GI Tract A&P and Esophagus
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
hollow, esophagus, small, large, liver, exocrine
GI Tract (Alimentary Canal)
___________ Tube → extends from mouth to anus
Mouth → __________ → stomach → ______ intestine → ________ intestine → rectum → anus
Accessory Organs
______
Gallbladder
____________ Pancreas
mechanical, chemical, food, water, wastes
Functions of Digestive System
Performs ____________ and ____________ breakdown of ingested food
Prepares _____ for uptake by the body’s cells
Provides body _______
Eliminates _________
chewing, mucus, bile, pancreas, storage, fluid, solid
Function of the Digestive System
Mouth
_________
Stomach
Food mixed with acid, _______, and enzymes
Small intestine
_____ and enzymes secreted by liver
Enzymes secreted by the __________
Absorption
Liver
Processing and ___________ of nutrients
Large Intestine
Non-absorbed substances continue to pass
______ absorbed
Rectum
________ waste eliminated
hormones, motility, autonomic, enteric, voluntary
Digestive System Control
Ingested substances trigger ___________ that stimulate or inhibit
Muscular contractions (GI __________)
Secretion of substances that aid in digestion
Autonomic Nerves
Extrinsic → ____________ nerves
Intrinsic → autonomic nerves AKA ____________ nervous system
Chewing, swallowing, and defecation are only part under ___________ control
