ECHO 2 (Diastolic Dysfunction)
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
what are the phases of diastole?**
isovolumetric relaxation
early rapid diastolic filling
diastasis
late diastolic filling by atrial contraction
what happens during isovolumetric relaxation? (valves and pressure)**
aortic and mitral valves closed but mitral will open soon
rapid decline in LV pressure
what happens during isovolumetric contraction?*** know on waveform
LV filled up and mitral and aortic valve closed but aortic will open soon
where you do see early rapid diastolic filling in EKG?
latter part of the T wave
what factors influence rate of blood flow from LA to LV?
pressure difference, ventricular relaxation, relative compliance of two chambers
what occurs during diastasis? (valves and pressure)
LV and LA pressures equalize → causing little flow from the LA to LV
MVLs remain in a semi open position
diastasis is indicated by what on the PW doppler of the mitral valve?
slope after E deceleration and before A wave
duration of diastasis dependens on
heart rate
slow heart rate = longer diastasis
fast heart rate = shorter diastasis/ absent
what happens during late diastolic filling by atrial contraction? (pressure and valves)
LA pressures exceed LV pressure
MVL opens and causes a second pulse of LV filling
atrial contribution is - of total ventricular filling
20%
review images
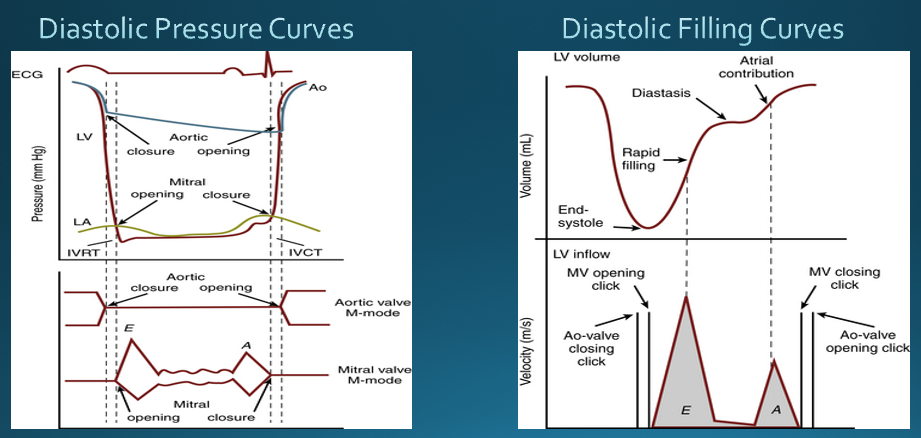
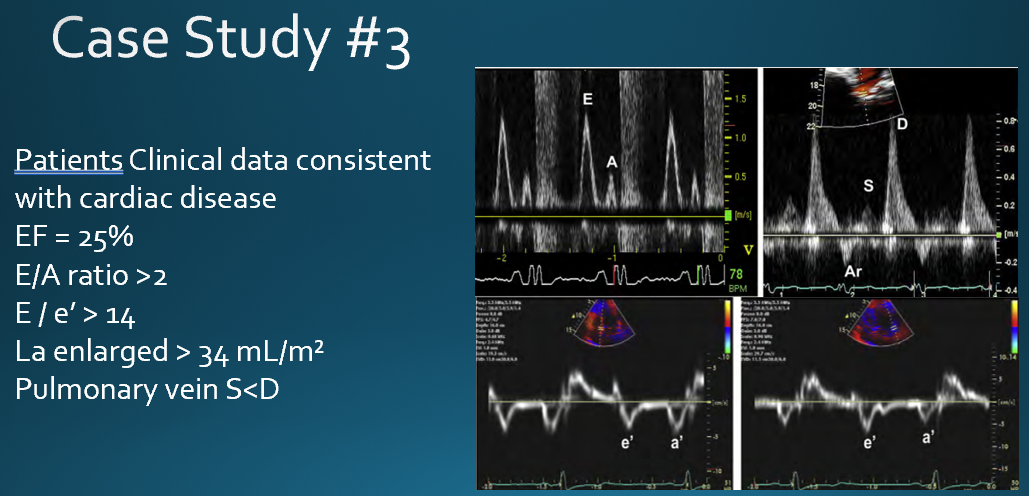
what are the clinically relevant parameters in diastolic function?
ventricular relaxation
myocardial/chamber compliance
filling pressures
when does ventricular relaxation occur?
