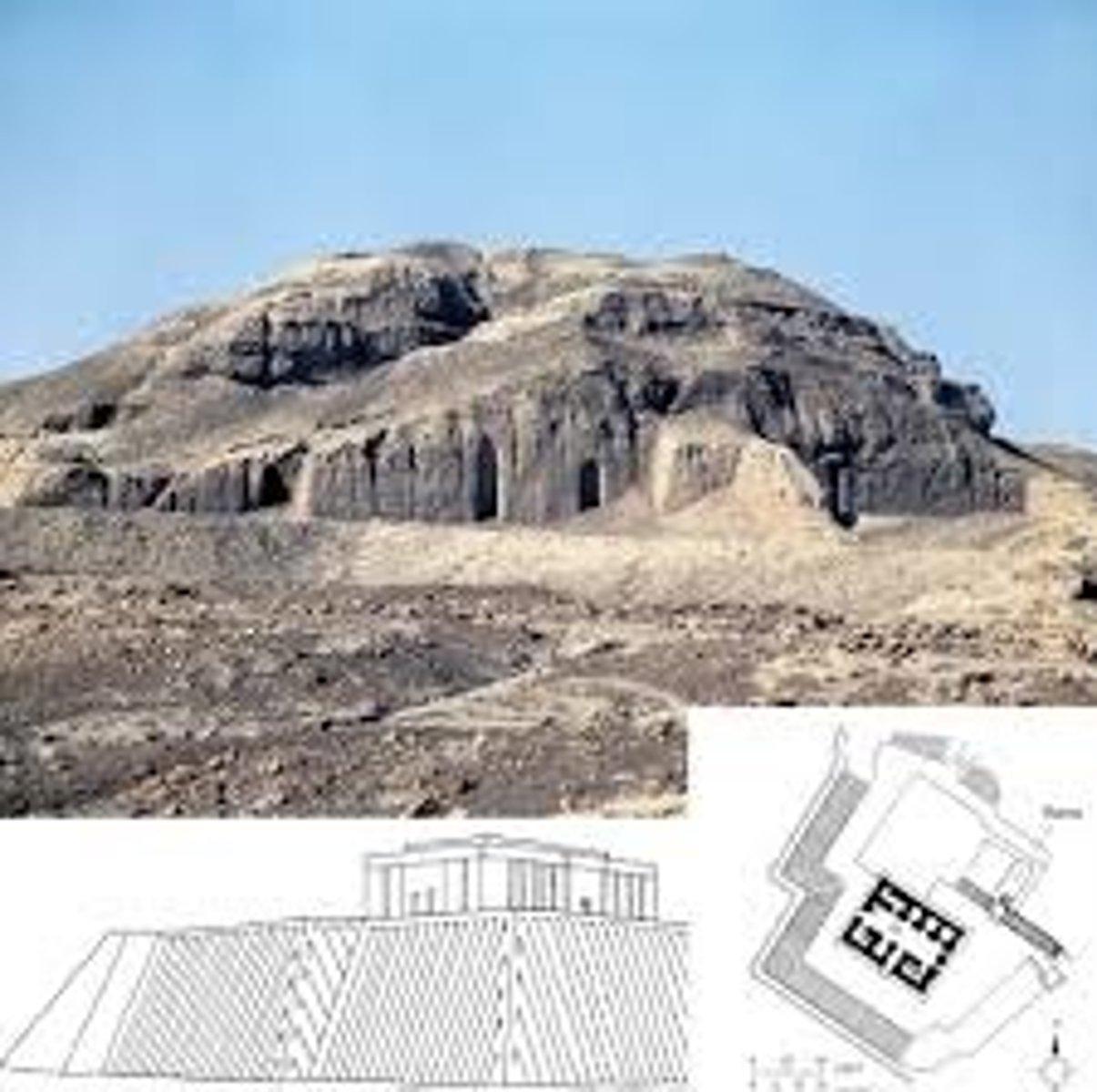
White Temple and its ziggurat
Uruk (modern Warka, Iraq). Sumerian. c. 3500-3000 B.C.E. Mud brick.