sympathetic, vertebral, ganglia, splanchnic, outlying, norepinephrine, epinephrine, inhibits
Sympathetic Autonomic Innervation of the Abdomen and Pelvis
______________ Trunks
Run along both sides of ___________ column (from base of skull to coccyx)
Contain sympathetic ____________
______________ nerves (Sympathetic)
Thoracic, lumbar, sacral
__________ ganglia
Celiac, mesenteric
Neurotransmitter
Mostly ____________
Some _____________
Action
____________ GI activity
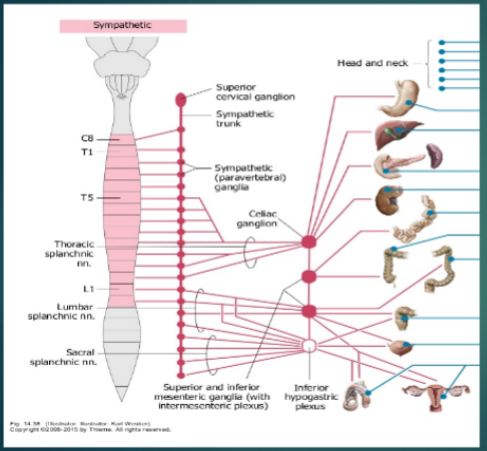
vagus, splanchnic, pelvic, acetylcholine, increases
Parasympathetic Autonomic Innervation of the Abdomen and Pelvis
___________ Nerve
Innervates mostly foregut and midgut
____________ nerves (parasympathetic)
__________ → innervates mostly hindgut
Neurotransmitter → ______________
Action
_____________ GI activity
Epithelium, Lamina Propria, connective, lymphoid, muscularis, smooth, mucosal, mucus, infectious
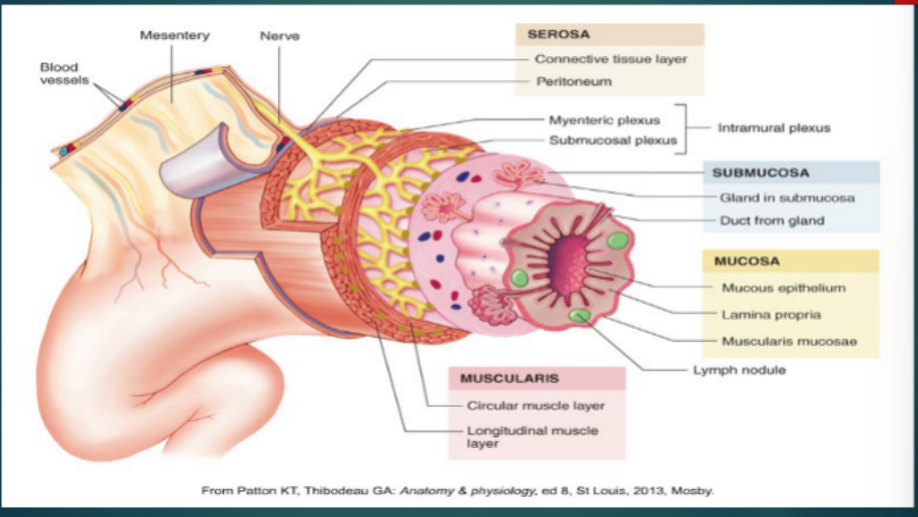
Histology of the GI Tract → Mucosa
______________
__________ ___________
a. Loose _____________ tissue
b. Contains capillaries and ____________ tissue
____________ mucosa
a. Thin Layer of ___________ muscle
b. Promotes ____________ movement
Functions
Secrete _________, digestive enzymes, and hormones
Absorb digested products
Protect against ___________ disease
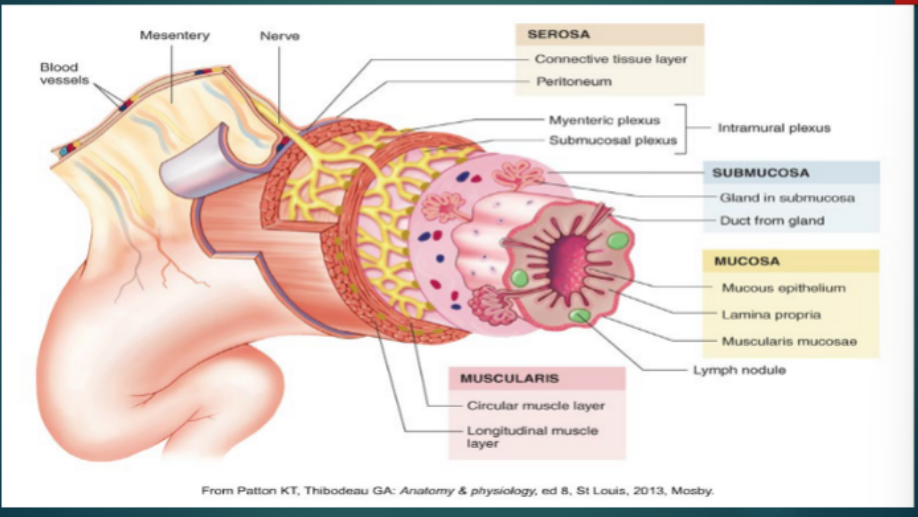