during isovolumetric relaxation and early diastollic filling
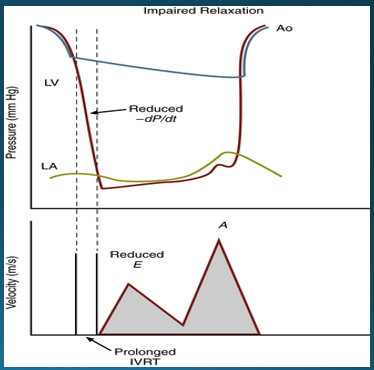
what factors will indicate impaired LV relaxation?
prolonged IVRT
slower rate of decline in ventricular pressure (reduced dP/dt)
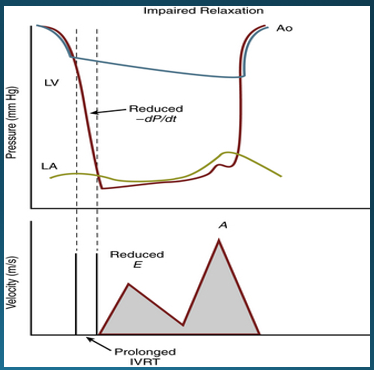
what doppler signs indicate impaired LV relaxation?
prolonged IVRT
reduced E velocity
increased A velocity
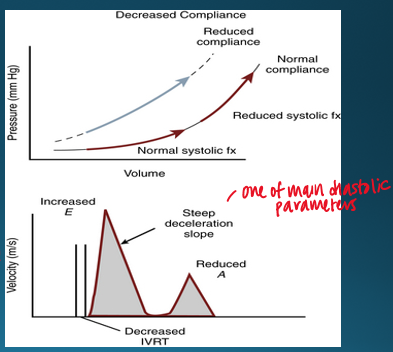
how is ventricular compliance measured?
ratio of change in volume to change in pressure (dV/dP)
ventricular compliance is affected by
size, shape, myocardium characteristics, extrinsice factors
what doppler characteristics will you see with decreased ventricular compliance?
decreased IVRT
steep deceleration slope
reduced a velocity
what are the causes of diastolic dysfunction?**
anything that causes heart to thicken**
primary myocardial disease
restrictive cardiomyopathy
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
secondary LV hypertrophy (thick heart → non compliant)
hypertension
coronary artery disease
fibrotic/stiff bc of infarcted tissue and less ability to relax
both systolic and diastolic
extrinsic constraint
what are examples of primary myocardial disease?
dilated cardiomyopathy (mainly systolic)
restrictive cardiomyopathy
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
what are examples of secondary hypertrophy?
hypertension
aortic stenosis
congenital heart disease
what are examples of coronary artery disease?
ischemia
infarction
what are examples of extrinsic constraint?
pericardial tamponade
pericardial constriction
what measures evaluation of LV diastolic function?
trans mitral inflow (valsalva)**
tissue doppler**
pulmonary venous flow
left atrium volume index
tricuspid regurgitation velocity
why do we measure LA volume index to evaluate LV diastolic function?
because if LV does not accept blood, it will back up into the LA and cause dilation
diastolic filling patterns for assessing diastolic function is valid only
in the absence of obstruction (mitral stenosis)
KNOW WIGGINS
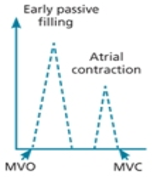
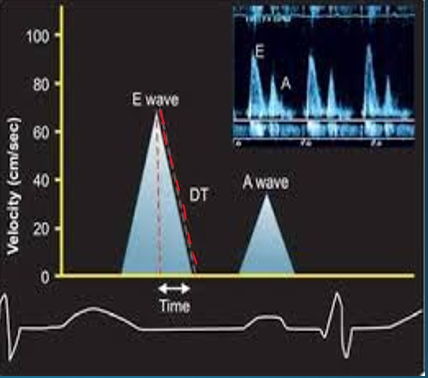
what does the E and A wave represent in mitral inflow?