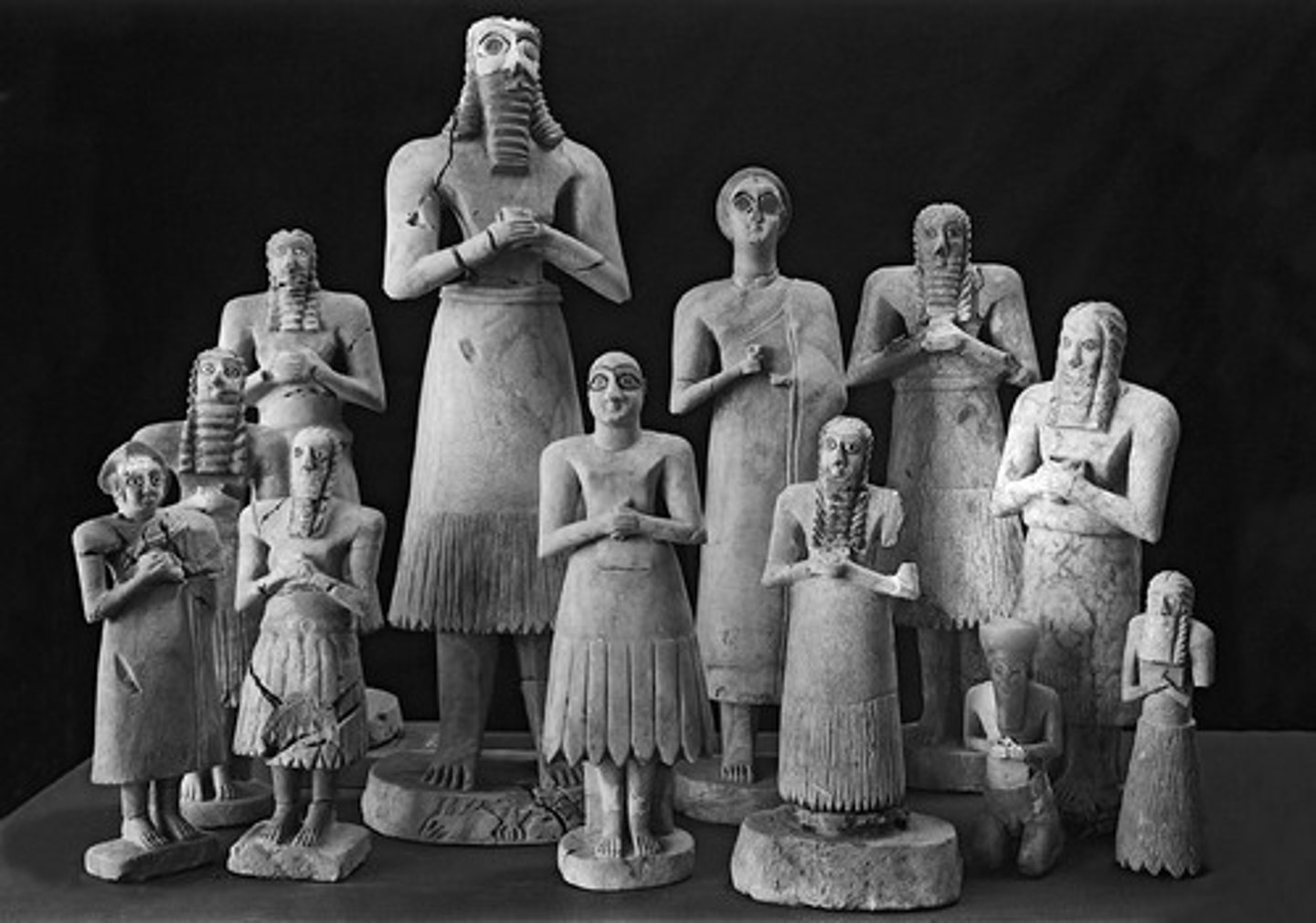
Statues of votive figures, from the Square Temple at Eshnunna
Eshnunna (modern Tell Asmar, Iraq). Sumerian. c. 2700 B.C.E. Gypsum inlaid with shell and black limestone.