connective, follicles, nerve, support, GI glands, lumen
Histology of the GI Tract → Submucosa
__________ tissue
Contains blood and lymph vessels, lymphoid ____________, and ___________ fibers
Main Functions
Provides __________ to the mucosa
Houses __ _________ with ducts extending to ________
smooth, circular, longitudinal, segmentation, peristalsis
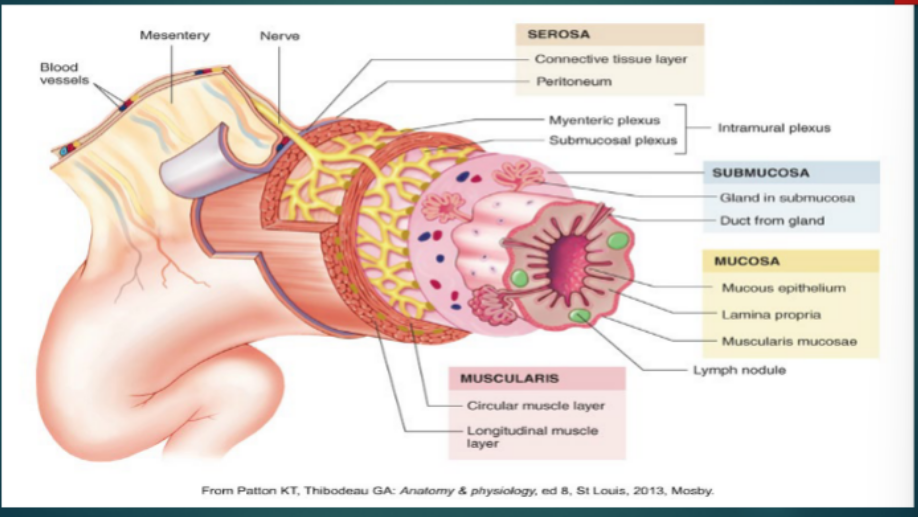
Histology of the GI tract → Muscularis Propria
____________ Muscle
Inner ____________ muscle
Outer ______________ muscle
Main function
Responsible for _______________ and ______________
intraperitoneal, squamous, retroperitoneal, serosa, adventitia, esophagus, fibrous
Histology of the GI Tract → Serosa (Visceral Peritoneum)
_______________ Organs → connective tissue covered with ___________ epithelial cells
______________ organs → _______ on parts facing peritoneal cavity and _____________ on parts against the body wall
Serosa is replaced by an adventitia in the _____________ (__________ connective tissue)
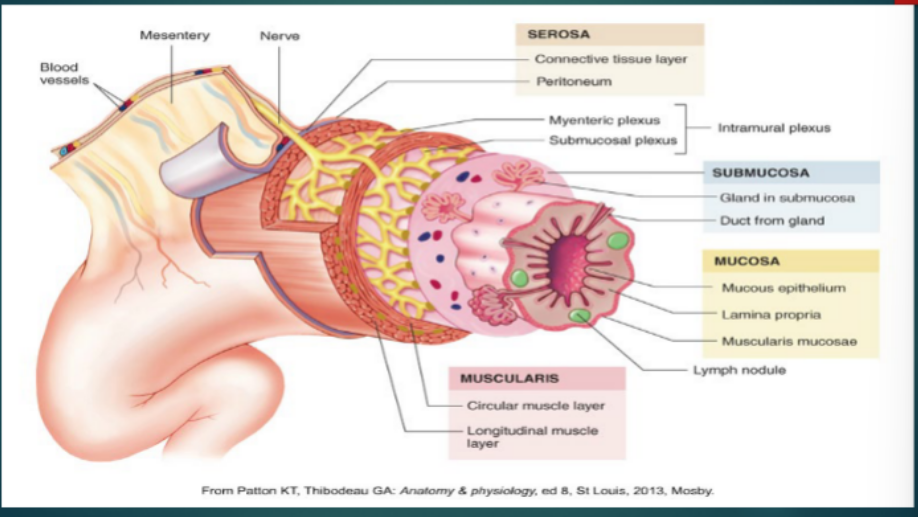
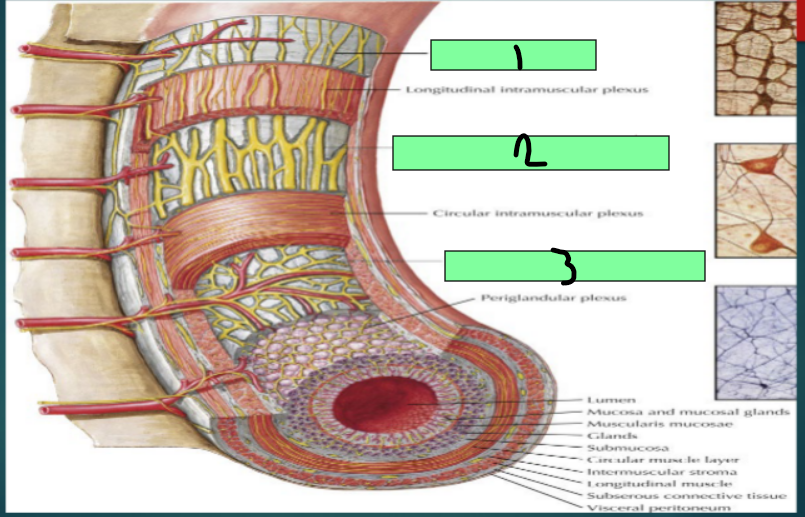
Enteric Nervous System
Regulates motility reflexes, blood flow, absorption, secretions, and immune response
Submucosal Plexus (Meissner plexus)
Enteric Nervous System Plexus
located in the submucosa
Controls GI secretion and local blood flow
myenteric plexus (Auerbach plexus)
Enteric Nervous System Plexus