E = rapid diastolic filling
A = atrial systole/kick
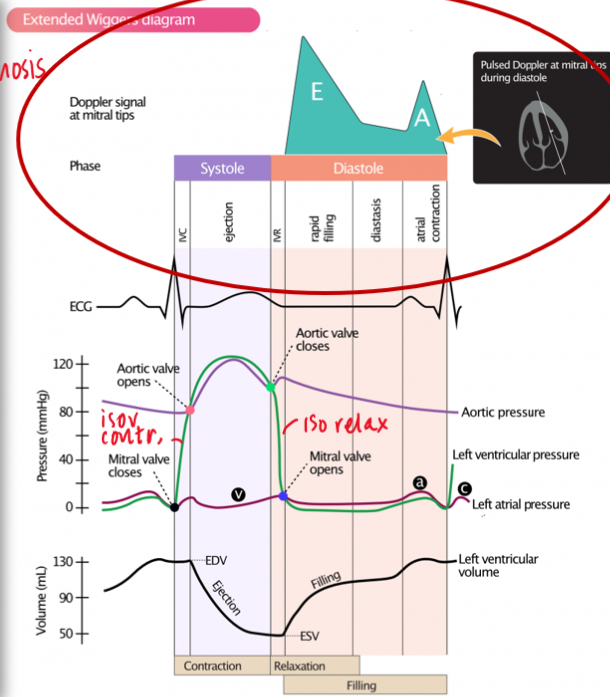
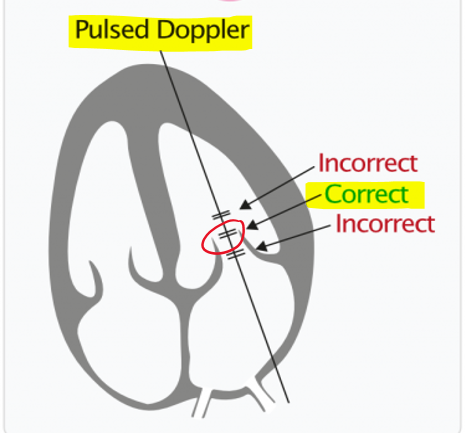
how is mitral inflow measured? (view, doppler)
apical 4CH
PW at opening of mitral valve leaflets
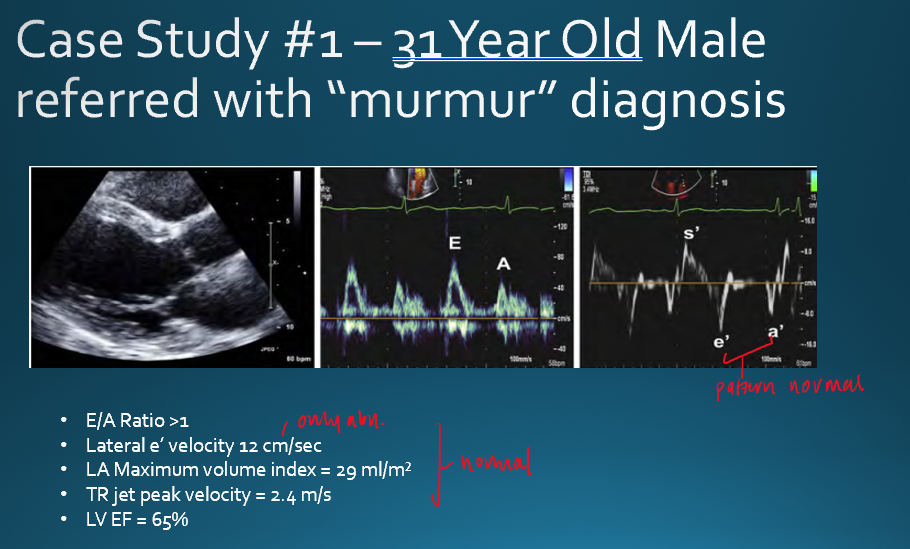
what is normal E/A ratio is healthy young adults?**
1.5
the E and A wave fuse when
pt is tachycardic (hihg heart rate)
what happens to A wave in Afib?