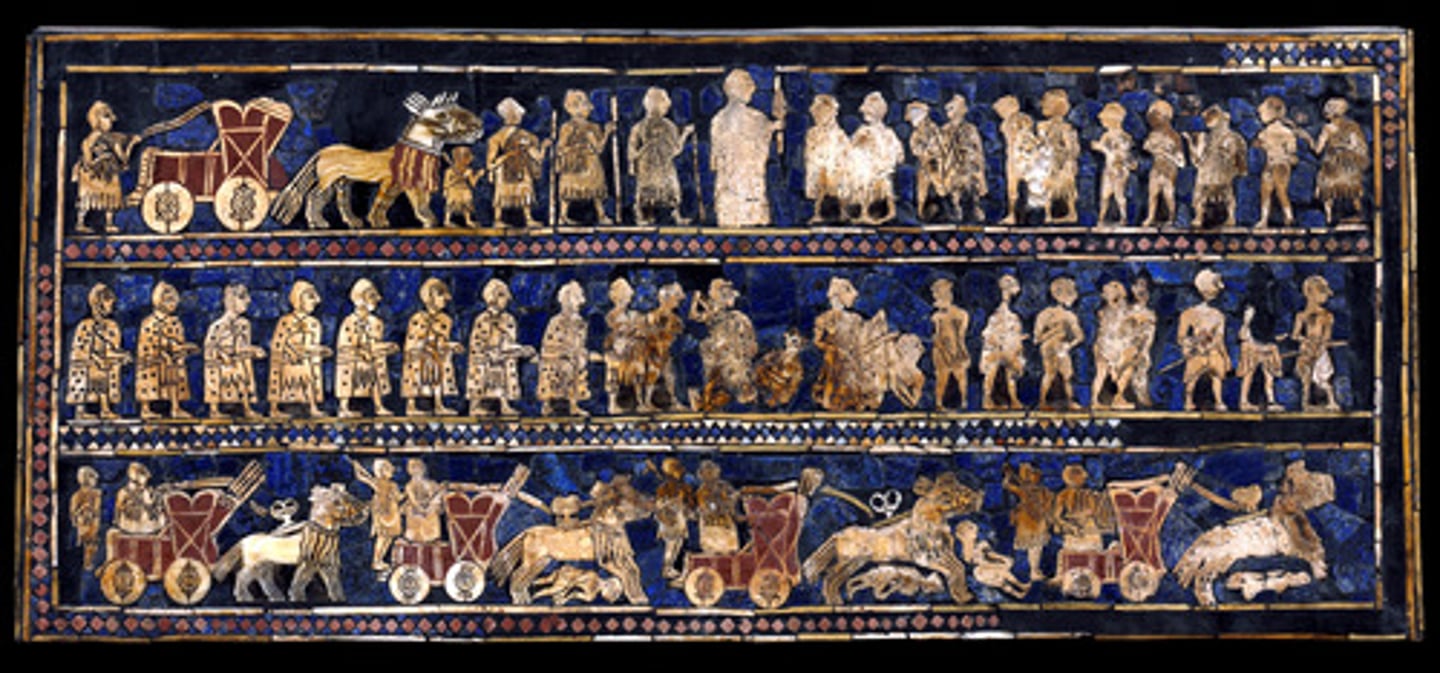
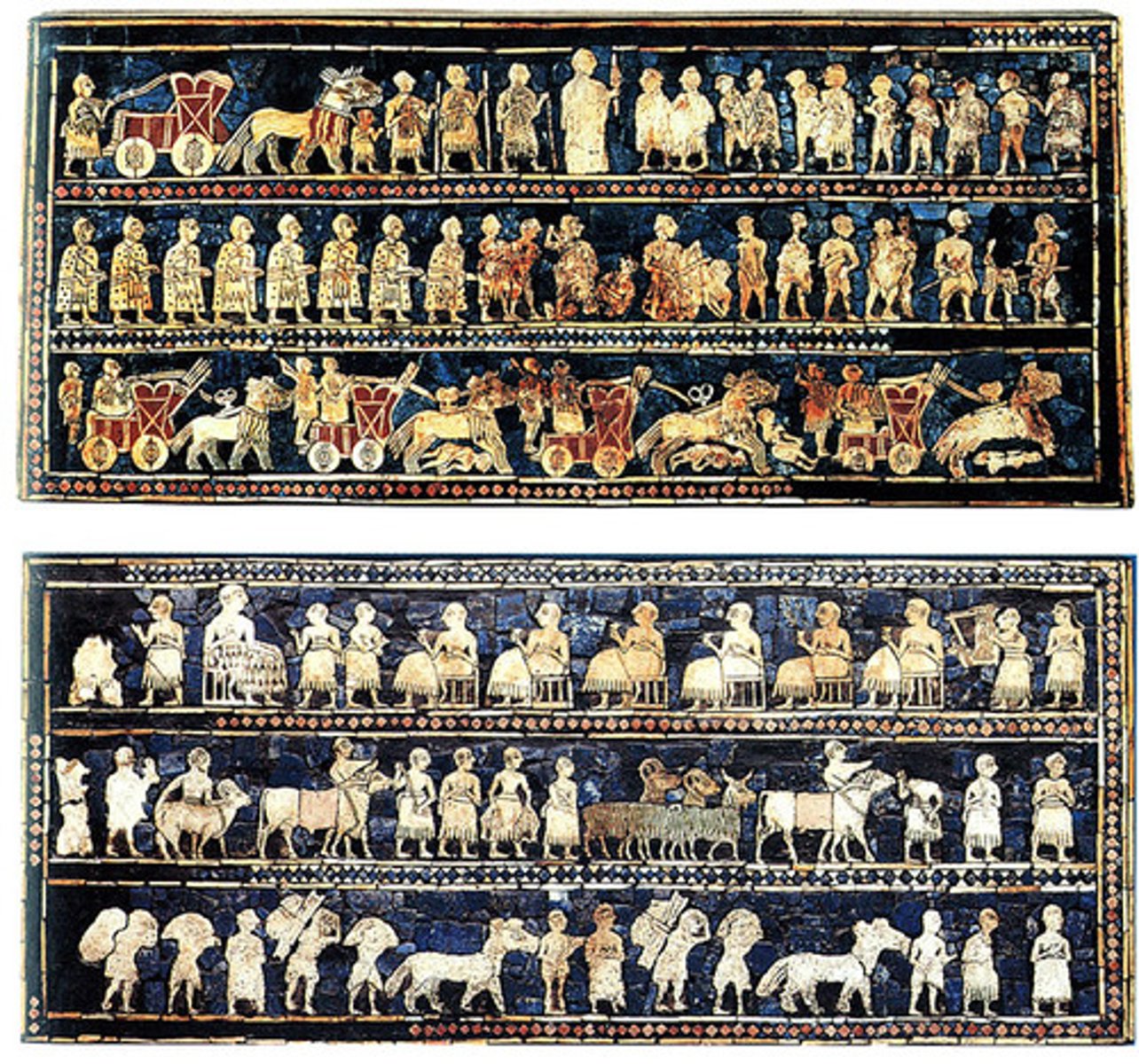
Standard of Ur from the Royal Tombs at Ur
Tell el-Muqayyar, Iraq. Sumerian. c. 