Between inner circular and outer longitudinal muscles of the muscularis propria
Controls GI movements
Subserosal plexus
Enteric Nervous System Plexus
Located beneath the serosa
Subserosal Plexus
1
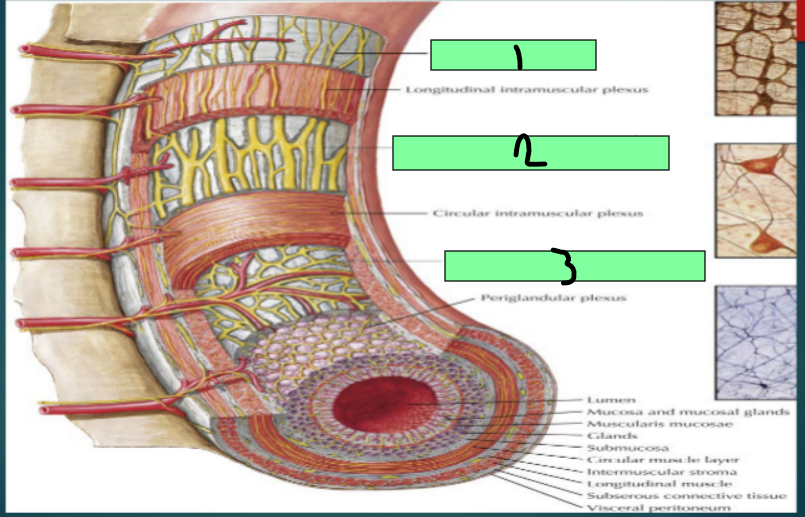
Myenteric plexus (Auerbach plexus)
2
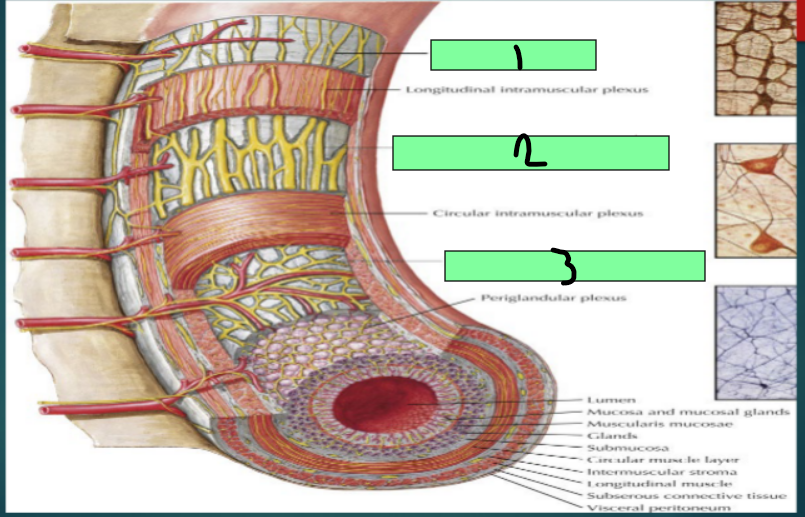
Submucosal plexus (Meissner plexus)
3
saliva, taste buds, olfactory
Mouth
Reservoir for chewing and mixing of food with ________
Digestion begins in the mouth, with chewing and salivation
______ _____ → identify salty, sour, bitter, and sweet tastes when stimulated
___________ nerves (smell)
parotid gland
1
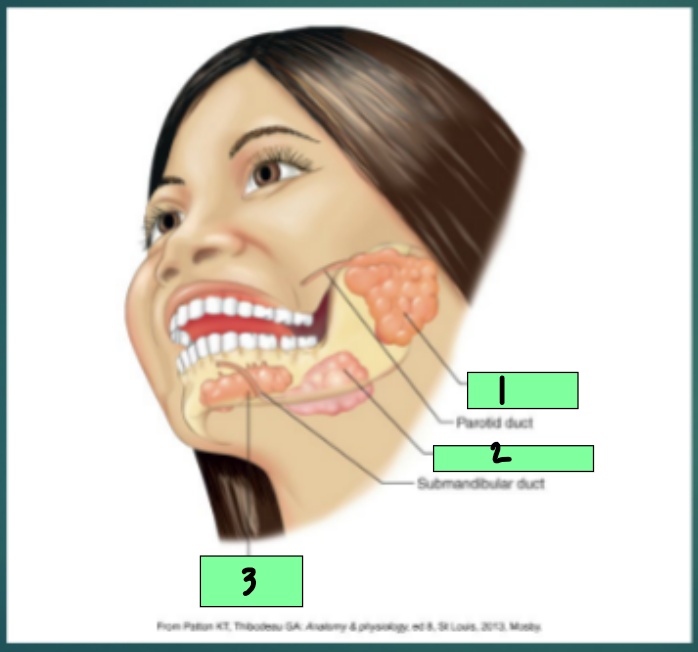
submandibular gland
2
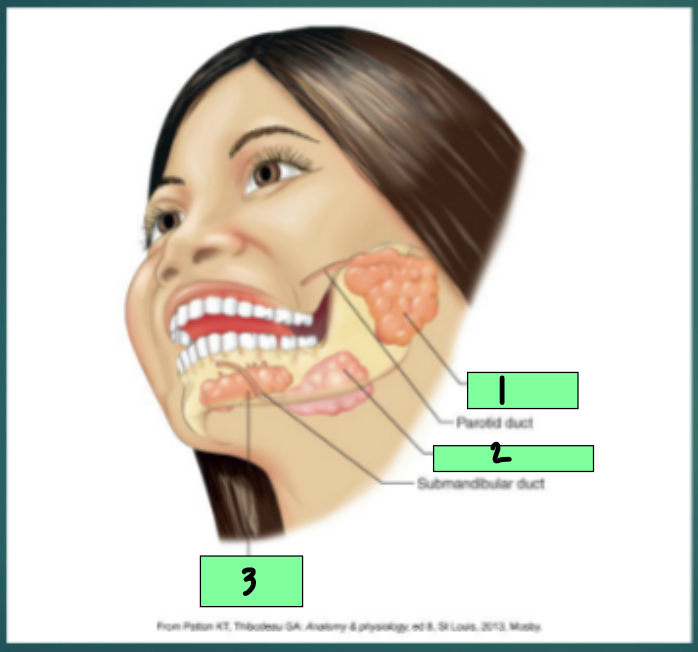
sublingual gland
3
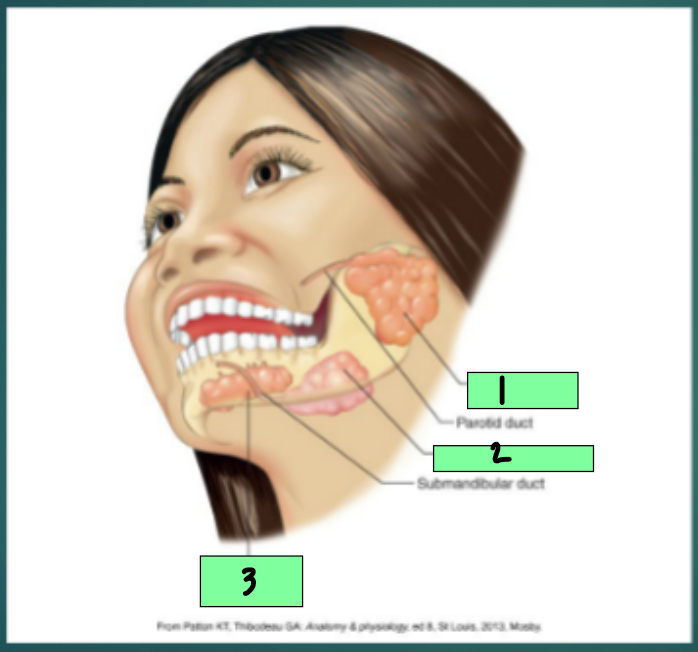
bicarbonate, amylase, carbohydrate, mucin, A, infection, fluoride, parotid, submandibular, sublingual
Saliva
Composed of water, sodium, ___________, chloride, potassium, and salivary a-____________
pH around 7.4
a-amylase (___________ digestion)
Contains _________ and Ig_ → helps prevent _________
Absorbed __________ from diet secreted in saliva
Helps prevent tooth decay
Controlled by sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers
CN IX (glossopharyngeal) = __________ gland
CN VII (facial) = _____________ and ____________ glands
muscular, striated, smooth, cricopharyngeal, air, regurgitation