absent because there is not atrial kick
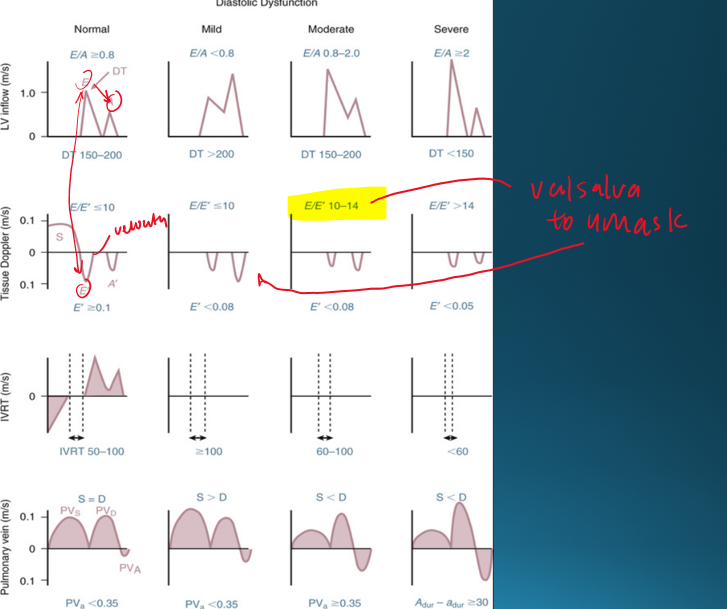
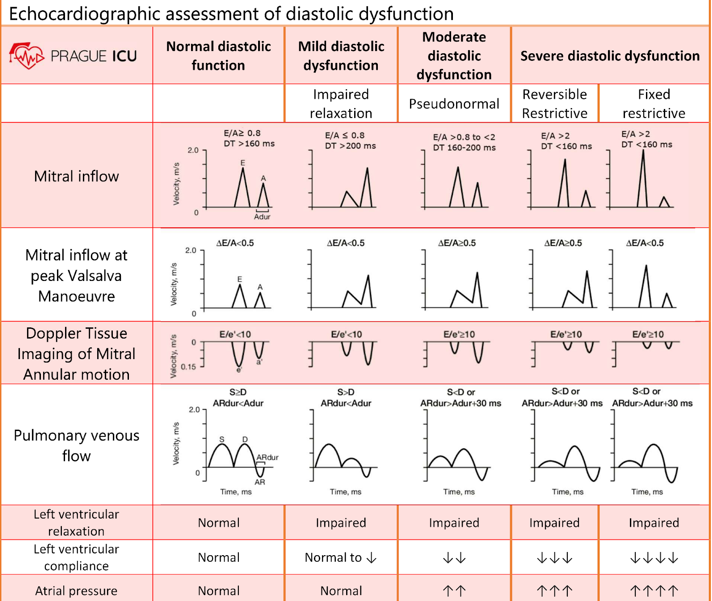
describe normal diastolic function
E/A ratio
LV relaxation
Atrial pressure
atrial contraction
E/A ratio : E>A
LV relaxation : normal
Atrial pressure : normal
atrial contraction : normal
describe mild diastolic dysfunction (grade 1)
E/A ratio
LV relaxation
Atrial pressure
atrial contraction
E/A ratio : E<A
LV relaxation : impaired
Atrial pressure : normal
atrial contraction : normal
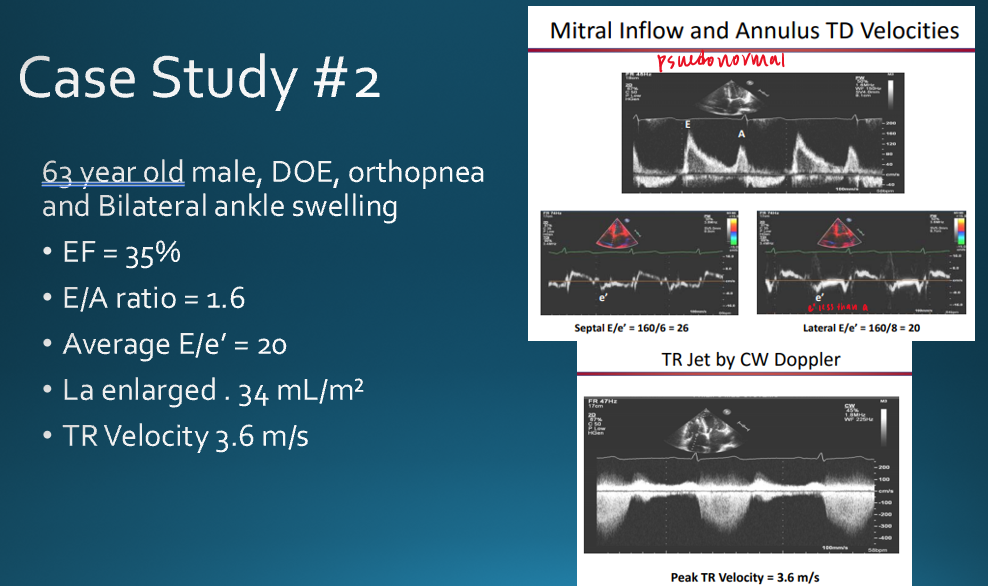
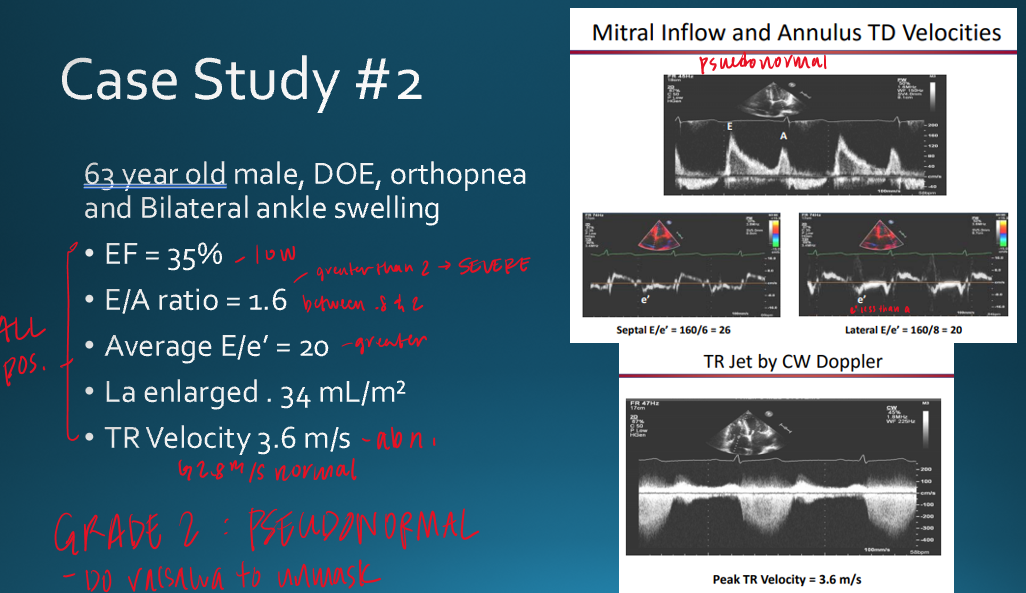
describe moderate diastolic dysfunction (grade 2)
E/A ratio
LV relaxation
Atrial pressure
atrial contraction
E/A ratio : E>A
LV relaxation : impaired
Atrial pressure : elevated
atrial contraction : normal
pseudonormal is considered
moderate diastolic dysfunction
how can you differentiate normal vs moderate diastolic dysfunction
in moderate/pseudonormal : elevated atrial pressure and impaired LV relaxation
describe severe diastolic dysfunction (grade 3)
E/A ratio : E»A
LV relaxation : impaired
Atrial pressure : very elevated
atrial contraction : impaired
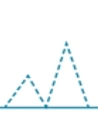
what is this
normal diastolic function OR moderate (pseudonormal)