2600-2400 B.C.E. Wood inlaid with shell, lapis lazuli, and red limestone.

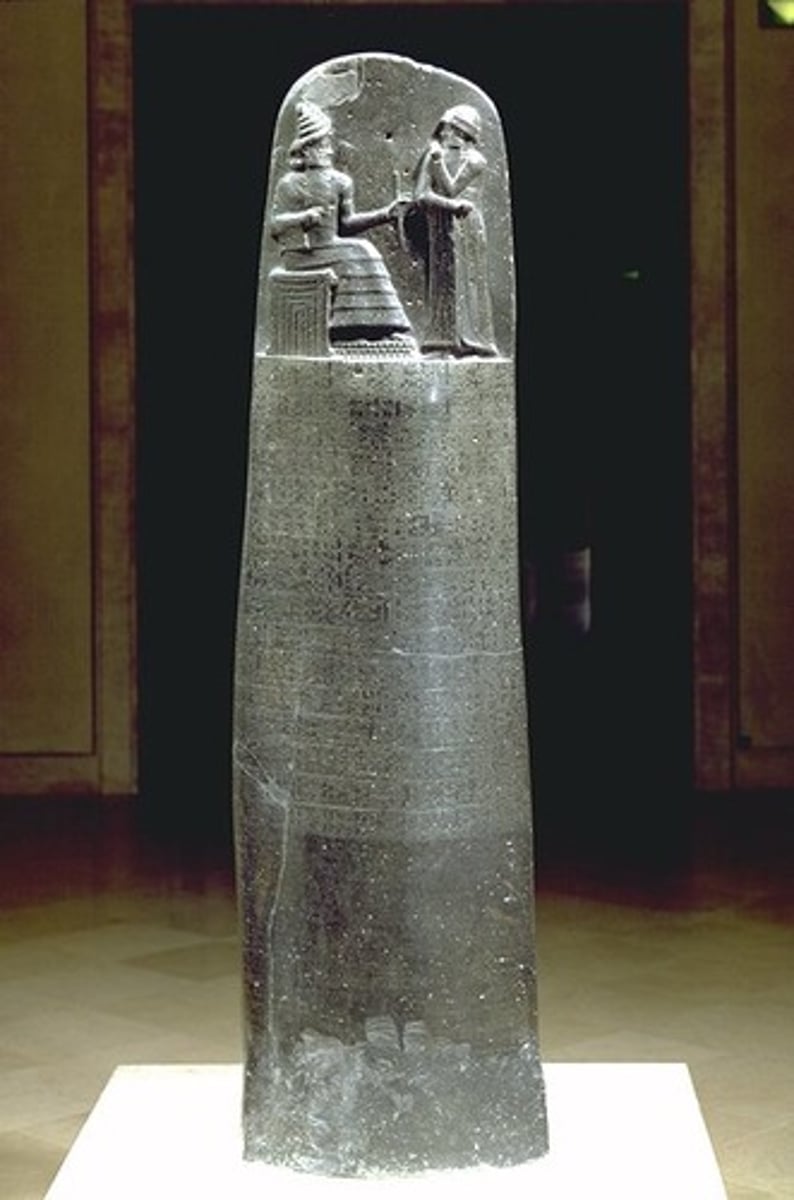
Code of Hammurabi
Babylonian
Dates: 1792-1750 B.C.E.
