ch. 13 carbohydrates
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ch 13, 14, 16, 18
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
the carbon cycle
6CO2 + 6H2O + energy ⇌ C6H12O6 + O6
carbohydrates broken down via _____ to gain energy
respiration
carbohydrates made by plants via ____
photosynthesis
aldehyde on the first carbon indicates what type of carbohydrate
aldose
ketone on the second carbon indicates what type of carbohydrate
ketose
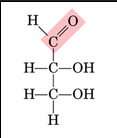
what type of carbohydrate does this fischer projection display
aldose
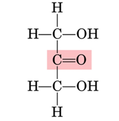
what type of carbohydrate does this fischer projection indicate
ketose
a carbohydrate with a three carbon chain
triose
a carbohydrate with a four carbon chain
tetrose
a carbohydrate with a five carbon chain
pentose
a carbohydrate with a six carbon chain
hexose
a carbohydrate with a seven carbon chain
heptose
what is a monosaccharide
the smallest form of a carbohydrate molecule
what is a disaccharide
2 monosaccharides bonded together
what type of bond allows for monosaccharides to bond to each other
a glycosidic bond
how is a glycosidic bond formed?
when a carbon from the first carbonyl group of the first monosaccharide bonds with the hydroxyl group on the fourth carbon of the second monosaccharide
what type of reaction occurs when a glycosidic bond is formed
dehydration reaction
what is a polysaccharide
more than 2 monosaccharides bonded together
what are chiral molecules
molecules that cannot be superimposed on its mirror image ex: hands with the palms facing up are not identical
what is the factor needed to identify if a molecule is chiral
if the carbon is bonded to 4 different things
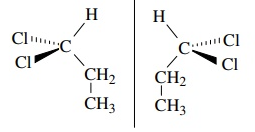
are these figures chiral or achiral
achiral
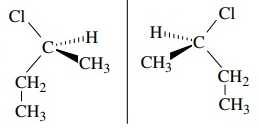
are these figures chiral or achiral
chiral
what is true about chiral molecules and carbohydrates
every monosaccharide has at least one chiral carbon
what are different isomers called (chiral)
enantiomers
how do you turn a fischer projection into its enantiomer
flip all the OH and H groups
the second to last carbon’s hydroxyl group being on the right side indicates that it is D or L isomer?
D isomer
the second to last carbon’s hydroxyl group being on the left side indicates that it is D or L isomer?
L isomer
what determines the identity of a chiral carbohydrate on a fischer projection
the orientation of the middle hydroxyl groups around the chiral carbons
what are the three most important carbohydrates?
D-glucose, D-galactose, D-fructose
what are essential facts about D-glucose
dextrose
found in blood, fruits, honey
basic building block for essential di and polysaccharides (cellulose, sucrose, glycogen, lactose, amylose)
What are essential facts about D-galactose
found in lactose
essential for membranes in the brain and nervous system
important fact about D-fructose
the sweetest natural carbohydrate that is found in fruits
what are haworth projections
a fischer projection that is turned clockwise by 90 degrees (on its side)
If the OH group is up on the first carbon what kind of isomer is the haworth projection
beta isomer
if the OH group is down on the first carbon what kind of isomer is the haworth projection
an alpha isomer
what is the process in which di- and polysaccharides are split up back into monosaccharides that uses acid or enzymes
hydrolysis
what is the other reactant necessary to perform a hydrolysis reaction other than the di- or polysaccharide?
water
are monosaccharides able to be oxidized and or reduced?
yes
an aldose that can be oxidized is called
a reducing sugar
what are prime examples of reducing sugars
glucose, fructose, and galactose
what is the product of an aldose being oxidized?
aldehyde becomes a carboxylic acid
what is the name change during an oxidation reaction of an aldose
-ose ending turns into -onic acid
what can fructose do to become a reducing sugar
rearrange to become a glucose (changing from a ketose to an aldose) ketohexose
how is a monosaccharide reduced
when a monosaccharide reacts with H2 (hydrogen gas) and platinum to be converted into an alditol (sugar alcohol)
what is the name change when the monosaccharide becomes an alditol
-ose to -itol
what does alpha(1→4) indicate
the first monosaccharide is the alpha isomer and is connected to the 4th carbon of the other monosaccharide in the form of a glycosidic bond to form the linkage
what is a reducing sugar
a carbohydrate that contains a free aldehyde or ketone group that allows it to act as a reducing agent, donating electrons to other molecules to cause them to be reduced
are all monosaccharides reducing sugars?
yes
what are the four most important biological polysaccharides
amylose, amylopectin, cellulose, glycogen
facts about amylose
starch found in plants
straight chain of glucose molecules connected by alpha (1→4) glycosidic bonds
no branching
amylopectin facts
starch found in plants
made of glucose connected by alpha (1→4) glycosidic bonds
glucose chains have branches that connect by alpha (1→6) glycosidic bonds
glycogen facts
found in animals
has more branches than amylopectin
stored in our livers and muscle tissue
cellulose facts
gives structure to plants
made of straight chains of glucose connected by beta(1→4) glycosidic bonds
due to body not producing the correct enzyme, cannot hydrolyze cellulose into glucose
what is the process of glucose being digested
glucose → blood stream → energy
what is the process of a polysaccharide being digested
polysaccharide → hydrolysis → monosaccharides → blood stream → energy
how is high blood sugar digested
high blood sugar → insulin released → dehydration of glucose to form glycogen
how is low blood sugar digested
low blood sugar → glucagon released → glycogen hydrolyzed to make glucose