can not tell with wave alone
why does normal diastolic and pseudonormal look the same?
elevated LAP so when valves open it pushes all the blood into LV making it appear normal
what is this
mild diastolic (E<A)
E : decreased pull from LV due to impaired relaxation
A : atrial kick pushes in excess blood flow

what is this
severe diastolic dysfunction
E : VERY high because of very elevated LAP
A : small
what occurs is moderate dysfunction that causes the wave to appear the way it does?
E : increased PUSH from LA due to increased LAP
A : most blood pushed in during early diastole (smaller A wave)
what are the E/A ratios for normal, mild, moderate and severe diastolic functions?**
normal : E/A ≥ .8
mild : E/A < .8
moderate : E/A ≥ .8
severe : E/A ≥ 2
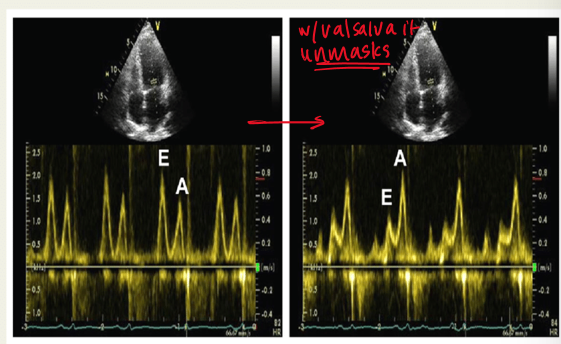
why would the mitral inflow be assessed with valsalva maneuver? explain
to unmask pseudonormal diastolic dysfunction;
valsalva decreases preload and causes E/A ratio to be less than 1
what is the deceleration time of mitral inflow and what does it indicate?
time interval from E peak to projected baseline
indicates duration of time it takes to equalize pressure difference between LA and LV
what is normal e wave deceleration time?