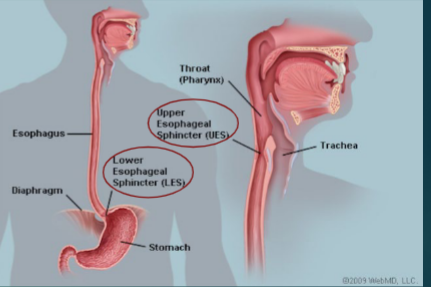
Esophagus
Hollow __________ tube (25-27 cm long)
1/3 _________ and 2/3 __________ muscle
Upper esophageal sphincter (_____________ muscle)
Prevents entry of ____ into the esophagus during respiration
Lower esophageal sphincter (LES)
Prevents ______________ from the stomach
oropharyngeal, voluntary, involuntary, esophageal, primary, secondary, independent
Swallowing
Phases
_____________ (voluntary/involuntary)
Food chewed and bolus forced posteriorly (____________)
Sensory impulses sent via CN 5 and 9 → motor impulses sent via CN 5, 9, 10, 12 (_____________)
_______________ (involuntary)
Peristalsis
___________ → immediately follows the oropharyngeal phase of swallowing
_____________ → bolus of food becomes stuck in the esophageal lumen, a wave of contraction and relaxation occurs that is ____________ of voluntary swallowing
regurgitation, cholinergic, gastrin, nonadrenergic, noncholinergic, secretin, vagus
Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES)
Prevents _______________ from the stomach
Barrier between the stomach and the esophagus
Control
Increase sphincter tone
_____________ vagal stimulation
__________ (digestive hormone)
Relax sphincter tone
____________, ________________ vagal impulses
Hormones: progesterone, ___________, and glucagon
Mediation of relaxation during swallowing → _______ nerve