Culture: (modern) Susian, Iran
Material: Basalt

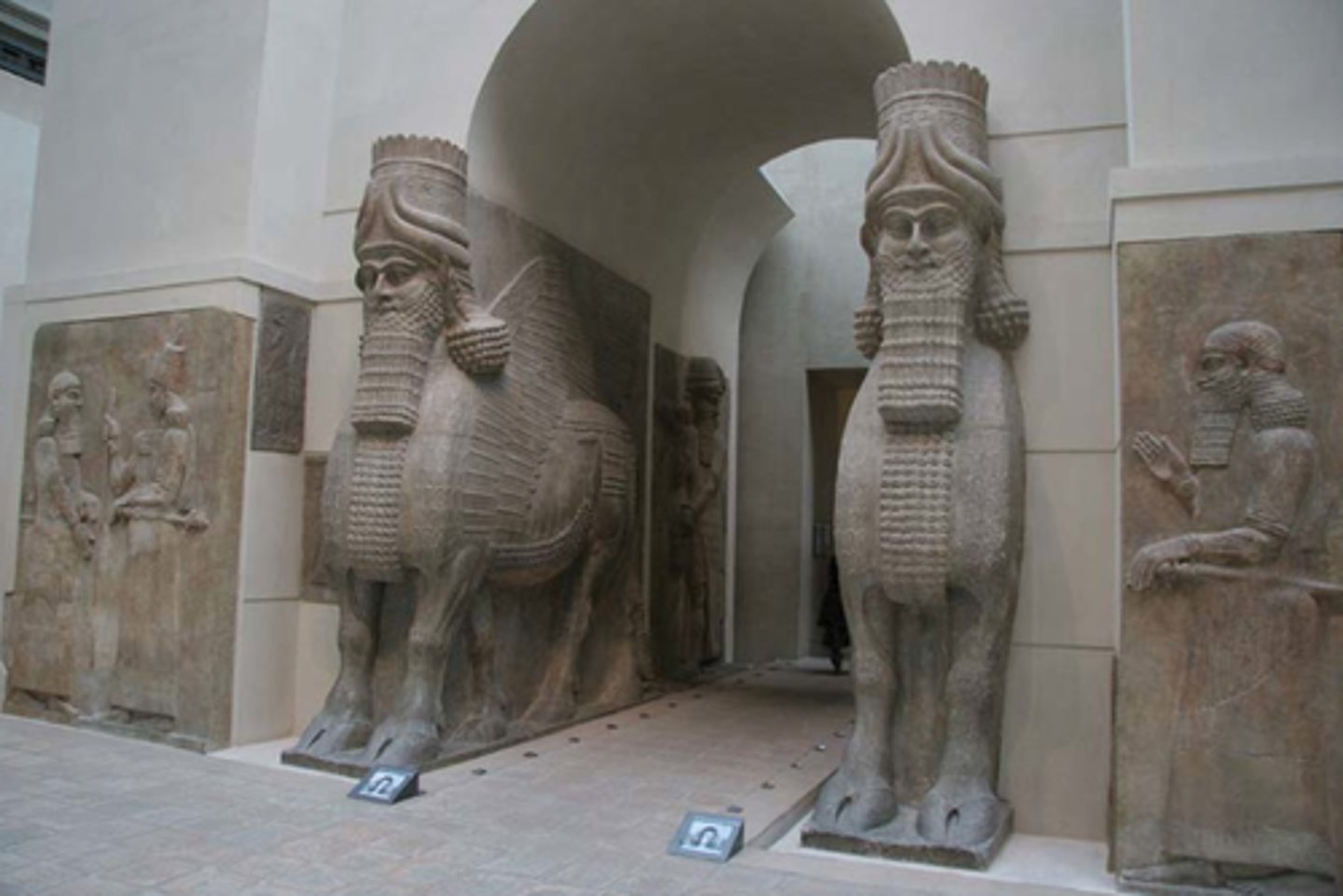
Lamassu from the citadel of Sargon II
Dur Sharrukin (modern Khorsabad, Iraq). Neo-Assyrian. c. 720-705 B.C.E. Alabaster.

Audience Hall (apadana) of Darius and Xerxes
Persepolis, Iran. Persian. c. 520-465 B.C.E. Limestone.