150-200 ms
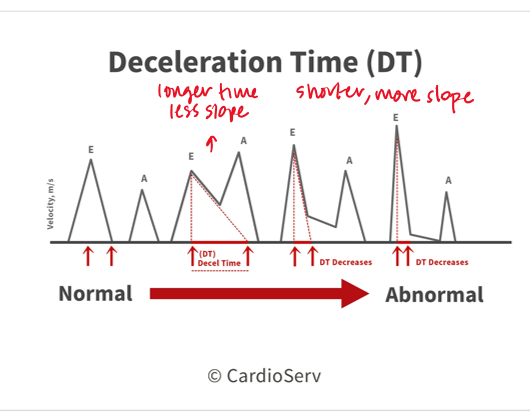
a deceleration time <150 indicates?
a deceleration time >200?
severe diastolic dysfucntion
mild diastolic dysfunction
what is the deceleration time in moderate dysfunction?
150-200
what does a shorter/longer deceleration time indicate?
shorter : moderate to severe diastolic function
this is because there is a large initial LA/LV pressure difference due to stiff ventricle → causes steep tall and steep E wave → quick filling and pressure equalizes faster
longer : mild diastolic function
what is the IVRT?
time interval between aortic closure and mitral opening
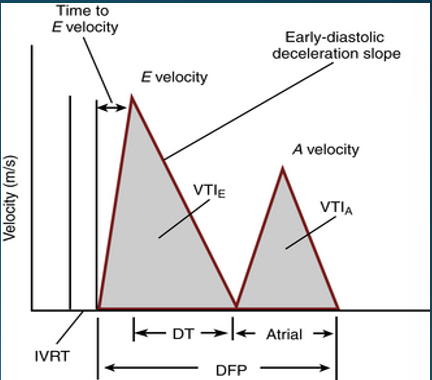
what does prolonged vs shortened IVRT indicate?
prolonged : impaired relaxation
shortened : decreased compliance
what does tissue doppler measure in regards to evaluating for diastolic dysfunction?
diastolic excursion of the atrioventricular annuli AWAY from the probe during diastole (measures velocity of tissue)
in TDI what is shown above and below the baseline?
above : how far annulus moves away from apex (diastole)
below : how far annulus moves towarsd apex (systole)
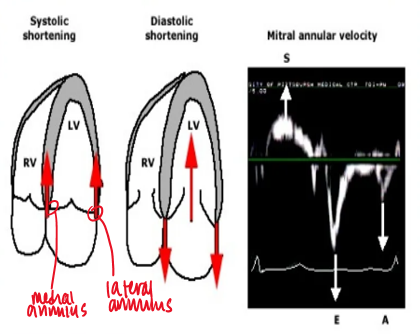
what measurements are taken on the TDI?
S’ (systolic above baseline)
E’ : diastolic below baseline
A’ : diastolic below baseline
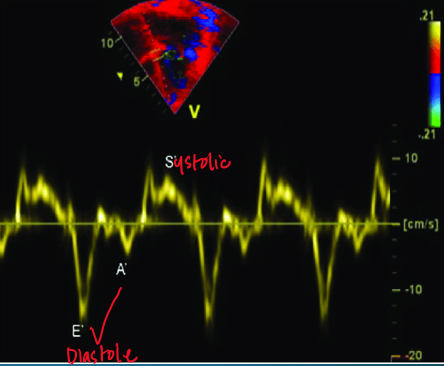
if e’ is less than a’ on TDI what is indicated?
diastolic dysfunction
what do S’, E’ and A’ represent?
S’ : ventricular ejection
E’ : ventricular filling
A’ : atrial kick
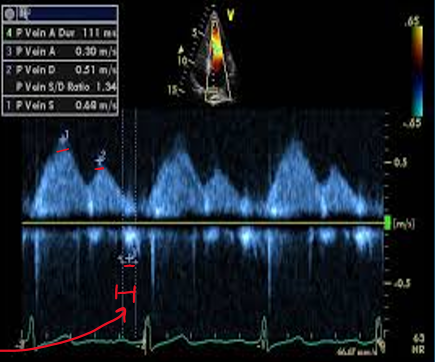
how do you obtain pulmonary venous flow? (view, doppler, cursor)
in 4CH view you can see paralel alignment with right superior pulmonary vein
pulsed wave doppler
1-2cm from orifice
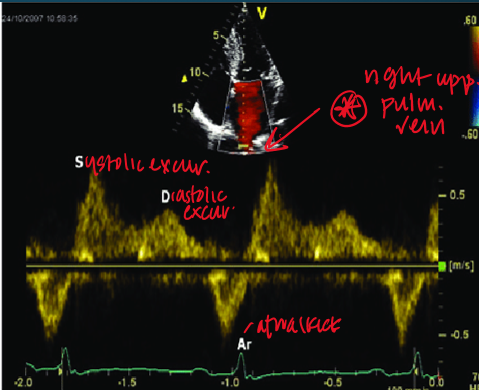
what clinical measurements are done with pulmonary venous flow?
peak systolic velocity (PVs)
peak diastolic velocity (PVd)
peak atrial reversal velocity (Pva)
duration of pulm vein atrial reversal (a-dur)
how is LA index measured?
use biplane method to measure LA in end diastole (right before MV valves open) in apical 2CH and 4CH
what LA index is considered abnormal?**
LA index ≥ 34ml/m2
how is TR systolic jet velocity measured?
obtain highest CW doppler from PLAX/apical view
meaure peak velocity during systole
what TR jet velocity is considered abnormal?
> 2.8 m/s
what are indications of elevated LV filling pressures?
e/e’ ratio
Pva
pulm a-dur vs mitral valve a-dur
pulm venous systolic flow vs pulm venous diastolic flow
e/e’ ratio >15
Pva >.35 m/s
pulm adur 20ms > than mitral a-dur
pulm venous syst flow < pulm venous diastolic flow
study this
study this
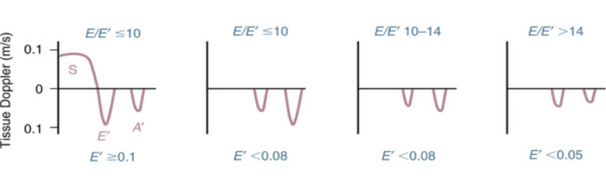
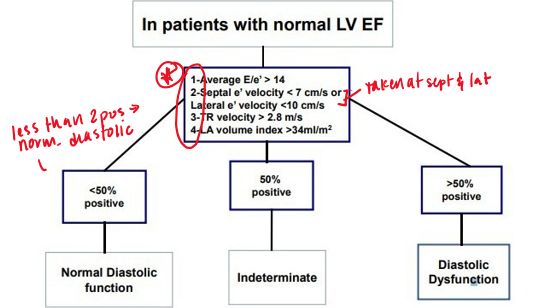
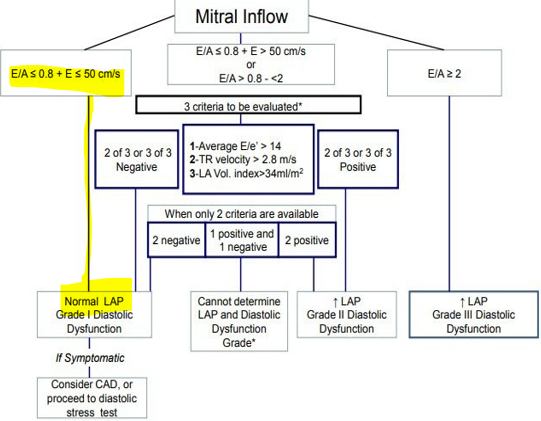
based on what variables is diastolic dysfunction diagnosed?
average e/e’ ratio
annular e’ velocity (Septal e’ velocity or lateral e’ velocity)
LA max volume index
Peak TR velocity
how do the variable indicate diastolic function vs dysfunction?
if less than 2 of the variables are positive → normal diastolic function
2 variables positive → indeterminate
more than 2 variables positive → diastolic dysfunction
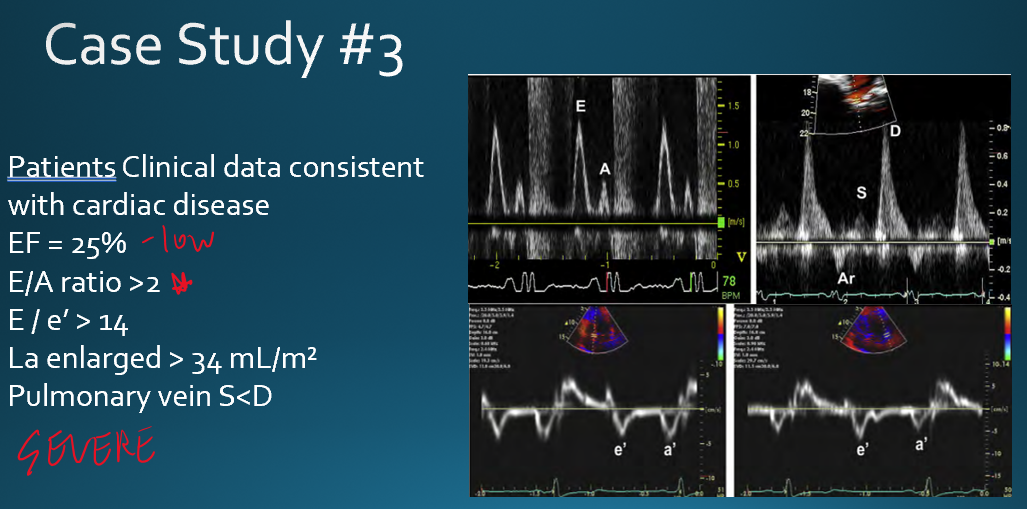
what are the normal values for normal LV EF? **
annular e’ velocity
average e/e’ ratio
LA max volume index
Peak TR velocity
annular e’ velocity : >14
avg e/e’ ratio :
septal e’ : <7 cm/s
lateral e’ : <10 cm/s
LA max volume index : >34 ml/m²
Peak TR velocity : >2.8 m/s
study this
study this
review qs
what are the phases of diastole?
isovolumetric relaxation
early rapid filling
diastasis
atrial filling
review qs
what is the purpose of the valsalva maneuver with E/A mitral flow?
unmask psuedonormal (grade 2 diastolic dysfunction)
review qs
when are diastolic inflow patterns no longer valid?
mitral stenosis
review qs
what is assess to grade diastolic dysfunction?
E/A mitral inflow, pulmonary venous flow, tissue dopple (mitral annulus → septal and lateral), LA volume, TR jet
what is the cutoff for tricuspid regurg jet velocity for diastolic dysfunction?
for LA volume?
TR jet regurg : 2.8 m/s
LA volume : 34 ml/m²
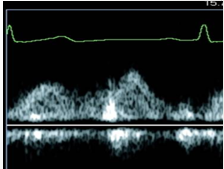
what is measured
pulmonary vein (PW)
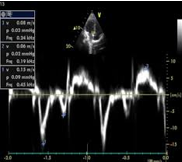
how would you characterize this pts diastolic function?
normal bc E’> A’
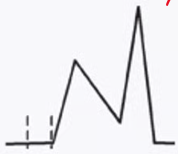
how would you characterize this patient?
mild dysfunction (grade1) because E is lower than A
if a pt has E/A ratio of >2 what is their diastolic function?
severe
what is the normal range for deceleration time?*
150-200
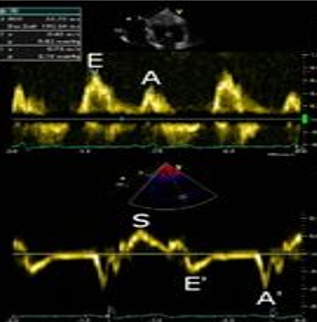
A patient's pulsed wave Doppler of the mitral valve had an E/A ratio of 1.5. The patients tissue Doppler had a decreased e' velocity and E/e' ratio >14. What is the most likely diagnosis?
moderate dysfunction
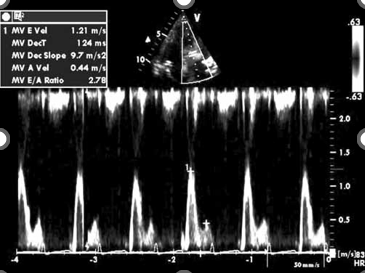
what diastolic pattern is shown here?
severe
deceleraion less than 150
E/A ratio : 2.78